Is Kermit An Accurate Example Of A Frog?
Is Kermit an accurate example of a frog?
Yes (except for being a muppet). Did you know that there are real frogs that DO look like Kermit? This is a glass frog I found at my research site in the rainforest in Honduras.

More Posts from Philosophical-amoeba and Others
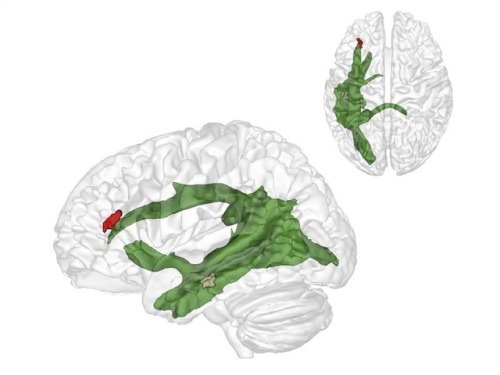
(Image caption: The maturation of fibres of a brain structure called the arcuate fascicle (green) between the ages of three and four years establishes a connection between two critical brain regions: a region (brown) at the back of the temporal lobe that supports adults thinking about others and their thoughts, and a region (red) in the frontal lobe that is involved in keeping things at different levels of abstraction and, therefore, helps us to understand what the real world is and what the thoughts of others are. Credit: © MPI CBS)
The importance of relating to others: why we only learn to understand other people after the age of four
When we are around four years old we suddenly start to understand that other people think and that their view of the world is often different from our own. Researchers in Leiden and Leipzig have explored how that works. Publication in Nature Communications on 21 March.
At around the age of four we suddenly do what three-year-olds are unable to do: put ourselves in someone else’s shoes. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences (MPI CBS) in Leipzig and at Leiden University have shown how this enormous developmental step occurs: a critical fibre connection in the brain matures. Senior researcher and Leiden developmental psychologist Nikolaus Steinbeis, co-author of the article, took part in the research. Lead author, PhD candidate Charlotte Grosse-Wiesmann, worked under his supervision.
Little Maxi
If you tell a 3-year-old child the following story of little Maxi, they will most probably not understand: Maxi puts his chocolate on the kitchen table, then goes to play outside. While he is gone, his mother puts the chocolate in the cupboard. Where will Maxi look for his chocolate when he comes back? A 3-year-old child will not understand why Maxi would be surprised not to find the chocolate on the table where he left it. It is only by the age of 4 years that a child will correctly predict that Maxi will look for his chocolate where he left it and not in the cupboard where it is now.
Theory of Mind
The researchers observed something similar when they showed a 3-year-old child a chocolate box that contained pencils instead of chocolates. When the child was asked what another child would expect to be in the box, they answered “pencils”, although the other child would not know this. Only a year later, around the age of four years, however, will they understand that the other child had hoped for chocolates. Thus, there is a crucial developmental breakthrough between three and four years: this is when we start to attribute thoughts and beliefs to others and to understand that their beliefs can be different from ours. Before that age, thoughts don’t seem to exist independently of what we see and know about the world. That is, this is when we develop a Theory of Mind.
Independent development
The researchers have now discovered what is behind this breakthrough. The maturation of fibres of a brain structure called the arcuate fascicle between the ages of three and four years establishes a connection between two critical brain regions: a region at the back of the temporal lobe that supports adult thinking about others and their thoughts, and a region in the frontal lobe that is involved in keeping things at different levels of abstraction and, therefore, helps us to understand what the real world is and what the thoughts of others are. Only when these two brain regions are connected through the arcuate fascicle can children start to understand what other people think. This is what allows us to predict where Maxi will look for his chocolate. Interestingly, this new connection in the brain supports this ability independently of other cognitive abilities, such as intelligence, language ability or impulse control.

(Image caption: Measurement of brain activity in a patient with phantom limb pain. Credit: Osaka University)
Cause of phantom limb pain in amputees, and potential treatment, identified
Researchers have discovered that a ‘reorganisation’ of the wiring of the brain is the underlying cause of phantom limb pain, which occurs in the vast majority of individuals who have had limbs amputated, and a potential method of treating it which uses artificial intelligence techniques.
The researchers, led by a group from Osaka University in Japan in collaboration with the University of Cambridge, used a brain-machine interface to train a group of ten individuals to control a robotic arm with their brains. They found that if a patient tried to control the prosthetic by associating the movement with their missing arm, it increased their pain, but training them to associate the movement of the prosthetic with the unaffected hand decreased their pain.
Their results, reported in the journal Nature Communications, demonstrate that in patients with chronic pain associated with amputation or nerve injury, there are ‘crossed wires’ in the part of the brain associated with sensation and movement, and that by mending that disruption, the pain can be treated. The findings could also be applied to those with other forms of chronic pain, including pain due to arthritis.
Approximately 5,000 amputations are carried out in the UK every year, and those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes are at particular risk of needing an amputation. In most cases, individuals who have had a hand or arm amputated, or who have had severe nerve injuries which result in a loss of sensation in their hand, continue to feel the existence of the affected hand as if it were still there. Between 50 and 80 percent of these patients suffer with chronic pain in the ‘phantom’ hand, known as phantom limb pain.
“Even though the hand is gone, people with phantom limb pain still feel like there’s a hand there – it basically feels painful, like a burning or hypersensitive type of pain, and conventional painkillers are ineffective in treating it,” said study co-author Dr Ben Seymour, a neuroscientist based in Cambridge’s Department of Engineering. “We wanted to see if we could come up with an engineering-based treatment as opposed to a drug-based treatment.”
A popular theory of the cause of phantom limb pain is faulty ‘wiring’ of the sensorimotor cortex, the part of the brain that is responsible for processing sensory inputs and executing movements. In other words, there is a mismatch between a movement and the perception of that movement.
In the study, Seymour and his colleagues, led by Takufumi Yanagisawa from Osaka University, used a brain-machine interface to decode the neural activity of the mental action needed for a patient to move their ‘phantom’ hand, and then converted the decoded phantom hand movement into that of a robotic neuroprosthetic using artificial intelligence techniques.
“We found that the better their affected side of the brain got at using the robotic arm, the worse their pain got,” said Yanagisawa. “The movement part of the brain is working fine, but they are not getting sensory feedback – there’s a discrepancy there.”
The researchers then altered their technique to train the ‘wrong’ side of the brain: for example, a patient who was missing their left arm was trained to move the prosthetic arm by decoding movements associated with their right arm, or vice versa. When they were trained in this counter-intuitive technique, the patients found that their pain significantly decreased. As they learned to control the arm in this way, it takes advantage of the plasticity – the ability of the brain to restructure and learn new things – of the sensorimotor cortex, showing a clear link between plasticity and pain.
Although the results are promising, Seymour warns that the effects are temporary, and require a large, expensive piece of medical equipment to be effective. However, he believes that a treatment based on their technique could be available within five to ten years. “Ideally, we’d like to see something that people could have at home, or that they could incorporate with physio treatments,” he said. “But the results demonstrate that combining AI techniques with new technologies is a promising avenue for treating pain, and an important area for future UK-Japan research collaboration.”
The Fibonacci sequence can help you quickly convert between miles and kilometers
The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where every new number is the sum of the two previous ones in the series.
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, etc. The next number would be 13 + 21 = 34.
Here’s the thing: 5 mi = 8 km. 8 mi = 13 km. 13 mi = 21 km, and so on.
Edit: You can also do this with multiples of these numbers (e.g. 5*10 = 8*10, 50 mi = 80 km). If you’ve got an odd number that doesn’t fit in the sequence, you can also just round to the nearest Fibonacci number and compensate for this in the answer. E.g. 70 mi ≈ 80 mi. 80 mi = 130 km. Subtract a small value like 15 km to compensate for the rounding, and the end result is 115 km.
This works because the Fibonacci sequence increases following the golden ratio (1:1.618). The ratio between miles and km is 1:1.609, or very, very close to the golden ratio. Hence, the Fibonacci sequence provides very good approximations when converting between km and miles.


Why did Vikings have ‘Allah’ embroidered into funeral clothes?
A new investigation into the garments - found in 9th and 10th Century graves - has thrown up new insights into contact between the Viking and Muslim worlds.
The breakthrough was made by textile archaeologist Annika Larsson of Uppsala University. To unlock the puzzle, she enlarged the letters and examined them from all angles, including from behind. Read on







The Christopher Robin Story Book from When we were very young, Now we are six, Winnie the Pooh, The House at Pooh Corner by AA Milne Illustrated by Ernest H Shepard London Methuen & Co Ltd. First Edition 1929

Rishi coffin for a commoner
Second Intermediate Period, Dynasty 17, 1580–1550 B.C. (find spot unknown)
In Dynasty 17 a new type of coffin appeared in Thebes: anthropoid, but no longer conceived solely as an inner coffin, and resting on its back because of a change in funerary customs whereby the deceased was no longer laid on one side. The anthropoid coffin was to become the burial container of choice among royals and commoners alike. The earliest examples are decorated in paint with a feather pattern, and so they are known by the Arabic word for “feathered,” rishi. Carved from local sycamore because the Thebans no longer had access to imported cedar, all rishi coffins, royal or private, show the deceased wearing the royal nemes headdress. This example was clearly a stock item made for a commoner, for a blank space was left for the owner’s name to be inserted at the end of the vertical inscription on the lid (a conventional offering formula for the dead).
Great vulture’s wings envelop the legs and lower abdomen. Even the top of the headdress is decorated with a feather pattern so that the deceased appears as a human-headed bird according to the concept of the ba, or mobile spirit. The ba could travel to any place and transform itself into anything it desired. The face on the coffin is painted black, not to represent the unknown owner’s race but to reinforce his identification with Osiris. The flesh of the god of death and resurrection was often shown as black or green to signify the black silt that fertilized the land with each year’s Nile flood, and the new life in the form of green vegetation that it brought forth. Painted on the chest is a pectoral, or chest ornament, in the form of a vulture and cobra, symbols of Nekhbet and Wadjyt, the tutelary goddesses of Upper and Lower Egypt.
Source: Museum of Fine Arts Boston


On this day, 14th February 1779, Captain James Cook was killed in Hawaii.
James Cook completed three major voyages of discovery. On his first, departing in 1768, he commanded the ‘Endeavour’ on an expedition to chart the transit of Venus. He returned to England in 1771, having also circumnavigated the globe, including exploring and charting New Zealand and Australia’s eastern coast.
On his second journey (1772-1775), he commanded the 'Resolution’ and the 'Adventure’ on an expedition to the South Pacific, disproving the rumour of a great southern continent, exploring the Antarctic Ocean, New Hebrides and New Caledonia.
Cook’s third and final voyage (1776-1779) of discovery was an attempt to locate a North-West Passage, an ice-free sea route which linked the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean. Again, Cook commanded the Resolution while Charles Clerke commanded Discovery. Leaving England in 1776, Cook first sailed south to Tahiti to return Omai, a Tahitian man, to his home. Omai had been taken on Cook’s second voyage and had been an object of curiosity in London. It was on this, Cook’s final voyage, that he discovered the Hawaiian Islands in January 1778. This major discovery would lead to his death – Cook was killed on a return visit to Hawaii at Kealakekua Bay, on 14 February 1779.
Kealakekua Bay was considered the sacred harbour of Lono, the fertility god of the Hawaiians. Cook and his compatriots were welcomed as gods but after one of the crewmen died, exposing the Europeans as mere mortals, relations became strained. On February 4, 1779, the British ships sailed from Kealakekua Bay, but rough seas damaged the foremast of the Resolution, and after only a week at sea the expedition was forced to return to Hawaii.
The Hawaiians greeted Cook and his men by hurling rocks; they then stole a small cutter vessel from the Discovery. Negotiations with King Kalaniopuu for the return of the cutter collapsed after a lesser Hawaiian chief was shot to death and a mob of Hawaiians descended on Cook’s party. The captain and his men fired on the angry Hawaiians, but they were soon overwhelmed, and only a few managed to escape to the safety of the Resolution. Captain Cook himself was killed by the mob. A few days later, the Englishmen retaliated by firing their cannons and muskets at the shore, killing some 30 Hawaiians. The Resolution and Discovery eventually returned to England.
The State Library of New South Wales holds significant original sources relating to James Cook, these paintings from the collection depict the death of Captain Cook.

Carved ditty box shaped like a coffin on silver stand, containing a rough watercolour sketch of the death of Cook, including a lock of Cook’s hair, ca. 1779 / carved by sailors on Cook’s last ship HMS Resolution. State Library of NSW.










Staff Pick of the Week
As a lover of mythology and folklore, my first staff pick is The Wonder-Smith and His Son, by Ella Young (1867-1956), with illustrations by Boris Artzybasheff (1899-1965). It was published by Longmans, Green Co. in 1927 and was a Newbery Honor recipient in 1928. The book is a collection of myths from Ireland and Scotland about a legendary wonder smith known as the Gubbaun Saor, a “maker of worlds and a shaper of universes.” There are fourteen stories in the collection, detailing how the Gubbaun Saor got his world-building abilities, which involved finding a bag of magical tools that were dropped from the sky by a bird. The book also includes tales about his adopted son Lugh and his daughter Aunya. In her memoir, Flowering Dusk: Things Remembered Accurately and Inaccurately, Young wrote “I have a fondness for The Wonder-Smith; perhaps because I did not invent the stories in the book. I gathered them through twenty-five years of searching, and put a thread of prose round them.” The folktales were collected from story-tellers in Clare, Achill Island, Aranmore, and the Curraun.
Ella Young’s interest in Celtic mythology led to her becoming involved with the growing Irish nationalist movement. Many nationalist writers and artists were looking to Ireland’s history and legends for inspiration, and she befriended fellow Irish writers Æ (George William Russell), Padraic Colum, and William Butler Yeats. Æ called her “a druidess reincarnated.” Aside from publishing poetry and folklore, Yong was also involved in running guns and ammunition to the Irish Republican Army, and was a member of Cumann na mBAn, a women’s paramilitary organization that took part in the 1916 Easter Rising. She continued to write throughout the war, and in 1925 embarked for America to do a speaking tour about Celtic mythology at universities across the country. She was eventually granted American citizenship and accepted a teaching position at the University of California, Berkeley. Often described as mystical and otherworldly, Young lived out the rest of her life near the California coast writing and publishing stories and sharing her love of folklore with those around her.
Ukrainian illustrator Boris Artzybasheff fled the Russian Revolution for the United States in 1919. Beginning his career as an engraver, Artzybasheff soon became a book illustrator, some of which he wrote himself, such as Seven Simeons: A Russian Tale, which received a Caldecott Honor award in 1938. He is best known for his magazine covers, and he created over 200 covers for Time magazine alone. Over the course of his career his work evolved to become wonderfully surrealist, he loved anthropomorphizing machines so they would have human attributes and emotions. Even his commercial work in advertising has elements of the absurd. I believe Artzybasheff’s playfulness is evident in the woodcuts he did for The Wonder-Smith, and his illustrations are what drew me to the book.
– Sarah, Special Collections Undergraduate Assistant
-
 cantdewwrite reblogged this · 4 years ago
cantdewwrite reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 cantdewwrite liked this · 4 years ago
cantdewwrite liked this · 4 years ago -
 rawrymakesartiguess liked this · 5 years ago
rawrymakesartiguess liked this · 5 years ago -
 frog-rag-blog liked this · 5 years ago
frog-rag-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 authenticaussie liked this · 6 years ago
authenticaussie liked this · 6 years ago -
 missjenca liked this · 6 years ago
missjenca liked this · 6 years ago -
 rikkitikkitaavi reblogged this · 6 years ago
rikkitikkitaavi reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 pinksdoll reblogged this · 6 years ago
pinksdoll reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 toomnyfeels liked this · 6 years ago
toomnyfeels liked this · 6 years ago -
 lennyisdyeing liked this · 6 years ago
lennyisdyeing liked this · 6 years ago -
 midnightsecretlittlerendezvous liked this · 6 years ago
midnightsecretlittlerendezvous liked this · 6 years ago -
 apocryph0n reblogged this · 6 years ago
apocryph0n reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 mephistophilies liked this · 6 years ago
mephistophilies liked this · 6 years ago -
 the-great-void reblogged this · 6 years ago
the-great-void reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 newtwarlock reblogged this · 6 years ago
newtwarlock reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 anotherbooklr-blog liked this · 6 years ago
anotherbooklr-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 pearlsandpetticoats liked this · 6 years ago
pearlsandpetticoats liked this · 6 years ago -
 cjskyelark liked this · 6 years ago
cjskyelark liked this · 6 years ago -
 swordbyte liked this · 6 years ago
swordbyte liked this · 6 years ago -
 marmarbaxter reblogged this · 6 years ago
marmarbaxter reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 marmarbaxter liked this · 6 years ago
marmarbaxter liked this · 6 years ago -
 bringoutthedead liked this · 6 years ago
bringoutthedead liked this · 6 years ago -
 sadinulou liked this · 6 years ago
sadinulou liked this · 6 years ago -
 chevengurskiye reblogged this · 6 years ago
chevengurskiye reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 aberrate reblogged this · 6 years ago
aberrate reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 arrtkid liked this · 6 years ago
arrtkid liked this · 6 years ago -
 butternutcrunch liked this · 6 years ago
butternutcrunch liked this · 6 years ago -
 justbitterandgayiguess liked this · 6 years ago
justbitterandgayiguess liked this · 6 years ago -
 readersinflammation liked this · 6 years ago
readersinflammation liked this · 6 years ago -
 gabbyam reblogged this · 6 years ago
gabbyam reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 cawamelcwunch liked this · 7 years ago
cawamelcwunch liked this · 7 years ago -
 dabitoya reblogged this · 7 years ago
dabitoya reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 deniigi liked this · 7 years ago
deniigi liked this · 7 years ago -
 velocicrafter liked this · 7 years ago
velocicrafter liked this · 7 years ago -
 filthygrayflowers reblogged this · 7 years ago
filthygrayflowers reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 karcathy reblogged this · 7 years ago
karcathy reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 colekaidos reblogged this · 7 years ago
colekaidos reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 colekaidos liked this · 7 years ago
colekaidos liked this · 7 years ago
A reblog of nerdy and quirky stuff that pique my interest.
291 posts






