Studyblr - Blog Posts
What is The Process Of Sleep?

Introduction
Sleep is a complex physiological process that encompasses more than merely closing one’s eyes and drifting into unconsciousness. It is an active state of unconsciousness in which the brain, while relatively at rest, remains responsive primarily to internal stimuli. Despite extensive research, the precise purpose of sleep remains incompletely understood. Several prominent theories attempt to elaborate the purpose of sleep, including the Inactivity Theory, Energy Conservation Theory, Restoration Theory, and Brain Plasticity Theory.
Inactivity Theory involves that inactivity during nighttime reduces the risk of predation, offering an evolutionary advantage. This theory suggests that creatures that remained inactive during the night were less likely to fall victim to predators, thereby enhancing survival and reproductive success.
Energy Conservation Theory proposes that the primary function of sleep is to decrease energy demand during periods when it is less efficient to procure food, supported by evidence of a 10% reduction in metabolism during sleep. This theory aligns with the observation that many species exhibit lower metabolic rates during sleep, thereby conserving energy.
Restorative Theory asserts that sleep facilitates the repair and replenishment of cellular components, as evidenced by processes such as muscle repair, tissue growth, protein synthesis, and hormone release occurring predominantly during sleep. This theory is supported by findings that various restorative functions are activated during sleep, promoting physical health and well-being.
Brain Plasticity Theory suggests that sleep is essential for neural reorganization and brain development, particularly in infants and children who require extensive sleep. This theory underscores the role of sleep in cognitive functions, learning, and memory consolidation.
These theories collectively indicate that sleep serves multiple functions, and a combination of these concepts likely explains the necessity of sleep.
Function

Sleep follows a cyclical pattern, alternating between two major phases: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is subdivided into stages 1 through 3, each representing different depths of sleep characterized by unique brain wave patterns, muscle tone, and eye movement patterns. NREM sleep comprises approximately 75–80% of total sleep time, while REM sleep accounts for the remaining 20–25%.
The sleep cycle begins with a short NREM stage 1 phase, progresses through NREM stages 2 and 3, and culminates in REM sleep. This cycle repeats throughout the night, with initial cycles lasting 70–100 minutes and subsequent cycles 90–120 minutes. As the night progresses, the duration of REM sleep increases, eventually comprising up to 30% of the sleep cycle later in the night. Typically, an individual undergoes 4 to 5 sleep cycles per night.
NREM Stage 1: A shallow sleep stage lasting 1–7 minutes, characterized by rhythmical alpha waves (8–13 Hz). This stage represents the transition from wakefulness to sleep, during which the individual can be easily awakened.
NREM Stage 2: A deeper sleep state lasting 10–25 minutes initially, progressing to encompass 50% of the total sleep cycle. EEG recordings during this stage show sleep spindles and K-complexes. Memory consolidation is believed to occur primarily in this stage.
NREM Stage 3: Lasting 20–40 minutes initially, characterized by high-voltage, slow-wave frequency on EEG. This stage, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), is crucial for restorative processes.
REM Sleep: Responsible for dreaming, characterized by muscle paralysis (except for the extraocular muscles) and sawtooth waveforms on EEG. REM sleep involves increased brain activity and is essential for cognitive functions such as learning, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation.
Mechanism

The regulation of sleep involves a delicate balance between homeostatic processes and circadian rhythms.
a) Homeostatic Processes
These processes reflect the body’s need for sleep, increasing the pressure to sleep the longer one stays awake. Sleep generation is initiated within the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO) of the anterior hypothalamus, which inhibits arousal regions in the brain, including the tuberomammillary nucleus, lateral hypothalamus, locus coeruleus, dorsal raphe, laterodorsally segmental nucleus. Hypocretin (orexin) neurons in the lateral hypothalamus facilitate this process synergistically.
b) Circadian Rhythm
The circadian rhythm, or the internal body clock, regulates the sleep-wake cycle and is influenced by light levels detected by the retina. The hypothalamus, particularly the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN),initiates this rhythm. Melatonin, produced by the pineal gland, modulates the circadian rhythm, with levels peaking at night and decreasing during the day. The circadian rhythm typically spans approximately 24.2 hours, and variations in body temperature also play a role, with lower temperatures in the morning and higher temperatures in the evening.
NREM sleep involves a functional disconnection between the brain stem, thalamus, and cortex, maintained by hyperpolarizing GABA neurons. During this phase, corticothalamic neurons signal the thalamus, causing hyperpolarization of thalamic reticular neurons, resulting in delta waves from both thalamic reticular and cortical pyramidal sources.
REM sleep is generated by “REM-on neurons” in the mesencephalic and pontine cholinergic neurons. The pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus and lateral dorsal tegmental neurons trigger desynchronized cortical waveforms. The tonic component of REM sleep is parasympathetically mediated, while the phasic component is sympathetically mediated.
Related Testing
Polysomnography is the primary modality used to study sleep. It is a comprehensive test that includes an electrocardiogram (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), electrooculography (EOG), electromyography (EMG), and oxygen saturation monitoring.
ECG: Measures the electrical activity of the heart to detect cardiac anomalies such as arrhythmias.
EEG: Non-invasively records brain wave activity to determine sleep stages and detect neurological abnormalities.
EOG: Measures eye movements to differentiate between NREM and REM sleep.
EMG: Assesses muscle activity, particularly in the respiratory muscles and peripheral limbs, to detect excessive movement or muscle tension during sleep.
Oxygen Saturation: Monitors respiratory function to ensure adequate oxygenation during sleep.
Clinical Significance

a) .Insomnia
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep and is the most common sleep disorder. It is often related to psychological stressors, poor sleep environments, irregular sleep schedules, or excessive mental, physical, or chemical stimulation. Treatment typically involves cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), sleep hygiene practices, and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions.
b) .Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
OSA is marked by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep due to airway obstruction, often caused by obesity or weak pharyngeal muscles. This condition leads to hypoxia and frequent awakenings, preventing restful sleep. OSA is classified into mild, moderate, and severe based on the frequency of apneic episodes per hour. Treatment options include Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) therapy, mandibular advancement devices, and surgical interventions such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, adenotonsillectomy, and maxillomandibular advancement.
c) .Central Sleep Apnea
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) results from a failure in the central respiratory drive, leading to diminished breathing effort during sleep. Conditions such as congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (Ondine’s curse) or congestive heart failure can cause CSA. Treatment includes CPAP, BiPAP, Adaptive-servo-ventilation, and medications like acetazolamide or theophylline.
d) .Mixed Sleep Apnea
Mixed Sleep Apnea, also known as Complex Sleep Apnea, involves symptoms of both OSA and CSA. This condition typically manifests when patients with OSA develop CSA symptoms upon treatment with CPAP. Treatment often involves low-pressure CPAP therapy.
d) .Ghrelin-Leptin Abnormalities
Sleep duration significantly influences hunger-regulating hormones, with reduced sleep linked to lower levels of leptin and higher levels of ghrelin. Leptin, produced by adipose cells, inhibits hunger, while ghrelin, produced in the gastrointestinal tract, stimulates appetite. Imbalances in these hormones due to inadequate sleep can increase appetite and contribute to higher body mass index (BMI), potentially leading to obesity. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in patients with OSA, where increased BMI is a risk factor.
e) .Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is characterized by a loss of orexin (hypocretin) neurons, leading to unstable transitions between sleep and wakefulness. Symptoms include excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, sleep paralysis, and hypnagogic hallucinations. Narcolepsy type 1 involves a significant loss of orexin neurons, while type 2 is less severe. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with medications such as stimulants, sodium oxybate, and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs and SNRIs), along with lifestyle modifications.
f) .Somnambulism (Sleepwalking)
Somnambulism, or sleepwalking, involves performing activities while in a state of combined sleep and wakefulness. Sleepwalking is associated with increased slow-wave sleep and sleep deprivation, and there is evidence of a genetic predisposition. Treatment includes ensuring a safe sleep environment, improving sleep hygiene, and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions such as benzodiazepines.
Conclusion
Sleep is a physiological process essential for various bodily functions, including energy conservation, cellular repair, brain development, and cognitive function. The precise mechanisms and purposes of sleep remain areas of active research. Understanding the complexities of sleep and its disorders is crucial for promoting overall health and addressing various medical conditions. Ongoing research aims to fully understand the mechanisms of sleep and its broad implications for human health..
Navigating the rigorous demands of medical studies requires support and collaboration. Whether you’re a nursing student, medical doctor, clinical student, pharmacist, or any other medical practitioner, don’t hesitate to seek assistance. Utilize available resources and value teamwork and mentorship.
For personalized support, expert advice, and comprehensive resources, contact Expert Academic Assignment Help at expertassignment46@gmail.com With the right support and dedication, you can achieve your goals and make significant contributions to healthcare.
Differentiating Gram Positive And Gram Negative Bacteria

The classification of bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative categories, predicated upon their distinctive cell wall structures, stands as a cornerstone of microbiology, bearing profound implications across diverse disciplines such as medicine, biotechnology, and environmental science. This foundational categorization underpins a broad understanding of microbial diversity and function, enabling great advancements in research, diagnostics, and practical applications.
Cell Wall Structure

Characterized by a robust layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall, Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain during the Gram staining procedure, manifesting a distinctive purple hue under microscopic examination. These organisms lack an outer lipid membrane, a defining feature that distinguishes them from their Gram-negative counterparts.

In stark contrast, Gram-negative bacteria feature a comparatively thin layer of peptidoglycan enclosed between an outer lipid membrane replete with lipopolysaccharides. During Gram staining, the limited peptidoglycan density fails to retain the crystal violet stain, facilitating decolorization upon exposure to the alcohol wash. Consequently, Gram-negative bacteria exhibit a reddish appearance owing to the safranin counterstain.
Significance of Gram Staining

a) Diagnostic Tool
Gram staining emerges as a main diagnostic tool in microbiology, facilitating the rapid differentiation of bacterial species based on their cell wall architecture. This technique serves as an initial step in microbial characterization, expediting the identification of potential pathogens and guiding subsequent diagnostic protocols.
b) Clinical Relevance
clinical settings, Gram staining of diverse specimens, including blood, sputum, and cerebrospinal fluid, furnishes invaluable insights for antibiotic selection and therapeutic management. Notably, Gram-positive bacteria often display susceptibility to specific antibiotics such as penicillin, while Gram-negative counterparts may necessitate tailored treatment regimens owing to their distinct cell wall composition and antibiotic resistance profiles.
Evolutionary Insights
The classification of bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative categories outlines profound insights into their evolutionary trajectories. While conventional wisdom once showed a linear evolution from Gram-positive progenitors to Gram-negative colony via the acquisition of an outer lipid membrane, contemporary genetic analyses unveil a far more comprehensive narrative. Convergent evolution emerges as a central theme, suggesting that the advent of the outer membrane occurred independently across diverse bacterial lineages, underscoring the dynamic nature of microbial evolution.
Applications Beyond Diagnosis
1.Food Safety
Discriminating between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria assumes paramount importance in food safety endeavors, facilitating keen monitoring and quality control protocols. Notably, certain Gram-negative pathogens such as Salmonella and Escherichia coli pose substantial health hazards if present in food products, necessitating stringent surveillance measures. Conversely, select Gram-positive bacteria contribute indispensably to food production processes, notably in fermentation applications.
2 .Environmental Monitoring
The application of Gram staining extends beyond clinical realms, finding utility in environmental microbiology for the identification and characterization of bacteria in diverse ecological niches. Comprehensive assessments of soil, water, and other environmental samples afford crucial insights into microbial community dynamics, enabling informed evaluations of environmental health and ecosystem resilience.
Technological Advancements
While traditional Gram staining remains a linchpin technique in microbiological practice, ongoing technological innovations herald a new era of bacterial identification and characterization. Molecular methodologies, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR), genome sequencing, and mass spectrometry, complement conventional approaches, offering heightened resolution and specificity in taxonomic classification and functional profiling of microbial communities. These cutting-edge techniques empower researchers to unravel microbial relationships and unravel the intricacies of microbial ecosystems with unprecedented precision.
In summary,
the dichotomous classification of bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative categories, predicated upon their cell wall architecture, transcends disciplinary boundaries, underpinning understanding of microbial biology and ecology. From diagnostic endeavors to evolutionary inquiries and practical applications in food safety and environmental stewardship, this foundational concept continues to shape and enrich our comprehension of the microbial world.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for assistance guidance.
The Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Intervention of Migraine

Introduction
Migraine, a prevalent neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches, sensory disturbances, and autonomic dysregulation, poses a significant global health burden. We are going to provide a comprehensive review citing out the unique pathophysiological mechanisms underlying migraine and discuss the evolving landscape of therapeutic interventions.
Understanding Migraine Pathophysiology

1. Genetic Predisposition
Migraine exhibits a strong familial aggregation, suggesting a genetic component in its etiology. Genome-wide association studies have identified numerous susceptibility loci implicated in migraine susceptibility, including genes involved in neuronal excitability, neurotransmitter release, and vascular regulation.
2.Environmental Factors
Environmental triggers such as stress, sleep disturbances, hormonal fluctuations, dietary factors, and sensory stimuli play a crucial role in migraine onset and exacerbation. These triggers interact with genetic predispositions to precipitate migraine attacks, underscoring the threshold nature of the disorder.
Sensory Processing Abnormalities
Migraine pathophysiology revolves around the concept of a cyclic sensory threshold model, wherein aberrant processing of sensory inputs leads to hypersensitivity and pain amplification. Dysregulation of cortical excitability, thalamocortical networks, and descending pain modulatory pathways contribute to the sensory manifestations of migraine.
Phases of Migraine

Migraine progression is characterized by distinct phases, including premonitory, aura, pain, and postdrome phase, each associated with specific neurophysiological changes. The premonitory phase, marked by various symptoms preceding the headache, reflects hypothalamic and brainstem activation. Aura, a transient neurological phenomenon, involves cortical spreading depression and cortical spreading depolarization, leading to visual, sensory, or motor disturbances. The pain phase, mediated by trigeminal vascular activation and central sensitization, culminates into headache and associated symptoms. The postdrome phase, characterized by residual symptoms following headache resolution, implicates persistent alterations in cortical and brainstem function.
a) Trigeminal vascular System

Central to migraine pathophysiology is the trigeminal vascular system, comprising peripheral trigeminal afferents and central brain nuclei involved in pain processing. Activation of trigeminal vascular pathways, mediated by neuropeptides like Calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P, and neurokinin A, initiates neurogenic inflammation and sensitization of meningeal nociceptors, contributing to headache generation.
b) Brainstem Nuclei
Brainstem regions, including the dorsolateral pons, periaqueductal gray, and locus coeruleus, serve as crucial modulators of trigeminal vascular transmission. Dysregulation of brainstem nuclei leads to unbearable pain processing and autonomic dysfunction, characteristic of migraine attacks.
c) Hypothalamic Involvement
The hypothalamus plays an important role in migraine initiation and progression, integrating nociceptive, autonomic, and circadian inputs. Dysregulation of hypothalamic neurotransmitters, including orexin, serotonin, and dopamine, contributes to migraine susceptibility and triggers stress-induced attacks.
d) Thalamic Dysfunction
The thalamus, a key relay station in sensory processing, exhibits structural and functional abnormalities in migraine. Altered thalamocortical connectivity, thalamic excitability, and neurotransmitter imbalance contribute to central sensitization, photophobia, and allodynia, hallmark features of migraine.
e) Cortical Alterations
Beyond aura generation, the cerebral cortex demonstrates widespread abnormalities in migraineurs, including changes in cortical thickness, gray matter volume, and functional connectivity. Genetic variants associated with glutamatergic neurotransmission and cortical excitability further implicate cortical dysfunction in migraine pathophysiology.
Therapeutic Approaches

a) Acute Treatments
Triptans, serotonin receptor agonists, have long been the mainstay of acute migraine therapy. However, emerging classes of medications, including ditans and gepants, offer alternative treatment options with improved tolerability and efficacy. Lasmiditan, a selective 5-HT1F receptor agonist, provides rapid relief without vasoconstrictive effects, making it suitable for patients with contraindications to triptans. Gepants, small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists, block CGRP-mediated vasodilation and neurogenic inflammation, offering effective pain relief without cardiovascular risks.
b) Preventive Treatments
Monoclonal antibodies targeting CGRP or its receptors represent a breakthrough in migraine prevention, providing sustained efficacy with monthly or quarterly dosing regimens. Erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab have demonstrated superior efficacy compared to placebo in reducing migraine frequency and severity, with favorable safety profiles. Gepants such as atogepant and Rimegepant offer additional options for migraine prophylaxis, particularly in patients intolerant to traditional preventive therapies.
c) Neuromodulation Techniques
Non-invasive neuromodulation modalities, including transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcutaneous supraorbital nerve stimulation, offer adjunctive therapeutic options for acute migraine management. TMS delivers magnetic pulses to cortical regions implicated in migraine pathophysiology, modulating cortical excitability and pain perception. tSNS targets the supraorbital nerve, inhibiting nociceptive transmission and providing rapid pain relief without systemic side effects. Additionally, vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) offers a promising approach for both acute and preventive migraine treatment, modulating autonomic function and central pain processing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, migraine represents a complex neurological disorder with a diverse clinical manifestations. Advances in our understanding of migraine pathophysiology have paved the way for the development of novel therapeutic agents targeting key molecular and neural pathways. By understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition, sensory processing abnormalities, and central pain modulation, clinicians can tailor treatment strategies to individual patient needs, optimizing therapeutic outcomes and improving quality of life for migraine patients worldwide. Continued research efforts and clinical innovations hold the promise of further advancements in migraine management, underscoring the collective commitment to alleviating the global burden of this devastating condition.
Understanding the pathophysiology of migraine is crucial for effective management, and this comprehensive analysis sheds light on the complex mechanisms underlying this neurological disorder. For medical students facing challenges in studying migraine or any other medical topic, seeking professional help from Expert Academic Assignment Help can provide valuable guidance and support. With our expert assistance, students can overcome obstacles and excel in their academic endeavors. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com to elevate your understanding and mastery of medical concepts.
How Does The Brain Work?

The brain stands as a marvel of biological engineering, Composing of a multitude of bodily functions ranging from cognition and memory to emotions and sensory perception. Together with the spinal cord, it constitutes the central nervous system (CNS), the command center of the human body.
Composition of the Brain

Weighing approximately 3 pounds in adults, the brain’s main structure comprises about 60% fat, interspersed with water, protein, carbohydrates, and salts. Unlike muscles, it houses a complex network of blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
a) Gray and White Matter
Within the central nervous system, gray matter and white matter occupies distinct regions. In the brain, gray matter forms the outer layer, rich in neuron somas, while white matter constitutes the inner section, primarily composed of axons unsheathed in myelin. Conversely, in the spinal cord, this arrangement is reversed.
b) Brain Functionality
The brain operates by transmitting and receiving chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. These signals regulate a myriad of processes, with the brain disseminating each input. Some signals remain confined within the brain, while others traverse the spinal cord and nerves, disseminating information across the body’s expanse. This composes neural network relies on billions of interconnected neurons.
Major Brain Regions and Their Functions

1.Cerebrum
Dominating the brain’s landscape, the cerebrum encompasses the cerebral cortex and underlying white matter. It governs a spectrum of functions, including motor coordination, temperature regulation, language processing, emotional regulation, and sensory perception.
2. Brainstem
Serving as the bridge between the cerebrum and spinal cord, the brainstem comprises the midbrain, pons, and medulla. It regulates vital autonomic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and reflexive responses.
3. Cerebellum
Nestled at the posterior aspect of the brain, the cerebellum coordinates voluntary muscle movements, posture, balance, and motor learning.
Brain Coverings

a) Meninges
Three layers of protective membranes, collectively known as meninges, enshroud the brain and spinal cord. These layers — dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater — shield the delicate neural tissue from physical trauma and infection.
b) Lobes of the Brain
Each hemisphere of the brain comprises four lobes, each harboring distinct functional domains:
Frontal Lobe: Governing executive functions, motor control, and higher cognitive processes.
Parietal Lobe: Integrating sensory information, spatial awareness, and perception of pain and touch.
Occipital Lobe: Specialized for visual processing and perception.
Temporal Lobe: Involved in auditory processing, language comprehension, and memory consolidation.
Deeper Brain Structures
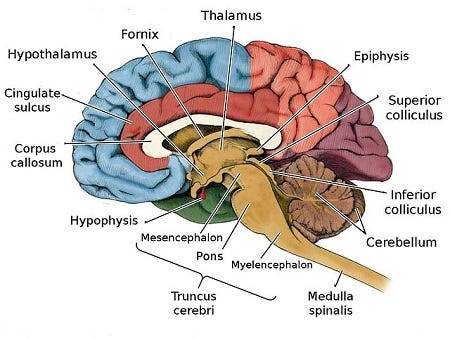
These encompass important structures such as the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and pineal gland, orchestrating hormone secretion, emotional regulation, memory consolidation, and circadian rhythms.
Blood Supply
The brain receives its oxygenated blood supply through the vertebral and carotid arteries, ensuring adequate perfusion of neural tissue. The main network of blood vessels, including the Circle of Willis, safeguards against ischemic insults and facilitates intraarterial communication.
Cranial Nerves

The twelve pairs of cranial nerves, originating from the brainstem, mediate a diverse array of sensory and motor functions, encompassing olfaction, vision, facial expression, and auditory perception.
Comprehending the anatomy and functionality of the brain fosters a deeper appreciation of its complexity and facilitates advances in neuroscientific research and therapeutic interventions aimed at diminishing neurological disorders.
Understanding the detailed anatomy and functionality of the brain is crucial for medical students embarking on their journey of study. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers invaluable assistance in navigating the complexities of neuroscience and related subjects. By leveraging expert guidance and support, students can excel in their medical education and contribute to advancements in the field of Medicine. Email us at expertassignment46@gmail.com to embark on your path to scholarly excellence and professional competency.
Medical microbiology


A clinical or medical microbiologist, typically with a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Microbiology and sometimes a Ph.D. in life sciences, studies the characteristics of pathogens, their transmission modes, and mechanisms of infection. They play a vital role in providing identification of pathogens, suggesting treatment options, and contributing to the development of health practices.

The historical milestones in medical microbiology include Anton van Leeuwenhoek’s observations of microorganisms in 1676, Edward Jenner’s development of the smallpox vaccine in 1796, and Louis Pasteur’s work on vaccines and pasteurization in 1857. Robert Koch’s germ theory and postulates in the late 19th century were pivotal. The Gram stain, developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884, revolutionized bacterial identification.

Infectious diseases, including bacterial, viral, parasitic, and fungal, are commonly treated in medical microbiology. Diagnostic tests involve microbial culture, microscopy, biochemical tests, and genotyping. Microbiological culture isolates pathogens in the laboratory, while microscopy provides detailed observations. Biochemical tests and serological methods aid in identifying infectious agents.

However, the rise of antibiotic resistance poses a significant challenge. Medical microbiologists must consider the specificity and effectiveness of antimicrobial drugs, as well as the presence of resistant strains. Phage therapy, an alternative to antibiotics, is being explored to combat antimicrobial resistance.
In conclusion, medical microbiology is a dynamic field that not only diagnoses and treats diseases but also explores the benefits of microbes for human health. With historical milestones and continuous advancements, this field plays a crucial role in shaping healthcare practices and combating infectious diseases.
Wishing you all the best in pursuing your studies in Medical Bacteriology. It involves a lot of detailed focus on the causative agents of diseases.
In case of any challenges or if you’re looking for guidance during the study period, do not hesitate to;
Email us at;williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@mail.com
7 steps to writing a dissertation.

1. Choose Your Topic Wisely
Selecting a topic for your dissertation is a critical first step that sets the foundation for your entire research endeavor. This involves a comprehensive approach.
Relevance to Academic Discipline and Personal Interests
Choose a topic that aligns with your academic discipline and personal interests. This ensures that you are passionate about the subject matter, making the research process more engaging.
Consideration of Career Goals

Reflect on your career goals and aspirations. opt for a topic that not only complements your academic journey but also contributes to your professional growth. This alignment can enhance the practicality and relevance of your dissertation.
Guidance from Supervisor
Engage in regular discussions with your supervisor. Seek their guidance to refine your topic, identify potential challenges, and gain insights into the research landscape. Your supervisor’s experience can prove invaluable in shaping your research direction.
2. Check What’s Required

Understanding the requirements and expectations for your dissertation is crucial for successful completion. This step involves a detailed examination of marking criteria, module guidelines, and additional instructions:
Scrutinizing Marking Criteria
Thoroughly analyze the marking criteria provided by your educational institution. This ensures that your dissertation aligns with the assessment standards, maximizing your chances of achieving a favorable grade.
Grasping Academic Writing Expectations
Familiarize yourself with the academic writing conventions specific to your discipline. This includes understanding citation styles, formatting guidelines, and language conventions. Adhering to these expectations enhances the professionalism of your dissertation.
Word Count and Submission Details
Take note of the stipulated word count for your dissertation. Understanding the limitations ensures that your research remains concise and focused. Additionally, pay attention to submission details, such as deadlines and submission formats (online or hard copy).
Additional Components
Many dissertations require supplementary elements like a project plan, literature review, or critical reflection. Acknowledge and incorporate these components as per the provided instructions. Neglecting these elements can result in grade deductions.
3. Conduct In-Depth Research

The research phase of your dissertation involves a comprehensive exploration of existing literature to inform and support your study.
Literature Review
Conduct a thorough literature review to identify relevant sources, articles, and studies related to your chosen topic. This process allows you to understand the existing research landscape and identify gaps or areas for further exploration.
Development of Research Questions
Based on your literature review, formulate clear and concise research questions. These questions should guide the direction of your study, addressing specific aspects of the chosen topic. Articulating well-defined research questions contributes to the coherence of your dissertation.
Note-Taking and Source Organization
Systematically take notes on each source, capturing key findings, methodologies, and arguments. Organize your sources for easy reference during the writing phase. Implement a consistent method for citation and annotation to enhance traceability.
Critical Evaluation with Advisor Guidance
Engage with your advisor throughout the research process. Seek their guidance on critically evaluating the credibility and relevance of your chosen sources. A collaborative approach ensures that your research aligns with academic standards.
4. Develop a Strong Thesis Statement

The thesis statement serves as the focal point of your dissertation, encapsulating the main argument or research question. Crafting a robust thesis statement involves several considerations:
Specificity and Focus
Ensure that your thesis statement is specific and focused, avoiding broad or vague assertions. The clarity of your thesis statement sets the tone for the entire dissertation, guiding readers on the scope of your research.
Arguability
A strong thesis statement is one that is arguable. It presents a stance or perspective that can be supported or refuted through evidence. This encourages critical engagement with your research, fostering a dynamic discourse.
Realism
Consider the feasibility of your thesis statement within the allocated time and space. Ensure that your chosen topic allows for comprehensive research and analysis without exceeding practical constraints.
Feedback from Peers and Supervisor
Share your draft thesis statement with your peers and supervisor. Solicit feedback on its clarity, coherence, and alignment with your research goals. Iterative refinement based on feedback enhances the strength of your thesis statement.
5. Proofread and Edit

Proofreading and editing are integral steps to refine the quality and presentation of your dissertation. This phase goes beyond mere error correction and involves a holistic evaluation:
Thorough Proofreading
After completing the initial draft, engage in thorough proofreading. Reading your dissertation aloud can reveal nuances and errors that might be overlooked during silent reading. Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
Environmental Change for Fresh Perspective
Changing your environment before proofreading allows you to view your work with fresh eyes. This change in perspective facilitates the identification of structural or stylistic improvements. Consider reviewing your dissertation in a quiet, distraction-free setting.
Focused Editing
Focus on specific aspects during the editing phase, such as grammar, syntax, and coherence. Addressing one element at a time prevents overwhelming and ensures a systematic refinement of your dissertation’s overall quality.
Structural Review
Conduct a comprehensive review of your dissertation’s structure and flow. Verify that your arguments are logically organized, and ideas progress in a coherent manner. Identify any sections that require clarification or expansion.
Formatting and Referencing
Check your dissertation’s adherence to formatting guidelines, including font, font size, margins, and line spacing. Ensure that all references are accurately cited following the preferred citation style of your academic institution.
6. Seek Feedback and Finalize

Gaining feedback from your advisor or board members is a pivotal step in enhancing the robustness of your dissertation. This phase involves a collaborative approach:
Specific Feedback Requests:
When seeking feedback, be specific about the areas you want to be reviewed. Request input on overall structure, argument strength, writing clarity, or any specific concerns you may have. This targeted approach streamlines the feedback process.
Openness to Constructive Criticism
Approach feedback with an open mind, understanding that constructive criticism is aimed at improvement. Embrace suggestions for refinement, even if they challenge your initial perspectives. Incorporating diverse feedback strengthens the scholarly merit of your work.
Implementation of Feedback
Actively implement the feedback received. Revise sections based on recommendations, clarify ambiguous points, and strengthen areas identified as weak. This iterative process ensures that your dissertation undergoes continuous improvement.
7. Submit

The final submission of your dissertation requires meticulous attention to guidelines and deadlines. Proper preparation ensures a smooth submission process.
Guideline Adherence
Review the submission guidelines provided by your educational institution. Ensure that your dissertation meets all specified requirements, including formatting, additional components, and submission format (online or hard copy).
Timely Submission
Adhere to the submission deadline to avoid penalties or rejections. Plan your submission well in advance, considering the time required for any administrative processes. Late submissions may impact your academic assessment.
Submission Format
If online submission is the designated method, prepare a PDF file according to the platform’s specifications. Include any additional information, such as your student ID number or dissertation title, as required by the submission portal.
Hard Copy Submission
For institutions requiring hard copy submission, follow the specified procedures. Submit a bound copy of your dissertation to the department office, adhering to any additional requirements such as multiple copies, title page, abstract, and table of contents.
Consultation with Advisor
Before final submission, consult with your advisor to ensure that all aspects of your dissertation align with institutional expectations. Address any last-minute queries or concerns to ensure a seamless submission process.
For All your Assignments Help;
Email us at;
williamsliason@outlook.com
10 Easy Ways To Tackle Homework

1) Get Organized
Organization is the cornerstone of effective homework management. Invest in a comprehensive planner or digital calendar to meticulously document all upcoming tests, quizzes, and assignments. This proactive approach ensures you stay ahead of deadlines and fosters a sense of control over your academic responsibilities. Break down tasks further within your planner, creating a roadmap that transforms daunting assignments into manageable steps.
2) Set Aside a Specific Time for Homework

Time management is pivotal for academic success. Instead of relying on post-school fatigue to magically complete homework, establish a dedicated time slot. Whether it’s immediately after school or later in the evening, adhering to a consistent schedule fosters discipline and minimizes procrastination. This intentional approach transforms homework from a vague obligation into a structured routine, enhancing productivity and reducing stress.
3) Create a Study Space

Crafting an optimal study environment is crucial. Identify a quiet, distraction-free space conducive to focused work. If the home environment lacks tranquility, consider alternatives such as the library or a coffee shop. This deliberate selection of a study space sets the stage for effective learning, minimizing disruptions and maximizing concentration.
4) Break Up Your Work
The strategy of breaking down assignments into smaller, more manageable components is a cognitive game-changer. When faced with a complex task, such as writing an essay or preparing for a test, dissect it into distinct phases. Begin with brainstorming, progress to outlining, and conclude with the execution of the task. This method not only enhances efficiency but also promotes a systematic understanding of the subject matter.
5) Take Breaks

Recognizing the importance of mental rejuvenation, incorporate regular breaks into your study routine. Prolonged study sessions are not only counter productive but also mentally exhausting. Incorporate short breaks every 20 minutes to engage in mindless activities like scrolling through social media or enjoying a snack. This strategic pause boost your mental activities, contributing to sustained focus and overall well-being.
6) Get Rid of Distractions

A focused study environment demands the elimination of potential distractions. Beyond choosing a quiet space, actively remove devices and stimuli that may divert your attention. Put away your phone, turn off the television, and, if necessary, employ noise-canceling headphones. This intentional decluttering of your study space enhances concentration, allowing for a more immersive and efficient study experience.
7) Find a Study mate

Collaborative learning is a powerful tool in mastering challenging subjects. If you encounter difficulties in a particular class, seek out a study buddy. Choose a friend who shares the same class and is willing to engage in joint study sessions. This collaborative effort fosters an exchange of ideas, clarification of concepts, and mutual support. Don’t hesitate to consult your tutor if additional guidance is needed.
8) Make Use of Technology
Leverage the wealth of technological resources available to streamline your homework experience. Applications of technology provide organizational support, helping you keep track of assignments and due dates. Online platforms offer interactive learning tools, including practice problems and flashcards. Integrating technology into your study routine enhances efficiency and facilitates a dynamic approach to learning.
9) Reward Yourself

The psychology of reward plays a significant role in maintaining motivation. Upon completing your daily tasks, implement a system of rewards. These need not be extravagant; simple indulgences like watching an episode of your favorite TV show or enjoying a tasty treat can serve as effective incentives. This positive reinforcement not only makes the homework process more enjoyable but also cultivates a sense of accomplishment.
10) Get Enough Sleep

Undoubtedly, the foundation of cognitive well-being lies in adequate sleep. Prioritize a consistent sleep schedule, aiming for at least 8 hours each night. Sufficient sleep contributes to enhanced concentration, improved focus, and heightened energy levels. By valuing your sleep, you not only optimize your academic performance but also promote overall physical and mental health. Your homework endeavors, as well as your grades, will undoubtedly reflect the benefits of a well-rested mind.
Conclusion
Concluding the discourse on tackling homework emphasizes the transformative power of proactive and disciplined study habits. Acknowledging that homework need not be a source of stress, the conclusion underscores the importance of approaching assignments systematically. By starting early, maintaining consistency, and adopting these strategies, students can not only navigate homework efficiently but may even find a sense of enjoyment in the learning process. The message emphasizes that practice, routine, and a positive mindset are integral to mastering the art of homework.
In essence, the journey of tackling homework transcends the immediate completion of assignments; it becomes a holistic approach to academic growth and personal development. Each tip serves as a building block, constructing a foundation upon which students can handle the academic landscape with confidence and competence. Through these strategies, the once formidable task of homework is not merely conquered but transformed into a constructive and fulfilling endeavor.
For Homework or Assignments;
Email us at;
williamsassignmentheplfredrick@gmail.com
Blood cell

The blood cells serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of hematopoiesis, the process through which various blood cell types are formed and function in the human body. This detailed discussion aims to unravel the key aspects presented in the article, delving into the structure, functions, and disorders associated with;
Red blood cells (erythrocytes),
2.White blood cells (leukocytes), and
platelets (thrombocytes).
Blood Cell Types and Composition
At the core of the circulatory system lie three major types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cellular components collectively contribute to 45% of blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% being plasma. This delicate balance underscores the dynamic nature of blood, serving as a conduit for various vital functions within the body.
1.Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
The discussion commences with a focus on red blood cells, the primary carriers of oxygen in the bloodstream. Erythrocytes, characterized by their unique biconcave shape and lack of a nucleus, play a crucial role in gas exchange facilitated by the iron-containing protein hemoglobin. The intricate details of erythropoiesis, the process of RBC formation in the red bone marrow, offer a glimpse into the remarkable physiological mechanisms that ensure a constant supply of oxygen carriers. The staggering production rate of 2.4 million RBCs per second in adults highlights the body’s continuous demand for these essential cells. The information regarding the lifespan of RBCs (100–120 days) and their subsequent removal by the spleen adds another layer to our understanding of the life cycle of these vital cells. The absence of a nucleus in mature red blood cells, a unique characteristic among human cells, is highlighted. The pathological conditions of anemia and polycythemia are thoroughly explored, shedding light on the consequences of an imbalance in red blood cell count. Additionally, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) provides valuable insights into the diagnostic tools used in assessing the health of red blood cells.
2.White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
The immune system, our body’s defense mechanism, relies on white blood cells to combat infectious diseases and foreign materials. These leukocytes, originating from multipotent cells in the bone marrow, are categorized into granulocytes (basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, mast cells) and agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes). The discussion delves into the roles these distinct white blood cell types play in the human immune system, offering a nuanced understanding of their functions. The conditions of leukopenia and leukocytosis, indicating low and high white blood cell counts, respectively, are explored, emphasizing the diagnostic significance of monitoring these counts. The increased white blood cell count during infections and its association with hematological cancers underscore the pivotal role leukocytes play in our overall health.
3.Platelets (Thrombocytes)
The section on platelets elucidates their role in hemostasis, the process of preventing and stopping bleeding. These small, irregularly shaped cell fragments, derived from megakaryocytes, circulate in the blood and are essential for the formation of blood clots. The average lifespan of platelets, a mere 5 to 9 days, emphasizes the continuous production required for maintaining hemostatic balance. The normal range of platelet counts and the potential consequences of low or high platelet numbers provide valuable insights into the delicate equilibrium necessary for preventing excessive bleeding or the formation of thrombosis. Thrombocytopathy, a broad term encompassing disorders related to platelets, is discussed, including thrombocytopenia, thrombasthenia, and thrombocytosis. The intricate relationship between platelets and growth factors, as well as their role in wound healing, showcases the multifaceted contributions of these small but crucial cellular fragments.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): The article introduces the Complete Blood Count (CBC) as a vital diagnostic tool providing a comprehensive analysis of blood cell composition. The historical transition from manual counting to automated analyzers reflects the evolving landscape of medical technology, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of blood cell analysis. The significance of CBC in offering an overview of a patient’s general health status is underscored, emphasizing its widespread use in medical diagnostics.
Historical Discoveries.
The historical perspective woven into the article traces the evolution of our understanding of blood cells. From Jan Swammerdam’s pioneering observation of red blood cells in 1658 to Paul Ehrlich’s techniques in staining blood films and differential blood cell counting in 1879, the narrative highlights key milestones in the establishment of hematology as a distinct field of medicine. The contributions of various scientists, including Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, Alfred Donne, and Gabriel Andal, collectively shaped our current knowledge of blood cells.
Conclusion
The blood cells provides a rich tapestry of information encompassing their structure, functions, and associated disorders. It serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the dynamic nature of blood and the pivotal roles played by red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in maintaining homeostasis within the human body. The integration of historical discoveries adds depth to the narrative, highlighting the continuous quest for knowledge that has defined the field of hematology. This article not only serves as an educational tool but also showcases the remarkable advancements in medical science and technology that have propelled our understanding of blood cells to new heights. As we unravel the mysteries of hematopoiesis, we gain valuable insights into the machinery that sustains life within our veins.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email us on;
williamsliason@outlook.com
This somehow always motivates me to study












Very honest photo dump about how the month is going (i need a miracle to get me through these exams)
Anatomy is so fun I wish I could just spend hours studying only anatomy.
It takes that long, anyway.




Quick time lapse of me studying the femoral triangle ^




Please support me and read my blog posts. And while you’re at it, subscribe for more content :)

Please support me and read my blogposts! And while you’re at it, please subscribe :)

I’d appreciate it if you could take a look at my blog!

26 Oct (Intro. Number Theory)
This is by far the worst class that I have taken. Consistently I have been with the lowest grade, and my overall understanding of this class is abysmal. Despite being in my professor’s office every day.
In any case I make a point to strive for perfection, and not understanding something haunts me to my core. In any case I am forever hopeful. Im happy to be back, and I have lots to share
🎧 Momma Told Me - Earthgang
Stay Up y’all
28 April (Diff Eq.)
The struggle has been very real over the course of the last week. I failed a test (it was in the teens), my mom is still in the hospital, and some days are definitely better than others, but I am holding on.
I can’t in good faith give up everything that I’ve worked so hard to build. I have also been procrastinating. The Howard deadline is 30 April, and tbh I haven’t put my all into it (despite really wanting to attend the school).
Small update, but that’s all for today.
Stay up✌🏿
🎧 Trappin in Japan 4 - Ryan Celsius
23 April (life update)
So, keeping things honest I’m not doing the best right now friends. Over the course of the last 2 weeks one of my parents had a heart attack and the other is now on life support.
I really appreciate all of you who continue to support me and this study blog.
Morale of the story is that bad things happen to all of us, but it’s our actions after the fact that define us
Stay up ✌🏾
🎧 Trappin in paradise 78 - smooth sounds

I just hit 100 followers, and I am truly grateful for all of you.
I would like to do a challenge.
For every interaction this post gets (from ANYONE) I will pick up 1 item of trash.
The earth has done so much for us, and I can’t think of a better way to give back
9 April (The joy of being in STEM)
Today was not the best by any stretch of the imagination. I was fighting myself most of the day trying to get my HW done despite putting in good time to try and complete it, the topics just aren’t resonating.
I find myself once again dragging behind the rest of my peers despite studying just as hard as they do. Sadly, I couldn’t tell you the last time I actually had a weekend to myself, or a nice moment that wasn’t overshadowed by the crippling weight of school.
I wish there were more instructors who truly understood that different students have different needs.
Stay up✌🏿
🎧 Einaudi: Fox Tracks (Day 1) - Ludovico Einaudi
7 April (Calc 4: happy exhaustion)
Today was rough, but I feel like I’m getting the hang of maximum and minimum values (thank you so much Lagrange).
I will say that I’m running into a bit of an existential crisis as far as my career is concerned. I feel like I really enjoy physics and am going to love making a job out of it, but this online learning environment is painful.
I want to actually do physics now that I have a better mathematical understanding, but at the same time I can only put forth so much effort in a class that has no social interaction. I can’t help but feel neglected considering I know how amazing my physics instructor is and knowing I’ll never officially have a “class” with him.
I’ve been struggling with my BPD as of late and it’s making me a bit more emotional than normal, but I’m taking strides to work through my issues.
A bit of positive news, I’m getting more comfortable on my skateboard, and am looking to land my first heelflip soon
You are strong
You are beautiful
You are powerful
Now go change the world
Stay up ✌🏿
🎧 The Watchtower - Sigimund

4 April (thoughts)
I never really took the time to explain what the big picture is, so I’m going to attempt to explain it here
I want to be a great dad. As cheesy as it might sound, I love the idea of being a positive father, and father-figure to those who need that person in their life. To this day my dad doesn’t claim me, and much as I love my mom, there are still some things that I would have looked for from him. I will be the change
I want to be a millionaire, and establish various forms of income that can be utilized after my journey on earth is complete. I have already began investing, and look to retire (read: not work as hard) around age 40.
I want to make the world a better place. The earth is OUR mother, and its OUR job to protect her. I have created an animal rights groups, organized adopt-a-highway’s, gone to and organized many protests (the March For Science being to this day the biggest protest I’ve ever helped create).





I want to own a RHD (right hand drive) Snow White FC-RX-7. I adored Initial-D growing up and Ryosuke’s was the first car I actually fell in love with. I was able to own one for a short while, but due to a lack of money, and time I was never actually able to complete the build. I try to play it off like it was no big deal, but that car really meant a lot to me, and it’s my goal to do it right.

I want to be an example of a great physicist, and a symbol of black excellence. I want to show that if I, a vegan, pan, non-binary person can get their Ph.D doing what they love DESPITE being homeless and abused, then you can too.
In case you need to hear this
1. You are loved
2. You are accepted no matter who you are
3. My inbox is always open
Stay up ✌🏿
🎧 my thoughts
2 April (Calc 4 and Diff. Eq)
These classes are the embodiment of a toxic relationship (but in the best of ways). The overall course load is a lot and most days I am struggling to get done by 10pm, but I can confidently say I FEEL LIKE A MATHEMATICIAN.
The math I’m doing now has real world applications. Yeah finding the slope of a line is cool, but when you find the vector tangent to the curve that accurately depicts the heating or cooling of a particular environment per mile THAT’S ACTUALLY USEFUL, AND HELPFUL TO THE WORLD.
On one hand, I have late nights followed by early mornings, and a fair amount of stress.
On the other, I have an overwhelming sense of validation, pride, and comfort.
This post goes out to @juicycupz, she was hands down the best partner I’ve ever had. While we may not be together now, she definitely played a major role in who I am now.
Stay up ✌🏿
🎧 Trappin in paradise 65 - Smooth Sounds

My desk/dorm area
the aftermath of studying for 11hrs
31 March (Calc 4)
Today seemed to me an uphill battle from the start. I woke up to heart issues and dealing with an embedded lip ring (again), but I didn’t let that stop me.
I managed to get all of my work done, and am now trying to get further ahead so hopefully I won’t get crushed later on down the line.
Apologies for the short video, my iPhone corrupted most of the time lapse
Stay up y’all ✌🏿
🎧 L’Enfant Sauvage - Gojira
So, I’ve been tasked with putting my playlist on shuffle and identifying the first 10 songs in hopes that y’all will get to know me better 😅.
Stone love - Pepper
I will never change - Benga
Everlasting Sleep - Chelsea Grin
Who’s the Man - ABN
Grove St. Party - Waka Flocka
Mechano - Datsik
Hoax - Jericho
Jazz (We’ve got) - A Tribe Called Quest
So High - Doja Cat
Plain Jane Remix (DJ HenDu Gotti) - ASAP Ferg and Nicki Minaj
And now to tag mutuals
@messy-does-cosmology @miss-biophys @caytheblkmermaid @karmahoudinii @caffeine-integral-studies @thegeekdomain @schrodingersstudent
30 March (the first day of classes)
I have mixed feelings about this quarter. On one hand I’ll be receiving a degree and moving on to an actual university. On the other I am faced with the fact that I won’t see many of my friends for quite some time after I graduate (not to mention the new course load and ops tempo)
In all I’m happy to be back, and look forward to future productivity
Stay up ✌🏿
🎧 Trappin in Paradise 78 - Smooth sounds