Study: Superconducting Technologies Will Soon Be Used For Transportation, Power Storage

Study: Superconducting Technologies Will Soon Be Used for Transportation, Power Storage
More Posts from Dotmpotter and Others


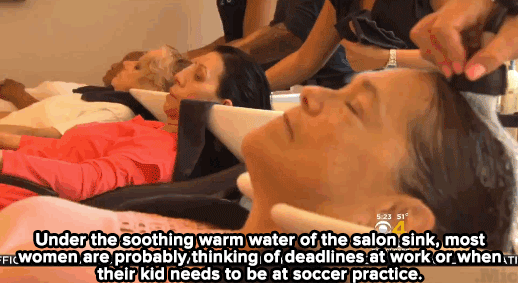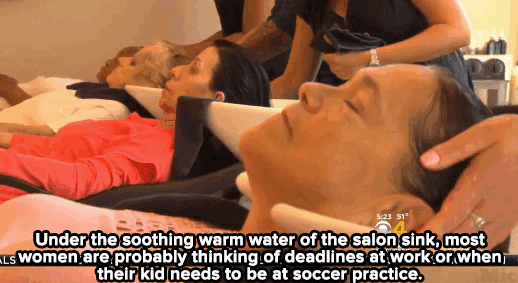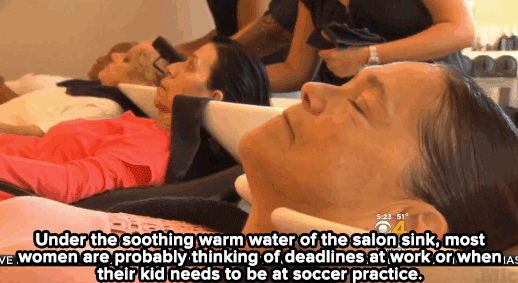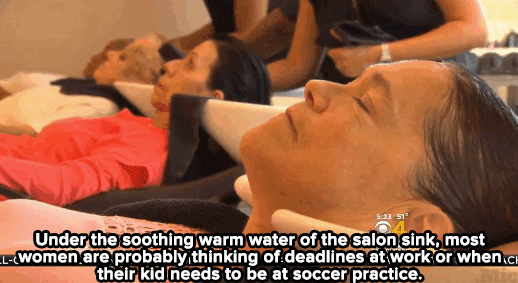
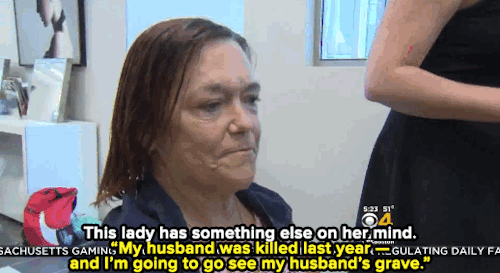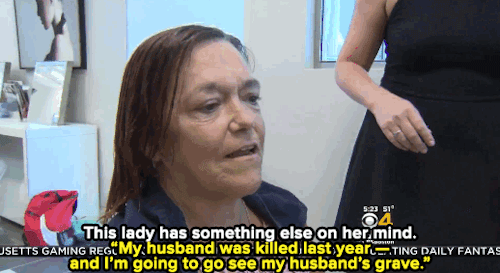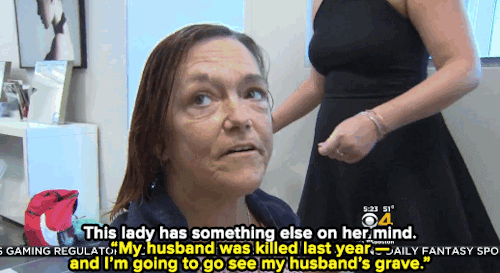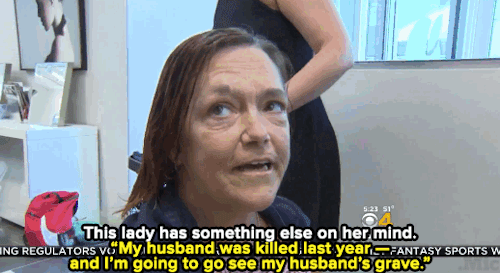






Watch: A haircut may not solve homelessness — but it can make all the difference for these women.
Follow @stylemic

Thursday is World Maritime Day which this year spotlights maritime transport as a cost-effective and energy-efficient link in the global supply chain.
Get more information from International Maritime Organization on shipping, sustainable development and the “future we want” here.










Breathtaking Images of Underwater Life Captured by Freediving Photographers Alex Voyer and Alex Roubaud

Earlier this year, BioDigital partnered with About.com to provide interactive visualizations for common health conditions. Patients searching for information about Type 2 diabetes, for instance, are presented with a 3D model of a cell’s response to insulin, in which they can explore the process from different angles while toggling between diabetic and normal cell function.
What’s revolutionary about the API launch, though, is that now developers can personalize the BioDigital human by integrating their own imaging data, movement data collected by wearables, and health record data, among other sources.
So essentially, instead of clicking around the standard human model on About.com, we could soon be exploring 3D models of our own bodies, constructed with our unique health data.
For athletes especially, the immediate advantages of virtually replicating a moving body are obvious. If you can see exactly which movements inflict pain or stress on your body, it’s much easier to understand how to avoid them.
For medical professionals, though, the ability to visualize vast amounts of health data in real time via the BioDigital human has the potential to change the way new information is analyzed and consumed.
“The human body is this incredible system of systems, and there’s an infinite amount of detail,” says Sculli. “So we can start mapping cellular mechanisms, and genomic and brain activity, and all of this information that’s being collected in masses from research and wearables, and make it consumable for people.”
(via 3D Modeling Startup BioDigital Launches An API For The Human Body | TechCrunch)

Holy shit! The single reason Republicans have no right to exist is climate denial on behalf of energy companies.

So, a new plant related to the potato is being named after Mark Watney and this makes me very happy.

“My lab group has decided to name this new species Solanum watneyi after Mark Watney, the book/film character who shows us all that botanists can be cool, too.” - Dr. Chris Martine, Professor at Bucknell University
Stephen Hawking: robots could give us all material abundance, unless rich people hoard all the wealth

In a Reddit AMA, the eminent physicist warns that while increasing automation could give us a world of “luxurious leisure,” that “most people can end up miserably poor if the machine-owners successfully lobby against wealth redistribution.”
Paging Thomas Piketty, your ride is here.
Read the rest







Brain, Bone and Blood Vessels Coming Hot Off the Press
Could the days of custom clavicles and bespoke bladders produced just in the knick of time for suffering patients be around the corner?
While keeping an eye on tissue engineering studies, we’ve been seeing some significant wins in the lab that are bringing the sci-fi future of on-demand 3-D printed organs, bone and blood vessels closer.
Harvard and Brown bioengineers are taking their own routes to build complex tissues in customized 3-D printers. And just the other week, we reported on newly unveiled work at the University of Florida to print complex soft structures in baths that could one day birth replacement human parts along with soft robots.
Now, Carnegie Mellon engineers reported on Friday that they had successfully printed simplified proof-of-concept anatomical structures like mini femurs, blood vessels and brains suspended in soft gelatin. Learn more and see a video below.
Keep reading
The Most Metal Mass Extinction Events, Ranked
in the style of The Toast
That One Unnamed Extinction Event That Happened When Blue-Green Algae Discovered Photosynthesis and Started Pumping the Environment Full of Oxygen, Which Was Toxic to All Other Life on Earth at That Point in Time
This extinction event did result in the extinction of more living organisms than any other, whether you rank by number of individuals, number of orders/genera/species, % of life, or amount of biomass, but they were all single-celled organisms, so they don’t even register on the metal scale.
The Current Slow Slide Due to Anthropogenic Environmental Modification
Habitat destruction isn’t very metal.
Late Devonian
Some super-weird shit died out, which is totally metal, but we have no idea why, which isn’t. It might not even have been an extinction event, just a decrease in the speciation rate. Jawed vertebrates totally unaffected.
End Ordovician
Second-largest extinction event after the End Permian (not counting those blue-green algae fuckers). Caused by tectonic plate shifting (kinda metal) and resulting glaciation (mildly metal).
Deep Impact
Pros: Giant asteroid hitting the earth.
Cons: Fictional.
End Triassic
Probably caused by massive volcanic eruptions, which is pretty metal, but mostly just wiped out some weird looking amphibians, which is only mildly metal.
End Permian
Greatest extinction event of all time (with the exception of that blue-green algae fiasco mentioned above), wiping out ~95% of all species: metal. Only known mass extinction of insects: metal. Probably caused by the biggest volcanic eruptions since life began (metal) which ignited massive coal beds (metal) and caused the release of methane from the ocean floor (metal) resulting in a runaway greenhouse effect that raised the average ocean temperature to 40C for several million years, essentially boiling the earth alive (super metal). Paved the way for dinosaurs to take over the earth: metal. Known as the ‘Great Dying’: totally metal.
However, most of the extinctions occurred in sessile marine organisms, which are way too boring to be metal, and for the first ~20 million years after the extinction event, land was dominated by Lystrosaurus, which is the most un-metal looking reptile you can think of.
End Cretaceous, aka the K-T Event
A GIANT FLAMING BALL OF ROCK HIT THE EARTH AND KILLED ALL THE (non-avian) DINOSAURS. ENOUGH SAID.
-
 dotmpotter reblogged this · 11 years ago
dotmpotter reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 dailyfusion reblogged this · 11 years ago
dailyfusion reblogged this · 11 years ago
