ASTROGENOUS

ASTROGENOUS
[adjective]
producing or creating stars.
Etymology: from Greek, from astron “star” + -genēs “born”.
[J. R. Slattum - Star Maker]
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others
Biggest Scientific Breakthroughs of 2013
From intergalactic neutrinos and invisible brains, to the creation of miniature human “organoids”, 2013 was an remarkable year for scientific discovery. Here are some of the biggest scientific breakthroughs, innovations and advances of 2013.
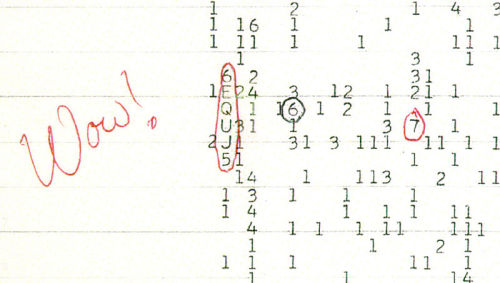
Voyager I Leaves the Solar System
Escaping the solar system is no mean feat. For 36 years, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has putting distance between itself and the Sun at speeds approaching 11 miles per second. At a pace like that, scientists knew Voyager was approaching the fringes of the heliosphere that surrounds and defines our solar neighborhood – but when would it break that barrier? When would it make the leap to interstellar space? After months of uncertainty, NASA finally made the news official this September. “Voyager 1 is the first human-made object to make it into interstellar space” said Don Gurnett, lead author of the paper announcing Voyager’s departure; “we’re actually out there.”
The Milky Way is Brimming with Habitable Worlds
Planet-hunting scientists announced in November that 22% of sunlike stars in the Milky Way are orbited by potentially habitable, Earth-size worlds. This remarkable finding suggests there could be as many as two-billion planets in our galaxy suitable for life — and that the nearest such planet may be only 12 light-years away. Is Earth 2.0 out there? With figures like that, it’s hard to imagine otherwise. Who knows – with all the Kepler data we’ve got to sift through, there’s a chance we’ve already found it.
Curiosity Confirms Mars Was Once Capable of Harboring Life
In March, NASA scientists released perhaps the most compelling evidence to date that the Red Planet was once capable of harboring life. Earlier this year, Curiosity drilled some samples out of a sedimentary rock near an old river bed in Gale Crater. This geological area used to feature a series of stream channels, leaving behind finely grained bedrock indicative of previously wet conditions. Using the rover’s onboard instrumentation, NASA scientists analyzed these samples to detect some of the critical elements required for life, including sulfur, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and carbon. The rover is currently on a trek to its primary scientific target – a three-mile-high peak at the center of Gale Crater named Mount Sharp – where it will attempt to further reinforce its findings.
Researchers Detect Neutrinos from Another Galaxy
By drilling a 1.5 mile hole deep into an Antarctic glacier, physicists working at the IceCube South Pole Observatory this year captured 28 neutrinos, those mysterious and extremely powerful subatomic particles that can pass straight through solid matter. And here’s the real kicker: the particles likely originated from beyond our solar system – and possibly even our galaxy. "This is a landmark discovery,“ said Alexander Kusenko, a UCLA astroparticle physicist who was not involved in the investigation, "possibly a Nobel Prize in the making.”
NASA Discovers “A Previously Unknown Surprise Circling Earth”
NASA’s recently deployed Van Allen probes — a pair of robotic spacecraft launched in August 2012 to investigate Earth’s eponymous pair of radiation belts — turned out out some very unexpected findings in February, when they spotted an ephemeral third ring of radiation, previously unknown to science, surrounding our planet.
Human Cloning Becomes a Reality
A scientific milestone 17 years in the making, researchers announced in May that they had derived stem cells from cloned human embryos.The controversial technology could lead to new treatments for diseases like Parkinson’s and diabetes — while bringing us one step closer to human reproductive cloning.
Giant “Pandoravirus” Could Redefine Life as we Know it
Scientists in July announced the discovery of a pair of viruses that defy classification. Bigger and more genetically complex than any viral genus known to science, these so-called “pandoraviruses” could reignite a longstanding debate over the classification of life itself.
Brain-to-Brain Interfaces Have Arrived
Back in February, researchers announced that they had successfully established an electronic link between the brains of two rats, and demonstrated that signals from the mind of one could help the second solve basic puzzles in real time — even when those animals were separated by thousands of miles. A few months later, a similar connection was established between the brain of a human and a rat. Just one month later, researchers published the results of the first successful human-to-human brain interface. The age of the mind-meld, it seems, is near at hand.
There is Life at the End of the World
There is life in Lake Whillans. For millions of years, the small body of liquid water has lurked hundreds of meters below Antarctica’s Ross Ice Shelf, sealed off from the outside world and the scientists who would explore its subglacial depths. Earlier this year, a team of researchers led by Montana State University glaciologist John Priscu successfully bored a tunnel to Whillans and encountered life, making Priscu and his colleagues the first people in history to discover living organisms in the alien lakes at the bottom of the world.
Doctors Cure HIV in a Baby Born With the Disease
In a monumental first for medicine, doctors announced in March that a baby had been cured of an HIV infection. Dr. Deborah Persaud, who presented the child’s case at the 20th annual Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infection, called it “definitely a game-changer.”
Newly Discovered Skulls Could Prune Humans’ Evolutionary Tree
An incredibly well-preserved, 1.8-million-year-old skull from Dmanisi, Georgia suggests the evolutionary tree of the genus Homo may have fewer branches than previously believed. In a report published in October, a team led by Georgian anthropologist David Lordkipanidze writes that it is “the world’s first completely preserved hominid skull.” And what a skull it is. When considered alongside four other skulls discovered nearby, it suggests that the earliest known members of the Homo genus (H. habilis, H.rudolfensis and H. erectus) may not have been distinct, coexisting species, at all. Instead, they may have been part of a single, evolving lineage that eventually gave rise to modern humans.
Neuroscientists Turn Brains Invisible
Gaze upon the stunning effects of CLARITY, a new technique that enables scientists to turn brain matter and other tissues completely transparent. It’s been hailed as one of the most important advances for neuroanatomy in decades, and it’s not hard to see why.
[source | gifs → galaxyclusters]

The hardest part of determining longitude was figuring out how sailors could find their longitudinal coordinates at sea. There were a lot of methods proposed but adding a ship into the equation makes precision difficult. Learn about the Longitude Act of 1714 and how, even though this podcast loves astronomy, the astronomical method might not always be the best option.
Below the cut are my sources, music credits, a timeline of the astronomers and engineers and clockmakers I mention, a vocab list, a really cool resource that lets you drag continents all over a flattened map of Earth to compare their sizes at different latitudes, and the transcript of this episode. Let me know what you think I should research next by messaging me here, tweeting at me at @HDandtheVoid, or asking me to my face if you know me in real life. And please check out the podcast on iTunes, rate it or review it if you’d like, subscribe, and maybe tell your friends about it if you think they’d like to listen!
(My thoughts on the next episode were the Voyager golden records, space race history, the transit of Venus, or maybe something about the Moon landing. I’m loving Edmond Halley again these days, too. I’m prepping to interview a friend about her graduate-level research into the history of the universe and possibly dark matter, too. Let me know by the 20th and I’ll hopefully have the next podcast up on September 25th! If not then, I’ll push for October 2nd.)
Glossary
azimuth - a section of the horizon measured between a fixed point and the vertical circle passing through the center of an object. See example in the link.
equator - Earth’s zero line of latitude. It’s the place on Earth where the Sun is directly overhead at noon on the vernal and autumnal equinoxes.
kamal - an Arabic navigation tool consisting of a knotted string and a piece of wood. A navigator would tie a knot in the string and, by holding it in their teeth, sight the North Star along the top of the wooden piece and the horizon along the bottom. To return home, the navigator would sail north or south to bring Polaris to the altitude they had observed in their home port, then turn left or right and sail down the latitude, keeping Polaris at a constant angle. Over time, Arab navigators started tying knots at regular intervals of a fingerwidth, called an issbah, that’s about 1 degree and 36 minutes.
magnetosphere - an invisible barrier that surrounds a celestial objet. It is often generated by the movement of the liquid metal core of the object. Around a planet, it deflects high-energy, charged particles called cosmic rays that can either come from the Sun or, less often, from interstellar space.
prime meridian - Earth’s zero degree of longitude. In current maps and time zones, this invisible, imaginary line runs through London, England.
sextant - a device used to determine an observer’s location based on the observation of a known celestial object and a lot of calculation. It is still in use by sailors.
tropic of cancer - a line of latitude that marks where the Sun will be at noon on the summer solstice.
tropic of capricorn - a line of latitude that marks where the Sun will be at noon on the winter solstice.
Script/Transcript
Sources
Longitude at Sea via The Galileo Project at Rice University
Vitamin C necessity via University of Maryland Medical Center
Scurvy via NHS
Scurvy via the Encyclopedia Britannica online
An interactive map that shows how our current map distorts land masses by letting you compare different countries’ sizes.
Sobel, Dava. Longitude. Walker & Co.; New York, 1995.
“anyone living below the Equator would melt into deformity from the horrible heat” (3).
“It simply urged Parliament to welcome potential solutions from any field of science or art, put forth by individuals or groups of any nationality, and to reward success handsomely” (53).
Timeline
Claudius Ptolemy, Greek (100-170 CE)
Johannes Werner (in Latin, Ioannis Vernerus), German (1468-1522)
Tycho Brahe, Danish (1541-1601)
Galileo Galilei, Italian (1564-1642)
Giovanni Cassini (in French, Jean-Dominique Cassini), Italian/French (1625-1712)
Christiaan Huygens, Dutch (1629-1695)
Sir Isaac Newton, English (1642-1726/7)
Ole Rømer, Danish (1644-1710)
John Flamsteed, English (1646-1719)
Edmond Halley, English (1656-1742)
John Hadley, English (1682-1744)
John Harrison, English (1693-1776)
Thomas Godfrey, American (1704-1749)
John Bird, English (1709-1776)
Larcum Kendall, English (1719-1790)
James Cook, English (1728-1779)
Nevil Maskelyne, English (1732-1811)
John Arnold, English (1736-1799)
Thomas Earnshaw, English (1749-1829)
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught
If Earth had Saturn’s Rings
From an excellent post by Jason Davis
From Washington, D.C., the rings would only fill a portion of the sky, but appear striking nonetheless. Here, we see them at sunrise.

From Guatemala, only 14 degrees above the equator, the rings would begin to stretch across the horizon. Their reflected light would make the moon much brighter.

From Earth’s equator, Saturn’s rings would be viewed edge-on, appearing as a thin, bright line bisecting the sky.

At the March and September equinoxes, the Sun would be positioned directly over the rings, casting a dramatic shadow at the equator.

At midnight at the Tropic of Capricorn, which sits at 23 degrees south latitude, the Earth casts a shadow over the middle of the rings, while the outer portions remain lit.

via x
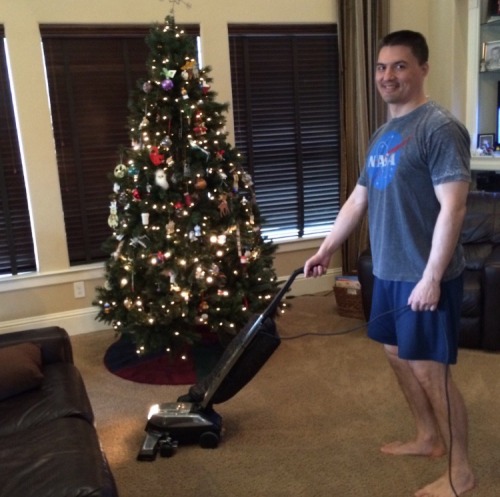


This is Kjell Lindgren. He’s a NASA astronaut who just got back from 5 months on the International Space Station. There are two reasons why this picture is hilarious:
His wife is flawless and makes bad space puns to make him do household chores.
I have that shirt. Thousands of people have that shirt. That shirt is available at Target. Which means actual astronaut Kjell Lindgren, with his wardrobe already full of NASA-issued and logo-emblazoned clothes, was at Target, saw a NASA shirt, and was like, “Yes, I am buying this because this is what I want to spend my actual astronaut salary on.”
tl;dr NASA employs a bunch of fucking nerds
How much of a daily threat is "Space junk"?
Good question, as this is a serious issue and one which we must monitor constantly in order to avoid harmful impacts on the International Space Station with objects in space. For example, the US Space Command in Colorado is monitoring all objects bigger than a few inches in order to assess any potential impact with the Space Station. We categorize the chance of impact and if there is a high probability, we will actually use thrusters to slightly change the position of the Space Station to avoid the impact. If it is something that we are unable to avoid, we will have the astronauts shelter in place in their spacecrafts and in case of a catastrophic impact, they will return to Earth.


Happy Labor Day. Today I learned about probably the first strike to happen IN SPACE.

This episode’s been a long time coming because the topic’s come up before. I originally conceived of this podcast as a way for me to learn about space things I’d always taken for granted, and truly, there is nothing closer to home that I’ve just agreed to believe than the statement that the tides are affected by the Moon. What? How? Why? All these questions and some I didn’t even realize I had will be answered in this episode on tidal forces!
Below the cut are my standard glossary, transcript, sources, and music credits. Send me any topic suggestions via Tumblr message (you don’t need an account for it!). You can also tweet at me on Twitter at @HDandtheVoid, or you can ask me to my face if you know me. Subscribe on iTunes to get the new episodes of my maybe now monthly-updated podcast (we’ll see how the weeks unfold), and please please please rate and review it. Go ahead and tell friends if you think they’d like to hear it, too!
(My thoughts on the next episode are Stephen Hawking and his theories, or famous comets. The next episode will go up in September—ideally, September 10th!)
Glossary
barycenter - the common center of mass between two objects that allows them to orbit.
Roche limit - the distance in which a celestial body will disintegrate because of a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction, or the force that’s holding it together. Within the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings, like how Saturn’s rings are within the Roche zone; outside the limit, material tends to coalesce.
spaghettification - when extreme tidal forces pull an object apart in space.
tidal force - an apparent force (sometimes also called the differential force) that stretches a body towards another, more gravitationally-strong body’s center of mass. This can cause such diverse phenomena as tides, tidal locking, breaking celestial bodies apart to form ring systems within a Roche limit, and in extreme cases, spaghettification. It arises because the gravitational force exerted on one body by another is not constant across its parts: the nearest side is attracted more strongly than the farthest side.
Types of ocean tides:
diurnal tide - a daily tidal cycle with only one high and low tide each lunar day, and a period of a little over 24 hours.
meteorological tide - a tidal change due to weather patterns. Wind, or unusually high or low barometric pressure causes variations between the actual sea level and its predicted height.
mixed tide - a daily tidal cycle with two high and low tides that differ in their peaks. This difference in height between successive high or low tides is called the diurnal inequality. They have a period of 12 hours and 25 minutes.
neap tide - a type of bi-monthly tidal cycle that occurs when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are positioned at a 90-degree angle, so the tidal forces of the Sun are acting against the tidal forces of the Moon. During a neap tide, the difference between high tide and low tide is the least extreme.
semidiurnal tide - a daily tidal cycle with two nearly equal high tides and low tides every lunar day. They have a period of 12 hours and 25 minutes.
spring tide - a type of bi-monthly tidal cycle that occurs when the Sun, Earth, and Moon line up so that the gravitational forces of Sun and Moon are working together to form a large tidal bulge. During a spring tide, the difference between high tide and low tide is at its maximum.
tidal locking - when long-term interaction between two co-orbiting astronomical bodies causes at least one of the bodies to rotate in such a way that one face of the body is always pointed at the body it’s orbiting. This is also called gravitational locking or captured rotation. An example is that the same side of the Moon always faces the Earth, and its synchronous rotation means that it takes just as long to rotate around its own axis as it does to revolve around the Earth.
Script/Transcript
Sources
Tidal Cycles in Tides Explained via beltoforian.de
“a tide is a distortion in the shape of one body induced by the gravitational pull of another nearby object.”
Meteorological effects on tides via the New Zealand Government website
Tides and Water Levels via the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
Tides by R. Nave, my dude, my guy, my friend and yours, of Georgia State University
The Tidal Force by Neil deGrasse Tyson via Hayden Planetarium (Nov 1995)
“A mild increase in distance between two objects can make a large difference in the strength of the tidal force. For example, if the Moon were just twice its current distance from us, then its tidal force on Earth would decrease by a factor of eight. At its current average distance of 240,000 miles from Earth, the Moon manages to create sizable atmospheric, oceanic, and crustal tides by attracting the part of Earth nearest the Moon more strongly than the part of Earth that is farthest. (The Sun is so far away that in spite of its generally strong gravity, its tidal force on Earth amounts to less than half that of the Moon.) The oceans respond most visibly in being stretched toward the direction of the Moon.”
“When Earth's rotation slows down until it exactly matches the orbital period of the Moon, then Earth will no longer be rotating within its oceanic tidal bulge and the Earth-Moon system will have achieved a double tidal lock. In what sounds like an undiscovered wrestling hold, double tidal locks are energetically favorable (like a ball coming to rest at the bottom of a hill), and are thus common in the universe.”
Forget “Earth-Like”—We’ll First Find Aliens on Eyeball Planets via Nautilus (Feb 2015)
High Tide on Io! via NASA (Mar 2012)
Tidal forces and spaghettification via NASA handout
Spaghettification via Cosmic Funnies
Single atoms feel tidal force via Physics World (May 2017)
Robbins, Tom. Still Life with Woodpecker. Bantam Books: New York, 1980.
“Being four times larger than the moon, the earth appeared to dominate. Caught in the earth’s gravitational web, the moon moved around the earth and could never get away. Yet, as any half-awake materialist well knows, that which you hold holds you.”
Sobel, Dava. The Planets. Viking: NY, 2005.
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Background Music: ‘Sad Business’ by Patients aka Ben Cooper, who primarily releases music as Radical Face but also has at least three other bands or band names he’s working with/has released music as.
Filler Music: ‘It’s Getting Boring by the Sea’ by Blood Red Shoes off their album Box of Secrets
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught
Hahaha, right after I start out a podcast talking about how we’ll never poke the Sun, it turns out we’re sending a probe to do just that!
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Mark your calendars for summer 2018: That’s when we’re launching a spacecraft to touch the sun.
In honor of our first-ever mission to the heart of the solar system, this week we’re delving into the life and times of this powerful yellow dwarf star.

1. Meet Parker
Parker Solar Probe, our first mission to go to the sun, is named after Eugene Parker, an American astrophysicist who first theorized that the sun constantly sends out a flow of particles and energy called the solar wind. This historic mission will explore one of the last regions of the solar system to be visited by a spacecraft and help scientists unlock answers to questions they’ve been pondering for more than five decades.

2. Extra SPF, Please
Parker Solar Probe will swoop within 4 million miles of the sun’s surface, facing heat and radiation like no spacecraft before it. The mission will provide new data on solar activity to help us better understand our home star and its activity - information that can improve forecasts of major space-weather events that could impact life on Earth.

3. Majorly Massive
The sun is the center of our solar system and makes up 99.8 percent of the mass of the entire solar system. If the sun were as tall as a typical front door, Earth would be about the size of a nickel.
4. Different Spin
Since the sun is not a solid body, different parts of the sun rotate at different rates. At the equator, the sun spins once about every 25 days, but at its poles the sun rotates once on its axis every 36 Earth days.

5. Can’t Stand on It
The sun is a star and a star doesn’t have a solid surface. Rather, it’s a ball of ionized gas 92.1% hydrogen (H2) and 7.8% helium (He) held together by its own gravity.
6. Center of Attention
The sun isn’t a planet, so it doesn’t have any moons. But, the sun is orbited by eight planets, at least five dwarf planets, tens of thousands of asteroids, and hundreds of thousands to trillions of comets and icy bodies.

7. It’s Hot in There
And we mean really, really hot. The temperature at the sun’s core is about 27 million degrees Fahrenheit. However, its atmosphere, the corona, can reach temperatures of 3 million degrees. (That’s as if it got hotter the farther away you got from a fire, instead of cooler!) Parker Solar Probe will help scientists solve the mystery of why the corona’s temperature is so much higher than the surface.

8. Travel Conditions
The sun influences the entire solar system, so studying it helps us better understand the space weather that our astronauts and spacecraft travel through.
9. Life on the Sun?
Better to admire from afar. Thanks to its hot, energetic mix of gases and plasma, the sun can’t be home to living things. However, we can thank the sun for making life on Earth possible by providing the warmth and energy that supply Earth’s food chain.
10. Chance of a Lifetime
Last but not least, don’t forget that the first total solar eclipse to sweep across the U.S. from coast-to-coast since 1918 is happening on August 21, 2017. Our toolkit has you need to know to about it.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Here’s the nose scratching sponge I talked about in Episode 19!

This is how astronauts clear our ears (and scratch our noses!) during a spacewalk.
-
 underwhelmedandoverstimulated reblogged this · 5 years ago
underwhelmedandoverstimulated reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 omnideus reblogged this · 5 years ago
omnideus reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 omnideus liked this · 5 years ago
omnideus liked this · 5 years ago -
 realismomagicoblr liked this · 5 years ago
realismomagicoblr liked this · 5 years ago -
 ace-miles liked this · 5 years ago
ace-miles liked this · 5 years ago -
 zehcnas-lojneh reblogged this · 6 years ago
zehcnas-lojneh reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 woundedheart77-blog liked this · 6 years ago
woundedheart77-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 goron-king-darunia reblogged this · 6 years ago
goron-king-darunia reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 artlandis reblogged this · 7 years ago
artlandis reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 artlandis liked this · 7 years ago
artlandis liked this · 7 years ago -
 aimlessandroiddreamer reblogged this · 7 years ago
aimlessandroiddreamer reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 collectx reblogged this · 7 years ago
collectx reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 skian22 reblogged this · 7 years ago
skian22 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 shonenmaru2 reblogged this · 7 years ago
shonenmaru2 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 nocturnusomnia reblogged this · 7 years ago
nocturnusomnia reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thefrogwitch reblogged this · 7 years ago
thefrogwitch reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 dark-owl-lucy reblogged this · 8 years ago
dark-owl-lucy reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 leomysticmagic liked this · 8 years ago
leomysticmagic liked this · 8 years ago -
 nonsensei reblogged this · 8 years ago
nonsensei reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sassyslytherinsister-blog liked this · 8 years ago
sassyslytherinsister-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 ocdickens reblogged this · 8 years ago
ocdickens reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 laughing-baubo liked this · 8 years ago
laughing-baubo liked this · 8 years ago -
 notsomolly reblogged this · 8 years ago
notsomolly reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 lepetitmonstre3 reblogged this · 8 years ago
lepetitmonstre3 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 a-quiet-nightmare reblogged this · 8 years ago
a-quiet-nightmare reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 hellboundwitch liked this · 8 years ago
hellboundwitch liked this · 8 years ago -
 satsekhem reblogged this · 8 years ago
satsekhem reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 dragonslover1 liked this · 8 years ago
dragonslover1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 merriquelovecraftgiger reblogged this · 8 years ago
merriquelovecraftgiger reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 jesselhicks reblogged this · 8 years ago
jesselhicks reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sleepygxrl liked this · 8 years ago
sleepygxrl liked this · 8 years ago -
 geezerart reblogged this · 8 years ago
geezerart reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 geezerart liked this · 8 years ago
geezerart liked this · 8 years ago -
 twentybubbles reblogged this · 8 years ago
twentybubbles reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 boxfullofcats reblogged this · 8 years ago
boxfullofcats reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 franjavier1259 liked this · 8 years ago
franjavier1259 liked this · 8 years ago -
 grendelkin-and-unicorns reblogged this · 8 years ago
grendelkin-and-unicorns reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 almostamongoose liked this · 8 years ago
almostamongoose liked this · 8 years ago -
 creeshtar liked this · 8 years ago
creeshtar liked this · 8 years ago -
 mandrakebrew reblogged this · 8 years ago
mandrakebrew reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 omniversal reblogged this · 8 years ago
omniversal reblogged this · 8 years ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts