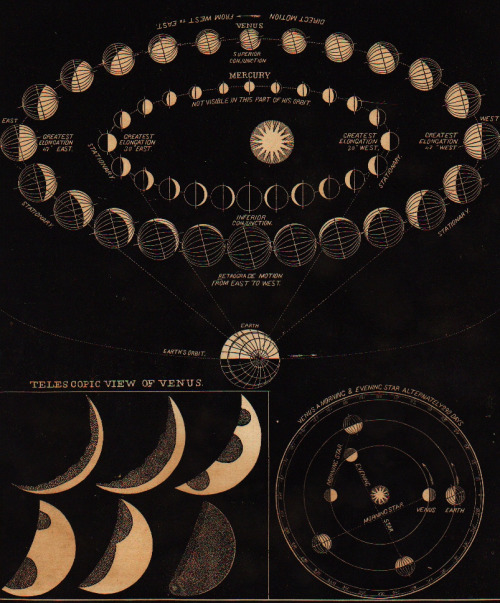
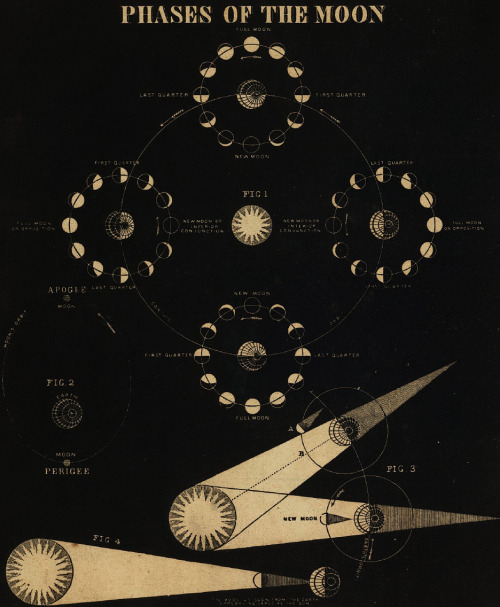
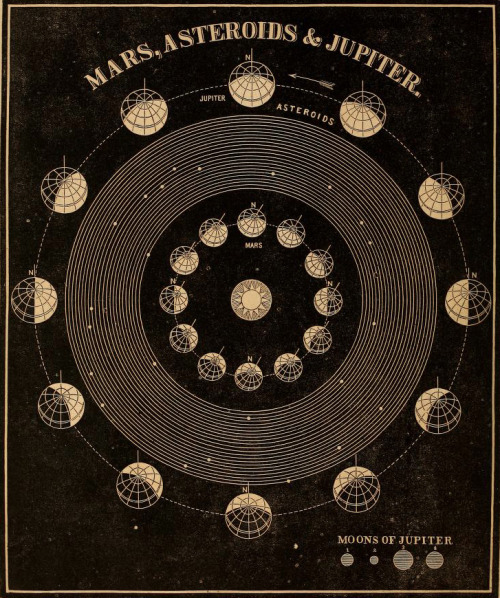
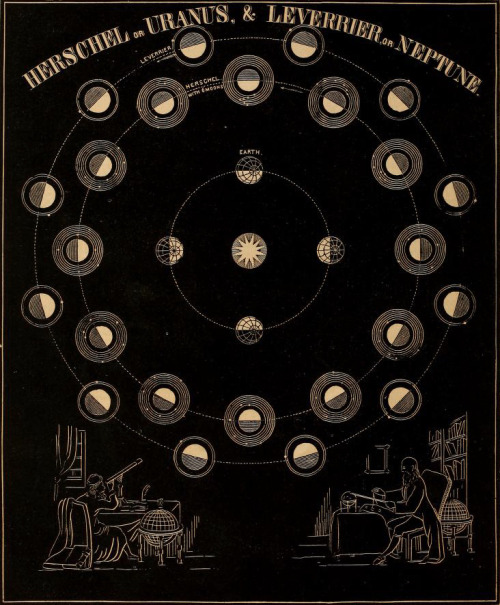
Fillthevoid-with-space - Fill The Void With... SPACE
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others


On this date in 1902, Greek archaeologist Valerios Stais sifted through some artifacts from a shipwreck at Antikythera. The wrecked Roman cargo ship was discovered two years earlier, but Stais was the first to notice an intriguing bit of bronze among the treasures. It looked like it might be a gear or wheel. That corroded chunk of metal turned out to be part of the Antikythera Mechanism, an ancient analog astronomical computer.
The Antikythera Mechanism tracked planetary positions, predicted lunar and solar eclipses, and even signaled the next Olympic Games. It was probably also used for mapping and navigation. A dial on the front combines zodiacal and solar calendars, while dials on the back capture celestial cycles. Computer models based on 3-D tomography have revealed more than 30 sophisticated gears, housed in a wooden and bronze case the size of a shoebox.




“It sounds far fetched even for the plot of a sci-fi film.
NASA scientists have proposed a radical idea to launch a magnetic field around Mars, with hopes it could protect the red planet from intense solar wind and allow humans to explore alongside rovers.
Jim Green, NASA’s Planetary Science Division Director, revealed the idea today at the Planetary Science Vision 2050 Workshop in Washington DC…
The proposal would create a dipole field –a pair of equal and oppositely charged magnets – in an orbit between Mars and the sun, at a point known as Mars L1.
This ‘artificial magnetic field’ would put Mars inside a ‘magnetotail,’ protecting it from the harsh solar wind.
Without the barrage of high-energy particles, Mars’ atmosphere would begin to rebuild itself over time.
In just a matter of years, the simulations show the planet could achieve an ‘Earth comparable field.’
Increasing the pressure would cause the equator to heat up, leading the polar cap to collapse, Green says…"
Source: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-4276210/NASA-unveils-plan-surround-Mars-magnetic-field.html?ITO=applenews
The Beauty of Webb Telescope’s Mirrors
The James Webb Space Telescope’s gold-plated, beryllium mirrors are beautiful feats of engineering. From the 18 hexagonal primary mirror segments, to the perfectly circular secondary mirror, and even the slightly trapezoidal tertiary mirror and the intricate fine-steering mirror, each reflector went through a rigorous refinement process before it was ready to mount on the telescope. This flawless formation process was critical for Webb, which will use the mirrors to peer far back in time to capture the light from the first stars and galaxies.

The James Webb Space Telescope, or Webb, is our upcoming infrared space observatory, which will launch in 2019. It will spy the first luminous objects that formed in the universe and shed light on how galaxies evolve, how stars and planetary systems are born, and how life could form on other planets.
A polish and shine that would make your car jealous

All of the Webb telescope’s mirrors were polished to accuracies of approximately one millionth of an inch. The beryllium mirrors were polished at room temperature with slight imperfections, so as they change shape ever so slightly while cooling to their operating temperatures in space, they achieve their perfect shape for operations.

The Midas touch
Engineers used a process called vacuum vapor deposition to coat Webb’s mirrors with an ultra-thin layer of gold. Each mirror only required about 3 grams (about 0.11 ounces) of gold. It only took about a golf ball-sized amount of gold to paint the entire main mirror!

Before the deposition process began, engineers had to be absolutely sure the mirror surfaces were free from contaminants.

The engineers thoroughly wiped down each mirror, then checked it in low light conditions to ensure there was no residue on the surface.

Inside the vacuum deposition chamber, the tiny amount of gold is turned into a vapor and deposited to cover the entire surface of each mirror.

Primary, secondary, and tertiary mirrors, oh my!
Each of Webb’s primary mirror segments is hexagonally shaped. The entire 6.5-meter (21.3-foot) primary mirror is slightly curved (concave), so each approximately 1.3-meter (4.3-foot) piece has a slight curve to it.

Those curves repeat themselves among the segments, so there are only three different shapes — 6 of each type. In the image below, those different shapes are labeled as A, B, and C.

Webb’s perfectly circular secondary mirror captures light from the 18 primary mirror segments and relays those images to the telescope’s tertiary mirror.

The secondary mirror is convex, so the reflective surface bulges toward a light source. It looks much like a curved mirror that you see on the wall near the exit of a parking garage that lets motorists see around a corner.

Webb’s trapezoidal tertiary mirror captures light from the secondary mirror and relays it to the fine-steering mirror and science instruments. The tertiary mirror sits at the center of the telescope’s primary mirror. The tertiary mirror is the only fixed mirror in the system — all of the other mirrors align to it.

All of the mirrors working together will provide Webb with the most advanced infrared vision of any space observatory we’ve ever launched!
Who is the fairest of them all?
The beauty of Webb’s primary mirror was apparent as it rotated past a cleanroom observation window at our Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. If you look closely in the reflection, you will see none other than James Webb Space Telescope senior project scientist and Nobel Laureate John Mather!

Learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope HERE, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Here’s a great example of the kinds of experiments astronauts perform on the International Space Station, just like I talked about in Episode 19! I absolutely want to high-five whoever called is ISS-CREAM.
From Frozen Antarctica to the Cold Vacuum of Space
A new experiment that will collect tiny charged particles known as galactic cosmic rays will soon be added to the International Space Station. The Cosmic Ray Energetics And Mass for the International Space Station payload, nicknamed ISS-CREAM, will soon be installed in its new home on the Station’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility. ISS-CREAM will help scientists understand more about galactic cosmic rays and the processes that produce them.

Wait, what are cosmic rays?
Cosmic rays are pieces of atoms that move through space at nearly the speed of light. Galactic cosmic rays come from beyond our solar system.

They provide us with direct samples of matter from distant places in our galaxy.
Why do these things go so fast?
Galactic cosmic rays have been sped up by extreme processes. When massive stars die, they explode as supernovas. The explosion’s blast wave expands into space along with a cloud of debris.

Particles caught up in this blast wave can bounce around in it and slowly pick up speed. Eventually they move so fast they can escape the blast wave and race away as a cosmic ray.
Where can we catch cosmic rays?
Cosmic rays are constantly zipping through space at these super-fast speeds, running into whatever is in their path – including Earth.

But Earth’s atmosphere is a great shield, protecting us from 99.9 percent of the radiation coming from space, including most cosmic rays. This is good news for life on Earth, but bad news for scientists studying cosmic rays.
So… how do you deal with that?
Because Earth has such an effective shield against cosmic rays, the best place for scientists to study them is above our atmosphere – in space. Since the 1920s, scientists have tried to get their instruments as close to space as possible. One of the simplest ways to do this is to send these instruments up on balloons the size of football stadiums. These balloons are so large because they have to be able to both lift their own weight and that of their cargo, which can be heavier than a car. Scientific balloons fly to 120,000 feet or more above the ground – that’s at least three times higher than you might fly in a commercial airplane!

Credit: Isaac Mognet (Pennsylvania State University)
Earlier versions of ISS-CREAM’s instruments were launched on these giant balloons from McMurdo Station in Antarctica seven times, starting in 2004, for a total of 191 days near the top of the atmosphere. Each of these flights helped the team test their hardware and work towards sending a cutting-edge cosmic ray detector into space!
How is going to space different than flying balloons?
Balloon flights allowed the team to collect a lot of cosmic rays, but even at 120,000 feet, a lot of the particles are still blocked. Scientists at the University of Maryland, College Park, who operate ISS-CREAM, expect to get about 10 times as much data from their new home on the International Space Station.

That’s because it will be both above the atmosphere and fly far longer than is possible with a balloon. As you might imagine, there are large differences between flying something on a balloon and launching it into space. The science instruments and other systems had to be changed so ISS-CREAM could safely launch on a rocket and work in space.
What will ISS-CREAM do?
While on the space station, ISS-CREAM will collect millions of cosmic rays – electrons, protons and atomic nuclei representing the elements found in the solar system. These results will help us understand why cosmic rays reach the wicked-fast speeds they do and, most important, what limits those speeds.
ISS-CREAM launches to the International Space Station aboard the latest SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, targeted to launch August 14. Want to learn more about ISS-CREAM and some of our scientific balloons? Check out our recent feature, NASA’s Scientific Balloon Program Reaches New Heights.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Biggest Scientific Breakthroughs of 2013
From intergalactic neutrinos and invisible brains, to the creation of miniature human “organoids”, 2013 was an remarkable year for scientific discovery. Here are some of the biggest scientific breakthroughs, innovations and advances of 2013.
Voyager I Leaves the Solar System
Escaping the solar system is no mean feat. For 36 years, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has putting distance between itself and the Sun at speeds approaching 11 miles per second. At a pace like that, scientists knew Voyager was approaching the fringes of the heliosphere that surrounds and defines our solar neighborhood – but when would it break that barrier? When would it make the leap to interstellar space? After months of uncertainty, NASA finally made the news official this September. “Voyager 1 is the first human-made object to make it into interstellar space” said Don Gurnett, lead author of the paper announcing Voyager’s departure; “we’re actually out there.”
The Milky Way is Brimming with Habitable Worlds
Planet-hunting scientists announced in November that 22% of sunlike stars in the Milky Way are orbited by potentially habitable, Earth-size worlds. This remarkable finding suggests there could be as many as two-billion planets in our galaxy suitable for life — and that the nearest such planet may be only 12 light-years away. Is Earth 2.0 out there? With figures like that, it’s hard to imagine otherwise. Who knows – with all the Kepler data we’ve got to sift through, there’s a chance we’ve already found it.
Curiosity Confirms Mars Was Once Capable of Harboring Life
In March, NASA scientists released perhaps the most compelling evidence to date that the Red Planet was once capable of harboring life. Earlier this year, Curiosity drilled some samples out of a sedimentary rock near an old river bed in Gale Crater. This geological area used to feature a series of stream channels, leaving behind finely grained bedrock indicative of previously wet conditions. Using the rover’s onboard instrumentation, NASA scientists analyzed these samples to detect some of the critical elements required for life, including sulfur, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and carbon. The rover is currently on a trek to its primary scientific target – a three-mile-high peak at the center of Gale Crater named Mount Sharp – where it will attempt to further reinforce its findings.
Researchers Detect Neutrinos from Another Galaxy
By drilling a 1.5 mile hole deep into an Antarctic glacier, physicists working at the IceCube South Pole Observatory this year captured 28 neutrinos, those mysterious and extremely powerful subatomic particles that can pass straight through solid matter. And here’s the real kicker: the particles likely originated from beyond our solar system – and possibly even our galaxy. "This is a landmark discovery,“ said Alexander Kusenko, a UCLA astroparticle physicist who was not involved in the investigation, "possibly a Nobel Prize in the making.”
NASA Discovers “A Previously Unknown Surprise Circling Earth”
NASA’s recently deployed Van Allen probes — a pair of robotic spacecraft launched in August 2012 to investigate Earth’s eponymous pair of radiation belts — turned out out some very unexpected findings in February, when they spotted an ephemeral third ring of radiation, previously unknown to science, surrounding our planet.
Human Cloning Becomes a Reality
A scientific milestone 17 years in the making, researchers announced in May that they had derived stem cells from cloned human embryos.The controversial technology could lead to new treatments for diseases like Parkinson’s and diabetes — while bringing us one step closer to human reproductive cloning.
Giant “Pandoravirus” Could Redefine Life as we Know it
Scientists in July announced the discovery of a pair of viruses that defy classification. Bigger and more genetically complex than any viral genus known to science, these so-called “pandoraviruses” could reignite a longstanding debate over the classification of life itself.
Brain-to-Brain Interfaces Have Arrived
Back in February, researchers announced that they had successfully established an electronic link between the brains of two rats, and demonstrated that signals from the mind of one could help the second solve basic puzzles in real time — even when those animals were separated by thousands of miles. A few months later, a similar connection was established between the brain of a human and a rat. Just one month later, researchers published the results of the first successful human-to-human brain interface. The age of the mind-meld, it seems, is near at hand.
There is Life at the End of the World
There is life in Lake Whillans. For millions of years, the small body of liquid water has lurked hundreds of meters below Antarctica’s Ross Ice Shelf, sealed off from the outside world and the scientists who would explore its subglacial depths. Earlier this year, a team of researchers led by Montana State University glaciologist John Priscu successfully bored a tunnel to Whillans and encountered life, making Priscu and his colleagues the first people in history to discover living organisms in the alien lakes at the bottom of the world.
Doctors Cure HIV in a Baby Born With the Disease
In a monumental first for medicine, doctors announced in March that a baby had been cured of an HIV infection. Dr. Deborah Persaud, who presented the child’s case at the 20th annual Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infection, called it “definitely a game-changer.”
Newly Discovered Skulls Could Prune Humans’ Evolutionary Tree
An incredibly well-preserved, 1.8-million-year-old skull from Dmanisi, Georgia suggests the evolutionary tree of the genus Homo may have fewer branches than previously believed. In a report published in October, a team led by Georgian anthropologist David Lordkipanidze writes that it is “the world’s first completely preserved hominid skull.” And what a skull it is. When considered alongside four other skulls discovered nearby, it suggests that the earliest known members of the Homo genus (H. habilis, H.rudolfensis and H. erectus) may not have been distinct, coexisting species, at all. Instead, they may have been part of a single, evolving lineage that eventually gave rise to modern humans.
Neuroscientists Turn Brains Invisible
Gaze upon the stunning effects of CLARITY, a new technique that enables scientists to turn brain matter and other tissues completely transparent. It’s been hailed as one of the most important advances for neuroanatomy in decades, and it’s not hard to see why.
[source | gifs → galaxyclusters]
A New Angle on Two Spiral Galaxies for Hubble’s 27th Birthday
In celebration of the 27th anniversary of the launch of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope on April 24, 1990, astronomers used the legendary telescope to take a portrait of a stunning pair of spiral galaxies. This starry pair offers a glimpse of what our Milky Way galaxy would look like to an outside observer. The edge-on galaxy is called NGC 4302, and the tilted galaxy is NGC 4298. These galaxies look quite different because we see them angled at different positions on the sky. They are actually very similar in terms of their structure and contents. Image credit: NASA, ESA, and M. Mutchler (STScI) Read more NASA Media Usage Guidelines
Allow us to reintroduce someone … the name’s Perseverance.
With this new name, our Mars 2020 rover has now come to life! Chosen by middle school student Alex Mather, Perseverance helps to remind ourselves that no matter what obstacles we face, whether it’s on the way to reaching our goals or on the way to Mars, we will push through. In Alex’s own words,
“We are a species of explorers, and we will meet many setbacks on the way to Mars. However, we can persevere. We, not as a nation but as humans, will not give up. The human race will always persevere into the future.”
Welcome to the family. ❤️
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 love-is-pain-by-bri liked this · 1 week ago
love-is-pain-by-bri liked this · 1 week ago -
 servungcint reblogged this · 1 month ago
servungcint reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 ohhoneyhoneyy reblogged this · 2 months ago
ohhoneyhoneyy reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 faeline liked this · 2 months ago
faeline liked this · 2 months ago -
 suppuration reblogged this · 5 months ago
suppuration reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 catsinspacesuits liked this · 5 months ago
catsinspacesuits liked this · 5 months ago -
 layziethelapras liked this · 5 months ago
layziethelapras liked this · 5 months ago -
 flairina reblogged this · 5 months ago
flairina reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 wretchie liked this · 6 months ago
wretchie liked this · 6 months ago -
 artoklasia reblogged this · 6 months ago
artoklasia reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 itsgonnabeasparklingday liked this · 8 months ago
itsgonnabeasparklingday liked this · 8 months ago -
 all-the-beautiful-chaos liked this · 9 months ago
all-the-beautiful-chaos liked this · 9 months ago -
 thepillarsofmarsandvenus liked this · 9 months ago
thepillarsofmarsandvenus liked this · 9 months ago -
 exaltedrevenge liked this · 9 months ago
exaltedrevenge liked this · 9 months ago -
 parttimepunner reblogged this · 9 months ago
parttimepunner reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 parttimepunner liked this · 9 months ago
parttimepunner liked this · 9 months ago -
 moss-sauce liked this · 10 months ago
moss-sauce liked this · 10 months ago -
 alwaysacurious1 liked this · 11 months ago
alwaysacurious1 liked this · 11 months ago -
 alice-quinn-at-oxford reblogged this · 11 months ago
alice-quinn-at-oxford reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 muigi1 liked this · 11 months ago
muigi1 liked this · 11 months ago -
 rabbitheads liked this · 1 year ago
rabbitheads liked this · 1 year ago -
 meissama liked this · 1 year ago
meissama liked this · 1 year ago -
 warcotuj8746 liked this · 1 year ago
warcotuj8746 liked this · 1 year ago -
 depressedgaylaughter reblogged this · 1 year ago
depressedgaylaughter reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 chaotically-gay reblogged this · 1 year ago
chaotically-gay reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 derecho-noah reblogged this · 1 year ago
derecho-noah reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 cherryboness liked this · 1 year ago
cherryboness liked this · 1 year ago -
 blueeyedjoy reblogged this · 1 year ago
blueeyedjoy reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 bluefrost-freewolf liked this · 1 year ago
bluefrost-freewolf liked this · 1 year ago -
 sythesizeher reblogged this · 1 year ago
sythesizeher reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 sythesizeher liked this · 1 year ago
sythesizeher liked this · 1 year ago -
 internetfriendsforever reblogged this · 1 year ago
internetfriendsforever reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 internetfriendsforever liked this · 1 year ago
internetfriendsforever liked this · 1 year ago -
 lostbetweenthenotes reblogged this · 1 year ago
lostbetweenthenotes reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 whatthelaughman reblogged this · 1 year ago
whatthelaughman reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 angelictroublemaker liked this · 1 year ago
angelictroublemaker liked this · 1 year ago -
 redredredcake liked this · 1 year ago
redredredcake liked this · 1 year ago -
 janokenmun reblogged this · 1 year ago
janokenmun reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 confused-and-slightly-disturbed liked this · 1 year ago
confused-and-slightly-disturbed liked this · 1 year ago -
 janokenmun liked this · 1 year ago
janokenmun liked this · 1 year ago -
 annalies liked this · 1 year ago
annalies liked this · 1 year ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts