The Beauty Of Webb Telescope’s Mirrors
The Beauty of Webb Telescope’s Mirrors
The James Webb Space Telescope’s gold-plated, beryllium mirrors are beautiful feats of engineering. From the 18 hexagonal primary mirror segments, to the perfectly circular secondary mirror, and even the slightly trapezoidal tertiary mirror and the intricate fine-steering mirror, each reflector went through a rigorous refinement process before it was ready to mount on the telescope. This flawless formation process was critical for Webb, which will use the mirrors to peer far back in time to capture the light from the first stars and galaxies.

The James Webb Space Telescope, or Webb, is our upcoming infrared space observatory, which will launch in 2019. It will spy the first luminous objects that formed in the universe and shed light on how galaxies evolve, how stars and planetary systems are born, and how life could form on other planets.
A polish and shine that would make your car jealous

All of the Webb telescope’s mirrors were polished to accuracies of approximately one millionth of an inch. The beryllium mirrors were polished at room temperature with slight imperfections, so as they change shape ever so slightly while cooling to their operating temperatures in space, they achieve their perfect shape for operations.

The Midas touch
Engineers used a process called vacuum vapor deposition to coat Webb’s mirrors with an ultra-thin layer of gold. Each mirror only required about 3 grams (about 0.11 ounces) of gold. It only took about a golf ball-sized amount of gold to paint the entire main mirror!

Before the deposition process began, engineers had to be absolutely sure the mirror surfaces were free from contaminants.

The engineers thoroughly wiped down each mirror, then checked it in low light conditions to ensure there was no residue on the surface.

Inside the vacuum deposition chamber, the tiny amount of gold is turned into a vapor and deposited to cover the entire surface of each mirror.

Primary, secondary, and tertiary mirrors, oh my!
Each of Webb’s primary mirror segments is hexagonally shaped. The entire 6.5-meter (21.3-foot) primary mirror is slightly curved (concave), so each approximately 1.3-meter (4.3-foot) piece has a slight curve to it.

Those curves repeat themselves among the segments, so there are only three different shapes — 6 of each type. In the image below, those different shapes are labeled as A, B, and C.

Webb’s perfectly circular secondary mirror captures light from the 18 primary mirror segments and relays those images to the telescope’s tertiary mirror.

The secondary mirror is convex, so the reflective surface bulges toward a light source. It looks much like a curved mirror that you see on the wall near the exit of a parking garage that lets motorists see around a corner.

Webb’s trapezoidal tertiary mirror captures light from the secondary mirror and relays it to the fine-steering mirror and science instruments. The tertiary mirror sits at the center of the telescope’s primary mirror. The tertiary mirror is the only fixed mirror in the system — all of the other mirrors align to it.

All of the mirrors working together will provide Webb with the most advanced infrared vision of any space observatory we’ve ever launched!
Who is the fairest of them all?
The beauty of Webb’s primary mirror was apparent as it rotated past a cleanroom observation window at our Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. If you look closely in the reflection, you will see none other than James Webb Space Telescope senior project scientist and Nobel Laureate John Mather!

Learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope HERE, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others
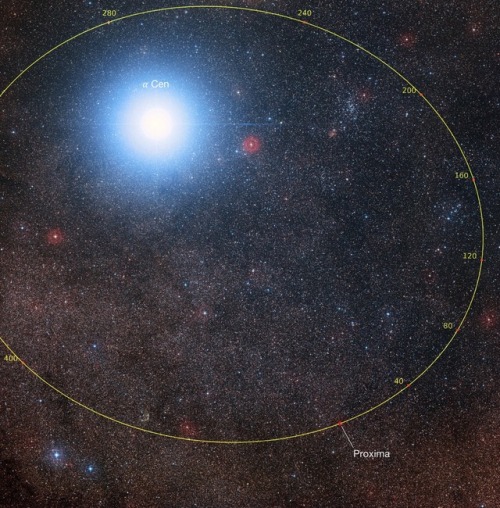



Life orbiting our closest star?
A planet has been found orbiting in the habitable zone of the closest star to earth, 4.2 light years away, named Proxima Centauri. The exoplanet, known as proxima b, has the mass of 1.27 earths but because of the shape of its orbit, the chances of it harbouring liquid water are fantastic. This vastly improves the chances that the planet sustains alien life.
SpaceX SES-10 Mission successfully Launch
SpaceX - Falcon 9 / SES-10 Mission patch. March 31, 2017
Falcon 9 carrying SES-10 satellite launch
SpaceX took a step into the future Thursday as it reused – for the first time – a recovered first stage of a previously-flown Falcon 9 rocket. Thursday’s mission, carrying the SES-10 communications satellite, lifted off from Pad 39A at Florida’s Kennedy Space Center Thursday 30 March at 18:27 local time (22:27 UTC) and once again landed the booster.
Falcon 9 launch of SES-10
Thursday’s mission made use Falcon 9 the second orbit-capable rocket – after the Space Shuttle – to achieve partial reusability. The Falcon 9 flew from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center, the same pad from which the Shuttle began eighty-two of its missions, including its first and final flights. Reusability has long been a key objective for SpaceX. Making the company’s first launch in March 2006, the small Falcon 1 vehicle carried a parachute system intended to bring its spent first stage back to Earth.
Falcon 9 first stage landed on drone barge
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket deliver SES-10, a commercial communications satellite for SES, to a Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO). SES is a world-leading satellite operator, providing reliable and secure satellite communications solutions across the globe.
SES-10 satellite
The SES-10 mission mark a historic milestone on the road to full and rapid reusability as the world’s first reflight of an orbital class rocket. Falcon 9’s first stage for the SES-10 mission previously supported the successful CRS-8 mission in April 2016. For more information about SpaceX, visit: http://www.spacex.com/ Images, Video, Text, Credits: SpaceX/SES. Greetings, Orbiter.ch Full article

ASTROGENOUS
[adjective]
producing or creating stars.
Etymology: from Greek, from astron “star” + -genēs “born”.
[J. R. Slattum - Star Maker]

This Black Eye Galaxy that got its name from the band of light absorbing dust appearing in front of the star systems bright center in the Hubble space telescope.
via reddit
Hubble Spots Two Interacting Galaxies Defying Cosmic Convention
NASA - Hubble Space Telescope patch. March 24, 2017
Some galaxies are harder to classify than others. Here, Hubble’s trusty Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) has captured a striking view of two interacting galaxies located some 60 million light-years away in the constellation of Leo (The Lion). The more diffuse and patchy blue glow covering the right side of the frame is known as NGC 3447 — sometimes NGC 3447B for clarity, as the name NGC 3447 can apply to the overall duo. The smaller clump to the upper left is known as NGC 3447A. Overall, we know NGC 3447 comprises a couple of interacting galaxies, but we’re unsure what each looked like before they began to tear one another apart. The two sit so close that they are strongly influenced and distorted by the gravitational forces between them, causing the galaxies to twist themselves into the unusual and unique shapes seen here. NGC 3447A appears to display the remnants of a central bar structure and some disrupted spiral arms, both properties characteristic of certain spiral galaxies. Some identify NGC 3447B as a former spiral galaxy, while others categorize it as being an irregular galaxy.
Hubble Space Telescope
For Hubble’s image of the Whirlpool Galaxy, visit: http://hubblesite.org/ http://www.nasa.gov/hubble http://www.spacetelescope.org/ Image, Animation, Credits: ESA/Hubble & NASA/Text Credits: European Space Agency/NASA/Karl Hille. Best regards, Orbiter.ch Full article
I mention New Horizons in today’s podcast but here’s some more up-to-date info!
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Time for a little reconnaissance.

Our New Horizons spacecraft won’t arrive at its next destination in the distant Kuiper Belt—an object known as 2014 MU69—until New Year’s Day 2019, but researchers are already starting to study its environment thanks to a few rare observational opportunities this summer, including one on July 17. This week, we’re sharing 10 things to know about this exciting mission to a vast region of ancient mini-worlds billions of miles away.
1. First, Some Background

New Horizons launched on Jan. 19, 2006. It swung past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February 2007, and conducted a six-month reconnaissance flyby study of Pluto and its moons in summer 2015. The mission culminated with the closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Now, as part of an extended mission, the New Horizons spacecraft is heading farther into the Kuiper Belt.
2. A Kuiper Belt refresher

The Kuiper Belt is a region full of objects presumed to be remnants from the formation of our solar system some 4.6 billion years ago. It includes dwarf planets such as Pluto and is populated with hundreds of thousands of icy bodies larger than 62 miles (100 km) across and an estimated trillion or more comets. The first Kuiper Belt object was discovered in 1992.
3. That’s Pretty Far

When New Horizons flies by MU69 in 2019, it will be the most distant object ever explored by a spacecraft. This ancient Kuiper Belt object is not well understood because it is faint, small, and very far away, located approximately 4.1 billion miles (6.6 billion km) from Earth.
4. Shadow Play

To study this distant object from Earth, the New Horizons team have used data from the Hubble Space Telescope and the European Space Agency’s Gaia satellite to calculate where MU69 would cast a shadow on Earth’s surface as it passes in front of a star, an event known as an occultation.
5. An International Effort

One occultation occurred on June 3, 2017. More than 50 mission team members and collaborators set up telescopes across South Africa and Argentina, aiming to catch a two-second glimpse of the object’s shadow as it raced across the Earth. Joining in on the occultation observations were NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and Gaia, a space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA).
6. Piecing Together the Puzzle

Combined, the pre-positioned mobile telescopes captured more than 100,000 images of the occultation star that can be used to assess the Kuiper Belt object’s environment. While MU69 itself eluded direct detection, the June 3 data provided valuable and surprising insights. “These data show that MU69 might not be as dark or as large as some expected,” said occultation team leader Marc Buie, a New Horizons science team member from Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
7. One Major Missing Piece

Clear detection of MU69 remains elusive. “These [June 3 occultation] results are telling us something really interesting,” said New Horizons Principal Investigator Alan Stern, of the Southwest Research Institute. “The fact that we accomplished the occultation observations from every planned observing site but didn’t detect the object itself likely means that either MU69 is highly reflective and smaller than some expected, or it may be a binary or even a swarm of smaller bodies left from the time when the planets in our solar system formed.”
8. Another Opportunity

On July 10, the SOFIA team positioned its aircraft in the center of the shadow, pointing its powerful 100-inch (2.5-meter) telescope at MU69 when the object passed in front of the background star. The mission team will now analyze that data over the next few weeks, looking in particular for rings or debris around MU69 that might present problems for New Horizons when the spacecraft flies by in 2019. “This was the most challenging occultation observation because MU69 is so small and so distant,” said Kimberly Ennico Smith, SOFIA project scientist.
9. The Latest

On July 17, the Hubble Space Telescope will check for debris around MU69 while team members set up another “fence line” of small mobile telescopes along the predicted ground track of the occultation shadow in southern Argentina.
10. Past to Present

New Horizons has had quite the journey. Check out some of these mission videos for a quick tour of its major accomplishments and what’s next for this impressive spacecraft.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
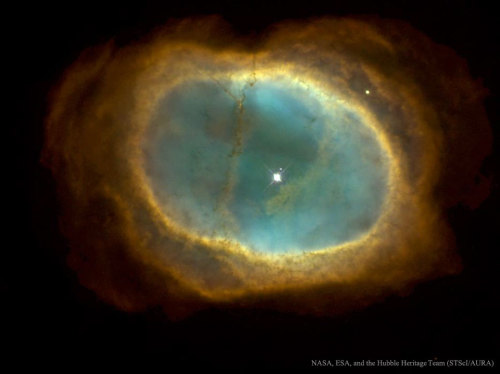
NGC 3132: The Eight Burst Nebula : Its the dim star, not the bright one, near the center of NGC 3132 that created this odd but beautiful planetary nebula. Nicknamed the Eight-Burst Nebula and the Southern Ring Nebula, the glowing gas originated in the outer layers of a star like our Sun. In this representative color picture, the hot blue pool of light seen surrounding this binary system is energized by the hot surface of the faint star. Although photographed to explore unusual symmetries, its the asymmetries that help make this planetary nebula so intriguing. Neither the unusual shape of the surrounding cooler shell nor the structure and placements of the cool filamentary dust lanes running across NGC 3132 are well understood. via NASA
js
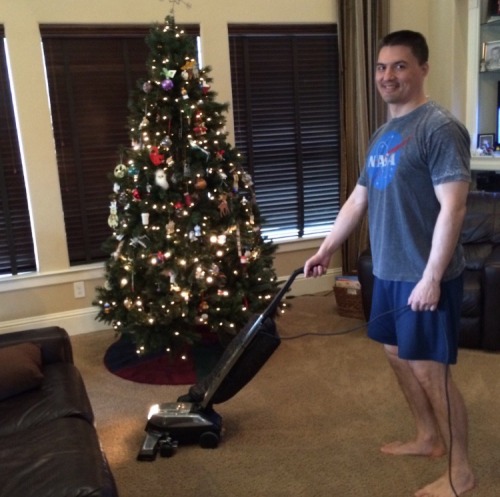


This is Kjell Lindgren. He’s a NASA astronaut who just got back from 5 months on the International Space Station. There are two reasons why this picture is hilarious:
His wife is flawless and makes bad space puns to make him do household chores.
I have that shirt. Thousands of people have that shirt. That shirt is available at Target. Which means actual astronaut Kjell Lindgren, with his wardrobe already full of NASA-issued and logo-emblazoned clothes, was at Target, saw a NASA shirt, and was like, “Yes, I am buying this because this is what I want to spend my actual astronaut salary on.”
tl;dr NASA employs a bunch of fucking nerds
-
 redskytag liked this · 4 years ago
redskytag liked this · 4 years ago -
 titaniumworld liked this · 4 years ago
titaniumworld liked this · 4 years ago -
 maisdahilcorny reblogged this · 5 years ago
maisdahilcorny reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 maisdahilcorny liked this · 5 years ago
maisdahilcorny liked this · 5 years ago -
 marvelblog123 liked this · 5 years ago
marvelblog123 liked this · 5 years ago -
 louiveee liked this · 5 years ago
louiveee liked this · 5 years ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts