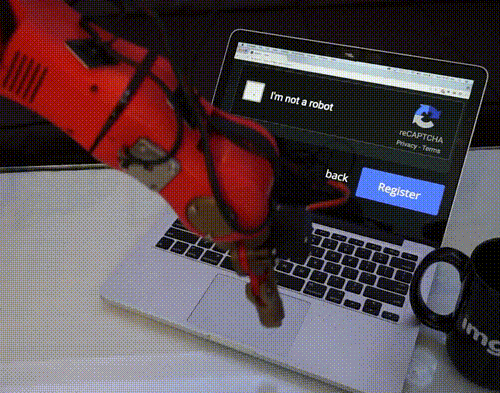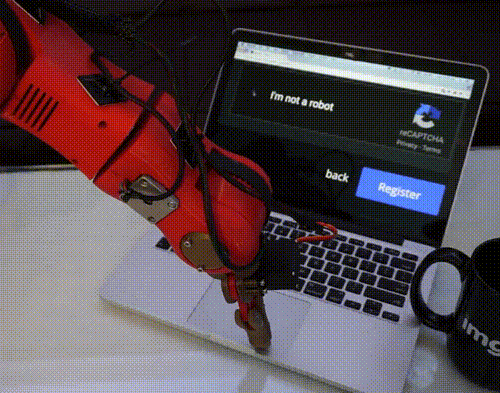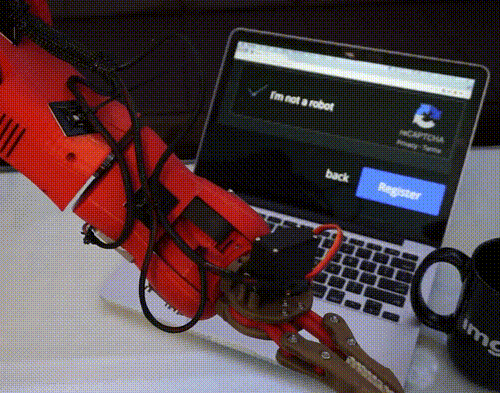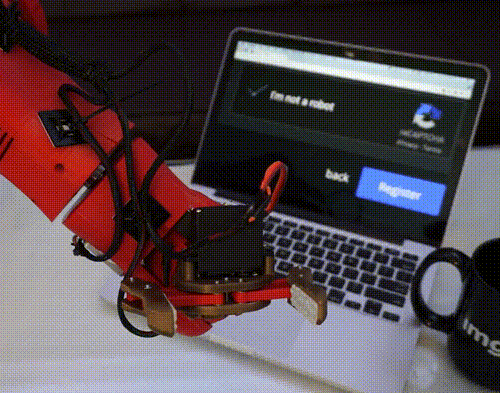
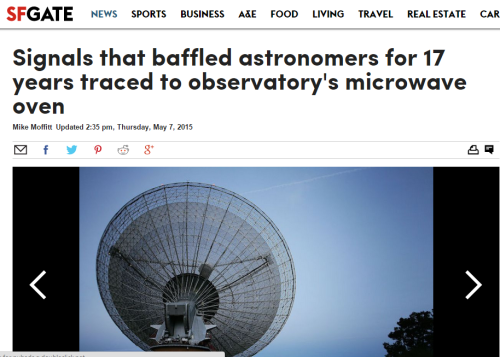
Tag Later - Blog Posts




Better late than never!
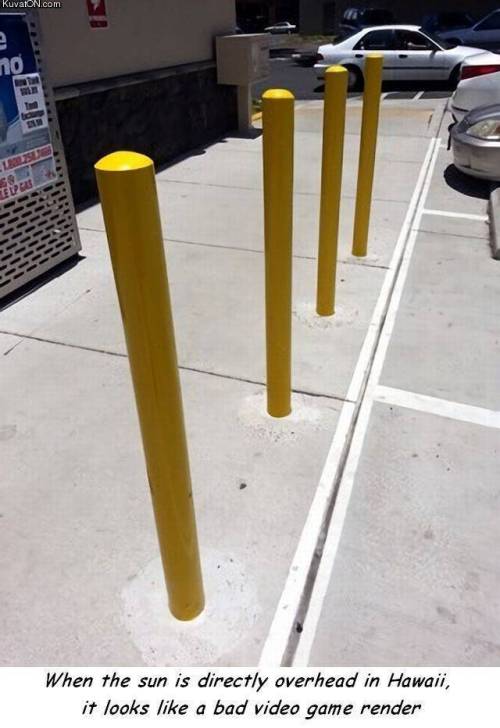
This week’s entry: Hot Jupiters
http://www.space.com/32011-extremely-hot-and-fast-planets-seem-to-defy-logic.html
https://astrobites.org/2015/03/04/hot-jupiters-are-very-bad-neighbors/

A bizarre new species of marine worm lacks a number of internal features common to other animals — including an anus, new research shows.

A group of astronomers is using a new method to search for hard to spot alien planets: By measuring the difference between the amount of light coming from the planets’ daysides and nightsides, astronomers have spotted 60 new worlds thus far.
Continue Reading.
Galaxies: Types and morphology
A galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter. Galaxies range in size from dwarfs with just a few hundred million (108) stars to giants with one hundred trillion (1014) stars, each orbiting its galaxy’s center of mass.

Galaxies come in three main types: ellipticals, spirals, and irregulars. A slightly more extensive description of galaxy types based on their appearance is given by the Hubble sequence.

Since the Hubble sequence is entirely based upon visual morphological type (shape), it may miss certain important characteristics of galaxies such as star formation rate in starburst galaxies and activity in the cores of active galaxies.
Ellipticals

The Hubble classification system rates elliptical galaxies on the basis of their ellipticity, ranging from E0, being nearly spherical, up to E7, which is highly elongated. These galaxies have an ellipsoidal profile, giving them an elliptical appearance regardless of the viewing angle. Their appearance shows little structure and they typically have relatively little interstellar matter. Consequently, these galaxies also have a low portion of open clusters and a reduced rate of new star formation. Instead they are dominated by generally older, more evolved stars that are orbiting the common center of gravity in random directions.
Spirals

Spiral galaxies resemble spiraling pinwheels. Though the stars and other visible material contained in such a galaxy lie mostly on a plane, the majority of mass in spiral galaxies exists in a roughly spherical halo of dark matter that extends beyond the visible component, as demonstrated by the universal rotation curve concept.
Spiral galaxies consist of a rotating disk of stars and interstellar medium, along with a central bulge of generally older stars. Extending outward from the bulge are relatively bright arms. In the Hubble classification scheme, spiral galaxies are listed as type S, followed by a letter (a, b, or c) that indicates the degree of tightness of the spiral arms and the size of the central bulge.
Barred spiral galaxy

A majority of spiral galaxies, including our own Milky Way galaxy, have a linear, bar-shaped band of stars that extends outward to either side of the core, then merges into the spiral arm structure. In the Hubble classification scheme, these are designated by an SB, followed by a lower-case letter (a, b or c) that indicates the form of the spiral arms (in the same manner as the categorization of normal spiral galaxies).
Ring galaxy

A ring galaxy is a galaxy with a circle-like appearance. Hoag’s Object, discovered by Art Hoag in 1950, is an example of a ring galaxy. The ring contains many massive, relatively young blue stars, which are extremely bright. The central region contains relatively little luminous matter. Some astronomers believe that ring galaxies are formed when a smaller galaxy passes through the center of a larger galaxy. Because most of a galaxy consists of empty space, this “collision” rarely results in any actual collisions between stars.
Lenticular galaxy

A lenticular galaxy (denoted S0) is a type of galaxy intermediate between an elliptical (denoted E) and a spiral galaxy in galaxy morphological classification schemes. They contain large-scale discs but they do not have large-scale spiral arms. Lenticular galaxies are disc galaxies that have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing star formation. They may, however, retain significant dust in their disks.
Irregular galaxy

An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure.
Dwarf galaxy

Despite the prominence of large elliptical and spiral galaxies, most galaxies in the Universe are dwarf galaxies. These galaxies are relatively small when compared with other galactic formations, being about one hundredth the size of the Milky Way, containing only a few billion stars. Ultra-compact dwarf galaxies have recently been discovered that are only 100 parsecs across.
Interacting

Interactions between galaxies are relatively frequent, and they can play an important role in galactic evolution. Near misses between galaxies result in warping distortions due to tidal interactions, and may cause some exchange of gas and dust. Collisions occur when two galaxies pass directly through each other and have sufficient relative momentum not to merge.
Starburst

Stars are created within galaxies from a reserve of cold gas that forms into giant molecular clouds. Some galaxies have been observed to form stars at an exceptional rate, which is known as a starburst. If they continue to do so, then they would consume their reserve of gas in a time span less than the lifespan of the galaxy. Hence starburst activity usually lasts for only about ten million years, a relatively brief period in the history of a galaxy.
Active galaxy
A portion of the observable galaxies are classified as active galaxies if the galaxy contains an active galactic nucleus (AGN). A significant portion of the total energy output from the galaxy is emitted by the active galactic nucleus, instead of the stars, dust and interstellar medium of the galaxy.

The standard model for an active galactic nucleus is based upon an accretion disc that forms around a supermassive black hole (SMBH) at the core region of the galaxy. The radiation from an active galactic nucleus results from the gravitational energy of matter as it falls toward the black hole from the disc. In about 10% of these galaxies, a diametrically opposed pair of energetic jets ejects particles from the galaxy core at velocities close to the speed of light. The mechanism for producing these jets is not well understood.

The main known types are: Seyfert galaxies, quasars, Blazars, LINERS and Radio galaxy.
source
images: NASA/ESA, Hubble (via wikipedia)
ELI5:How come people can't be cryogenically frozen safely as the ice crystals destroy the cell membranes, but sex cells such as sperm are kept frozen for long periods of time yet remain functional?
I work in a lab where we freeze down cells all of the time. We freeze our cells in a medium that contains 5% DMSO, which among other things can be used as a cryoprotectant. However, DMSO is also toxic to cells at the concentrations necessary for cryoprotection. Consequently, when you freeze cells in DMSO, you add the DMSO medium at ice-cold temperatures and don’t allow the cells to warm up. When you later thaw the cells, you have to dilute out the DMSO as quickly as possible without causing osmotic shock, which can pop the cells. Such restrictions on freezing and thawing would basically be impossible to control at the level of a complete organism.
However, to contradict a lot of previous posts, individual cells can be recovered from freezing with high viability. When performed properly (and this varies quite a bit by cell type), you can expect >90% of cells to be alive following thaw.
The chemicals that allow cells to survive freezing are toxic to the body. Keeping the cells cold minimized the damage that this chemical does to the cells. With single cell solutions, adding the chemical at ice-cold temperatures and immediately diluting it out when you thaw the cells can keep 90% of the cells alive. There’s no way to do this with an intact body.
It’s also worth noting that this is probably not the only reason that this technique doesn’t scale to organisms.
Explain Like I`m Five: good questions, best answers.
The Neuroscience of Drumming

According to new neuroscience research, rhythm is rooted in innate functions of the brain, mind, and consciousness. As human beings, we are innately rhythmic. Our relationship with rhythm begins in the womb. At twenty two days, a single (human embryo) cell jolts to life. This first beat awakens nearby cells and incredibly they all begin to beat in perfect unison. These beating cells divide and become our heart. This desire to beat in unison seemingly fuels our entire lives. Studies show that, regardless of musical training, we are innately able to perceive and recall elements of beat and rhythm.
It makes sense then that beat and rhythm are an important aspect in music therapy. Our brains are hard-wired to be able to entrain to a beat. Entrainment occurs when two or more frequencies come into step or in phase with each other. If you are walking down a street and you hear a song, you instinctively begin to step in sync to the beat of the song. This is actually an important area of current music therapy research. Our brain enables our motor system to naturally entrain to a rhythmic beat, allowing music therapists to target rehabilitating movements. Rhythm is a powerful gateway to well-being.
Neurologic Drum Therapy
Neuroscience research has demonstrated the therapeutic effects of rhythmic drumming. The reason rhythm is such a powerful tool is that it permeates the entire brain. Vision for example is in one part of the brain, speech another, but drumming accesses the whole brain. The sound of drumming generates dynamic neuronal connections in all parts of the brain even where there is significant damage or impairment such as in Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD). According to Michael Thaut, director of Colorado State University’s Center for Biomedical Research in Music, “Rhythmic cues can help retrain the brain after a stroke or other neurological impairment, as with Parkinson’s patients ….” The more connections that can be made within the brain, the more integrated our experiences become.
Studies indicate that drumming produces deeper self-awareness by inducing synchronous brain activity. The physical transmission of rhythmic energy to the brain synchronizes the two cerebral hemispheres. When the logical left hemisphere and the intuitive right hemisphere begin to pulsate in harmony, the inner guidance of intuitive knowing can then flow unimpeded into conscious awareness. The ability to access unconscious information through symbols and imagery facilitates psychological integration and a reintegration of self.
In his book, Shamanism: The Neural Ecology of Consciousness and Healing, Michael Winkelman reports that drumming also synchronizes the frontal and lower areas of the brain, integrating nonverbal information from lower brain structures into the frontal cortex, producing “feelings of insight, understanding, integration, certainty, conviction, and truth, which surpass ordinary understandings and tend to persist long after the experience, often providing foundational insights for religious and cultural traditions.”
It requires abstract thinking and the interconnection between symbols, concepts, and emotions to process unconscious information. The human adaptation to translate an inner experience into meaningful narrative is uniquely exploited by drumming. Rhythmic drumming targets memory, perception, and the complex emotions associated with symbols and concepts: the principal functions humans rely on to formulate belief. Because of this exploit, the result of the synchronous brain activity in humans is the spontaneous generation of meaningful information which is imprinted into memory. Drumming is an effective method for integrating subjective experience into both physical space and the cultural group.

This is what a star nursery looks like
Astronomers have spotted a beautiful blue ribbon in space that will one day ignite into a cluster of baby stars.
Astronomers try to track down hot spots for new stars by searching for clouds of dust in gas in the coldest parts of the Milky Way. The ESA’s Herschel space observatory is giving us rare glimpses inside these super-cold star nurseries.
The blue ribbon in this new image shows the coldest part of the cloud. It’s about minus 259 degrees Celsius and holds about 800 times the mass of the sun. Soon all that mass will crunch together and sprout new stars. Yet, one big piece of the star-birth puzzle is still a mystery.
Follow @the-future-now


One of the most dangerous pictures ever taken - Elephant’s Foot, Chernobyl. This is a photo of a now dead man next the ‘Elephant’ Foot’ at the Chernobyl power plant.
The image distortions in the photo are created by intense level of radiation almost beyond comprehension. There is no way the person in this photo and the person photographing him could have survived for any more that a few years after being there, even if they quickly ran in, took the photos and ran out again. This photo would be impossible to take today as the rates of radioactive decay are even more extreme now due to a failed military experiment to bomb the reactor core with neuron absorbers. The foot is made up of a small percentage of uranium with the bulk mostly melted sand, concrete and other materials which the molten corium turns into a kind of lava flow. In recent years, it has destroyed a robot which tried to approach it, and the last photos were taken via a mirror mounted to a pole held at the other end of the corridor for a few seconds. It is almost certainly the most dangerous and unstable creation made by humans. These are the effects of exposure: 30 seconds of exposure - dizziness and fatigue a week later 2 minutes of exposure - cells begin to hemorrhage (ruptured blood vessels) 4 minutes - vomiting, diarrhea, and fever 300 seconds - two days to live

whoa-o-o-o-o-oh-oh
WHOA-O-O-O-O-OH-OH
UPTOWN RAT



The complete ‘Women Who Changed Science - And The World" collection in honor of the 95th Women’s Equality Day.
Purchase Here!
Today is Copernicus’s 540th birthday. You may remember Copernicus as the man who said “Hey, what if the Earth went around the sun?” To which the Catholic Church replied “Hey, what if we set you on fire?”
Some intriguing exoplanets
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet that orbits a star other than the Sun. The first scientific detection of an exoplanet was in 1988. However, the first confirmed detection came in 1992; since then, and as of 1 April 2017, there have been 3,607 exoplanets discovered in 2,701 planetary systems and 610 multiple planetary systems confirmed.

1- Kepler-186f
was the first rocky planet to be found within the habitable zone – the region around the host star where the temperature is right for liquid water. This planet is also very close in size to Earth. Even though we may not find out what’s going on at the surface of this planet anytime soon, it’s a strong reminder of why new technologies are being developed that will enable scientists to get a closer look at distant worlds.

2- CoRoT 7b
The first super-Earth identified as a rocky exoplanet, this planet proved that worlds like the Earth were indeed possible and that the search for potentially habitable worlds (rocky planets in the habitable zone) might be fruitful.

3- Kepler-22b
A planet in the habitable zone and a possible water-world planet unlike any seen in our solar system.

4- Kepler 10-b
Kepler’s first rocky planet discovery is a scorched, Earth-size world that scientists believe may have a lava ocean on its surface.

5- 55 Cancri e
55 Cancri e is a toasty world that rushes around its star every 18 hours. It orbits so closely – about 25 times closer than Mercury is to our sun – that it is tidally locked with one face forever blisters under the heat of its sun. The planet is proposed to have a rocky core surrounded by a layer of water in a “supercritical” state, where it is both liquid and gas, and then the whole planet is thought to be topped by a blanket of steam.

6- 51 Pegasi b
This giant planet, which is about half the mass of Jupiter and orbits its star every four days, was the first confirmed exoplanet around a sun-like star, a discovery that launched a whole new field of exploration.

7- Kepler-444 system
The oldest known planetary system has five terrestrial-sized planets, all in orbital resonance. This weird group showed that solar systems have formed and lived in our galaxy for nearly its entire existence.

8- PSR B1257+12 system
Discovered in 1992 and 1994, the planets that orbit pulsar PSR B1257+12 are not only the smallest planetary bodies known to exist outside our solar system, they also orbit a neutron star. These weird “pulsar planets” demonstrated that planets exist in all environments in the galaxy – even around the remnants of an exploded star.

9- HD 80606 b
This world has the most eccentric orbit, and as one scientist put it, “wears its heart on its sleeve,” with storms, rotation, atmospheric heating, and a crazy orbit all plainly visible.

10- OGLE-2005-BLG-390
Considered to be the first cold super Earth, this exoplanet began to form a Jupiter-like core of rock and ice, but couldn’t grow fast enough in size. Its final mass is five times that of Earth. The planet’s nickname is Hoth, after a planet from Star War
Credits: NASA / JPL-Caltech