Writing Tips - Blog Posts
World Building
Types of Government
♛
⤷ anarchy
➝ society without enforced government
⤷ aristocracy
➝ small, elite ruling class holds power over lower socioeconomic strata ; members chosen based on wealth
⤷ autocracy
➝ controlled by one singular person of power without restraints
⤷ communism
➝ state owns and operates industry on behalf of the people ; citizens are apart of a classless society that distributes goods & services as needed
⤷ democracy
➝ power held by the people through voting in order to ensure fair representation and prevention of abuse of power
⤷ dictatorship
➝ power held by one person or a group of people who control the masses
⤷ fascism
➝ control of the people by promoting ancestral/cultural values & eradicating foreign influences
⤷ federalism
➝ union of smaller states which are self-governed yet united under a central government
⤷ junta
➝ militaristic rule after taking over by force
⤷ monarchy
➝ authority is vested in a single figure for life and passed down hereditarily ; level of power may vary from absolution to nonexistent
➝ constitutional monarchy: limited power as outlined in a constitution // absolute monarchy: unlimited power
⤷ oligarchy
➝ authoritative power rests with a small faction of people or families who are deemed worthy due to wealth, education, and/or family history
⤷ plutocracy
➝ ruled by the wealthy
⤷ republic
➝ democratic model in which the people elect representatives
⤷ socialism
➝ collective and cooperative ownership of production, opposed to private
⤷ stratocracy
➝ ruled by the military following wars and expansion
⤷ technocracy
➝ scientists are decision makers ; rulers are chosen based on experience/knowledge/skill
⤷ theocracy
➝ power rests with religious figures ; scriptural laws and legal codes are coincided
⤷ totalitarian
➝ total control by government including the prohibition of opposition & extreme regulation of public/private life
⤷ tyranny
➝ absolute control by ruler with an oppressive power
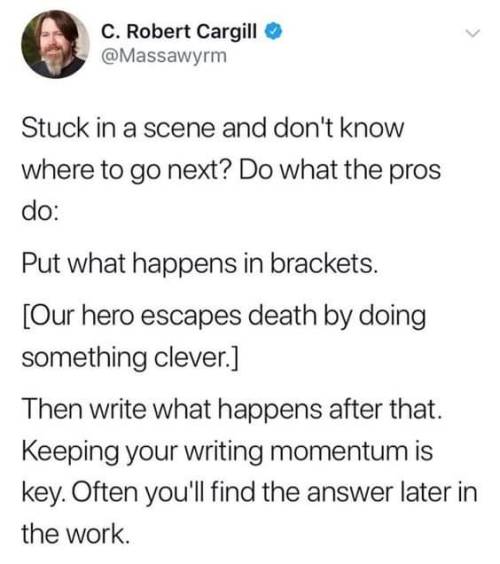
my writing fundamentally changed forever ten years ago when i realized you could use sentence structure to control people’s heart rates. is this still forbidden knowledge or does everyone know it now
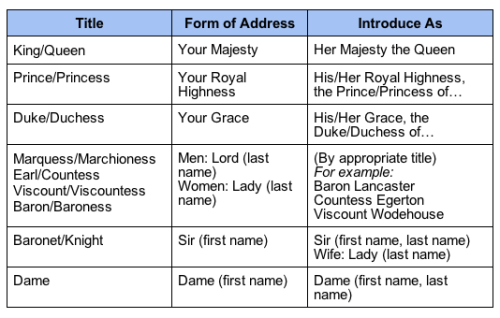
//Absurdly helpful for people writing royal characters and/or characters who interact with royalty and members of the nobility.
[x]










I’m pretty sure I’m not the only one who has trouble remembering developmental milestones. I put these together, but can’t take credit for any of the photography. Hope someone finds them helpful!
• An Oxford comma walks into a bar, where it spends the evening watching the television, getting drunk, and smoking cigars.
• A dangling participle walks into a bar. Enjoying a cocktail and chatting with the bartender, the evening passes pleasantly.
• A bar was walked into by the passive voice.
• An oxymoron walked into a bar, and the silence was deafening.
• Two quotation marks walk into a “bar.”
• A malapropism walks into a bar, looking for all intensive purposes like a wolf in cheap clothing, muttering epitaphs and casting dispersions on his magnificent other, who takes him for granite.
• Hyperbole totally rips into this insane bar and absolutely destroys everything.
• A question mark walks into a bar?
• A non sequitur walks into a bar. In a strong wind, even turkeys can fly.
• Papyrus and Comic Sans walk into a bar. The bartender says, "Get out -- we don't serve your type."
• A mixed metaphor walks into a bar, seeing the handwriting on the wall but hoping to nip it in the bud.
• A comma splice walks into a bar, it has a drink and then leaves.
• Three intransitive verbs walk into a bar. They sit. They converse. They depart.
• A synonym strolls into a tavern.
• At the end of the day, a cliché walks into a bar -- fresh as a daisy, cute as a button, and sharp as a tack.
• A run-on sentence walks into a bar it starts flirting. With a cute little sentence fragment.
• Falling slowly, softly falling, the chiasmus collapses to the bar floor.
• A figure of speech literally walks into a bar and ends up getting figuratively hammered.
• An allusion walks into a bar, despite the fact that alcohol is its Achilles heel.
• The subjunctive would have walked into a bar, had it only known.
• A misplaced modifier walks into a bar owned by a man with a glass eye named Ralph.
• The past, present, and future walked into a bar. It was tense.
• A dyslexic walks into a bra.
• A verb walks into a bar, sees a beautiful noun, and suggests they conjugate. The noun declines.
• A simile walks into a bar, as parched as a desert.
• A gerund and an infinitive walk into a bar, drinking to forget.
• A hyphenated word and a non-hyphenated word walk into a bar and the bartender nearly chokes on the irony
- Jill Thomas Doyle
Ways To Describe Someone's Voice
adenoidal (adj): if someone’s voice is adenoidal, some of the sound seems to come through their nose
appealing (adj): an appealing look/voice shows that you want help, approval, or agreement
breathy (adj): with loud breathing noises
brittle (adj): if you speak in a brittle voice, you sound as if you are about to cry
croaky (adj): if someone’s voice sounds croaky, they speak in a low, rough voice that sounds as if they have a sore throat
dead (adj): if someone’s eyes or voice are dead, they feel or show no emotion
disembodied (adj): a disembodied voice comes from someone who you cannot see
flat (adj): spoken in a voice that does not go up and down; this word is often used for describing the speech of people from a particular region
fruity (adj): a fruity voice or laugh is deep and strong in a pleasant way
grating (adj): a grating voice, laugh, or sound is unpleasant and annoying
gravelly (adj): a gravelly voice sounds low and rough
gruff (adj): this voice has a rough, low sound
guttural (adj): a guttural sound is deep and made at the back of your throat
high-pitched (adj): true to its name, a high-pitched voice or sound is very high
hoarse (adj): someone who is hoarse, or has a hoarse voice, speaks in a low, rough voice, usually because their throat is sore
honeyed (adj): honeyed words or a honeyed voice sound very nice, but you cannot trust the person who is speaking
husky (adj): a husky voice is deep and sounds hoarse (as if you have a sore throat), often in an attractive way
low (adj): a low voice is quiet and difficult to hear; also used for describing a deep voice that has a long wavelength
matter-of-fact (adj): usually used if the person speaking knows what they are talking about (or absolutely think they know what they are talking about)
modulated (adj): a modulated voice is controlled and pleasant to listen to
monotonous (adj): this kind of voice is boring and unpleasant due to the fact that it does not change in loudness or become higher/lower
nasal (adj): someone with a nasal voice sounds as if they are speaking through their nose
orotund (adj): an orotund voice is loud and clear
penetrating (adj): a penetrating voice is so high or loud that it makes you slightly uncomfortable
plummy (adj): a plummy voice or way of speaking is considered to be typical of an English person of a high social class; this word shows that you dislike people who speak like this
quietly (adj): in a soft, quiet voice
raucous (adj): a raucous voice or noise is loud and sounds rough
ringing (adj): a ringing voice is very loud and clear
rough (adj): a rough voice is not soft and is unpleasant to listen to
shrill (adj): a shrill voice is very loud, high, and unpleasant
silvery (adj): this voice is clear, light, and pleasant
singsong (adj): if you speak in a singsong voice, your voice rises and falls in a musical way
small (adj): a small voice is quiet
smoky (adj): a smoky voice is sexually attractive in a slightly mysterious way
softly spoken (adj): someone who is softly spoken has a quiet, gentle voice
soft-spoken (adj): speaking or said in a quiet, gentle voice
sotto voce (adj, adv): in a very quiet voice
stentorian (adj): a stentorian voice sounds very loud and severe
strangled (adj): a strangled sound is one that someone stops before they finish making it
strident (adj): this voice is loud and unpleasant
taut (adj): used about something such as a voice that shows someone is nervous or angry
thick (adj): if your voice is thick with an emotion, it sounds less clear than usual because of the emotion
thickly (adv): with a low voice that comes mostly from your throat
thin (adj): a thin voice or sound is high and unpleasant to listen to
throaty (adj): a throaty sound is low and seems to come from deep in your throat
tight (adj): shows that you are nervous or annoyed
toneless (adj): does not express any emotion
tremulous (adj): if your voice is tremulous, it is not steady; for example, because you are afraid or excited
wheezy (adj): a wheezy noise sounds as if it is made by someone who has difficulty breathing
wobbly (adj): if your voice is wobbly, it goes up and down, usually because you are frightened, not confident, or are going to cry
booming (adj): very loud and attention-getting
quavering (adv): if your voice quavers, it is not steady because you are feeling nervous or afraid
a voice like a foghorn: very loud voice
in an undertone: using a quiet voice so that someone cannot hear you
someone’s dulcet tones: the sound of someone’s voice as they speak
Actually
The question I get the most is how I write characters that feel like real people.
Generally when I’m designing a human being, I deconstruct them into 7 major categories:
1. Primary Drive 2. Fear: Major and Secondary 3. Physical Desires 4. Style of self expression 5. How they express affection 6. What controls them (what they are weak for) 7. What part of them will change.
1. Primary Drive: This is generally related to the plot. What are their plot related goals? How are they pulling the plot forward? how do they make decisions? What do they think they’re doing and how do they justify doing it. 2. Fear: First, what is their deep fear? Abandonment? being consumed by power? etc. Second: tiny fears. Spiders. someone licking their neck. Small things that bother them. At least 4. 3. Physical desires. How they feel about touch. What is their perceived sexual/romantic orientation. Do their physical desires match up with their psychological desires.
4. Style of self expression: How they talk. Are they shy? Do they like to joke around and if so, how? Are they anxious or confident internally and how do they express that externally. What do words mean to them? More or less than actions? Does their socioeconomic background affect the way they present themselves socially? 5. How they express affection: Do they express affection through actions or words. Is expressing affection easy for them or not. How quickly do they open up to someone they like. Does their affection match up with their physical desires. how does the way they show their friends that they love them differ from how they show a potential love interest that they love them. is affection something they struggle with?
6. What controls them (what they are weak for): what are they almost entirely helpless against. What is something that influences them regardless of their own moral code. What– if driven to the end of the wire— would they reject sacrificing. What/who would they cut off their own finger for. What would they kill for, if pushed. What makes them want to curl up and never go outside again from pain. What makes them sink to their knees from weakness or relief. What would make them weep tears of joy regardless where they were and who they were in front of.
7. WHAT PART OF THEM WILL CHANGE: people develop over time. At least two of the above six categories will be altered by the storyline–either to an extreme or whittled down to nothing. When a person experiences trauma, their primary fear may change, or how they express affection may change, etc. By the time your book is over, they should have developed. And its important to decide which parts of them will be the ones that slowly get altered so you can work on monitoring it as you write. making it congruent with the plot instead of just a reaction to the plot.
That’s it.
But most of all, you have to treat this like you’re developing a human being. Not a “character” a living breathing person. When you talk, you use their voice. If you want them to say something and it doesn’t seem like (based on the seven characteristics above) that they would say it, what would they say instead?
If they must do something that’s forced by the plot, that they wouldn’t do based on their seven options, they can still do the thing, but how would they feel internally about doing it?
How do their seven characteristics meet/ meld with someone else’s seven and how will they change each other?
Once you can come up with all the answers to all of these questions, you begin to know your character like you’d know one of your friends. When you can place them in any AU and know how they would react.
They start to breathe.
fellas im about to join a writing competition for my school, but currently have no ideas. Suggestions?
the theme is Stories for Strange Times
Writing tips for long fics that helped me that no one asked for.
1.) Don't actually delete content from your WIP unless it is minor editing - instead cut it and put it in a secondary document. If you're omitting paragraphs of content, dialog, a whole scene you might find a better place for it later and having it readily available can really save time. Sometimes your idea was fantastic, but it just wasn't in the right spot.
2.) Stuck with wording the action? Just write the dialog then revisit it later.
3.) Stuck on the whole scene? Skip it and write the next one.
4.) Write on literally any other color than a white background. It just works. (I use black)
5.) If you have a beta, while they are beta-ing have them read your fic out loud. Yes, I know a lot of betas/writers do not have the luxury of face-timing or have the opportunity to do this due to time constraints etc but reading your fic out loud can catch some very awkward phrasing that otherwise might be missed. If you don't have a beta, you read it out loud to yourself. Throw some passion into your dialog, you might find a better way to word it if it sounds stuffy or weird.
6.) The moment you have an idea, write it down. If you don't have paper or a pen, EMAIL it to yourself or put it in a draft etc etc. I have sent myself dozens of ideas while laying down before sleep that I 10/10 forgot the next morning but had emailed them to myself and got to implement them.
7.) Remember - hits/likes/kudos/comments are not reflective of the quality of your fic or your ability to write. Most people just don't comment - even if they say they do, they don't, even if they preach all day about commenting, they don't, even if they are a very popular blog that passionately reminds people to comment - they don't comment (I know this personally). Even if your fic brought tears to their eyes and it haunted them for weeks and they printed it out and sent it to their friends they just don't comment. You just have to accept it. That being said - comment on the fic you're reading now, just do it, if you're 'shy' and that's why you don't comment the more you comment the better you'll get at it. Just do it.
8.) Remove unrealistic daily word count goals from your routine. I've seen people stress 1500 - 2000 words a day and if they don't reach that they feel like a failure and they get discouraged. This is ridiculous. Write when you can, but remove absurd goals. My average is 500 words a day in combination with a 40 hour a week job and I have written over 200k words from 2022-2023.
9.) There are dozens of ways to do an outline from precise analytical deconstruction that goes scene by scene to the minimalist bullet point list - it doesn't matter which one you use just have some sort of direction. A partial outline is better than no outline.
10.) Write for yourself, not for others. Write the fic you know no one is going to read. Write the fic that sounds ridiculous. You will be so happy you put it out in the world and there will be people who will be glad it exists.
To Write Better Antagonists, Have Them Embody the Protagonist's Struggles
(Spoilers for The Devil Wears Prada, Avatar the Last Airbender, Kung Fu Panda 2, and The Hunger Games triology).
Writing antagonists and villains can be hard, especially if you don't know how to do so.
I think a lot of writers' first impulse is to start off with a placeholder antagonist, only to find that this character ends up falling flat. They finish their story only for readers to find the antagonist is not scary or threatening at all.
Often the default reaction to this is to focus on making the antagonist meaner, badder, or scarier in whatever way they can- or alternatively they introduce a Tragic Backstory to make them seem broken and sympathetic. Often, this ends up having the exact opposite effect. Instead of a compelling and genuinely terrifying villain, the writer ends up with a Big Bad Edge Lord who the reader just straight up does not care about, or actively rolls their eyes at (I'm looking at you, Marvel).
What makes an antagonist or villain intimidating is not the sheer power they hold, but the personal or existential threat they pose to the protagonist. Meaning, their strength as a character comes from how they tie into the themes of the story.
To show what I mean, here's four examples of the thematic roles an antagonist can serve:
1. A Dark Reflection of the Protagonist
The Devil Wears Prada
Miranda Priestly is initially presented as a terrible boss- which she is- but as the movie goes on, we get to see her in a new light. We see her as an bonafide expert in her field, and a professional woman who is incredible at what she does. We even begin to see her personal struggles behind the scenes, where it’s clear her success has come at a huge personal cost. Her marriages fall apart, she spends ever waking moment working, and because she’s a woman in the corporate world, people are constantly trying to tear her down.
The climax of the movie, and the moment that leaves the viewer most disturbed, does not feature Miranda abusing Andy worse than ever before, but praising her. Specifically, she praises her by saying “I see a great deal of myself in you.” Here, we realize that, like Miranda, Andy has put her job and her career before everything else that she cares about, and has been slowly sacrificing everything about herself just to keep it. While Andy's actions are still a far cry from Miranda's sadistic and abusive managerial style, it's similar enough to recognize that if she continues down her path, she will likely end up turning into Miranda.
In the movie's resolution, Andy does not defeat Miranda by impressing her or proving her wrong (she already did that around the half way mark). Instead, she rejects the values and ideals that her toxic workplace has been forcing on her, and chooses to leave it all behind.
2. An Obstacle to the Protagonist's Ideals
Avatar: The Last Airbender
Fire Lord Ozai is a Big Bad Baddie without much depth or redemptive qualities. Normally this makes for a bad antagonist (and it's probably the reason Ozai has very little screen time compared to his children), but in Avatar: The Last Airbender, it works.
Why?
Because his very existence is a threat to Aang's values of nonviolence and forgiveness.
Fire Lord Ozai cannot be reasoned with. He plans to conquer and burn down the world, and for most of the story, it seems that the only way to stop him is to kill him, which goes against everything Aang stands for. Whether or not Aang could beat the Fire Lord was never really in question, at least for any adults watching the show. The real tension of the final season came from whether Aang could defeat the Fire Lord without sacrificing the ideals he inherited from the nomads; i.e. whether he could fulfill the role of the Avatar while remaining true to himself and his culture.
In the end, he manages to find a way: he defeats the Fire Lord not by killing him, but by stripping him of his powers.
3. A Symbol of the Protagonist's Inner Struggle
Kung Fu Panda 2
Kung Fu Panda 2 is about Po's quest for inner peace, and the villain, Lord Shen, symbolizes everything that's standing in his way.
Po and Lord Shen have very different stories that share one thing in common: they both cannot let go of the past. Lord Shen is obsessed with proving his parents wrong and getting vengeance by conquering all of China. Po is struggling to come to terms with the fact that he is adopted and is desperate to figure out who he is and why he ended up left in a box of radishes as a baby.
Lord Shen symbolizes Po's inner struggle in two main ways: one, he was the source of the tragedy that separated him from his parents, and two, he reinforces Po's negative assumptions about himself. When Po realizes that Lord Shen knows about his past and confronts him, Lord Shen immediately tells Po exactly what he's afraid of hearing: that his parents abandoned him because they didn't love him. Po and the Furious Five struggle to beat Shen not because he's powerful, but because Po can't let go of the past, and this causes him to repeatedly freeze up in battle, which Shen uses to his advantage.
Po overcomes Shen when he does the one thing Shen is incapable of: he lets go of the past and finds inner peace. Po comes to terms with his tragic past and recognizes that it does not define him, while Shen holds on to his obsession of defying his fate, which ultimately leads to his downfall.
4. A Representative of a Harsh Reality or a Bigger System
The Hunger Games
We don't really see President Snow do all that much on his own. Most of the direct conflict that Katniss faces, but with his underlings and the larger Capitol government. The few interactions we see between her and President Snow are mainly the two of them talking, and this is where we see the kind of threat he poses.
President Snow never lies to Katniss, not even once, and this is the true genius behind his character. He doesn't have to lie to or deceive Katniss, because the truth is enough to keep her complicit.
Katniss knows that fighting Snow and the Capital will lead to total war and destruction- the kind where there are survivors, but no winners. Snow tells her to imagine thousands upon thousands of her people dead, and that's exactly what happens. The entirety of District 12 gets bombed to ashes, Peeta gets brainwashed and turned into a human weapon, and her sister Prim, the very person she set out to protect at the beginning of the story, dies just before the Capitol's surrender. The districts won, but at a devastating cost.
Even after President Snow is captured and put up for execution, he continues to hurt Katniss by telling her the truth. He tells her that the bombs that killed her sister Prim were not sent by him, but by the people on her side. He brings to her attention that the rebellion she's been fighting for might just implement a regime just as oppressive and brutal as the one they overthrew and he's right.
In the end, Katniss is not the one to kill President Snow. She passes up her one chance to kill him to take down the new threat of President Coin.
''Useless'' Writing Reminders
Save your documents. Strive to be safe, not sorry.
Back-up your documents. Strive to be safe, not sorry.
Placeholder names can quickly turn into forever names. Picking name(s) on a whim can lead to great things, or it can become your worst nightmare (😁).
Your writing has value. Yes, even the most inadequate of writing. You don't have to boast or even like everything you've ever written, but even the most questionable of writing will have contributed to your growth as a storyteller. Cherish it for what it is.
You can take a break. It is absolutely okay.
First drafts are scary. But you know what's more scary? Not having a draft at all.
Using clichés or ''overdone'' tropes will not kill your story. Firstly, tropes are building blocks. Secondly, humans actively search to consume stories revolving around these tropes.
Write your heart out. Boast about your writing. Boast about your friends' and fellow writers' writing. Everyone deserves recognition, even you, from within your own heart. (Sorry. That's really cheesy. But it's true).
Hello! This is my first time asking but I could I have some advice on how to write a story that starts in the climax of the plot already? The context is my MC woke up and they are not able to remember anything, but suddenly, he just woke up in the wards of his family (a very strong political figure in their world might I add) whom he told what his life was but the narratives they are telling does not match even in the slightest of the flashback that's plaguing him as the time stretches. And they were in the middle of the war, too. I'm having a hard time to achieve that mind-blowing... thrill I suppose? They also got a love interest that is unmistakably not the one his family claimed ‘their-spouse’ to be.
Starting with Inciting Incident
Remember: your story's climax is the moment your character faces off against the antagonist once and for all. While some stories do start at the climax, and then flashback to the beginning of the story to build back up to it, it doesn't mean you start at the climax and move forward from there.
I think there can be a lot of confusion with the concept of "In Media Res" which a lot of people confuse as meaning starting in the literal middle of the story, or at the inciting incident or climax. Instead, "in media res" simply means starting in the middle of the action. That action can be the inciting incident, the climax, or the literal middle, but again, it doesn't mean the story moves forward from there.
If you're starting your story at the point where your character wakes up without their memories, this isn't the climax but rather the inciting incident. This is the moment when their life and world are turned upside down. Starting at this moment in a story about memory loss is a great way to go, because your reader knows as little about the character and their world as the character does. It puts the reader in your character's shoes right from the start, and they'll be learning everything right alongside your character.
So, that's really the key is to make sure you're filling in the gaps left by not having an exposition. You'll need to make sure to fairly quickly illustrate this character's natural personality, the world they've woken up into, and what their life was apparently like before they lost their memories. If they're being lied to, you may want to build in some clues that hint at what their actual life was like--such as feeling a place is familiar to them even if they're told "no, you would never have been to such a place."
As far as creating that thrill in that opening moment, it's really going to come down to emotional and sensory description. In lieu of recognizing who they are, where they are, and what happened to them, they're going to focus on their immediate surroundings. What can they see, hear, smell, taste, feel? What does that sensory input tell them about who they are and where they are? How does that sensory input--and what they can learn from it--make them feel? What emotions are they feeling as they process this unfamiliar environment and realize they have no idea who they are, where they are, or what happened to them?
I hope that helps!
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
I’ve been writing seriously for over 30 years and love to share what I’ve learned. Have a writing question? My inbox is always open!
LEARN MORE about WQA
SEE MY ask policies
VISIT MY Master List of Top Posts
COFFEE & COMMISSIONS ko-fi.com/wqa
Everything You Need To Know About Writing Bruises

Welcome to the latest instalment in my ongoing series on crafting realistic wounds in fiction. After delving into stab wounds, burns, and gunshot wounds, we're turning our attention to another crucial element in bringing your characters and their stories to life: bruises.
Bruises are possibly the most common miswritten injury in fiction. As tempting as it might be to make the protagonist's skin bruise when the morally grey characters clutches her wrist, scenes like this only serve to ruin immersion and make your readers wonder whether this could realistically happen.
Unlike the other wound types I've covered in this series, the internet doesn't seem to have a lot of writing advice for bruises. So, here's my comprehensive guide to writing bruises.
Types of Bruises
Understanding Bruise Formation:
Bruises are a common occurrence in everyday life, from the accidental bump into a table corner to the aftermath of an intense sporting event. But before we dive into the art of crafting realistic bruises in your writing, let's start by understanding how bruises form.
Bruises, also known as contusions, result from the rupture of blood vessels beneath the skin's surface, typically veins and capillaries. When these vessels break, blood leaks into the surrounding tissue. The body's natural response to this injury is to initiate the healing process, causing inflammation and discolouration.
Differentiating Types of Bruises:
Not all bruises are created equal. Understanding the various types of bruises will help you describe them accurately in your writing. Here, we'll explore the common distinctions among bruise types.
Contusions: Contusions are the most typical type of bruises. They often occur due to blunt force or trauma, resulting in pain and discolouration.
Subcutaneous Bruises: These are the most typical bruises resulting from blunt force trauma. Subcutaneous bruises appear as dark, discoloured areas under the skin and can change in colour as they heal, starting with red or purple and transitioning to green, yellow, and eventually fading away.
Hematoma: A hematoma is a more severe type of bruise caused by the collection of blood outside of blood vessels. Hematomas often appear as a raised lump under the skin and can take longer to heal.
Petechiae: Petechiae are tiny, red or purple pinpoint spots that can form when small blood vessels near the skin's surface break. These are often a sign of more severe underlying medical conditions.
Ecchymosis: Ecchymosis is a large bruise that covers a wider area, typically caused by substantial trauma or medical conditions. These bruises tend to be darker and may require more time to heal.
Tattoo Bruises: Sometimes, an object's pattern or texture may leave a distinct mark, resembling a tattoo. These can occur when someone is subjected to direct pressure from an object with an intricate or textured surface.
These distinctions will enable you to convey the type of bruise accurately in your storytelling, reflecting the nature and severity of the injury your character has endured. So, when crafting a scene in which your character sustains a bruise, you can choose the type that best suits your narrative.
Causes of Bruises:
Bruises can occur for various reasons, and knowing these causes will help you craft believable narratives. It's important to note that not every physical interaction results in a bruise, and your characters shouldn't bruise from actions that typically don't lead to bruising. For instance, someone holding another person's arm tightly is unlikely to cause a bruise.
Common Causes of Bruises:
Blunt Force: The most common cause of bruises is blunt force trauma. This can occur from falls, accidents, or impacts, such as bumping into furniture or being struck by an object.
Pinching or Squeezing: Intense pinching or squeezing, especially on delicate skin areas, can lead to bruises. For example, if a character pinches their arm or thigh too hard in frustration, a bruise may develop.
Repetitive Motion: Overusing or repeatedly striking a particular area, like through strenuous exercise or certain work activities, can cause tiny blood vessels to rupture and lead to bruising.
Medical Conditions: Some medical conditions, like blood disorders or certain medications, can make a person more prone to bruising.
Ageing: As skin becomes thinner and more fragile with age, it's more susceptible to bruising even from minor bumps or impacts.
It's crucial to consider the appropriateness of a bruise in your story. Understanding when and how a character can realistically develop a bruise will help maintain the credibility of your narrative.
Characteristics of Bruises:
Accurately depicting bruises in your writing involves considering various characteristics, such as:
Colour Changes: Bruises typically undergo a series of colour changes during the healing process. They usually start with shades of red, purple, or blue due to the initial bleeding under the skin. As the bruise heals, it can turn green, yellow, or brown before fading entirely. These colour shifts can be an essential detail when describing the progression of a character's injuries.
Size and Shape: The size and shape of a bruise depend on the impact's force and the underlying blood vessels' distribution. Bruises can be small, like a fingertip mark, or large, covering a significant portion of the body. Irregularly shaped bruises may indicate multiple impacts or trauma.
Tenderness and Swelling: A fresh bruise is often tender to the touch, and the area around it may be swollen. Describing your characters' reactions to this tenderness and swelling can make the injuries feel more lifelike.
Pain and Discomfort: Bruises can be painful, and the level of pain may vary depending on their size and location. Detailing your character's pain and discomfort can enhance the realism of your narrative.
Itching and Healing: As a bruise heals, it may become itchy. This can be an interesting detail to add, showing the progress of the injury and your character's recovery.
Duration: Mention the duration of a bruise. Some may heal relatively quickly, while others can linger for weeks. Knowing how long a character's bruise lasts can impact their daily life and the story's timeline.
Factors Affecting Bruise Appearance and Healing:
Bruises aren't one-size-fits-all injuries. Their appearance and healing process can vary based on several factors:
Location: Bruises can look different depending on where they occur on the body. For instance, a bruise on a bony area, like the shin, might appear more pronounced compared to a bruise on a fleshier part, like the thigh.
Age and Health: The age and overall health of your character play a significant role. Younger, healthier characters may heal faster and have bruises that change colour and fade more quickly. Conversely, older characters or those with health issues might have bruises that take longer to heal.
The severity of the Injury: The force and severity of the impact determine the size, shape, and colours of the bruise. Consider whether the injury was caused by a minor bump, a hard fall, or a violent struggle.
Character's Skin Tone: The appearance of a bruise can be affected by the character's skin tone. It might be more challenging to spot a bruise on darker skin, and the colours may appear differently.
Treatment and First Aid: The way a character treats a bruise can affect its healing. Mention how characters apply ice, warmth, or topical remedies to their bruises.
Character's Pain Tolerance: Some characters may have a higher pain tolerance and can bear a bruise without much discomfort, while others might find even a small bruise painful.
Clothing and Cover-Up: Characters may conceal bruises with clothing or makeup. This can impact how they are perceived by others.
By understanding these factors, you can tailor your descriptions to create a more authentic portrayal of bruises in your writing.
Healing Process of Bruises:
A key element in writing realistic bruises is depicting their healing process. Here's how to effectively describe it:
Gradual Changes: Highlight the evolving nature of the bruise over time. The progression of colours—red to blue, green, and yellow—is a visual cue that indicates the bruise's age. This chronological shift in colour offers readers insights into the passage of time within your narrative.
Concealment and Exposure: Address the issue of concealing or revealing the bruise. Depending on its location, characters may need to don concealing clothing, apply makeup, or use other means to hide or reveal their injuries. Such choices can significantly impact the character's interactions and relationships.
Medical Care: Mention whether the character seeks medical attention for their bruise. Medical professionals can provide insights into the severity of the injury and the potential complications that might arise during the healing process. Additionally, you can explore any treatments, remedies, or advice offered by healthcare providers.
Impact on the Character: Describe how the presence of a bruise affects the character's daily life, activities, and interactions with others. A prominent facial bruise, for instance, can influence the character's self-esteem, social interactions, or how they are perceived by those around them. Emotions and psychological effects should not be overlooked.
Varied Healing Timelines: Recognize that the healing process can vary from one character to another. Factors such as age, overall health, and the severity of the injury can affect how quickly the bruise fades. This variation can add depth and authenticity to your character's experiences.
Scarring and Discoloration: Note that severe injuries may leave lasting scars or discolouration on the skin. Explore any permanent marks or changes that remain after the bruise has healed.
By incorporating these aspects into your narrative, you can create a nuanced portrayal of the healing process of bruises and its impact on your characters.
I hope this blog on Everything You Need To Know About Writing Bruises will help you in your writing journey. Be sure to comment any tips of your own to help your fellow authors prosper, and follow my blog for new blog updates every Monday and Thursday.
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Are you an author looking for writing tips and tricks to better your manuscript? Or do you want to learn about how to get a literary agent, get published and properly market your book? Consider checking out the rest of Haya’s book blog where I post writing and publishing tips for authors every Monday and Thursday! And don’t forget to head over to my TikTok and Instagram profiles @hayatheauthor to learn more about my WIP and writing journey!
HOW TO WRITE A FINAL DRAFT
(From Someone Who’s Been Working on the Same Book for Over Ten Years)

Listen, I know what you might be thinking: “why the hell would I want advice on how to work on my final draft from someone who can’t even get her shit together for her own book?”
However, because I’ve had to re-draft my own novel so many times (Primarily due to poor outlining, lack of time and inspiration, and my own insecurities as a writer), I’ve learned a lot over the years on when to know if your book is done (or not!) and how to keep motivated.
Just a disclaimer that these are my own tips and tricks that you may not agree with, and that everyone’s writing process is different! Don’t feel pressured to do things my way if you feel like it doesn’t work for you as a writer; everyone’s experience varies, and there are always exceptions!
1. Know If You’re Ready to Start a Final Draft
Some vocabulary for writers to know:
Content editing is a form of editing that revises the overall style, substance, and content of a story. Copyediting is a form of editing that revises grammatical, spelling, readability, continuity, and factual errors within a story.
A way I would know if I’m ready to make a final draft is if I am no longer doing major content editing on the book. This means I am no longer making major changes to the plot, characters, setting, and other facets of the book. There isn’t any re-writing of entire scenes, or major plot holes that require an overhauling of the entire book.
You know you’re ready for a Final Draft if your primary concerns are copyediting.
Of course, with copyediting errors such as continuity, there will inevitably be some re-writing required, but I personally would not want to start a “final draft” at a stage where the book’s major plot points must be constantly changed during the editing process.
This varies so much, from writer to writer; so my best advice is to start your final draft when you think you’re ready!
2. Consider Getting Some Beta Readers
Again, this is an incredibly complex process; some people like to have beta readers on their earlier drafts, while others like to have beta readers for their later drafts.
A beta reader is someone who reads a work of fiction before it is published in order to mark errors and suggest improvements, typically without receiving payment (although it’s nice to swap stories and beta read for each other!) You can find people willing to be beta readers all over, especially on tumblr!
Having a round of beta readers is a great opportunity to have unbiased eyes on your work, and to have people pointing out plot holes and inconsistencies that maybe you hadn’t noticed! It also gives you a much-needed break from writing your story, and helps you come back to it with fresh eyes once everyone is done.
I personally am waiting to finish my current rewrite before having a round of beta readers, and after they look it over, doing a draft of my own editing before moving on to a final draft.
(Things don’t work out the way you think they will, though—that’s life! Take as long or as little time as you need!)
3. Consider Taking a Break
In my opinion, the best way to start editing a final draft is doing so with fresh eyes. After finishing your second-to-last draft, shelf your project for a few weeks (or maybe a few months!) and move on to another work. Then, you can come back to your story as if you were a new reader, and catch mistakes that you may have missed if you were still in the groove of writing!
This can sometimes be dangerous for writers who struggle with inspiration and getting back into things, though, so do whatever works best for you!
4. Tips to Keep Inspired
How to Overcome Writer’s Block
How to Write Consistently
Writer’s block and lack of inspiration will be your greatest enemies on your final draft! Oftentimes, people lose steam once they see the finish line is ahead. Check out the tips in the above post to help keep you on task!
5. Learn How to Stop Editing: It Will NEVER be Perfect
You are your own worst critic. You will always find something to tweak every single time you comb through your own writing; hell, even published authors sometimes read their own books and think of ways they could’ve improved certain sentences or scenes! Understand that “Final Draft” does not mean “Devoid of Flaws.”
Sometimes, the best thing you can do for your book is to know when you need to stop overworking it and send it out to the world. Writers who struggle with liking their writing can find this especially difficult, which is why it can be helpful to have beta readers or a writing buddy who can put their foot down and say: it’s done! You’re ready!
Hope this helped, and happy writing! I believe in you!
Symbolism Associated With Flowers For Writers
Acacia: Since ancient times, acacia has been associated with purity and innocence. It is also a symbol of resurrection and new beginnings.
Amaryllis: Amaryllis is a symbol of passion and desire. It is also associated with strength and courage.
Anemone: Anemone is a symbol of grief and sorrow. It is also associated with hope and new beginnings.
Azalea: Azalea is a symbol of love, passion, and desire. It is also associated with beauty and elegance.
Carnation: Carnation is a symbol of love, affection, and appreciation. It is also associated with motherhood and childbirth.
Chrysanthemum: Chrysanthemum is a symbol of longevity, happiness, and good luck. It is also associated with death and mourning.
Daisy: Daisy is a symbol of innocence, purity, and simplicity. It is also associated with childhood and new beginnings.
Delphinium: Delphinium is a symbol of wisdom, knowledge, and understanding. It is also associated with royalty and nobility
Frangipani: Frangipani is a symbol of love, passion, and desire. It is also associated with beauty and elegance.
Gardenia: Gardenia is a symbol of purity, innocence, and grace. It is also associated with love and admiration.
Gerbera Daisy: Gerbera daisy is a symbol of new beginnings, happiness, and joy. It is also associated with optimism and hope.
Hyacinth: Hyacinth is a symbol of love, passion, and desire. It is also associated with grief and sorrow.
Iris: Iris is a symbol of faith, hope, and wisdom. It is also associated with royalty and nobility.
Lily: Lily is a symbol of purity, innocence, and chastity. It is also associated with resurrection and new beginnings.
Lily of the Valley: Lily of the valley is a symbol of purity, innocence, and sweetness. It is also associated with new beginnings and springtime.
Magnolia: Magnolia is a symbol of love, beauty, and elegance. It is also associated with femininity and motherhood.
Orchid: Orchid is a symbol of love, passion, and desire. It is also associated with beauty, rarity, and luxury.
Rose: Rose is the most popular flower in the world and has a wide range of symbolism. It can symbolize love, passion, desire, beauty, romance, friendship, gratitude, and respect.
Tulip: Tulip is a symbol of love, passion, and desire. It is also associated with springtime and new beginnings.
Why Symbolism With Flowers Is Important For Writers
Flowers can be used to foreshadow events or themes in a story. For example, a writer might use a white rose to foreshadow a character's death, or a red rose to foreshadow a romantic encounter.
Flowers can be used to represent characters' emotions or motivations. For example, a character who is feeling sad might be described as holding a wilted flower, or a character who is feeling passionate might be described as surrounded by roses.
Flowers can be used to create symbolism that is specific to a particular culture or region. For example, in some cultures, the lotus flower is a symbol of purity and enlightenment, while in other cultures, it is a symbol of death and rebirth.
What is an Unreliable Narrator? And How to Write One.
An unreliable narrator is a storytelling technique where the narrator's credibility or truthfulness is questionable. The narrator either intentionally or unintentionally provides a distorted or biased account of the events, characters, or situations in the story. This narrative approach can add complexity, suspense, and intrigue to your writing. Here's how you can create an unreliable narrator:
1. Establish a motive: Determine why the narrator is unreliable. It could be due to personal bias, mental instability, deception, or a hidden agenda. Develop their backstory, motivations, and beliefs to understand why they might present a skewed version of events.
2. Use subjective language: Incorporate language and descriptions that reflect the narrator's personal viewpoint and biases. Their opinions, emotions, and interpretations should color their narration, influencing how readers perceive the story.
3. Include contradictions and inconsistencies: Allow the narrator to make contradictory statements or present conflicting information. This creates doubt and keeps the readers engaged as they try to unravel the truth.
4. Reveal information selectively: The unreliable narrator might withhold or reveal information strategically, manipulating the readers' understanding of the story. This can create suspense and surprise as readers discover hidden truths.
5. Showcase unreliable perceptions: Explore how the narrator's perceptions and interpretations of events differ from reality. They may misinterpret actions, misremember details, or even hallucinate. These discrepancies add depth to the character and raise doubts about their reliability.
6. Use other characters as contrasting sources: Introduce other characters who present alternative perspectives or contradict the narrator's version of events. This contrast allows readers to question the reliability of the narrator and form their own interpretations.
7. Employ narrative techniques: Experiment with techniques like foreshadowing, symbolism, or unreliable memory to emphasize the narrator's unreliability. These devices can help blur the line between truth and fiction, leaving readers intrigued and uncertain.
8. Provide hints and clues: Drop subtle hints or clues throughout the story that suggest the narrator's unreliability. This allows readers to piece together the truth gradually and encourages them to engage actively with the narrative.
How do you set a scene without overusing visual descriptions?
Practical Tips to Show, Don’t Tell
Show, don’t tell is probably the most common writing advice any author will ever receive. Instead of explicitly telling readers what is happening or how characters are feeling, showing allows them to experience the story firsthand. It’s good advice, and important for writers to take to heart, but sometimes it can be difficult to get the balance right. Here are some practical tips to show, don’t tell:
Set the scene
To really immerse your readers in your story, you want them to feel as if they’re in it – experiencing the world you’ve built. By writing about how characters perceive and interact with their surroundings, you’ll draw your readers in.
Examples:
Telling: It was winter, and the water was cold.
Showing: I hunched my shoulders up, burrowing deeper into my coat as my heavy boots crunched through the thin ice forming at the water’s edge.
Keep up the pace
Excess scene description will almost always bring your narrative pacing to a screeching halt. Instead of describing the scene every time, describe your characters’ actions within it.
Examples:
Telling: The lake was frozen and the trees were covered in snow.
Showing: My heart pounded as I almost lost my balance on the ice beneath my feet. I ducked and weaved my way home, dodging the snow that the howling wind shook loose from the treetops above me.
Keep your language descriptive, but simple
When it comes to show, don’t tell, it can be easy to fall into the trap of over-describing. Language that is too flowery or over the top can be just as bad as telling. You want to set a scene, not explain it to death.
Examples:
Too much: The azure-blue lake glinted like diamonds under a glittering sun that shone like a lightbulb in the darkness.
Just right: The sun reflected off the ice brightly, highlighting the deep blue of the water beneath it.
Create a sense of character
The way a character speaks and acts can be the perfect way to show your readers who they are and set a scene without over-describing it. For example, you can use body language, like gestures and posture to reveal a character’s emotions or attitude in a way you can’t reveal by simply describing the scene. Sometimes an intricate description of the location is not as important as how the character feels in the moment
Examples:
Telling: The room was the same as he remembered as a child, with its red carpets, brown-papered walls, high ceilings, and huge wooden table propped in front of large bay windows. It made him anxious.
Showing: He shuffled anxiously to the table overlooking the garden, his mind heavy with the weight of childhood memories.
Hi! Thank you so much for all the time and help you provide, can't think of a better writing blog to go to. So my question is, what do you think are the most important elements to take into consideration when creating a timeline? How do you make a timeline I guess I'm asking lol :)
Making a Timeline for Your Story
I’m not sure if you’re asking about figuring out the timeline of your story’s events or creating an actual timeline as part of the planning process, so I’ll address both. :)
Figuring Out Your Story’s Timeline of Events
1. First and foremost, figure out a general span of time for your story in terms of the year/s it takes place and the months. If you’re not sure what month your story should begin, consider what needs to be happening then. For example, if there’s going to be snow falling in the first scene, you know your story begins during a winter month.
2. Create a calendar for your story covering the months/years in question. You may just want to download a blank calendar template and print out several that you can fill in by hand.
3. Once you have your calendar printed out, fill in the days of the first month. Then you can choose an appropriate “day one” for your story and jot down what scene or event happens on what day. Remember there will be blank days and that’s fine. Those will be “time skipped.” Doing it on a calendar like this allows you to get a bird’s eye view of the story so you can figure out a likely timeline of events.
Creating a Reference Timeline for Your Story
If you want to do a physical timeline for reference, all that’s really important to include are the date and the actual event.
If you want to, however, you may consider doing a scene list instead. A scene list will include: chapter, scene (I do two scene numbers, the scene within the chapter and then the total scene), the date, and what happens in the scene. So, ultimately, it would look something like this:

This not only helps you keep track of when your scene takes place, but it helps you map out your story so you’re never lost. You can also add other data to the table if you want to, like setting and characters present. You can modify it in any way that works for your story. :)
I hope that helps!
————————————————————————————————-Have a question? My inbox is always open, but make sure to check through my FAQ and post master lists first to see if I’ve already answered a similar question. :)
i've been writing a book and the feedback i've gotten from family members is that i have been using a lot of description, that the plot is moving along pretty slowly, and "something" needs to happen. do you have any tips or advice on moving plots along quicker in order to keep the reader's attention? thanks so much!!
How to Move a Story Forward
When your character is just milling about in their world describing what they see, what they’re doing, and what’s happening to them, that’s not really a plot. It’s just a random string of events happening to your character, and typically it doesn’t make for very interesting reading. This kind of story moves slowly because nothing’s actually happening. Imagine following an average person through their average day versus following Katniss Everdeen through day three of The Hunger Games. It’s a big difference. And that’s not to say every plot has to be as exciting or dramatic as The Hunger Games, but there does need to be a conflict.
So, the first thing you have to do is sit down and figure out what your story is really about. What is going on in this person’s life that is worth writing about? Is there some sort of inner conflict they’re struggling with? Or is there an external conflict of some kind? Usually there are both with the focus being more on one than the other.
How stories begin…
Most stories start when a character’s life is still normal but just about to change. Katniss was getting ready to go hunting with Gale. Bella was settling in at her new high school after moving in with her dad, and Harry Potter was just living life as the boy in the cupboard.
What happens next…
And then something happens. This is called the “inciting incident” because it “incites” the conflict and brings on the important events of the story. Katniss volunteers as tribute when her sister is drafted into The Hunger Games. Bella meets Edward Cullen and an instant attraction develops between them. Harry Potter receives his letter to Hogwarts.
The character responds and forms a goal…
The character’s normal life has been turned upside down. Now what? For Katniss, the most important thing in the world to her was the safety and well being of her sister and mother, and since she is the one who keeps them safe and fed, her survival of The Hunger Games is vital. That’s her motivation, and her goal is to win the game. Bella becomes obsessed with learning more about Edward and who, or what, he is, and she falls for him and the magic his world brings into her otherwise boring life. Being part of that world is her motivation, staying alive in the process is her goal. Harry finally has a ticket out of his life of being abused and unloved, and he has a chance to connect with the legacy his parents left behind. Leaving his old life behind and embracing this new one is is motivation. Surviving his first year at Hogwarts is his goal.
But goals aren’t supposed to be easy to reach…
If the character can just sail smoothly right up to their goal, mission accomplished, that makes for a pretty boring story. You never hear people say, “WOW! THAT WAS AN INCREDIBLE GAME!” when the score was 20 to nothing. What makes the game exciting is when the teams are neck and neck, one getting ahead for a little while, then the other one being ahead for a little while. It’s the trying, and often failing, to get over obstacles that makes the conflict more interesting. In a lot of ways, that struggle actually is the conflict. What obstacles stand in the way of your character and their goal, and who (or what) put them there? For Katinss, the obstacles were the other tributes and all the frightening things added to the game by the gamemakers. For Bella, it was the nomad vampires who caused trouble at first for fun, and then later for revenge. The obstacles Harry faces are partly due to conflict with other students and teachers, and partly due to the first “shots fired” in what would become the overarching battle against Voldemort.
You win some, you lose some…
And it’s important that you show some wins along with the failures. Sometimes the character tries to overcome an obstacle, fails, tries again and succeeds. Sometimes they fail and have to come up with a work around. Either way, the fails add to the tension and drama while the wins add excitement and interest in what happens next.
The final showdown…
Eventually you get to the big showdown, aka “the climax.” This is when your character faces down the biggest challenge that stands in the way of reaching their goal. This could be an epic battle between your character and the villain. It could be the moment where your character realizes they’re in love with their best friend and they chase them to the airport to admit their undying love for them before they move away. Or it could be surviving one last night of a terrible storm before crawling out of hiding to assess the damage. Whatever it is, the culmination of that moment is achieving or failing to achieve their goal.
The dust settles…
Whatever crazy chain of events was set off by the inciting incident, they’ve come to an end now thanks to the actions of your protagonist and their friends. Or, if they haven’t come to an end, they’ve at least been waylaid for now, or things are at least moving in a better direction. Now your characters can clean up, rebuild, mend wounds, tie up loose threads, and get back to life as normal. Or, in the case of a series, they can re-group and figure out what happens next. And that’s the end.
… But some stories happen on the inside.
Some stories are more about people and their experiences than about any big crazy thing that happens to them. Stories like these are more emotional and are more about dealing with the inner conflict than an outer one. But even in stories like these, you’ll still have a similar structure to what I laid out above. It’s just a lot looser and tied up with an emotional journey rather than the physical one. Which isn’t to say they can’t have a parallel physical journey, but the important stuff is happening on the inside.
Whichever kind of story you’re writing, if you make sure you’re hitting the important points I’ve laid out above, whether they relate to an internal conflict, an external conflict, or a little of both, you can be sure you’re writing a story that is moving forward and will keep your audience engaged. Everything I’ve outlined above is the “something” that needs to happen to make your story interesting.
Good luck! :)
How to write dynamic scenes
Here’s how you can inject some dynamics into your scenes where characters may be idling during their conversations! This is my favourite trick to use when I want to round out a scene.
Sometimes you may have a static scene in your book with characters simply sitting and chatting. So how do you make this more interesting?
The answer is to add in some dynamics!
🤔 What does that mean?
Creating dynamics in a scene means that you add some form of repetitive or changing background element throughout the scene to keep it moving, despite it being in the same spot.
For example, if you have a scene set in a restaurant with two characters having dinner, pick out an element from the setting that could create some kind of dynamic, pressure or conflict to your scene.
✍️ In a restaurant this may be:
An annoying cast of waiters circling around and offering refills
A scorching radiator by the side of the table raising temperature and shortening patience levels
A loud party of people in the background who make it difficult for your characters to understand each other
A partner’s phone buzzing on the table every other minute
A character’s personal tendencies - like fidgeting with the table cloth and eventually unthreading it, or coming close to dropping things until they shatter a glass at a high point of the scene
Think of background elements, or ways to externalise the way your characters are feeling in a particular scene can add so much life to a scene!
It also makes it feel more interesting, dynamic, and immersive, even a scene you’re writing is a simple conversation.
Whenever you find your characters having a conversation while they’re simply walking or sitting, think of whether you can externalise any of their emotions or inject some background element to make the scene more interesting!
Did you hear my first book is coming out August 15th? Pre-order it now through the [link here] or below!
Hi there! I was wondering if you have any advice/opinions on the importance of originality vs. the finer mechanics of a story (plot, character motivations, etc). I've always been insecure about having unoriginal ideas, but the few times I've had an idea that feels genuinely unique, every other important element of the work feels lacking. The characters are passive and unmotivated, the plot is full of holes, etc. Currently, I have an idea which I'm not confident in the originality of, but the character has clear motivations and the plot, while tropey and not the most original, has a clear direction and no immediately obvious holes. So I'm a bit torn up over whether it is better to bend over backwards to try to make the unique ideas work or to go with the one that is less original, but comes easily to me and ticks all the other important boxes. Ultimately, I'm writing it for me, but if I ever did decide to publish, I worry the premise alone wouldn't catch the attention of potential publishers or readers. Any input you might have would be much appreciated!
Here's what I'm going to recommend: Throw out ideas of originality and marketability for now. They're both holding you back from making the real decision you need to make. Sit down and ask yourself some questions:
Which story concept has more appeal (to you)? Does thinking about working on it make you feel excited, or fill you with dread? Wanting to work on the story is the most important factor here. Trying to force something because you think you must do it won't work.
Which story concept is easier for you to write? You already have the answer to that, but I want you to think about why. What about your more conventional story makes it easier to make characters for and plot? Is it because that's where you feel more comfortable at? Is it because that's the kind of story you most like to read?
Which story concept do you see yourself finishing (and editing)? Carrying the story through to the end is the biggest factor here. If writing the story is a slog from beginning to end, you're probably not going to end up with a finished book that you like.
Now obviously, I am leaning toward one way - the story that comes more easily for you. I'm doing that for a couple of reasons, but mainly a finished story with interesting characters and a cohesive plot is going to be a much easier sell than a unique story with no appealing characters and a plot that's confusing. Most readers are sold on good character arcs and fun plots, not the uniqueness of the premise. If uniqueness is all you have, there's little appeal to the reader.
This does not mean you should toss out those unique and appealing story ideas! You want to write them, and they will not go away, but you're not going to suddenly wake up and become the next China Mieville or Jeff VanderMeer overnight. Getting those unique story ideas to work means giving them time to become something you can write while in the meantime still writing and working on stories that you know you can write.
Put those little plot mushrooms in a dark place and let them grow while you continue to develop the skills you need to bring them to life. Review them from time to time, but if they aren't ready and other stories are, don't force them. One day you will find the key you need to pull them together in a way in a story you're ready and excited to write, but in the meantime, give yourself permission to become.
Uniqueness doesn't sell books; good stories do.
How should I go about describing a character who goes through a lot, becoming more disheveled and desperate as the plot goes on?
Desperation is the emotion that drives characters to their limits, leading to their most intense and extreme behaviours.
By showing how characters become more desperate as your plot progresses, you can create characters that are interesting, dynamic, and relatable.
Here are some ways you can show desperation in your characters. As the plot moves forward, these elements can get worse, showing their decline.
How do they behave?
Obsessive and/or compulsive
Repetitive actions like hand wringing, or overuse of stock phrases
Self-destructive and risk-seeking
Enhanced aggression
Avoidant and isolationist
Manipulative
Exploitative
Short-tempered
Impulsive decision-making
Unrelenting pursuit of something
What physical signs do they show?
Heart palpitations and short, rapid breathing
Sweating profusely
Shaking or trembling
Sudden onset of nausea
Feeling weak or dizzy
Muscle tension
Headaches
Insomnia caused by worry and stress
Feelings of fatigue
Stomach pain and cramping
How do they interact?
Begging or pleading with others
Manipulating others to get what they want
Increasing paranoia and questioning other's motives
Pushing away loved ones
Becoming overly clingy
Either an inability to trust or being too quick to trust others
Self-sabotage
Single-focus conversations
What do they look like?
Unkempt hair and poor hygiene
Rumpled, slept-in clothing
Nervous tics, like fidgeting, pacing, or picking at nails
Extreme and unexplained weight loss
A haunted, faraway, or panicked look
Dark-rimmed, bruised eyes from lack of sleep or exhaustion
A constant sheen of sweat and clammy skin
Unusual clothing choices
What body language do they display?
Hunching over, as if trying to protect themselves
Fidgeting or pacing
Avoiding eye contact
Clenching fists or grinding teeth
Sweating or shaking
Staring intently at something
Repeatedly touching hair or face
Darting eyes and biting lips
Meek and under-confident stance
Pleading look
What is their attitude?
Feeling hopelessness
Sad and dejected
Becoming increasingly irrational
A loss of faith in themselves and others
Obsession to the point of resorting to extreme measures
A sense of helplessness
Blaming others
Feeling powerless
A sense of urgency
What are some positive things that can come out of desperation?
Increased motivation to achieve their goals or solve their problems
Resilience and adaptability in the face of adversity
Heightened creativity and resourcefulness
The ability to form deep and meaningful connections with those who share their struggles
Catharsis or character growth through their struggles
What are some negative things that can come out of desperation?
A tendency to become self-destructive or engage in risky behaviour
Difficulty forming and maintaining healthy relationships
Increased isolation or loneliness
Chronic stress and physical health problems
A tendency to make impulsive or irrational decisions
Prone to depression and anxiety
Can you talk more about height and combat? Like for example a taller woman fighting a shorter man? I usually see the opposite (and the woman having all of the disadvantages) but how would it look the other way around? Assuming neither is skinny.
In most circumstances, height is less important than a lower center of gravity. Height can be useful in some situations, such as being able to see over obstructing obstacles. Reach is very useful, though overall height results in a negligible increase to reach.
So, generally speaking, any object with a lower center of gravity will be more stable than one with a higher center of gravity. Obviously, when we're talking about inanimate objects, you can get some weird examples where this isn't the case, but when you're talking about your normal, roughly humanoid object, a lower center of gravity will be more stable than a higher one.
This leads into another general statement that won't be true in every possible case, but is important to be aware of, if someone says that women have, “all of the disadvantages,” in a match-up, they don't know what they're talking about. The low hanging fruit is that women are more resistant to exertion and exhaustion than men, and that will become important in a prolonged fight. As mentioned earlier, they have a lower center of gravity (in most cases), meaning that they'll be more stable than a male foe.
If you've ever watched Judo videos of a five-foot-nothing girl casually tossing a massive guy around, what you're seeing is a practical consequence of that lower center of gravity. This is just a practical application of basic physics. If your center of gravity is below your opponent's it is far easier to leverage them off the ground and deposit them in a tangled pile of limbs at the location of your choosing.
Beyond that, while getting into ground fighting can be very dangerous for the smaller fighter (regardless of their sex), being able to put your foe on the ground before getting dragged down yourself, does open the door to some options for ending the fight, if you have the stomach for it.
A taller woman versus a shorter man will narrow the difference between their respective centers of gravity, and may make it possible for the man to get his center of gravity lower than his foe, but it depends on the relative height difference, and you'd be looking at some pretty extreme differences before this starts to become a realistic possibility.
In the grand scheme of things, the total amount of mass is less important than where that mass is located. This is why ground fighting, that is to say, when both combatants have already fallen over, and are continuing to fight without getting back on their feet, can be very hazardous. At that point, both participants are about as stable as they'll ever be, and sheer volume of mass can be used effectively. When you're standing, not so much. Also, yes, there is a window in the transition to ground fighting where one combatant has gone down, and does have a stability advantage. Some martial arts (again, Judo comes to mind) specifically train to act in this window. You're not going to fall over again, so you may as well take the opportunity to maneuver and drag your foe down, with an eye for making their trip to the ground less pleasant than yours.
Something we've said, many, many, times is that reach is very important, and this is true. So, it would follow that a shorter person would have less reach, which is also true. On average, your arm-span should be roughly equivalent to your height. So, if you're 6ft, you should have a 6ft armspan. If you're 5ft8in, you should have a 5'8” arm span. (There's some slight variation based on gender here, which has more to do with the length of your individual arms. The average arm length for an adult male is ~14.5”, while the average arm length for an adult female is ~13.5”, even though the average height difference is ~5”.) However, in most combat situations, when we're talking about the importance of reach, we're talking about a difference measured in multiple feet. Someone armed with a 4” dagger is going to have a difficult time countering someone armed with a 60” greatsword, for example. However, when you're talking about a difference in a few inches, that's not nearly as decisive. Unless your shorter character is dramatically shorter, they shouldn't have any difficulty reaching their opponent, so while reach is an exceptionally important consideration in armed combat, gender isn't likely to be an important factor when calculating overall reach.
The big thing to understand about height, and this is very true when looking at authors interpreting its importance in writing, is the factor of intimidation. A taller person will generally feel more intimidating up front, and a lot of visual narratives use this as a cue to show that a character is at a disadvantage. Adventure fiction, like Indiana Jones for example, uses this to great effect and so do most martial arts action movies. When someone is talking about the importance of size, that's usually what they're referencing. When you see a massive person walking on screen or popping up in your favorite anime, your brain mentally checks itself and goes, “oh. Oh no.” This, of course, has nothing to do with reality, it's just our brains interpreting danger.
We say this a lot on the blog, but really, you learn to fight with the body you have. Men and women fight the way they're trained to fight, so they don't have intrinsically gendered fighting styles after release into the real world. The concept of gendered fighting styles really comes from anime and other fighting games or as a reaction against socially constructed systems such as 'fight like a girl!'
If you ask Michi, who grew up doing martial arts, what it looks like when a tall woman fights a short guy, her reaction is to shrug and say, “it looks like two people fighting.” There just isn't a discernible difference outside of personal, stylistic preferences.
-Starke
This blog is supported through Patreon. Patrons get access to new posts three days early, and direct access to us through Discord. If you’re already a Patron, thank you. If you’d like to support us, please consider becoming a Patron.
Are you Exploring your Concepts to their Fullest?
There’s nothing worse than getting hooked into a piece of media by a really cool concept—only to be let down through shallow exploration. The entire story I’m distracted from what’s happening by what could have been had they gone more in depth into what they promised.
The good news is, avoiding this in your own writing is fairly easy as long as you remember to continuously do one thing: ask questions.
I talk about this a lot, but making room to explore the implications (especially of worldbuilding and events, not just actions) is only going to deepen your narrative and create a more satisfying, well-rounded world. As well, the decisions you make here are going to set the use of your concept apart from the other stories we’ve seen it in.
If your concept is a character who has lived on a boat their entire life finally hits the shore, think about what it would mean for someone to have never seen land—how would they feel about trees, valleys, mountains, buildings. They would probably be very familiar with stars and constellations, navigation, the dark, swimming, fishing, and danger surrounding the water. They may prefer cramped spaces, sleeping under a low roof, a gentle rocking or white noise.
If there’s magic in the world but say only some people have it, how does that impact politics, healthcare, parenting? Do people have biases against magic users or non-magic users? Are there laws set to prevent or limit magic use in certain places, or at all?
You could ask endless amounts of questions about a concept, and you should. If you introduce something big, exciting, and full of consequences—you must also be willing to commit to it, and explore it to its fullest.
Good luck! If you feel like sharing, tag a concept you’ve come up with and some interesting implications that go with it!
Hello! Do you have any advice/resources on how to write sounds? Speaking and singing in particular but also maybe sounds at different volumes and sounds that could be considered "noise."
Describing Sounds Using Sound Words
Description of sound is all about knowing sound-related vocabulary. Here's a mini-list to get you started, but you can do some research to learn more. Also, be sure to look up these words before using them to make sure they're right for the context.
High Volume - blaring, blasting, booming, bray, din, deafening, ear-piercing, ear-popping, earsplitting, full volume, loud, pealing, roaring, sonorous, thundering, thunderous
Low Volume - buzz, faint, gentle, hushed, low, muffled, murmur, muted, peaceful, quiet, soft, subdued, whisper
Noise - cacophony, clamor, clatter, commotion, discord, disquiet, fracas, hullabaloo, racket, ruckus, uproar Pitch and Tone - atonal, discordant, dulcet, harmonic, harsh, high-frequency, low-frequency, mellow, resonant, sonic, soprano, tenor, timbre
Rhythm - beat, cadence, flow, lilt, lyrical, measured, melodic, metered, monotone, pulsing, staccato, stutter, tempo
Sounds - babble, bang, bark, beep, belch, boom, burble, burp, chirr, chirp, clack, clatter, clang, clank, click, clink, clip-clop, clomp, crackle, crash, creak, ding, echo, groan, gurgle, hiss, hoot, hum, jangle, jingle, kerplunk, howl, melodic, mewl, moan, murmur, patter, pitter-patter, peal, plop, pop, purr, rattle, roar, rumble, rustle, screech, shriek, sizzle, splash, splat, swoosh, squawk, squeak, strum, thud, thrum, thump, wail, whimper, whinny, whine, whir, whistle, whiz, yelp, yowl, zing How to Research Sounds - If you're struggling to describe the sound of a particular thing, like "thunder," go to Google and type in, "how to describe the sound of thunder" and look for inspiration. You can also search for things like "horse sounds" or "what sounds do cars make?"
Also, two previous posts specific to describing the sound of singing and music:
Describing Music How to Describe a Singing Voice
I hope that helps!
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
I’ve been writing seriously for over 30 years and love to share what I’ve learned. Have a writing question? My inbox is always open!
Learn more about WQA
Visit my Master List of Top Posts
Go to ko-fi.com/wqa to buy me coffee or see my commissions
DESCRIBING THE PHYSICAL ATTRIBUTES OF CHARACTERS:
Body
descriptors; ample, athletic, barrel-chested, beefy, blocky, bony, brawny, buff, burly, chubby, chiseled, coltish, curvy, fat, fit, herculean, hulking, lanky, lean, long, long-legged, lush, medium build, muscular, narrow, overweight, plump, pot-bellied, pudgy, round, skeletal, skinny, slender, slim, stocky, strong, stout, strong, taut, toned, wide.
Eyebrows
descriptors; bushy, dark, faint, furry, long, plucked, raised, seductive, shaved, short, sleek, sparse, thin, unruly.
shape; arched, diagonal, peaked, round, s-shaped, straight.
Ears
shape; attached lobe, broad lobe, narrow, pointed, round, square, sticking-out.
Eyes
colour; albino, blue (azure, baby blue, caribbean blue, cobalt, ice blue, light blue, midnight, ocean blue, sky blue, steel blue, storm blue,) brown (amber, dark brown, chestnut, chocolate, ebony, gold, hazel, honey, light brown, mocha, pale gold, sable, sepia, teakwood, topaz, whiskey,) gray (concrete gray, marble, misty gray, raincloud, satin gray, smoky, sterling, sugar gray), green (aquamarine, emerald, evergreen, forest green, jade green, leaf green, olive, moss green, sea green, teal, vale).
descriptors; bedroom, bright, cat-like, dull, glittering, red-rimmed, sharp, small, squinty, sunken, sparkling, teary.
positioning/shape; almond, close-set, cross, deep-set, downturned, heavy-lidded, hooded, monolid, round, slanted, upturned, wide-set.
Face
descriptors; angular, cat-like, hallow, sculpted, sharp, wolfish.
shape; chubby, diamond, heart-shaped, long, narrow, oblong, oval, rectangle, round, square, thin, triangle.
Facial Hair
beard; chin curtain, classic, circle, ducktail, dutch, french fork, garibaldi, goatee, hipster, neckbeard, old dutch, spade, stubble, verdi, winter.
clean-shaven
moustache; anchor, brush, english, fu manchu, handlebar, hooked, horseshoe, imperial, lampshade, mistletoe, pencil, toothbrush, walrus.
sideburns; chin strap, mutton chops.
Hair
colour; blonde (ash blonde, golden blonde, beige, honey, platinum blonde, reddish blonde, strawberry-blonde, sunflower blonde,) brown (amber, butterscotch, caramel, champagne, cool brown, golden brown, chocolate, cinnamon, mahogany,) red (apricot, auburn, copper, ginger, titain-haired,), black (expresso, inky-black, jet black, raven, soft black) grey (charcoal gray, salt-and-pepper, silver, steel gray,), white (bleached, snow-white).
descriptors; bedhead, dull, dry, fine, full, layered, limp, messy, neat, oily, shaggy, shinny, slick, smooth, spiky, tangled, thick, thin, thinning, tousled, wispy, wild, windblown.
length; ankle length, bald, buzzed, collar length, ear length, floor length, hip length, mid-back length, neck length, shaved, shoulder length, waist length.
type; beach waves, bushy, curly, frizzy, natural, permed, puffy, ringlets, spiral, straight, thick, thin, wavy.
Hands; calloused, clammy, delicate, elegant, large, plump, rough, small, smooth, square, sturdy, strong.
Fingernails; acrylic, bitten, chipped, curved, claw-like, dirty, fake, grimy, long, manicured, painted, peeling, pointed, ragged, short, uneven.
Fingers; arthritic, cold, elegant, fat, greasy, knobby, slender, stubby.
Lips/Mouth
colour (lipstick); brown (caramel, coffee, nude, nutmeg,) pink (deep rose, fuchsia, magenta, pale peach, raspberry, rose, ) purple (black cherry, plum, violet, wine,) red (deep red, ruby.)
descriptors; chapped, cracked, dry, full, glossy, lush, narrow, pierced, scabby, small, soft, split, swollen, thin, uneven, wide, wrinkled.
shape; bottom-heavy, bow-turned, cupid’s bow, downturned, oval, pouty, rosebud, sharp, top-heavy.
Nose
descriptors; broad, broken, crooked, dainty, droopy, hooked, long, narrow, pointed, raised, round, short, strong, stubby, thin, turned-up, wide.
shape; button, flared, grecian, hawk, roman.
Skin
descriptors; blemished, bruised, chalky, clear, dewy, dimpled, dirty, dry, flaky, flawless, freckled, glowing, hairy, itchy, lined, oily, pimply, rashy, rough, sagging, satiny, scarred, scratched, smooth, splotchy, spotted, tattooed, uneven, wrinkly.
complexion; black, bronzed, brown, dark, fair, ivory, light, medium, olive, pale, peach, porcelain, rosy, tan, white.