In Slow Motion, Vortex Rings Can Be Truly Stunning. This Video Shows Two Bubble Rings Underwater As They

In slow motion, vortex rings can be truly stunning. This video shows two bubble rings underwater as they interact with one another. Upon approach, the two low-pressure vortex cores link up in what’s known as vortex reconnection. Note how the vortex rings split and reconnect in two places – not one. According to Helmholtz’s second theorem a vortex cannot end in a fluid–it must form a closed path (or end at a boundary); that’s why both sides come apart and together this way. After reconnection, waves ripple back and forth along the distorted vortex ring; these are known as Kelvin waves. Some of those perturbations bring two sides of the enlarged vortex ring too close to one another, causing a second vortex reconnection, which pinches off a smaller vortex ring. (Image source: A. Lawrence; submitted by Kam-Yung Soh)
Note: As with many viral images, locating a true source for this video is difficult. So far the closest to an original source I’ve found is the Instagram post linked above. If you know the original source, please let me know so that I can update the credit accordingly. Thanks!
More Posts from Philosophical-amoeba and Others

(Image caption: Measurement of brain activity in a patient with phantom limb pain. Credit: Osaka University)
Cause of phantom limb pain in amputees, and potential treatment, identified
Researchers have discovered that a ‘reorganisation’ of the wiring of the brain is the underlying cause of phantom limb pain, which occurs in the vast majority of individuals who have had limbs amputated, and a potential method of treating it which uses artificial intelligence techniques.
The researchers, led by a group from Osaka University in Japan in collaboration with the University of Cambridge, used a brain-machine interface to train a group of ten individuals to control a robotic arm with their brains. They found that if a patient tried to control the prosthetic by associating the movement with their missing arm, it increased their pain, but training them to associate the movement of the prosthetic with the unaffected hand decreased their pain.
Their results, reported in the journal Nature Communications, demonstrate that in patients with chronic pain associated with amputation or nerve injury, there are ‘crossed wires’ in the part of the brain associated with sensation and movement, and that by mending that disruption, the pain can be treated. The findings could also be applied to those with other forms of chronic pain, including pain due to arthritis.
Approximately 5,000 amputations are carried out in the UK every year, and those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes are at particular risk of needing an amputation. In most cases, individuals who have had a hand or arm amputated, or who have had severe nerve injuries which result in a loss of sensation in their hand, continue to feel the existence of the affected hand as if it were still there. Between 50 and 80 percent of these patients suffer with chronic pain in the ‘phantom’ hand, known as phantom limb pain.
“Even though the hand is gone, people with phantom limb pain still feel like there’s a hand there – it basically feels painful, like a burning or hypersensitive type of pain, and conventional painkillers are ineffective in treating it,” said study co-author Dr Ben Seymour, a neuroscientist based in Cambridge’s Department of Engineering. “We wanted to see if we could come up with an engineering-based treatment as opposed to a drug-based treatment.”
A popular theory of the cause of phantom limb pain is faulty ‘wiring’ of the sensorimotor cortex, the part of the brain that is responsible for processing sensory inputs and executing movements. In other words, there is a mismatch between a movement and the perception of that movement.
In the study, Seymour and his colleagues, led by Takufumi Yanagisawa from Osaka University, used a brain-machine interface to decode the neural activity of the mental action needed for a patient to move their ‘phantom’ hand, and then converted the decoded phantom hand movement into that of a robotic neuroprosthetic using artificial intelligence techniques.
“We found that the better their affected side of the brain got at using the robotic arm, the worse their pain got,” said Yanagisawa. “The movement part of the brain is working fine, but they are not getting sensory feedback – there’s a discrepancy there.”
The researchers then altered their technique to train the ‘wrong’ side of the brain: for example, a patient who was missing their left arm was trained to move the prosthetic arm by decoding movements associated with their right arm, or vice versa. When they were trained in this counter-intuitive technique, the patients found that their pain significantly decreased. As they learned to control the arm in this way, it takes advantage of the plasticity – the ability of the brain to restructure and learn new things – of the sensorimotor cortex, showing a clear link between plasticity and pain.
Although the results are promising, Seymour warns that the effects are temporary, and require a large, expensive piece of medical equipment to be effective. However, he believes that a treatment based on their technique could be available within five to ten years. “Ideally, we’d like to see something that people could have at home, or that they could incorporate with physio treatments,” he said. “But the results demonstrate that combining AI techniques with new technologies is a promising avenue for treating pain, and an important area for future UK-Japan research collaboration.”
Why do men have Adam's apples. It's so sexy but seems so unnecessary
It basically is unnecessary lol
It’s not that only men have Adam’s apples, women do too, but it’s less prominent. An Adam’s apple is just a piece of cartilage that protects your larynx (the voicebox) directly behind it. As boys & girls go through puberty, our voicebox grows which:
1. Causes our voice to deepen 2. Pushes the cartilage further forwards
In boys, the larynx grows in size significantly more which therefore pushes forward the evident bump of cartilage we like to call an Adam’s Apple.

Kilroy Was Here!
He’s engraved in stone in the National World War II Memorial in Washington, DC – back in a small alcove where very few people have seen it. For the WWII generation, this will bring back memories. For younger folks, it’s a bit of trivia that is an intrinsic part of American history and legend.
Anyone born between 1913 to about 1950, is very familiar with Kilroy. No one knew why he was so well known….but everybody seemed to get into it. It was the fad of its time!

At the National World War II Memorial in Washington, DC
So who was Kilroy?
In 1946 the American Transit Association, through its radio program, “Speak to America,” sponsored a nationwide contest to find the real Kilroy….now a larger-than-life legend of just-ended World War II….offering a prize of a real trolley car to the person who could prove himself to be the genuine article.

Almost 40 men stepped forward to make that claim, but only James Kilroy from Halifax, Massachusetts, had credible and verifiable evidence of his identity.
“Kilroy” was a 46-year old shipyard worker during World War II (1941-1945) who worked as a quality assurance checker at the Fore River Shipyard in Quincy, Massachusetts (a major shipbuilder for the United States Navy for a century until the 1980s).
His job was to go around and check on the number of rivets completed. (Rivets held ships together before the advent of modern welding techniques.) Riveters were on piece work wages….so they got paid by the rivet. He would count a block of rivets and put a check mark in semi-waxed lumber chalk (similar to crayon), so the rivets wouldn’t be counted more than once.

A warship hull with rivets
When Kilroy went off duty, the riveters would surreptitiously erase the mark. Later, an off-shift inspector would come through and count the rivets a second time, resulting in double pay for the riveters!
One day Kilroy’s boss called him into his office. The foreman was upset about unusually high wages being “earned” by riveters, and asked him to investigate. It was then he realized what had been going on.
The tight spaces he had to crawl in to check the rivets didn’t lend themselves to lugging around a paint can and brush, so Kilroy decided to stick with the waxy chalk. He continued to put his check mark on each job he inspected, but added ”KILROY WAS HERE!“ in king-sized letters next to the check….and eventually added the sketch of the guy with the long nose peering over the fence….and that became part of the Kilroy message.

Kilroy’s original shipyard inspection “trademark” during World War II
Once he did that, the riveters stopped trying to wipe away his marks.
Ordinarily the rivets and chalk marks would have been covered up with paint. With World War II on in full swing, however, ships were leaving the Quincy Yard so fast that there wasn’t time to paint them. As a result, Kilroy’s inspection “trademark” was seen by thousands of servicemen who boarded the troopships the yard produced.
His message apparently rang a bell with the servicemen, because they picked it up and spread it all over the European and the Pacific war zones.

Before war’s end, “Kilroy” had been here, there, and everywhere on the long hauls to Berlin and Tokyo.
To the troops outbound in those ships, however, he was a complete mystery; all they knew for sure was that someone named Kilroy had “been there first.” As a joke, U.S. servicemen began placing the graffiti wherever they landed, claiming it was already there when they arrived.

As the World War II wore on, the legend grew. Underwater demolition teams routinely sneaked ashore on Japanese-held islands in the Pacific to map the terrain for coming invasions by U.S. troops (and thus, presumably, were the first GI’s there). On one occasion, however, they reported seeing enemy troops painting over the Kilroy logo!
Kilroy became the U.S. super-GI who had always “already been” wherever GIs went. It became a challenge to place the logo in the most unlikely places imaginable. (It is said to now be atop Mt. Everest, the Statue of Liberty, the underside of the Arc de Triomphe in Paris, and even scrawled in the dust on the moon by the American astronauts who walked there between 1969 and 1972.

In 1945, as World War II was ending, an outhouse was built for the exclusive use of Allied leaders Harry Truman, Joseph Stalin, and Winston Churchill at the Potsdam Conference. It’s first occupant was Stalin, who emerged and asked his aide (in Russian), “Who is Kilroy?”
To help prove his authenticity in 1946, James Kilroy brought along officials from the shipyard and some of the riveters. He won the trolley car….which he attached to the Kilroy home and used to provide living quarters for six of the family’s nine children….thereby solving what had become an acute housing crisis for the Kilroys.

The new addition to the Kilroy family home.
* * * *
And the tradition continues into the 21st century…

In 2011 outside the now-late-Osama Bin Laden’s hideaway house in Abbottabad, Pakistan….shortly after the al-Qaida-terrorist was killed by U.S. Navy SEALs.
>>Note: The Kilroy graffiti on the southwest wall of the Bin Laden compound pictured above was real (not digitally altered with Microsoft Paint, as postulated by some). The entire compound was leveled in 2012 for redevelopment by a Pakistani company as an amusement park….and to avoid it becoming a shrine to Bin Laden’s nefarious memory.
* * * *
A personal note….
My Dad’s trademark signature on cards, letters and notes to my sisters and I for the first 50 or so years of our lives (until we lost him to cancer) was to add the image of “Kilroy” at the end. We kids never ceased to get a thrill out of this….even as we evolved into adulthood.
To this day, the “Kilroy” image brings back a vivid image of my awesome Dad into my head….and my heart!
Dad: This one’s for you!
Marine biology basics: a reading list
Someone recently asked me to “explain to me the basics of marine biology“ and I didn’t even know where to begin because that’s a HUGE topic with so much interesting stuff to think about. I asked some of my fellow scientists on twitter and we put together a list of good reading and watching to get an overview of what marine biology is all about. This list is broken down by ages. Comment with any more suggestions and I’ll add them!
Kids:
1)National Geographic Kids, Really Wild Animals, Deep Sea Dive (recommended by @DrKatfish on twitter) I watched this video when I was a kid and have been hooked on cephalopods ever since. If you listened to me on NPR’s Science Friday, this was the video I was talking about!
2) The Magic Schoolbus- on the ocean floor (recommended by @easargent184 and @mirandaRHK on twitter)

Amazon link: https://www.amazon.com/Magic-School-Bus-Ocean-Floor/dp/0590414313#reader_0590414313
3) Ocean Sunlight- How tiny plants feed the seas (recommended by @ColemanLab on twitter)

Amazon link:https://www.amazon.com/Ocean-Sunlight-Tiny-Plants-Feed/dp/0545273226
All ages
There are a TON of resources on The Bridge, so that’s a good place to start.
1) Blue Planet Series (recommended by @PaulSFenton on twitter) Great series, it’s on netflix and amazon
2) A Day in the life of a marine biologist (recommended by @Napaaqtuk on twitter)
3) Diving Deep with Sylvia Earle (recommended by @Napaaqtuk on twitter)
4) My wish: Protext our Oceans (Sylvia Earle) (also recommended by @Napaaqtuk on twitter)
Adults
1) At the Water’s Edge (Recommended by @PaulSFenton on twitter) “More a book about evolution featuring marine animals but still a v. good read.“

2) Four Fish: The future of the last wild Food (Recommended by me!) A great book about fisheries

3) Kraken : The Curious, Exciting, and Slightly Disturbing Science of Squid (Recommended by me)

4) The Edge of the Sea by Rachel Carson (recommended by @MirandaRHK on twitter)

5) The Sea Around Us- Rachel Carson (Recommended by @aecahill on twitter)

6) An Unnatural History of the Sea- Callum Roberts



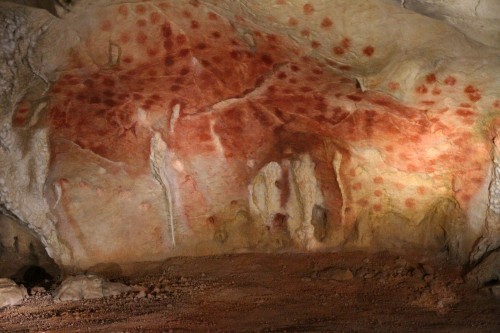



CHAUVET CAVE:
THE Chauvet Cave (also known as the Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc Cave) is a Palaeolithic cave situated near Vallon-Pont-d’Arc in the Ardèche region of southern France that houses impeccably preserved, exquisite examples of prehistoric art.
Now reliably dated to between c. 33,000 and c. 30,000 years ago, the numerous and diverse animals that dot the interior walls of the cave – both painted and engraved – show such high artistic quality that they were initially thought to have been closer in age to the similarly stunning, but much younger art in caves such as the Lascaux Cave. Its age and artistry have made us reconsider the story of art as well as the capabilities of these humans. The cave has been granted UNESCO World Heritage status.
Read More
Article by Emma Groeneveld on AHE
Survivorship Bias
I have posted about survivorship bias and how it affects your career choices: how a Hollywood actor giving the classic “follow your dreams and never give up” line is bad advice and is pure survivorship bias at work.
When I read up on the wikipedia page, I encountered an interesting story:
During WWII the US Air Force wanted to minimize bomber losses to enemy fire. The Center for Naval Analyses ran a research on where bombers tend to get hit with the explicit aim of enforcing the parts of the airframe that is most likely to receive incoming fire. This is what they came up with:

So, they said: the red dots are where bombers are most likely to be hit, so put some more armor on those parts to make the bombers more resilient. That looked like a logical conclusion, until Abraham Wald - a mathematician - started asking questions:
- how did you obtain that data? - well, we looked at every bomber returning from a raid, marked the damages on the airframe on a sheet and collected the sheets from all allied air bases over months. What you see is the result of hundreds of those sheets. - and your conclusion? - well, the red dots are where the bombers were hit. So let’s enforce those parts because they are most exposed to enemy fire. - no. the red dots are where a bomber can take a hit and return. The bombers that took a hit to the ailerons, the engines or the cockpit never made it home. That’s why they are absent in your data. The blank spots are exactly where you have to enforce the airframe, so those bombers can return.
This is survivorship bias. You only see a subset of the outcomes. The ones that made it far enough to be visible. Look out for absence of data. Sometimes they tell a story of their own.
BTW: You can see the result of this research today. This is the exact reason the A-10 has the pilot sitting in a titanium armor bathtub and has it’s engines placed high and shielded.










Staff Pick of the Week
As a lover of mythology and folklore, my first staff pick is The Wonder-Smith and His Son, by Ella Young (1867-1956), with illustrations by Boris Artzybasheff (1899-1965). It was published by Longmans, Green Co. in 1927 and was a Newbery Honor recipient in 1928. The book is a collection of myths from Ireland and Scotland about a legendary wonder smith known as the Gubbaun Saor, a “maker of worlds and a shaper of universes.” There are fourteen stories in the collection, detailing how the Gubbaun Saor got his world-building abilities, which involved finding a bag of magical tools that were dropped from the sky by a bird. The book also includes tales about his adopted son Lugh and his daughter Aunya. In her memoir, Flowering Dusk: Things Remembered Accurately and Inaccurately, Young wrote “I have a fondness for The Wonder-Smith; perhaps because I did not invent the stories in the book. I gathered them through twenty-five years of searching, and put a thread of prose round them.” The folktales were collected from story-tellers in Clare, Achill Island, Aranmore, and the Curraun.
Ella Young’s interest in Celtic mythology led to her becoming involved with the growing Irish nationalist movement. Many nationalist writers and artists were looking to Ireland’s history and legends for inspiration, and she befriended fellow Irish writers Æ (George William Russell), Padraic Colum, and William Butler Yeats. Æ called her “a druidess reincarnated.” Aside from publishing poetry and folklore, Yong was also involved in running guns and ammunition to the Irish Republican Army, and was a member of Cumann na mBAn, a women’s paramilitary organization that took part in the 1916 Easter Rising. She continued to write throughout the war, and in 1925 embarked for America to do a speaking tour about Celtic mythology at universities across the country. She was eventually granted American citizenship and accepted a teaching position at the University of California, Berkeley. Often described as mystical and otherworldly, Young lived out the rest of her life near the California coast writing and publishing stories and sharing her love of folklore with those around her.
Ukrainian illustrator Boris Artzybasheff fled the Russian Revolution for the United States in 1919. Beginning his career as an engraver, Artzybasheff soon became a book illustrator, some of which he wrote himself, such as Seven Simeons: A Russian Tale, which received a Caldecott Honor award in 1938. He is best known for his magazine covers, and he created over 200 covers for Time magazine alone. Over the course of his career his work evolved to become wonderfully surrealist, he loved anthropomorphizing machines so they would have human attributes and emotions. Even his commercial work in advertising has elements of the absurd. I believe Artzybasheff’s playfulness is evident in the woodcuts he did for The Wonder-Smith, and his illustrations are what drew me to the book.
– Sarah, Special Collections Undergraduate Assistant
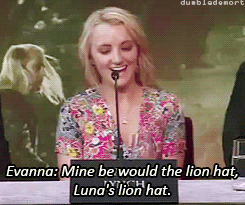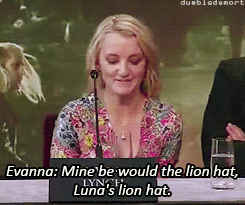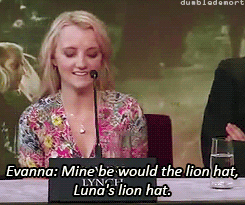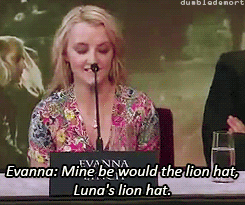

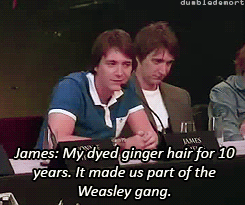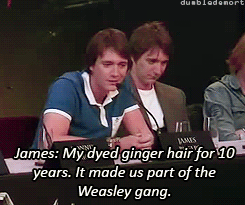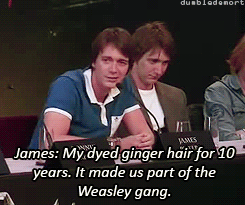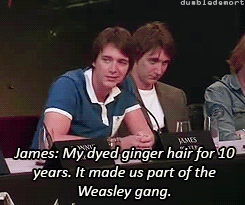
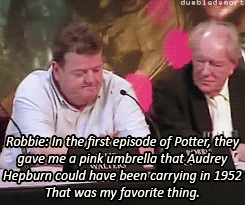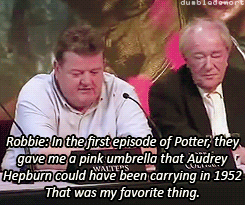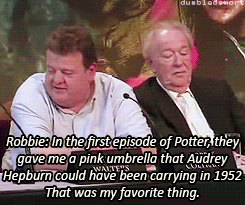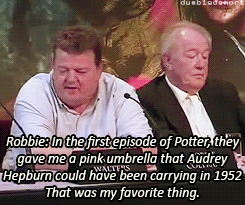




What was your favorite prop or costume from the “Harry Potter” films?
-
 udulotaborkemencevel liked this · 6 months ago
udulotaborkemencevel liked this · 6 months ago -
 vald1n reblogged this · 6 months ago
vald1n reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 xmorcix liked this · 6 months ago
xmorcix liked this · 6 months ago -
 luxy-amigo liked this · 6 months ago
luxy-amigo liked this · 6 months ago -
 nyeznajka liked this · 6 months ago
nyeznajka liked this · 6 months ago -
 pajjorimre liked this · 6 months ago
pajjorimre liked this · 6 months ago -
 meginttuloktulok reblogged this · 6 months ago
meginttuloktulok reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 meginttuloktulok liked this · 6 months ago
meginttuloktulok liked this · 6 months ago -
 dulimano reblogged this · 6 months ago
dulimano reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 lassukmiboolelunk reblogged this · 6 months ago
lassukmiboolelunk reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 seantm liked this · 6 months ago
seantm liked this · 6 months ago -
 such-reblog reblogged this · 6 months ago
such-reblog reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 spirallyxstimmingxmermaid liked this · 6 months ago
spirallyxstimmingxmermaid liked this · 6 months ago -
 alienshifter reblogged this · 6 months ago
alienshifter reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 alienshifter liked this · 6 months ago
alienshifter liked this · 6 months ago -
 jamesmassino liked this · 6 months ago
jamesmassino liked this · 6 months ago -
 superdragonfireus liked this · 6 months ago
superdragonfireus liked this · 6 months ago -
 skredworks liked this · 6 months ago
skredworks liked this · 6 months ago -
 coopergriggs reblogged this · 6 months ago
coopergriggs reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 coopergriggs liked this · 6 months ago
coopergriggs liked this · 6 months ago -
 jdshepherd reblogged this · 7 months ago
jdshepherd reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 jdshepherd liked this · 7 months ago
jdshepherd liked this · 7 months ago -
 byenoonmoons reblogged this · 7 months ago
byenoonmoons reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 byenoonmoons liked this · 7 months ago
byenoonmoons liked this · 7 months ago -
 truthofthesignal reblogged this · 7 months ago
truthofthesignal reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 wetwicksdry liked this · 7 months ago
wetwicksdry liked this · 7 months ago -
 roguetelemetry reblogged this · 7 months ago
roguetelemetry reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 eclectichellmouth reblogged this · 1 year ago
eclectichellmouth reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 furrytreasurehunter liked this · 1 year ago
furrytreasurehunter liked this · 1 year ago -
 simply-pixeling liked this · 2 years ago
simply-pixeling liked this · 2 years ago -
 caveman-musings liked this · 3 years ago
caveman-musings liked this · 3 years ago -
 garamoba reblogged this · 3 years ago
garamoba reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 darncool reblogged this · 3 years ago
darncool reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 sashaexmachina liked this · 3 years ago
sashaexmachina liked this · 3 years ago -
 m00ndingochan reblogged this · 3 years ago
m00ndingochan reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 m00ndingochan liked this · 3 years ago
m00ndingochan liked this · 3 years ago -
 drummerofthought reblogged this · 3 years ago
drummerofthought reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 d--r--i--f--t--w--o--o--d reblogged this · 4 years ago
d--r--i--f--t--w--o--o--d reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 techjum reblogged this · 4 years ago
techjum reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 gagle liked this · 5 years ago
gagle liked this · 5 years ago -
 lawlkay liked this · 5 years ago
lawlkay liked this · 5 years ago -
 bewrabawa reblogged this · 5 years ago
bewrabawa reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 analysisrr liked this · 5 years ago
analysisrr liked this · 5 years ago -
 heartoftheempire reblogged this · 5 years ago
heartoftheempire reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 heartoftheempire liked this · 5 years ago
heartoftheempire liked this · 5 years ago
A reblog of nerdy and quirky stuff that pique my interest.
291 posts

