Chapter 5 - Hess’s Law Pt.2: Problem Solving // Science Scribbles A-Level / IB HL Chemistry Collection

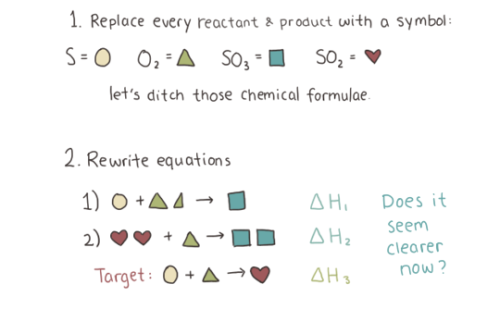
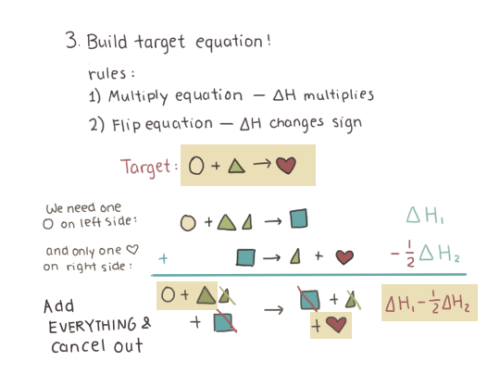

Chapter 5 - Hess’s Law pt.2: Problem solving // Science Scribbles A-Level / IB HL Chemistry collection
(Hess’s Law part 1 | other syllabus topics)
And here is part 2. Hope I managed to explain it somewhat ^^ The reason I drew all these symbols is to explain the method, but once you get it there is no need to draw them every time!
More Posts from Swirlspill-study and Others
FREE MEDICAL PDFs
Anatomy:
1–> KLM for Gross Anatomy
2–> Snell’s Anatomy
3–> BD Churassia
4–> RJ Last
5–> Grey’s Anatomy
6–> Langman Embryology
7–> KLM for Embryology
8–> BD For General Anatomy
9–> Dissector
10–> Di Fore Histology
11–> Junqueira’s Histology
12–> Netter Atlas of human Aantomy
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LYV9KQ3lxY29FY28
Physiology:
1–> Guyton
2–> Ganong
3–> Sheerwood
4–> Sembulingam
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LdXlCSjdZM214dEE
Biochemistry:
1–> Harper
2–> Lippincott
3–> Chatterjea
4–> Satyanarayan
5–> Stryer
6–> MRS Biochemistry
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0Ld0o3WnhCR2VEczg
Pathology:
1–> Big Robins
2–> Medium Robins
3–> Pathoma
4–> Goljan
5–> Harsh Mohan Pathology
6–> Atlas of Histopathology
7–> Levinson
8–> MRS microbiology
9–> Microbiology by Jacquelyn G. Black
10–> Color Atlas of Microbiology
11–> Kaplan Pathology
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LYkRYdjFrTm5MR0U
Pharmacology:
1–> Big Katzung
2–> Mini Katzung
3–> Kaplan Review
4–> Lippincott
5–> Pocket Katzung
6–> Rang and Dale’s Pharmacology
7–> Atlas of Pharmacology
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LMkE1UUVRZGwtTlU
Forensic Medicine:
1–> Simpson’s Forensics
2–> Krishan’s Forensics
3–> Atlas of Autopsy
4–> Atlas of Forensic Medicine
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LQXVwOGoyWnFSV2s
Ophthalmology:
1–> Jogi
2–> Jatoi
3–> Parson’s Textbook of Eye
4–> Kanski
5–> AK Khurana
6–> Atlas of ophthalmology
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LOHc5WVZMdkJjX2M
Otorhinolaryngology:
1–> Dhingra
2–> Logans Turner
3–> Color Atlas of Otorhinolaryngology
4–> Maqbool’s Text Book of ENT
5–> Clinical Methods in ENT by PT Wakode
6–> ENT at a Glance
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LaDY2a0lFNDlfTGc
Community Medicine:
1–> Monica’s Text Book Community Medicine
2–> Mahajan And Gupta Text Book of Community Medicine
3–> Bancroft’s Text Book of Community Medicine
Folder link–> https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0Lc1RCMml2NjhFNjA
Internal Medicine:
1–> Churchill’s Pocketbook of DD
2–> MTB Step 2 Ck
3–> Davidson Essentials
4–> Davidson Principals and practice
5–> Harrison’s Internal Medicine
6–> Internal Medicine USMLE Nuggets
7–> Internal Medicine on call bt LANGE 8–> Oxfords Specialties
Folder link–>https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LeEFJNG5TMlc4eWc
Surgery:
1–> Bailey_love short practice of Surgery
2–> Churchill’s pocketbook of Surgery
3–> Deja Review of surgery
4–> Farquharson’s Textbook of Operative General Surgery
5–> Hamilton Bailey’s Physical Signs
6–> Oxford Handbook of Clinical Surgery
7–> Schwartz’s Principles of Surgery
8–> Macleod’s Clinical Examination
9–> Macleod’s Clinical Diagnosis
Folder link–>https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LRFpFSG5hZ1pVWkE
Obstetrics & Gynecology:
1–> Case Discussions in Obstetrics and Gynecology
2–> Deja Review of Obstetrics Gynecology
3–> Obstetrics by Ten Teachers
4–> Gynaecology illustrated
5–> Gynaecology by Ten Teachers
Folder link–>https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LMU1LRjFDa1FrbjA
Pediatrics:
1–> Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics
2–> Nelson Complete
3–> Pediatrics Review
Folder link–>https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B3WdpdsqpX0LUkdTQkVuNV92Yzg
I hope this helps everyone, it’s not mine. But has been shared to me and I am sharing this with all of you.
Free Online Language Courses

Here is a masterpost of MOOCs (massive open online courses) that are available, archived, or starting soon. I think they will help those that like to learn with a teacher or with videos. You can always check the audit course or no certificate option so that you can learn for free.
American Sign Language
ASL University
Arabic
Arabic for Global Exchange (in the drop down menu)
Arabic Without Walls
Intro to Arabic
Madinah Arabic
Moroccan Arabic
Catalan Sign Language
Intro to Catalan Sign Language
Chinese
Beginner
Basic Chinese
Basic Chinese I. II, III, IV , V
Basic Mandarin Chinese I & II
Beginner’s Chinese
Chinese for Beginners
Chinese Characters
Chinese for HSK 1
First Year Chinese I & II
HSK Level 1
Mandarin Chinese I
Mandarin Chinese for Business
More Chinese for Beginners
Start Talking Mandarin Chinese
UT Gateway to Chinese
Chino Básico (Taught in Spanish)
Intermediate
Chinese Stories
Intermediate Business Chinese
Intermediate Chinese Grammar
Dutch
Introduction to Dutch
English
Online Courses here
Resources Here
Faroese
Faroese Course
Finnish
A Taste of Finnish
Basic Finnish
Finnish for Immigrants
Finnish for Medical Professionals
French
Beginner
AP French Language and Culture
Basic French Skills
Beginner’s French: Food & Drink
Diploma in French
Elementary French I & II
Français Interactif
French in Action
French for Beginners
French Language Studies I, II, III
French:Ouverture
Intermediate & Advanced
French: Le Quatorze Juillet
Passe Partout
La Cité des Sciences et de Industrie
Frisian
Introduction to Frisian (Taught in English)
Introduction to Frisian (Taught in Dutch)
German
Beginner
Beginner’s German: Food & Drink
Conversational German I, II, III, IV
Deutsch im Blick
Diploma in German
Rundblick-Beginner’s German
Advanced
German:Regionen Traditionen und Geschichte
Landschaftliche Vielfalt
Hebrew
Biblical Hebrew
Know the Hebrew Alphabet
Teach Me Hebrew
Hindi
A Door into Hindi
Business Hindi
Virtual Hindi
Icelandic
Icelandic 1-5
Indonesian
Learn Indonesian
Irish
Introduction to Irish
Italian
Beginner
Beginner’s Italian: Food & Drink
Beginner’s Italian I
Introduction to Italian
Italian for Beginners 1 , 2, 3 , 4 , 5, 6
Intermediate & Advaned
Intermediate Italian I
Advanced Italian I
La Commedia di Dante
Japanese
Genki
Japanese JOSHU
Japanese Pronunciation
Sing and Learn Japanese
Tufs JpLang
Kazakh
A1-B2 Kazakh (Taught in Russian)
Korean
Beginner
First Step Korean
How to Study Korean
Learn to Speak Korean
Pathway to Spoken Korean
Intermediate
Intermediate Korean
Nepali
Beginner’s Conversation and Grammar
Norwegian
Introduction to Norwegian
Norwegian on the Web
Portuguese
Curso de Português para Estrangeiros
Pluralidades em Português Brasileiro
Russian
Beginner
Easy Accelerated Learning for Russian
Advanced
Reading Master and Margarita
Russian as an Instrument of Communication
Siberia: Russian for Foreigners
Spanish
Beginner
AP Spanish Language & Culture
Basic Spanish for English Speakers
Beginner’s Spanish:Food & Drink
Fastbreak Spanish
Introduction to Spanish
Restaurants and Dining Out
Spanish for Beginners
Spanish for Beginners 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Spanish Vocabulary
Intermediate
Spanish:Ciudades con Historia
Spanish:Espacios Públicos
Advanced
Corrección, Estilo y Variaciones
Leer a Macondo
Spanish:Con Mis Propias Manos
Spanish: Perspectivas Porteñas
Swedish
Intro to Swedish
Swedish Made Easy 1, 2, & 3
Ukrainian
Read Ukrainian
Ukrainian Language for Beginners
Welsh
Beginner’s Welsh
Discovering Wales
Multiple Languages
Ancient Languages
More Language Learning Resources & Websites!
Last updated: March 1, 2017

GENERAL SCHOLARSHIP SEARCHES
scholarships.com
Fastweb
SALT
School Soup
CollegeNET
free scholarship search
Scholarship Hunter
collegescholarships.org
Peterson’s
BigFuture
Common Knowledge Scholarship Foundation
INTERNATIONAL STUDENT RESOURCES
EastChance (specifically for eastern european students)
EducationUSA (US government state department website)
International Education Financial Aid (IEFA)
International Student
eduPASS
STATE-SPECIFIC (by residency, not place of education)
Alaska
Arkansas
California
Iowa
Louisiana
Maine
Missouri
Montana
North Carolina
Oregon
Washington
TIPS AND GUIDES
CollegeBoard: the basics of financial aid
Watching out for scholarship scams
Department of Education student guide

adapted from this response
1. Write your notes in a way where you can test your retention and understanding.
Many people write notes that do a great job summarizing their materials but their notes are not designed to promote learning, retention or diagnosis of their weaknesses. But my notes can – and so can yours. Simply put my notes can be used like flashcards because I write them in a form where I separate a “stimulus” from a “response.” The stimulus are cues or questions (think: front side of flashcard), while the response is the answer to the cue (think: back of flashcard). But the stimuli are to the left of a margin, while the responses are to the right. The key advantage of this is that just by putting a sheet of paper on top of your notes, you can hide the responses, while leaving the stimuli visible. You can have multiple margins and multiple levels of stimuli and response for greater information density. When you get good at this you can write notes in this form in real-time. To get some idea of what I’m talking about google for “Cornell Notetaking method”. My notetaking method is a variant of this. I usually use completely blank paper to do this because regular lined paper has too small a margin. To give you an idea of how powerful this notetaking method can be, I learned several courses just hours before the exam and still got an “A” in all of them during a difficult semester where I had too many competing priorities to spend long hours studying. Had it not been for this notetaking method I don’t think that would be possible. 2. Develop the ability to become an active reader (this is the perhaps the most important advice I have to share).
Don’t just passively read material you are given. But pose questions, develop hypotheses and actively test them as you read through the material. I think the hypotheses are part of what another poster referred to when he advised that you should develop a “mental model” of whatever concept they are teaching you. But a mental model can be much more than simple hypotheses. Sometimes the model resembles a story. Other times it looks more like a diagram. But what they all have in common is that the explain what is going on. Having a mental model will give you the intuition and ability to answer a wider range of questions than would be otherwise possible if you lacked such a mental model. Where do you get this model? You creatively develop one as you are reading to try to explain the facts as they are presented to you. It’s like guessing how the plot of a movie, before it unfolds. Sometimes you have to guess the model based on scarce evidence. Sometimes it is handed to you. If your model is a good one it should at least be able to explain what you are reading. Having a model also allows you to make predictions which can then be used to identify if your model is wrong. This allows you to be hypersensitive to disconfirming evidence that can quickly identify if your model is wrong. Oftentimes you may have two or more models that can explain the evidence, so your task will be to quickly formulate questions that can prove one model while disconfirming the others. To save yourself time, I suggest focusing on raising questions that could confirm/disprove the mostly likely model while disproving the others (think: differential diagnoses in medicine). But once you have such a model that (i) explains the evidence and (ii) passes all the disconfirming tests you can throw at it then you have something you can interpolate and extrapolate from to answer far more than was initially explained to you. Such models also make retention easier because you only need to remember the model as opposed to the endless array of facts it explains. But perhaps more importantly, such models give you intuition. Of course, your model could be wrong, but that is why you actively test it as you are reading, and adjust as necessary. Think of this process as the scientific method being applied by you, to try to discover the truth as best you can. Sometimes you will still be left with contradictions that even your best models cannot explain. I often found speaking to the professor after class to be a time efficient of resolving these contradictions. I discovered mental modelling as a survival mechanism to pass my studies at the University of Waterloo – where their teaching philosophy is misnomer because their teaching philosophy is to not teach as well as they could. You can see this from their grading philosophy. Although they don’t use a bell curve or other statistical grade adjustment, they make their exams so hard that the class average is usually between 68 (C+) and 72 (B-) in spite of the fact that their minimum admission grades are among the highest in Canada (you need more than A+ to get into several of their engineering programs). The only way they can achieve such low test averages from otherwise high performing students is by holding back some of what they know, and then testing what they didn’t explain well in lecture on their exams; or by not teaching to the best of their ability. This forces students to develop the ability to teach themselves, often from materials that do not explain things well, or lack the introductory background knowledge needed to understand the material. I realized I could defend against such tactics by reverse engineering the results into theories that would produce those same results; i.e. mental model induced from scarce facts. Then when I got to MIT I found myself in a place with the opposite teaching philosophy. Unlike Waterloo, if the whole class got an “A” the MIT professors would be happy and proud (whereas at Waterloo an “A” class average would be the cause for a professor’s reprimand). The mental modelling skills I developed at Waterloo definitely came in handy at graduate school because they enabled me to learn rapidly with scarce information. 3. Be of service to your fellow classmates.
I’ve personally observed and heard anecdotal stories that many students in highly competitive programs are reluctant to share what they know with their peers; a good example being the vast number of students in a top ranked science programs competing for the very few coveted spots in med school. I’ve seen people in such situations be afraid to share what they know because the fear it could lead to the other students “getting ahead” while leaving them behind. I would actually recommend doing the opposite: share liberally. You can’t expect help from others if you are unwilling to help others yourself. I spent hours tutoring people in subjects I was strong in. But, conversely those same people were usually happy to help me with my weaknesses when I needed it. I also found it easier to get good teammates – which is essential to getting good grades in team-based classes. I found I learned a LOT from other people. And their questions helped me to prepare for questions I may not have thought of – some of which would appear on the exams. 4. Understand how the professor grades.
Like the real world, the academic world is not always fair. You need to understand who is grading you and what they are looking for. Oddly, if you actually answer questions as written, you won’t get full marks from some teachers. Some professors expected more than the answer. Some only accepted the answers taught in class as opposed to other factually correct answers – which coincidentally can easily happen if you rely heavily on mental models. Some expected you to not even evaluate whether the answers to their multiple choice answers were true or not; only to notice which answer choices aligned or did not align with the theories taught in class. Some highly value participation in which case you ought to have a mental model of what they are teaching based on their assigned readings. The sooner you know who you are dealing with, the sooner you can adjust to their way of grading. Thankfully I considered the vast majority of my professors to have graded in a fair manner. 5. Get involved in research while still in undergrad.
Academics is a means to an end. To me that end was “solving problems” and “building stuff” specifically systems and organizations. Depending on the school you apply for, your research may be just as important, if not more important, than your grades. In fact if all you have are good grades your chances of getting into a top ranked CS program with a research component (e.g. MIT, CMU) are slim to nil; though you might still be able to get into a top-ranked courseware-based Masters (such as Stanford where there is no masters thesis). I did an Artificial Intelligence research project in undergrad and posted it on the internet. Not long after it was cited in three patents from IBM, AOL and another inventor. Then 40 other people cited my work. I feel this helped me get into MIT because they saw that I could come up with theories with practical applications. It also led to internships with top research teams whose work I am still in awe of. This research also helped my graduate application. None of this would have been possible if I didn’t do research in undergrad. 6. Attend classes.
I do not understand the students who claim they did well without attending class. Many professors will only say certain things in class. Many classes only present some of the material in class. If you don’t attend class you simply won’t get that material. You also won’t be able to ask immediate follow-up questions. I also found speaking to the professor after class was an efficient way to resolve contradictions I had found with my mental model. 7. Time management is key – especially in undergrad.
In my competitive undergrad program I once learned that a friend who achieved top 5% status actually timed how long he ate. While I do not suggest going to such extremes I offer this modest advice. I suggest spending no more than 30 minutes trying to solve a problem you can’t solve by yourself before appealing to office hours or another knowledgeable student. I also suggest you ask questions of your professor during or after class as opposed to leaving the class confused. This reduces wasted time in an environment when time is a very precious commodity. 8. Going out and having fun is conducive to good grades.
In my early undergrad years I studied as hard as I could. And I thought this meant putting in as many studying hours as possible. But I later realized that going out and having fun refreshed the mind and increased grades. Unfortunately it took at least 2 years for me to understand this lesson. 9. Learn how to do advanced Google searches.
This is an essential skill that enables you to answer your own questions, quickly. At a minimum I suggest you learn how to use the following Google search operators ~, -,*, AND,OR, and numeric ranges via the double dot (“..”) operator. The “site:” operator is also often helpful. I also found adding the word “tutorial” to a Google search often yields great introductory materials.
10. Turn weaknesses into strengths.
While studying for standardized exams I learned the importance of addressing one’s weaknesses as opposed to ignoring them. If you make a mistake on a question, it is because of a weakness within you. If you do not address that weakness it will follow you to the exam. I learned this lesson when studying for standardized exams. I was able to legally buy 30 old exams and thought the best approach to studying for the exam was to do as many old problems as possible. But as I completed each exam I kept getting the same score (+/- 5%) over and over. I had plateaued! But then I made a tiny tweak and my scores kept going up. Specifically, after each old exam, I would identify my weaknesses that led to each wrong answer, prioritize the weaknesses according to the degree to which they affected my score, and would address them in that order. When I did that, my scores increased steadily all the way to the highest possible percentile (99%). I later realized that such standardized tests are designed to provide consistent scores (if the student does not study in between the subsequent exams to address their weaknesses). In fact that is one of the statistical measures used to measure the quality of a standardized exam and it’s called “Reliability” (Google for “psychometric reliability” to see what I’m talking about).
general language learning resources
dictionaries:
wordreference - has spanish, french, italian, portuguese, catalan, german, swedish, dutch, russian, polish, romanian, czech, greek, turkish, chinese, japanese, korean, & arabic
reverso translation - has arabic, chinese, dutch, french, german, hebrew, italian, japanese, polish, portuguese, romanian, russian, spanish & turkish
bab.la - has spanish, arabic, chinese, czech, danish, dutch, finnish, french, german, greek, hindi, hungarian, indonesian, italian, japanese, korean, norwegian, polish, portuguese, romanian, russian, swedish, swahili, thai, turkish, vietnamese, & esperanto
digital dictionaries of south asia - has dictionaries for assamese, baluchi, bengali, divehi, hindi, kashmiri, khowar, lushai, malayalam, marathi, nepali, oriya, pali, panjabi, pashto, persian, prakrit, rajasthani, sanskrit, sindhi, sinhala, tamil, telugu & urdu
resources for learning words in context:
reverso context - has arabic, chinese (in beta), dutch, french, german, hebrew, italian, japanese, polish, portuguese, romanian, russian, spanish & turkish (in beta)
linguee - has german, spanish, portuguese, french, italian, russian, japanese, chinese, polish, dutch, swedish, danish, finnish, greek, czech, romanian, hungarian, slovak, bulgarian, slovene, lithuanian, latvian, maltese, & estonian
for learning different writing systems
omniglot - an encyclopedia with literally any language you could think of including ancient languages
scripts - an app for learning other writing systems with a limited amount for free (you can do 5 minutes a day for free) - has the ASL alphabet, Russian cyrillic, devanagari, Japanese kana, Chinese hanzi, & Korean hangul
Wikipedia is also helpful for learning different writing systems honestly!
pronunciation
forvo - a pronunciation dictionary with MANY languages (literally an underrated resource i use it all the time)
a really helpful video by luca lampariello with tips on how to get better pronunciation in any language
ipachart.com - an interactive chart with almost every sound!! literally such an amazing resource for learning the IPA (however does not include tones)
another interactive IPA chart (this one does have tones)
language tutoring
italki - there’s many websites for language tutoring but i think italki has the most languages (i have a referral link & if you use it we can both get $10 toward tutoring lol) - they say they support 130 languages!
there’s also preply and verbling which are also good but there aren’t as many options for languages - preply has 27 and verbling has 43
(obviously these are not free but if you have the money i think tutoring is a great way to learn a language!)
getting corrections/input from native speakers
hellotalk - an app for language exchanges with native speakers & they also have functions where you can put up a piece of writing and ask for corrections - honestly this app is great
tandem - language exchange app but unlike hellotalk you can choose multiple languages (although i think hellotalk is a little bit better)
LangCorrect - supports 170 languages!
HiNative - supports 113 languages!
Lang-8 - supports 90 languages!
verb conjugation
verbix - supports a ton of languages
Reverso conjugation - only has english, french, spanish, german, italian, portuguese, hebrew russian, arabic, & japanese
apps
duolingo - obviously everybody knows about duolingo but i’m still going to put it here - i will say i think duolingo is a lot more useful for languages that use the latin alphabet than languages with another writing system however they do have a lot of languages and add more all the time - currently they have 19 languages but you can see what languages they’re going to add on the incubator
memrise - great for vocab! personally i prefer the app to the desktop website
drops - you can only do 5 minutes a day for free but i still recommend it because it’s fun and has 42 languages!
LingoDeer - specifically geared towards asian languages - includes korean, japanese, chinese & vietnamese (as well as spanish, french, german, portuguese and russian), however only a limited amount is available for free
busuu - has arabic, chinese, french, german, italian, japanese, polish, portuguese, spanish, russian, spanish, & turkish,
Mondly - has 33 languages including spanish, french, german, italian, russian, japanese, korean, chinese, turkish, arabic, persian, hebrew, portuguese (both brazilian & european), catalan, latin, dutch, swedish, norwegian, danish, finnish, latvian, lithuanian, greek, romanian, afrikaans, croatian, polish, bulgarian, czech, slovak, hungarian, ukrainian, vietnamese, hindi, bengali, urdu, indonesian, tagalog & thai
misc
a video by the polyglot Lýdia Machová about how different polyglots learn languages - this video is great especially if you don’t know where to start in terms of self study
LangFocus - a youtube channel of this guy who talks about different languages which is always a good place to start to understand how a specific language works also his videos are fun
Polyglot: How I Learn Languages by Kató Lomb - this book is great and available online completely for free!
Fluent Forever by Gabriel Wyner (on pdfdrive) - another great book about language learning
Anki - a flashcard app (free on desktop for any system & free on android mobile - not free on ios mobile) that specifically uses spaced repetition to help you learn vocabulary, it’s got a slightly ugly design but it’s beloved by many language learners & is honestly so helpful
YouTube - literally utilize youtube it is so good.
Easy Languages - a youtube channel with several languages (basically they go around asking people on the street stuff so the language in the videos is really natural) & they also have breakaway channels for german, french, spanish, polish, italian, greek, turkish, russian, catalan & english
there’s also the LanguagePod101 youtube channels (e.g. FrenchPod101, JapanesePod101, HebrewPod101) which are super great for listening practice & language lessons as well as learning writing systems!

Researching for a project? Looking for open-access, high quality databases, encyclopedias and resources to help you write your next paper? Here’s a list of some great ones to help you find exactly what you were looking for.
Research Managers
Zotero
Mendeley
Qiqqa
General
List of academic databases and search engines
Our World in Data
Search Engines
100 Time-Saving Search Engines for Serious Scholars
Top 11 Trusted (And Free) Search Engines For Scientific and Academic Research
Ten search engines for researchers that go beyond Google
12 Fabulous Academic Search Engines
The 6 BEST Search Engines for Academic Research
20 of the Best Search Engines for Students
Best Educational Search Engines For Academic Researchers
Databases
Directory of Open Access Journals
New York Public Library Articles and Databases
UCSB Article Indexes & Research Databases
DATABASES: Library of Congress E-Resources Online Catalog
FINDING CURRENT RESEARCH USING FREE ONLINE RESOURCES
Free Databases for Magazine/Journal Articles, etc.
Free Full-Text Resources for Grad School Papers
Online Reference: Open Access Databases
Free Online Full-text Articles
Free scholarly resources
International Education Research Database
PubMed
Sci-Hub
Database checklist: Key academic research resources — both free and restricted
Research Databases and Other Online Tools
Encyclopedias
Top Encyclopedia Sites for Student Research Papers
RefSeek’s Encyclopedias
Encyclopedia.com
Infoplease
Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
Medline Plus
Dictionaries
RefSeek’s dictionaries and thesauri
The 10 Best Online Dictionaries
Essay and Paper Writing
Essay and Paper Writing Masterpost
How to Write a Resume LIKE A BOSS
So you’re ready to assume some responsibility and apply for your first job (or your fifth job or your fiftieth job) and you want some tips on writing a good resume, huh? Well, are you are in luck because 1) I’ve edited and proofed so many resumes I could probably write one for each of my friends without their input and 2) I’ve actually taken some classes on this shit. So, basing this primarily on comments I’ve made while correcting someone else’s resume (and while looking at my own for reference), here are my tips on writing a resume.

Keep reading

scholarships are the bomb!! free money to get urself an education!! here’s my best advice aaand resources for applying + getting some of that sweet sweet money :D
advice
use all of the databases!! the scholarships are right there for you. Take advantage of them, srsly!!! many let you input your criteria + they’ll match you up with some, and they help to organize your applications. You can subscribe to their newsletter and get alerts for new scholarships. there’s a whole bundle below all this advice to getchu started :D
start early + don’t stop: your eligibility for scholarships starts pretty much freshman year of high school, and basically doesn’t stop until you’re out of education, so take advantage of them!!! Logically, applying to more gives you a higher chance of winning one, so keep ploughing through them
don’t let essays scare you off: sweepstakes scholarships are easiest to apply for, but this also means they have more applicants. Do your best work + put time into essay-based scholarship contests, and up your chance of winning something!! Factor them into your normal routine like you would a homework assignment and just keep at it.
keep track of what you’ve applied for: seriously. Do it. It’ll motivate you when you’re not feeling like it, + keep you organized. Set up a spreadsheet (google sheets, excel, whatever floats your boat) and give it 5 columns: title of the scholarship, amount worth, whether or not you’ve applied, if you were successful, + the organization offering it. It’s also a great reminder of scholarships to reapply for next year.
check local scholarships: they’re waayyyy more restricted so the applicant pool is a lot smaller!!! Check your school, organizations you belong to, your parents’ companies, + local businesses. You’ll be competing against people in your town/county/district + it’ll give you a much better shot at winning. Check out your school’s website + talk to your guidance counsellors!
be specific: narrow down that applicant pool early. When you’re googling, look for scholarships that will apply only to you, so don’t just search ‘scholarships’. Look for ‘scholarships for bisexual women’, or ‘scholarships for international students’, or ‘scholarships for left-handed volleyball players’. Less applicants=better outcomes.
don’t apply to scams: be wary!!! Two big things: be careful of scholarships which want you to pay to apply, and guaranteed scholarships. Research pay-to-apply ones to make sure they’re legit. There’s more info here, here, and here on avoiding scholarship scams. Stay safe!!
scholarship databases
unigo goodcall scholarships.com niche scholarshipmonkey fastweb chegg cappex dosomething scholarshippoints nextstudent college board
more scholarship masterposts
college scholarships masterpost by @wonderstudying
how to search for scholarships by @adamparresh
scholarships! by @the-regular-student
it’s ya girl’s college scholarship masterpost by @jesussbabymomma
scholarship 101 by @thisexpedition
scholarships: how to find them and apply by @futurecristinayang
good luck!! you’ve got this :D
If you spend a lot of time on your laptop for work, study, etc., you should definitely check out this app called Noizio. It provides ambient background sounds that help calm you or keep you focused. You can even make and save your own combination of sounds. My personal favourite is winter wind + wind chimes + sea waves. Each sound’s volume can be adjusted individually as well!
-
 letscandyme liked this · 2 years ago
letscandyme liked this · 2 years ago -
 nadiakg71 reblogged this · 4 years ago
nadiakg71 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 swirlspill-study reblogged this · 6 years ago
swirlspill-study reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 honeysweetthalia reblogged this · 6 years ago
honeysweetthalia reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 honeysweetthalia liked this · 6 years ago
honeysweetthalia liked this · 6 years ago -
 whip-dab-blog liked this · 6 years ago
whip-dab-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 breakfastwithandi reblogged this · 6 years ago
breakfastwithandi reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 breakfastwithandi liked this · 6 years ago
breakfastwithandi liked this · 6 years ago -
 calharker liked this · 6 years ago
calharker liked this · 6 years ago -
 simply-one-hell-of-a-fangrell liked this · 6 years ago
simply-one-hell-of-a-fangrell liked this · 6 years ago -
 precciousx liked this · 6 years ago
precciousx liked this · 6 years ago -
 the-little-prophet reblogged this · 7 years ago
the-little-prophet reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 kimberlydashian liked this · 7 years ago
kimberlydashian liked this · 7 years ago -
 studybeans reblogged this · 7 years ago
studybeans reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 studybeans liked this · 7 years ago
studybeans liked this · 7 years ago -
 abovethecloudsofpompeii-blog liked this · 7 years ago
abovethecloudsofpompeii-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 starlsx reblogged this · 7 years ago
starlsx reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 im-at-nurseings-now reblogged this · 7 years ago
im-at-nurseings-now reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 agirlnameddivine liked this · 7 years ago
agirlnameddivine liked this · 7 years ago -
 ibhelpblog-blog1 reblogged this · 7 years ago
ibhelpblog-blog1 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 insert-cleverurl liked this · 7 years ago
insert-cleverurl liked this · 7 years ago -
 lola00003-blog liked this · 7 years ago
lola00003-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 chocogrades reblogged this · 7 years ago
chocogrades reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 starkdelinquents liked this · 7 years ago
starkdelinquents liked this · 7 years ago -
 emma-studies-ib reblogged this · 7 years ago
emma-studies-ib reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 undergroundchemist reblogged this · 7 years ago
undergroundchemist reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 undergroundchemist liked this · 7 years ago
undergroundchemist liked this · 7 years ago -
 akademea reblogged this · 7 years ago
akademea reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 uhhhokayybye liked this · 7 years ago
uhhhokayybye liked this · 7 years ago -
 unemployedgolem liked this · 8 years ago
unemployedgolem liked this · 8 years ago -
 pretty-butterfly16 liked this · 8 years ago
pretty-butterfly16 liked this · 8 years ago -
 sarahsdesk liked this · 8 years ago
sarahsdesk liked this · 8 years ago -
 rosiestudying reblogged this · 8 years ago
rosiestudying reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 vmjustforfun liked this · 8 years ago
vmjustforfun liked this · 8 years ago -
 the-evergreen-faery liked this · 8 years ago
the-evergreen-faery liked this · 8 years ago -
 mxntagues liked this · 8 years ago
mxntagues liked this · 8 years ago -
 studysthetic reblogged this · 8 years ago
studysthetic reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 pend-ing-blog liked this · 8 years ago
pend-ing-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 supernovaexplosion liked this · 8 years ago
supernovaexplosion liked this · 8 years ago -
 aioliend-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
aioliend-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
a study blog for collected references, advice, and inspiration
267 posts


