Brain, Bone And Blood Vessels Coming Hot Off The Press







Brain, Bone and Blood Vessels Coming Hot Off the Press
Could the days of custom clavicles and bespoke bladders produced just in the knick of time for suffering patients be around the corner?
While keeping an eye on tissue engineering studies, we’ve been seeing some significant wins in the lab that are bringing the sci-fi future of on-demand 3-D printed organs, bone and blood vessels closer.
Harvard and Brown bioengineers are taking their own routes to build complex tissues in customized 3-D printers. And just the other week, we reported on newly unveiled work at the University of Florida to print complex soft structures in baths that could one day birth replacement human parts along with soft robots.
Now, Carnegie Mellon engineers reported on Friday that they had successfully printed simplified proof-of-concept anatomical structures like mini femurs, blood vessels and brains suspended in soft gelatin. Learn more and see a video below.
Keep reading
More Posts from Dotmpotter and Others
Setting up any business is a challenge but in Ethiopia those range from daily operating headaches such as on-off internet to even more fundamental business challenges
“The internet goes out a couple of times a week — when that happens, there is not much we can do but rely on phone lines to take orders,” said Feleg Tsegaye, manager of Deliver Addis.
But he also believes the Horn of Africa nation — the second most populous on the continent — offers enormous opportunities.
Tsegaye was born and brought up in the US but moved to Ethiopia, the homeland of his parents, hoping to tap into a still largely untapped but swiftly growing market he believes is one of the most promising on the continent.
“The IT sector is still in its infancy — typically in these markets there is a way to transfer money very quickly and very easily, but here that doesn’t exist quite yet,” he added.
“Once you have a way for entrepreneurs to make money through technology, I think you are going to see that change very quickly.”
With a growth rate of nearly 10 per cent a year over the past decade, according to the World Bank, Ethiopia has attracted entrepreneurs eager to take their cut of a market with over 94 million potential consumers.
The Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa now has three “start-up incubators”, some supported by foreign investors, to help Ethiopian entrepreneurs launch their own business.

The Fracking Science Compendium by Physicians for Social Responsibility shows overwhelming harms. Learn more below:
http://concernedhealthny.org/compendium/ http://www.psr.org/resources/fracking-compendium.html
Wyoming's Ag-Gag law makes it a crime to gather evidence of crime

With this year’s “ag-gag” law, Wyoming has made it a crime to gather evidence of agricultural wrongdoing, from illegal pollution to animal cruelty, even from public land – and also prohibits regulators from acting on information gathered in violation of the law.
Many public interest groups are challenging the law. A similar – but less Draconian – law in Idaho was struck down this year as unconstitutional.
Read the rest

Pew Research Center analyzed 1,041,336 apps in the Google Play Store as of September 2014 to determine the specific permissions requested by each app. We found that across all Android apps, 165 permissions allowed access to device hardware and 70 allowed access to various types of user information.
Apps Permissions in the Google Play Store

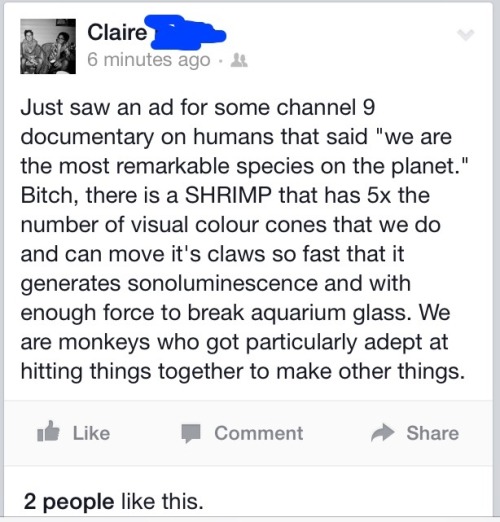
I am not here for the idea that humans > everything else.

Energy conversion: Speeding up material discovery
Algorithm take months, not years, to find material for improved energy conversion
In even the most fuel-efficient cars, about 60 percent of the total energy of gasoline is lost through heat in the exhaust pipe and radiator. To combat this, researchers are developing new thermoelectic materials that can convert heat into electricity. These semiconducting materials could recirculate electricity back into the vehicle and improve fuel efficiency by up to 5 percent.
The challenge is, current thermoelectric materials for waste heat recovery are very expensive and time consuming to develop. One of the state of the art materials, made from a combination of hafnium and zirconium (elements most commonly used in nuclear reactors), took 15 years from its initial discovery to optimized performance.
Now, researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have developed an algorithm that can discover and optimize these materials in a matter of months, relying on solving quantum mechanical equations, without any experimental input.
“These thermoelectric systems are very complicated,” said Boris Kozinsky, a recently appointed Associate Professor of Computational Materials Science at SEAS and senior author of the paper. “Semiconducting materials need to have very specific properties to work in this system, including high electrical conductivity, high thermopower, and low thermal conductivity, so that all that heat gets converted into electricity. Our goal was to find a new material that satisfies all the important properties for thermoelectric conversion while at the same time being stable and cheap.”
Read more.

-
 nocturnalsouls liked this · 6 years ago
nocturnalsouls liked this · 6 years ago -
 unlikelyuserhere liked this · 6 years ago
unlikelyuserhere liked this · 6 years ago -
 dildo-cornucopia liked this · 6 years ago
dildo-cornucopia liked this · 6 years ago -
 goingtowales liked this · 6 years ago
goingtowales liked this · 6 years ago -
 perpetually-attempting-man liked this · 6 years ago
perpetually-attempting-man liked this · 6 years ago -
 pinkprogram reblogged this · 6 years ago
pinkprogram reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 pz3000 liked this · 6 years ago
pz3000 liked this · 6 years ago -
 graveyardshipper liked this · 6 years ago
graveyardshipper liked this · 6 years ago -
 araiarira liked this · 6 years ago
araiarira liked this · 6 years ago -
 loukazade liked this · 6 years ago
loukazade liked this · 6 years ago -
 librelly reblogged this · 6 years ago
librelly reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 dumbassheirofhope reblogged this · 7 years ago
dumbassheirofhope reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 acheellies liked this · 7 years ago
acheellies liked this · 7 years ago -
 sun-skalli liked this · 7 years ago
sun-skalli liked this · 7 years ago -
 complexience-blog liked this · 7 years ago
complexience-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 country-toads reblogged this · 7 years ago
country-toads reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 majesticmastermind reblogged this · 7 years ago
majesticmastermind reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 crystiamvalbuena reblogged this · 7 years ago
crystiamvalbuena reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 dakatndahat liked this · 7 years ago
dakatndahat liked this · 7 years ago -
 funcoolmathgames reblogged this · 7 years ago
funcoolmathgames reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 themarketingarea reblogged this · 8 years ago
themarketingarea reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 themarketingarea reblogged this · 8 years ago
themarketingarea reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 themarketingarea reblogged this · 8 years ago
themarketingarea reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 eclipse-phase-aesthetic reblogged this · 8 years ago
eclipse-phase-aesthetic reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 paranoidrobots liked this · 8 years ago
paranoidrobots liked this · 8 years ago -
 myarkadia liked this · 8 years ago
myarkadia liked this · 8 years ago -
 rulerofmyownplanet liked this · 8 years ago
rulerofmyownplanet liked this · 8 years ago -
 pharmaceutism reblogged this · 8 years ago
pharmaceutism reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 nadaya21-blog liked this · 8 years ago
nadaya21-blog liked this · 8 years ago
![Map Of The Humongous Fungus: The Largest Living Organism On Earth [1936x1310][OC] CLICK HERE FOR MORE](https://64.media.tumblr.com/db929150f86f0c503804f329c0244a28/tumblr_nyulclrmRz1s6c1p2o1_500.jpg)