Online Writing - Blog Posts
Confused by ontology & epistemology? A short guide to help you navigate this aspect of research design

Introduction
For many graduate students pursuing advanced degrees like PhDs or Master’s, the realm of philosophical paradigms, ontology, and epistemology often appears daunting and abstract. Terms like positivism, constructivism, and critical realism can seem overwhelming, especially when these concepts play a fundamental role in shaping research methodologies and approaches. This guide aims to demystify these concepts step by step, providing clarity on their definitions, significance, and implications for academic research.
Understanding Ontology and Epistemology

At the heart of research design lie two foundational concepts: ontology and epistemology. Ontology concerns itself with the nature of reality — what exists and how it exists. It indulges into questions about the fundamental nature of the world, whether objective reality exists independently of human perception, or if reality is constructed through subjective experiences. Epistemology, on the other hand, investigates the nature of knowledge — how knowledge is acquired, validated, and understood. It explores the ways researchers come to know and understand phenomena, addressing questions about the validity of different sources of knowledge and the role of perception and interpretation in knowledge production.
The Role of Philosophical Paradigms
Philosophical paradigms provide overarching frameworks that guide researchers in defining their ontological and epistemological positions and in choosing appropriate research methods and methodologies. These paradigms include:
a). Positivism: Positivism asserts that knowledge is derived from observable phenomena and empirical evidence. It emphasizes objectivity, replicability, and the use of quantitative methods to test hypotheses.
b). Interpretivism: Interpretivism posits that knowledge is socially constructed through subjective experiences and interpretations. It focuses on understanding the meanings individuals attribute to their experiences, often using qualitative methods such as interviews, observations, and textual analysis.
c). Critical Realism: Critical realism seeks to bridge the gap between positivism and interpretivism by acknowledging the existence of an objective reality that is independent of human perception but also recognizing that our understanding of this reality is mediated through our perceptions and interpretations. It advocates for the exploration of underlying structures and mechanisms that generate observable phenomena while allowing for the influence of social contexts and human agency.
d). Constructivism: Constructivism proposes that knowledge is actively constructed by individuals based on their experiences and interactions with the world. It highlights the role of social and cultural contexts in shaping knowledge and emphasizes qualitative research methods that explore subjective meanings and interpretations.
e). Post-positivism: Post-positivism acknowledges the critiques of positivism while retaining its commitment to empirical observation and scientific vigor. It introduces concepts like theory-laden observation and the acknowledgment of researcher biases, aiming to refine positivist approaches to account for the complexities of social phenomena.
Navigating Different Philosophical Positions

Each philosophical position has implications for research design, methodology, data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Researchers must align their chosen paradigm with their research questions and objectives to ensure coherence and vigor in their studies. For instance:
1.Methodological Implications: Positivist research often employs quantitative methods to measure variables and test hypotheses, whereas interpretivist research favors qualitative methods to explore meanings and subjective experiences.
2. Ontological and Epistemological Assumptions: Understanding whether one believes in an objective reality (ontology) and how one believes knowledge is obtained and validated (epistemology) is crucial in selecting appropriate research methods and interpreting findings.
Advocating for Critical Realism
Critical realism emerges as a compelling philosophical stance that integrates insights from both positivism and interpretivism. It acknowledges the existence of an objective reality while recognizing that our understanding of this reality is mediated through social contexts, perceptions, and interpretations. Critical realism advocates for:
a) Causal Mechanisms: Exploring underlying structures and mechanisms that generate observable phenomena.
b) Contextual Understanding: Acknowledging the role of social contexts, historical conditions, and human agency in shaping phenomena.
c) Methodological Pluralism: Embracing a variety of research methods, both quantitative and qualitative, to capture different facets of complex social realities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating philosophical paradigms, ontology, and epistemology is essential for any researcher aiming to conduct rigorous and impactful research. By understanding these foundational concepts and choosing an appropriate philosophical stance such as critical realism, researchers can enhance the depth and validity of their studies. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of these concepts, empowering graduate students and researchers to articulate their research approaches confidently and contribute meaningfully to their fields of study.
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at expertassignment46@gmail.com and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
Pneumonia In Children And Adults

Introduction
Pneumonia stands as a prevalent respiratory infection, exerting a significant burden on global public health. Its impact extends beyond mere morbidity, contributing to substantial healthcare costs and socioeconomic consequences. This discussion aims to elucidate the general nature of pneumonia, encompassing its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, complications, and preventive measures. By indulging into these factors, we aim to provide a better understanding of pneumonia’s complexity and underscore the importance of timely recognition and management.
Pathophysiology

Pneumonia ensues from the infiltration of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and less commonly, parasites, into the lower respiratory tract. Upon inhalation or aspiration of these pathogens, they gain access to the alveoli, where they incite an inflammatory response. This inflammatory cascade triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, recruiting immune cells to the site of infection. Neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes converge to eradicate the invading pathogens, leading to the characteristic consolidation and exudate formation within the affected lung tissue. As the infection progresses, alveolar edema, impaired gas exchange, and parenchymal damage ensue, culminating in the clinical manifestations of pneumonia.
Clinical Presentation

The clinical presentation of pneumonia encompasses a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild respiratory complaints to life-threatening respiratory failure. Common symptoms include cough, productive sputum production, fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, and systemic manifestations such as malaise and fatigue. The severity of symptoms varies depending on factors such as the underlying pathogen, the extent of lung involvement, the host’s immune status, and comorbidities. In pediatric populations, pneumonia may present with nonspecific symptoms such as feeding difficulties, lethargy, and irritability, posing diagnostic challenges. Conversely, elderly individuals may exhibit atypical presentations characterized by confusion, hypothermia, and exacerbations of underlying chronic conditions.
Diagnostic Modalities

The diagnosis of pneumonia hinges on a comprehensive clinical assessment, augmented by various diagnostic modalities to confirm the presence of pulmonary infection and reveal its etiology. A thorough history and physical examination provide invaluable insights into the patient’s symptomatology, risk factors, and clinical trajectory. Symptomatic findings such as crackles, wheezes, and diminished breath sounds may aid in localizing the site of infection and assessing disease severity. Radiographic imaging, notably chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, serves as the cornerstone of pneumonia diagnosis, revealing characteristic radiographic findings such as airspace opacities, lobar consolidation, and interstitial infiltrates. Laboratory investigations, including complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin levels, may corroborate the clinical suspicion of pneumonia and guide therapeutic decisions. Additionally, microbiological testing of respiratory specimens through techniques such as sputum culture, blood cultures, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays facilitates pathogen identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing, thereby informing targeted therapy.
Treatment Strategies

The management of pneumonia hinges on prompt initiation of empiric antimicrobial therapy tailored to the likely causative pathogen(s) and disease severity. Antibiotics represent the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia, with the choice of agent dictated by factors such as local antimicrobial resistance patterns, patient age, comorbidities, and recent antibiotic exposure. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include beta-lactam agents (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, and combination regimens for severe or healthcare-associated infections. Conversely, viral pneumonia necessitates supportive care measures, given the limited efficacy of antiviral agents in most cases. Influenza-associated pneumonia may benefit from neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir, while respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia may warrant ribavirin therapy in select cases. Adjunctive therapies such as oxygen supplementation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids may mitigate respiratory distress and improve clinical outcomes, particularly in severe or hypoxemic patients. The duration of antimicrobial therapy varies depending on factors such as the causative pathogen, clinical response, radiographic resolution, and the presence of complications. Close monitoring of clinical parameters and serial imaging studies guide the decision-making process, enabling clinicians to tailor therapy to individual patient needs.
Complications

Pneumonia harbors the potential for various complications, ranging from mild to life-threatening sequelae, necessitating vigilant monitoring and timely intervention. Common complications include pleural effusion, empyema, lung abscess, respiratory failure, septic shock, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pleural effusion denotes the accumulation of fluid within the pleural space, secondary to inflammation or impaired lymphatic drainage, manifesting as dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and dullness to percussion on physical examination. Empyema represents a purulent collection within the pleural cavity, often complicating bacterial pneumonia and necessitating drainage via thoracentesis or chest tube placement. Lung abscesses manifest as circumscribed cavities containing necrotic debris and pus within the lung parenchyma, triggered by persistent fever, productive cough, and hemoptysis. Respiratory failure ensues from impaired gas exchange and alveolar hypoventilation, caused by worsening hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, necessitating mechanical ventilation and intensive care support. Septic shock represents a life-threatening complication of severe pneumonia, characterized by systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and end-organ dysfunction, requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. ARDS denotes a severe form of acute lung injury, characterized by diffuse alveolar damage, refractory hypoxemia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, necessitating lung-protective ventilation and supportive care in the intensive care unit (ICU). The occurrence of complications portends a poor prognosis and underscores the need for early recognition and intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Preventive Measures

Preventing pneumonia entails a broad approach encompassing vaccination, infection control measures, and health promotion strategies aimed at reducing the risk of respiratory infections and their sequelae. Vaccination stands as a cornerstone of pneumonia prevention, targeting common bacterial and viral pathogens implicated in pneumonia pathogenesis. Vaccines such as the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) confer protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae, the leading bacterial cause of pneumonia, particularly in high-risk populations such as young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. Influenza vaccination remains paramount in mitigating influenza-associated pneumonia and reducing disease transmission, underscoring the importance of annual vaccination campaigns targeting vulnerable populations. Additionally, adherence to infection control measures, including hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and environmental sanitation, plays a pivotal role in reducing the spread of respiratory pathogens in healthcare settings and the community at large. Health promotion efforts aimed at smoking cessation, optimizing nutrition, and addressing underlying comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and immunodeficiency bolster immune resilience and mitigate pneumonia risk. Furthermore, early identification and management of predisposing factors such as malnutrition, homelessness, and overcrowded living conditions attenuate pneumonia susceptibility and enhance overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumonia emerges as a formidable respiratory infection, posing significant challenges to global public health. Its diverse etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment modalities, complications, and preventive measures underscore the nature of pneumonia management. Timely recognition and intervention are imperative in mitigating the morbidity and mortality associated with pneumonia, necessitating a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, public health authorities, and policymakers. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of pneumonia’s manifest and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can strive towards reducing its burden and improving patient outcomes. Through ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts, we can envision a future where pneumonia-related morbidity and mortality are substantially diminished, paving the way for enhanced respiratory health and well-being worldwide.
In managing pneumonia, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are essential alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice allows us to enhance respiratory medicine and patient outcomes.
As we address pneumonia and broader cardiovascular health complexities, let’s remain committed to optimal patient care. Together, we can impact lives positively and foster a healthier future.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance
Cervical Cancer

Introduction
Cervical cancer is a significant health concern affecting women worldwide. It arises from abnormal cell growth in the cervix, often linked to the human papillomavirus (HPV). Despite advancements in prevention and treatment, cervical cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women. Understanding its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies is crucial for early detection and effective management.
1. Understanding Cervical Cancer

Cervical cancer originates in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus connecting to the vagina.
HPV, a common sexually transmitted infection, is a primary cause of cervical cancer, with certain strains posing higher risks.
The body’s immune response typically clears HPV infections, but persistent infections can lead to cervical cell abnormalities and eventually cancer.
2. Symptoms and Diagnosis

Cervical cancer may not present noticeable symptoms initially, making regular screenings essential for early detection.
Symptoms can include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and unusual discharge.
Diagnostic methods include Pap tests, HPV DNA testing, colposcopy, and biopsy to confirm cervical cancer and determine its stage.
3. Treatment Options

Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage, size, and type, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
Surgical interventions, such as hysterectomy or removal of cancerous tissue, are common for early-stage cervical cancer.
Advanced stages may require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy to eliminate cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
4. Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors increase the risk of developing cervical cancer, including HPV infection, smoking, early sexual activity, and weakened immune system.
Prevention strategies include HPV vaccination, routine Pap tests for early detection of precancerous lesions, practicing safe sex, and smoking cessation.
5. Impact on Women’s Health

Cervical cancer not only affects physical health but also has emotional, social, and financial repercussions on women and their families.
Access to screening, vaccination, and treatment services significantly impacts the prognosis and survival rates of women diagnosed with cervical cancer.
Addressing disparities in healthcare access and promoting awareness about cervical cancer prevention are crucial for improving women’s health outcomes globally.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer remains a significant public health challenge despite advancements in prevention and treatment. Early detection through regular screenings and vaccination against HPV can significantly reduce the burden of this disease. Moreover, addressing risk factors such as smoking and promoting safe sexual practices are vital for cervical cancer prevention. By raising awareness, improving access to healthcare services, and advocating for comprehensive cervical cancer prevention programs, we can strive towards reducing the incidence and mortality associated with this preventable disease, ultimately enhancing women’s health and well-being worldwide.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
Digestive System

The digestive system is a marvel of biological engineering, orchestrating the journey of food through the body, from the moment it enters the mouth to its exit through the anus. This complex process involves a network of organs, each playing a crucial role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. In this detailed exploration, we delve into the anatomy, functions, common conditions, care practices, and the importance of seeking medical attention for digestive system issues.
Anatomy of the Digestive System

Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract:
1.Mouth:
Initiating Digestion: Salivary glands activate as the sight and scent of food trigger the digestive process.
Chewing and Mixing: Food is chewed into digestible pieces, mixed with saliva to facilitate breakdown.
Swallowing: The tongue propels the food into the throat and esophagus.
2. Esophagus:
Transportation: A muscular tube conducting food to the stomach through peristalsis.
Sphincter Function: The lower esophageal sphincter relaxes to allow food entry and contracts to prevent stomach content reflux.
3.Stomach:
Container and Mixer: A hollow organ holding and mixing food with stomach enzymes for further breakdown.
Acid Secretion: Cells in the stomach lining secrete powerful acids and enzymes crucial for digestion.
Release to Small Intestine: Processed stomach contents move to the small intestine for further digestion.
4.Small Intestine:
Segments and Functions: Comprising the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, each segment has distinct roles in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Enzymatic Breakdown: Pancreatic enzymes and bile from the liver aid in breaking down food.
Nutrient Absorption: The jejunum and ileum absorb nutrients into the bloodstream.
Consistency Changes: Contents transition from semi-solid to liquid as water, bile, enzymes, and mucus contribute to the process.
Biliary System

a. pancreas:
Enzyme Secretion: Releases digestive enzymes into the duodenum to break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Insulin Production: The pancreas produces insulin, a key hormone for sugar metabolism.
b. Liver:
Nutrient Processing: Processes nutrients absorbed by the small intestine.
Bile Production: Secretes bile into the small intestine, aiding in fat digestion and vitamin absorption.
Detoxification: Acts as the body’s chemical “factory,” detoxifying harmful substances.
c. Gallbladder:
Bile Storage: Stores and concentrates bile from the liver.
Release into Duodenum: Releases bile into the duodenum to assist in fat absorption.
Large Intestine (Colon):
Colon:
Waste Processing: Responsible for transforming waste into a convenient form for bowel movements.
Peristalsis: Propels stool through the colon, removing water and transitioning it from a liquid to a solid state.
Storage and Elimination: Stool is stored in the sigmoid colon until mass movements propel it into the rectum for elimination.
Rectum:
Chamber Function: A straight chamber connecting the colon to the anus.
Signaling and Holding: Signals the brain about stool presence and holds stool until evacuation.
Anus:
Final Elimination: The last part of the digestive tract, consisting of pelvic floor muscles and sphincters.
Sphincter Control: Surrounding sphincter muscles control stool release, preventing involuntary bowel movements.
Conditions and Disorders
Digestive system health can be affected by a spectrum of conditions, ranging from temporary issues to chronic diseases:
Temporary Conditions:
Constipation:
Frequency and Characteristics: Reduced bowel movements with dry and hard stool.
Difficulty and Pain: Straining during bowel movements, leading to discomfort.
2.Diarrhea:
Loose and Watery Stool: Abnormal stool consistency often caused by various factors.
Potential Causes: Bacterial infections, dietary issues, or unknown triggers.
3.Heartburn:
Misleading Name: Despite the name, heartburn is a digestive issue.
Acidic Backflow: Occurs when stomach acids move up the esophagus, causing discomfort in the chest.
4.Hemorrhoids:
Swollen Veins: Enlarged veins inside and outside the anus and rectum.
Symptoms: Pain, discomfort, and rectal bleeding.
5.Stomach Flu (Gastroenteritis):
Viral Infection: Infection of the stomach and upper part of the small intestine.
Duration: Typically lasts less than a week.
6.Ulcers:
Sore Development: Sores on the lining of the esophagus, stomach, or small intestine.
Causes: Helicobacter pylori infection and prolonged use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
7.Gallstones:
Solid Material Formation: Small pieces formed from digestive fluid in the gallbladder.
Chronic Diseases:
GERD (Chronic Acid Reflux):
Frequent Acid Backflow: Acid-containing contents in the stomach frequently leak into the esophagus.
Symptoms: Persistent heartburn and regurgitation.
2,Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
Colon Muscle Dysfunction: Irregular contractions leading to excessive gas, abdominal pain, and cramps.
Chronic Nature: A long-term condition affecting bowel function.
3.Lactose Intolerance:
Inability to Digest Lactose: Results in digestive discomfort after consuming milk and dairy products.
Common Symptoms: Bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
4.Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis:
Colon Pockets Formation: Diverticula (pockets) in the wall of the colon.
Complications: Inflammation (diverticulitis) can occur, causing pain and infection.
5.Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancers:
Tissue and Organ Affliction: Cancers affecting the digestive system, including esophageal, gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers.
6.Crohn’s Disease:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): A lifelong condition causing inflammation in the digestive tract.
7.Celiac Disease:
Autoimmune Disorder: Gluten consumption damages the small intestine.
Trigger: Found in wheat, barley, and rye.
Care Practices for Digestive Health

Maintaining a healthy digestive system involves adopting proactive lifestyle and dietary habits:
1.Hydration:
Importance of Water: Drinking water facilitates smooth food flow, preventing dehydration-related constipation.
Dehydration Consequences: Insufficient water intake can lead to dry and hard stool.
2.Fiber-Rich Diet:
Benefits of Fiber: Supports digestion and regular bowel movements.
Soluble and Insoluble Fiber: Both types contribute to digestive health.
3.Balanced Nutrition:
Fruits and Vegetables: Multiple servings daily for essential vitamins and minerals.
Whole Grains: Choosing whole grains over processed grains.
Limiting Processed Foods: Reducing intake of processed and sugary foods.
4.Probiotics:
Role of Probiotics: Supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
Post-Antibiotic Use: Especially beneficial after antibiotic treatments.
5.Mindful Eating:
Chewing and Digestion: Thorough chewing aids in proper digestion.
Eating Pace: Slower eating allows the body to signal fullness.
6.Physical Activity:
Exercise and Digestion: Physical activity and gravity aid in moving food through the digestive system.
Post-Meal Walks: Taking a walk after meals can enhance digestion.
7.Avoiding Harmful Habits:
Alcohol and Smoking: Limiting alcohol intake to prevent acid-related issues.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking improves digestive symptoms.
8.Stress Management:
Stress and Digestive Issues: Association between stress and conditions like constipation, diarrhea, and IBS.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Incorporating stress-relief practices into daily life.
Seeking Medical Attention
While occasional digestive issues are common, persistent symptoms warrant attention:
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider:
Frequent Symptoms: Constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, excessive gas, or heartburn.
Potential Underlying Issues: Frequent occurrences may indicate a more serious digestive system problem.
2.Importance of Medical Evaluation:
Diagnostic Assessment: Identifying the cause of persistent symptoms.
Early Intervention: Timely treatment prevents potential complications.
3.Collaborative Approach:
Healthcare Professional Guidance: Seeking advice on managing and preventing digestive issues.
Individualized Care: Tailoring interventions based on the individual’s health status and conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the details of the digestive system provides a foundation for promoting digestive health. The collaboration of organs in the GI tract and the biliary system highlights the complexity of the digestive process. Awareness of common conditions, care practices, and the significance of seeking medical attention empowers individuals to prioritize their digestive well-being. Adopting a holistic approach that combines a healthy lifestyle, balanced nutrition, and regular medical check-ups ensures a resilient and well-functioning digestive system, contributing to overall health and vitality.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
14 Common Lung Diseases

Introduction
Lung diseases represent some of the most severe health threats globally. The rise of industrialization, environmental pollution, and tobacco usage significantly contribute to the prevalence of these diseases. This article, outlines the most common lung diseases, their symptoms, causes, and treatments.
1. Pneumonia

Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens. It poses a significant risk to the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and those with chronic conditions but can also affect healthy individuals. Pneumonia can be classified based on the causative agent, such as bacterial pneumonia (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae), viral pneumonia (e.g., influenza virus), or fungal pneumonia (e.g., Pneumocystis jirovecii).
Symptoms
Fever
Cough with sputum
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Sweating and shaking chills
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (less common)
Diagnosis Diagnosis of pneumonia typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures. Blood tests may also be conducted to identify the causative agent.
Treatment Depending on the cause, treatments may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia.
Antiviral medications for viral pneumonia.
Antifungal therapies for fungal pneumonia. Supportive care such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to reduce fever and manage pain can also alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to provide intravenous antibiotics, oxygen therapy, or mechanical ventilation.
2. Bronchitis

Bronchitis involves the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. It can be acute, often following colds or the flu, or chronic, usually resulting from smoking or long-term exposure to irritants like pollution or dust.
Symptoms
Persistent cough (productive or dry)
Sputum production (clear, white, yellowish-gray, or green)
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Slight fever and chills
Chest discomfort
Diagnosis Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, where a doctor listens to the patient’s lungs with a stethoscope. Additional tests, such as a chest X-ray, sputum tests, or pulmonary function tests, may be conducted to rule out other conditions like pneumonia or asthma.
Treatment
Acute bronchitis: Symptomatic treatment includes rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers and cough medications. Inhalers or nebulizers may be prescribed to ease breathing.
Chronic bronchitis: Management may involve bronchodilators, steroids, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Smoking cessation and avoiding lung irritants are crucial for treatment.
3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)

COPD is a progressive, irreversible disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways, primarily due to smoking, environmental pollutants, or long-term exposure to respiratory irritants. COPD includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, conditions that often coexist and lead to airflow obstruction.
Symptoms
Chronic cough
Sputum production
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities
Wheezing
Chest tightness
Frequent respiratory infections
Fatigue
Unintended weight loss (in advanced stages)
Diagnosis COPD is diagnosed through a combination of patient history, physical examination, and spirometry, a test that measures the amount of air a person can exhale and how quickly they can do so. Chest X-rays, CT scans, and arterial blood gas analysis may also be used.
Prevention and Treatment Preventive measures include:
Smoking cessation
Vaccinations (influenza and pneumococcal vaccines)
Reducing exposure to lung irritants
Treatments involves;
Bronchodilators to relax the muscles around the airways
Inhaled steroids to reduce airway inflammation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs
Oxygen therapy for severe cases
Surgery (e.g., lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplant) in advanced cases
4. Lung Cancer

Lung cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the lung tissues. Major risk factors include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, exposure to carcinogens (e.g., asbestos, radon), and genetic predisposition.
Types
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Often linked to heavy smoking, SCLC is aggressive and spreads quickly.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): More common and includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Symptoms
Persistent cough
Chest pain
Weight loss
Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
Shortness of breath
Hoarseness
Bone pain (in advanced stages)
Headache (if cancer spreads to the brain)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves imaging tests (chest X-rays, CT scans, PET scans), sputum cytology, and tissue biopsy. Molecular testing may be done to identify specific genetic mutations that can be targeted with specific treatments.
Treatment
Surgery to remove the tumor or part of the lung
Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells
Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors
Targeted drug therapies to attack specific genetic changes in cancer cells
Immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer
5. Pleurisy
Pleurisy, or pleuritis, is the inflammation of the pleura, the tissue lining the lungs and chest cavity. It can be caused by infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal), injuries, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), or other underlying conditions.
Symptoms
Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens with breathing, coughing, or sneezing
Shortness of breath
Cough
Fever (if infection is present)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a physical examination, chest X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans, and blood tests to identify the underlying cause. Thoracentesis, a procedure to remove and analyze pleural fluid, may be performed.
Treatment Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include:
Antibiotics for bacterial infections
Antiviral medications for viral infections
Anti-inflammatory medications (e.g., NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
Pain management with medications
Thoracentesis to drain excess fluid from the pleural space
6. Pulmonary Embolism

A pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot, usually originating in the legs (deep vein thrombosis), travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow and causing tissue damage. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgery, cancer, and certain genetic conditions.
Symptoms
Sudden shortness of breath
Chest pain (may be sharp and worsen with deep breathing or coughing)
Cough (sometimes with bloody sputum)
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Lightheadedness or dizziness
Leg pain or swelling (if DVT is present)
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves imaging tests such as chest X-rays, CT pulmonary angiography, and ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scans. D-dimer blood tests and ultrasound of the legs may also be conducted.
Treatment Immediate treatment includes:
Anticoagulants (blood thinners) to prevent further clotting
Thrombolytics (clot-dissolving medications) for severe cases
Surgical or catheter-based procedures to remove the clot
Long-term anticoagulation therapy to prevent recurrence
7. Pulmonary Edema

Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of fluid in the lung alveoli, making breathing difficult. It can result from heart failure (cardiogenic pulmonary edema), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), or exposure to high altitudes (non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema).
Symptoms
Difficulty breathing (dyspnea), especially when lying down
Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
Wheezing or gasping for breath
Coughing up frothy, pink-tinged sputum
Excessive sweating
Cyanosis (bluish skin or lips)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves physical examination, chest X-rays, and blood tests. Echocardiography and pulmonary artery catheterization may be used to determine the underlying cause and severity.
Treatment Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause and may include:
Diuretics to remove excess fluid
Medications to improve heart function (for cardiogenic pulmonary edema)
Supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation
Treating underlying conditions such as infections or high altitude exposure
8. Pulmonary Fibrosis

Pulmonary fibrosis is the thickening and scarring of lung tissue, leading to reduced oxygen absorption. Causes include chronic exposure to environmental pollutants, infections, genetic factors, and autoimmune diseases (e.g., scleroderma).
Symptoms
Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
Persistent dry cough
Fatigue
Unexplained weight loss
Aching muscles and joints
Clubbing (widening and rounding) of the fingertips or toes
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, imaging tests (chest X-rays, high-resolution CT scans), pulmonary function tests, and sometimes lung biopsy. Blood tests may be used to identify underlying autoimmune diseases.
Treatment While there is no cure for pulmonary fibrosis, treatments focus on symptom management and slowing progression:
Medications such as pirfenidone and nintedanib to slow disease progression
Oxygen therapy
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Lung transplant in severe cases
9. Pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is a lung disease caused by inhaling dust particles, such as asbestos, silica, or coal dust, leading to lung scarring. It is a type of occupational lung disease commonly seen in miners, construction workers, and industrial workers.
Symptoms:
Chronic cough
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Progressive loss of lung function
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed occupational history, physical examination, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess the extent of lung damage.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Avoiding further exposure to dust
Medications to manage symptoms, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids
Respiratory therapies
Pulmonary rehabilitation
10. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
PAH is a form of high blood pressure affecting the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. It can be idiopathic, familial, or associated with other conditions such as connective tissue diseases, congenital heart disease, or chronic liver disease.
Symptoms
Breathing difficulties (dyspnea), especially during physical activities
Dizziness or fainting (syncope)
Chest pain
Fatigue
Swelling in the ankles, legs, and abdomen (edema)
Cyanosis (bluish lips and skin)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves echocardiography, right heart catheterization, chest X-rays, and CT scans. Blood tests and pulmonary function tests may also be conducted to assess lung and heart function.
Treatment Treatment strategies include:
Medications to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, such as endothelin receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, and prostacyclin analogs
Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
Oxygen therapy
Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots
In severe cases, surgical procedures such as atrial septostomy or lung transplant
11. Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, leading to thick, sticky mucus buildup in the lungs and other organs. This results in frequent infections, respiratory issues, and digestive problems.
Symptoms
Persistent cough with thick mucus
Recurrent lung infections
Wheezing or shortness of breath
Poor growth and weight gain in children
Salty-tasting skin
Severe constipation
Frequent greasy, bulky stools
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves genetic testing, sweat chloride tests, and newborn screening. Pulmonary function tests, chest X-rays, and sputum cultures may also be conducted to assess lung health.
Treatment Management includes:
Medications to thin mucus, antibiotics to treat infections, and bronchodilators to open airways
Chest physiotherapy to clear mucus
Enzyme supplements and high-calorie diets to manage digestive issues
Newer therapies targeting the underlying genetic defect, such as CFTR modulators
12. Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
RDS primarily affects premature infants due to a lack of surfactant, a substance necessary to keep the lungs open and facilitate gas exchange. Risk factors include premature birth, maternal diabetes, and multiple births.
Symptoms
Rapid, shallow breathing
Grunting sounds while breathing
Nasal flaring
Chest retractions (pulling in of the chest muscles)
Cyanosis (bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves clinical assessment, chest X-rays, and blood gas analysis to measure oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Prenatal tests can also help identify at-risk pregnancies.
Treatment Treatment includes:
Surfactant replacement therapy to improve lung function
Mechanical ventilation or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) to support breathing
Oxygen therapy
Supportive care such as fluids and nutrition
13. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is characterized by the growth of granulomas (small clusters of inflammatory cells) in the lungs and other organs, likely as an immune response to unknown triggers. The exact cause remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
Symptoms
Dry cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Fatigue
Fever
Swollen lymph nodes
Skin lesions (e.g., erythema nodosum)
Diagnosis Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, chest X-rays, CT scans, and pulmonary function tests. Biopsy of affected tissues may be performed to confirm the presence of granulomas.
Treatment While sarcoidosis is often self-limiting and may resolve without treatment, severe cases may require:
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Immunosuppressive medications (e.g., methotrexate, azathioprine)
Antimalarial drugs (e.g., hydroxychloroquine) for skin lesions
Regular monitoring and follow-up care to manage chronic cases
14. Asthma
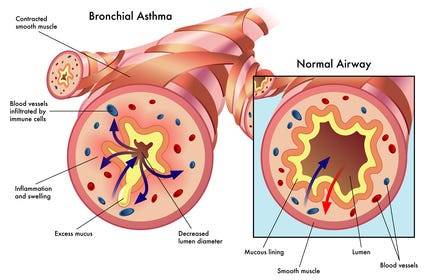
Definition and Causes: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways, causing episodes of wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness, often triggered by allergens, exercise, cold air, or respiratory infections. Genetic and environmental factors contribute to its development.
Symptoms
Wheezing
Shortness of breath
Chest tightness
Coughing, especially at night or early morning
Increased mucus production
Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests (spirometry, peak flow measurement). Allergy testing and chest X-rays may also be conducted to identify triggers and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Management includes:
Avoiding known triggers
Inhalers (bronchodilators for quick relief, corticosteroids for long-term control)
Long-term control medications (e.g., leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta agonists)
Immunotherapy (allergy shots) for severe allergies
Asthma action plans to manage symptoms and prevent attacks
Conclusion
Lung diseases encompass a wide range of conditions, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. Preventive measures such as avoiding smoking, reducing exposure to environmental pollutants, and timely vaccinations can significantly reduce the risk of developing many of these diseases. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by lung diseases. For personalized medical advice and treatment, consult with healthcare professionals.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Email us: expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional guidance.
What Are The Benefits Of Online Exam Assistance?

Introduction
In today’s dynamic academic and professional landscape, the prevalence of online exams has surged, offering learners unparalleled flexibility and convenience. This comprehensive guide explores the pivotal role of online exam assistance in facilitating effective exam preparation and maximizing success. From understanding the significance of online exam support to actionable tips for optimizing the exam-taking experience, this guide aims to equip learners with the knowledge and strategies necessary to excel in online assessments.
Understanding the Importance of Online Exam Assistance
Online exam assistance has revolutionized the traditional approach to assessments, offering learners unparalleled flexibility and convenience. In an era characterized by hectic schedules and diverse commitments, the ability to schedule exams according to personal convenience transcends geographical constraints and empowers individuals to pursue academic and professional goals with unprecedented ease. Moreover, online exam assistance encompasses a myriad of valuable resources and support mechanisms, ranging from practice tests to personalized guidance, that enhance the learning experience and foster academic excellence.
Tips to Maximize the Benefits of Online Exam Assistance
a). Familiarize Yourself with the Exam Format: A thorough understanding of the exam format is essential for devising effective strategies and managing time efficiently during assessments. By familiarizing oneself with the structure and types of questions, learners can approach each section with confidence, thereby maximizing their chances of success.
b). Practice Regularly with Mock Exams: Mock exams serve as indispensable tools for assessing readiness and identifying areas for improvement. By simulating the exam environment, learners can gauge their performance, alleviate test anxiety, and build confidence, ultimately enhancing their preparedness for the actual exam.
c). Develop a Structured Study Plan: A well-structured study plan tailored to individual needs ensures comprehensive coverage of the exam syllabus and minimizes the risk of last-minute cramming. By breaking down the material into manageable sections and incorporating regular review sessions, learners can reinforce learning and retain key concepts effectively.
d). Utilize Online Resources Wisely: The plethora of online resources available, including video tutorials, interactive quizzes, and discussion forums, provides learners with diverse avenues for enhancing understanding and reinforcing concepts. Seeking personalized assistance from online exam assignment help services further augments exam preparation and offers expert guidance when needed.
e). Minimize Distractions During Exam Sessions: Creating a conducive exam environment free from distractions is paramount for maintaining focus and concentration. By selecting a quiet location and minimizing electronic notifications, learners can mitigate interruptions and uphold exam integrity, thereby optimizing performance.
f). Manage Your Time Effectively: Effective time management is critical for success in online exams, particularly those with timed or strict deadlines. Prioritizing questions, pacing oneself accordingly, and revisiting challenging items strategically enhance efficiency and productivity during the assessment.
g). Review and Revise Your Answers: Allocating time to review and revise answers before submission is essential for identifying errors or omissions and ensuring clarity and accuracy in responses. Attention to detail, including spelling, grammar, and formatting, reflects positively on the candidate’s proficiency and enhances the overall quality of the answers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, online exam assistance offers a myriad of benefits for learners, ranging from flexibility and convenience to valuable resources and support mechanisms. By implementing the recommended tips and strategies outlined in this guide, individuals can harness the full potential of online exam assistance and maximize their chances of success in academic and professional endeavors. With a proactive approach, meticulous preparation, and utilization of available resources, learners can navigate online assessments with confidence and achieve their desired outcomes.
For additional academic support, turn to Expert Academic Assignment Help. Our services span online classes, assignments, essay writing, research, and more. We understand the challenges students face and offer personalized assistance to help you excel. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for tailored solutions and achieve academic success with our expertise by your side.
What Are The Tips & Tricks for Writing an Effective Rhetorical Analysis Essay ?

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can be a challenging yet highly rewarding task. It requires a deep and thorough examination of how authors use rhetoric to convey their messages and persuade their audiences. Whether you are a student looking to enhance your essay writing skills or someone seeking professional assistance, this comprehensive guide will provide you with the tips and tricks needed to craft a compelling rhetorical analysis essay.
Understand the Purpose of a Rhetorical Analysis Essay
Before getting into the writing process, it is crucial to fully understand the purpose of a rhetorical analysis essay. Unlike a summary or a simple critique, a rhetorical analysis focuses on how the author uses language to influence the audience. This includes examining the use of ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), and logos (logic). By understanding these elements, you can better appreciate the author’s techniques and their effectiveness.
A rhetorical analysis essay goes beyond merely discussing what the author is saying; it analyzes the techniques used to communicate the message and their impact on the audience. Understanding the purpose of the essay sets the foundation for a detailed and insightful analysis.
Develop a Strong Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
An effective rhetorical analysis essay begins with a well-organized outline. A clear outline will guide you through the writing process and ensure that you include all necessary components. Here’s a basic structure for a rhetorical analysis essay outline:
Introduction
Hook: Start with an engaging opening sentence to grab the reader’s attention.
Background Information: Provide context about the text you are analyzing.
Thesis Statement: Present your main argument or the purpose of your analysis.
Body Paragraphs
Ethos: Discuss how the author establishes credibility. Provide examples and analyze their effectiveness.
Pathos: Examine how the author appeals to the audience’s emotions. Use specific instances from the text to support your points.
Logos: Analyze the logical arguments and evidence presented by the author. Evaluate their validity and impact.
Conclusion
Restate your thesis in a new light based on the analysis conducted.
Summarize key points discussed in the body paragraphs.
Provide a final thought or call to action, emphasizing the importance of your analysis.
Detailed Breakdown of Each Section
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for your analysis. Begin with a compelling hook to grab your reader’s attention. This could be an intriguing quote, a startling statistic, or a thought-provoking question related to the text you are analyzing. The goal is to pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
Next, provide some background information about the text. This includes the title, author, publication date, and any relevant historical or cultural context. This information helps the reader understand the context of the rhetorical strategies you will analyze.
Finally, present your thesis statement. This should be a clear and concise statement that outlines your main argument or the purpose of your analysis. Your thesis should indicate the rhetorical strategies you will discuss and their overall effectiveness in conveying the author’s message.
Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are the heart of your rhetorical analysis essay. Each paragraph should focus on a specific rhetorical strategy and provide detailed examples from the text to support your analysis.
Ethos: Ethos refers to the credibility of the author. Discuss how the author establishes their credibility and authority on the subject matter. This could include their qualifications, experience, or the use of reputable sources. Analyze how the author’s credibility impacts the audience’s perception and trust in the message.
Pathos: Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions. Examine how the author uses emotional appeals to connect with the audience. This could include vivid descriptions, personal anecdotes, or evocative language. Analyze specific instances where the author evokes emotions such as sympathy, anger, or joy, and discuss their effectiveness in persuading the audience.
Logos: Logos refers to logical arguments and evidence. Analyze how the author uses logical reasoning and factual evidence to support their arguments. This could include statistics, logical deductions, or empirical evidence. Evaluate the strength and validity of the logical appeals and their role in reinforcing the author’s message.
Each body paragraph should follow a clear structure: start with a topic sentence that introduces the rhetorical strategy, provide specific examples from the text, analyze the effectiveness of these examples, and connect them back to your thesis.
Conclusion
The conclusion should provide a concise summary of your analysis. Restate your thesis in a new light based on the analysis conducted in the body paragraphs. Summarize the key points discussed, highlighting the most significant rhetorical strategies and their impact on the audience.
Finally, provide a final thought or call to action. This could be a reflection on the broader implications of your analysis, a suggestion for future research, or a statement about the overall importance of understanding rhetorical strategies. Your conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader and emphasize the significance of your analysis.
Utilize an Essay Typer for Inspiration
If you’re struggling to get started, using an essay typer can be a helpful tool. An essay typer can generate essay examples based on the topic you provide. While you should not copy the generated content verbatim, it can give you ideas and structure for your own writing. Use it as a brainstorming tool to develop your unique analysis.
Essay typers can help you overcome writer’s block by providing a starting point for your essay. They can suggest potential topics, provide examples of thesis statements, and outline possible structures for your analysis. However, it is important to critically evaluate and customize the generated content to ensure it aligns with your own insights and arguments.
Seek Essay Writing Help Online

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can be daunting, especially if you’re unfamiliar with the nuances of rhetorical strategies. Fortunately, numerous online services offer essay writing help. But Expert Academic Assignment Help is Exceptional ,it can provide you with professional guidance, from developing your thesis to structuring your essay and refining your arguments. Don’t hesitate to seek help if you need it professional assistance can significantly improve the quality of your essay.
Expert Academic Assignment Help writing services can offer personalized feedback and suggestions to enhance your writing. They can help you refine your thesis, develop a coherent structure, and ensure your analysis is thorough and insightful. Additionally, they can provide editing and proofreading services to ensure your essay is polished and free of errors.
Focus on a Compelling Essay Conclusion
A compelling conclusion is essential to leave a lasting impression on your reader. Your conclusion should not merely restate the thesis but also synthesize the key points discussed in your essay. Highlight the significance of your analysis and suggest broader implications or future areas of study. If you find this challenging, consider seeking Expert Academic Assignment Help writing help to ensure your essay ends on a strong note.
A strong conclusion should provide a sense of closure and completeness. It should reinforce the main arguments presented in your essay and emphasize their importance. Consider discussing the broader impact of the author’s rhetorical strategies on the audience or the relevance of your analysis in a larger context. This will help underscore the significance of your work and leave a lasting impression on your reader.
Proofread and Revise

Finally, always proofread and revise your essay. Look for grammatical errors, awkward phrasing, and inconsistencies in your analysis. It’s helpful to read your essay aloud to catch mistakes you might have missed during silent reading. Revising your essay ensures that your arguments are clear and that your writing is polished and professional.
Proofreading and revision are crucial steps in the writing process. They help you identify and correct errors, improve clarity and coherence, and enhance the overall quality of your essay. Consider seeking feedback from peers or using online editing tools to ensure your essay is free of errors and effectively communicates your analysis.
Additional Tips……
Analyze, Don’t Summarize: Focus on analyzing the rhetorical strategies rather than summarizing the content of the text. Your goal is to examine how the author uses language to achieve their purpose and persuade the audience, not to simply restate what the author says.
Use Quotes Sparingly: Include relevant quotes from the text to support your analysis, but ensure they are integrated seamlessly into your writing. Avoid overusing quotes and ensure that each quote is followed by your own analysis and interpretation.
Stay Objective: Maintain an objective tone and avoid letting your personal opinions overshadow the analysis. Focus on the author’s rhetorical strategies and their effectiveness, rather than expressing your own views on the topic.
Write Frequently: Just like any other skill, writing improves with practice. Regularly write and analyze different texts to own your rhetorical analysis skills. Practice will help you develop a keen eye for rhetorical strategies and improve your ability to articulate your analysis effectively.
Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure your writing is clear and concise. Avoid unnecessary jargon or overly complex sentences. Your goal is to communicate your analysis effectively, so clarity is key.
Develop Your Analytical Skills: Improve your ability to identify and analyze rhetorical strategies by reading and analyzing a wide range of texts. This will help you develop a deeper understanding of how authors use rhetoric and improve your analytical skills.
Seek Feedback: Share your essay with peers or instructors to get feedback on your analysis. Constructive feedback can help you identify areas for improvement and refine your writing.
In conclusion, writing a rhetorical analysis essay involves a careful examination of how authors use rhetorical strategies to persuade their audience. By following a structured outline, seeking essay writing help online, and focusing on a strong conclusion, you can develop a compelling and insightful analysis. Remember, the key is to analyze, not summarize, and to back up your points with concrete examples from the text. Happy Excellent writing!
For any enquiries and professional assistance ,
Email:expertassignment46@gmail.com
What Are The Steps to Writing a Book Summary?

Writing a book summary is a valuable skill that enables you to convey the essence of a book concisely and effectively. Whether for academic purposes, book reviews, or personal use, a well-crafted summary captures the main ideas and key details without unnecessary elaboration. This comprehensive guide indulges into the detailed steps and provides examples for writing a book summary. It also integrates keywords to demonstrate how these resources can enhance the summary-writing process.
Step 1: Read the Book Carefully
Reading the book carefully is the foundation of writing a good summary. This step involves:
Active Reading: Engage with the text by asking questions and making connections to other readings or real-life situations.
Note-Taking: Highlight important passages and take notes on key events, character developments, and significant quotes.
Understanding the Context: Research the historical, cultural, and biographical context of the book to gain a deeper understanding of its themes and messages.
Step 2: Identify the Main Themes and Ideas
Identifying the main themes and ideas requires:
Theme Analysis: Look for recurring subjects or concepts throughout the book. Themes are often explored through the actions and experiences of the characters.
Character Analysis: Understand the motivations, growth, and conflicts of the main characters. How do they contribute to the overall themes?
Plot Analysis: Break down the plot into its essential components (exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution) and see how each part contributes to the overall message.
Step 3: Create an Outline
Creating an outline helps organize your thoughts and ensures a logical flow in your summary. The outline should include:
Introduction: Briefly introduce the book’s setting, main characters, and initial situation.
Body: Divide the body into sections corresponding to the book’s major plot points. Include the rising action, climax, and falling action.
Conclusion: Summarize the resolution of the story and restate the main themes.
Step 4: Write the Summary
Writing the summary involves:
Conciseness: Avoid unnecessary details and focus on the main points. Each sentence should add value to the summary.
Clarity: Use clear and straightforward language. Ensure that your summary is easy to read and understand.
Accuracy: Make sure your summary accurately reflects the book’s content and the author’s intentions.
Step 5: Review and Revise
Reviewing and revising your summary ensures its quality. This process includes:
Checking for Errors: Correct any grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors.
Improving Coherence: Ensure that your summary flows logically from one point to the next.
Enhancing Clarity: Rewrite any ambiguous or confusing sentences. Make sure that each point is clearly explained.
Conclusion
Writing a book summary is a multi-step process that involves careful reading, theme identification, outlining, writing, and revising. Utilizing tools and services like “summary maker Assignment Help,” “write my essay online,” “Write My Essay service,” “my assignment help,” and “online assignment help” can greatly enhance your ability to produce high-quality summaries. By following these steps and leveraging available resources, you can effectively convey the essence of any book. This skill not only contributes to academic success but also enhances your ability to critically engage with and communicate about various texts, making it an invaluable asset in both educational and professional contexts.
Expert Academic Assignment Help offers top-tier support for university students. Our services include expert assistance with essays, dissertations, assignments, research projects, and writing book summaries. Enhance your academic performance with our professional guidance and support.
For help and guidance, email us at: expertassignment46@gmail.com
The Pathophysiology Of Spondylitis

Spondylitis is a comprehensive term used to describe a group of chronic inflammatory diseases that primarily affect the joints of the spine and the sacroiliac region, which includes the pelvis and lower spine. These conditions are characterized by arthritis-like symptoms and can lead to significant discomfort, reduced mobility, and other systemic complications. This detailed exploration will indulge into the nature of spondylitis, how it differs from the related condition known as spondylosis, the various types of spondylitis, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and complementary therapies.
What is Spondylitis?

Spondylitis involves inflammation of the joints, tendons, and ligaments within the spine and sacroiliac region. Tendons are connective tissues that attach muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones. This inflammation can result in the fusion of bones (ankylosis) and the formation of new bone, leading to stiffness and reduced flexibility in the spine. In severe cases, excessive bone growth can cause significant curvature of the spine, known as kyphosis.
Spondylitis vs. Spondylosis
While both spondylitis and spondylosis cause pain in the hip and back, they are distinct conditions with different etiologies and characteristics.
Spondylitis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation, bone fusion, and excessive bone formation. This condition typically develops in teenagers and young adults and can affect multiple organs and systems within the body.
Spondylosis, on the other hand, is a degenerative condition associated with aging and the natural wear and tear of the spine. It involves the degeneration of spinal joints and discs, often accompanied by the formation of bone spurs (osteophytes). Spondylosis primarily affects older individuals, with more than 85% of people over the age of 60 experiencing this condition.
Types of Spondylitis

Medical professionals categorize spondylitis using two primary classification systems: the traditional system and the newer system. The traditional system recognizes six specific types of spondylitis, whereas the newer system categorizes spondylitis into two broad types based on the affected body region.
Traditional Spondylitis Classifications:
a) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Symptoms: Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine, causing symptoms such as fatigue, chronic back pain, stiffness, and inflammation in various areas of the body, including joints and tendons. Over time, the vertebrae may fuse, leading to reduced mobility and flexibility.
Causes: The exact cause of AS is unknown, but a strong genetic association exists with the HLA-B27 gene. Approximately 90% of individuals with AS carry this gene, although not all carriers develop the disease.
b) Reactive Arthritis
Symptoms: Reactive arthritis typically presents with a triad of symptoms including arthritis (swelling and pain in joints), conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eyes with a sticky discharge), and urethritis (genital and bladder inflammation with painful urination). However, not all patients exhibit all three symptoms.
Causes: often follows a gastrointestinal infection or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). The immune system overreacts to the initial infection, leading to inflammation and joint pain. The HLA-B27 gene is also strongly linked to ReA, with 30–50% of affected individuals carrying this gene.
c) Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Symptoms: Psoriatic arthritis is associated with the inflammatory skin condition psoriasis. Symptoms include dactylitis (swelling in toes and fingers), changes in nails (such as pitting), eye pain, joint pain, reduced range of motion, and fatigue. PsA typically affects people aged 30–50.
Causes: PsA often follows psoriasis, but it can also develop in individuals without skin symptoms. There is a genetic predisposition to PsA, with at least 10% of the population inheriting genes that increase susceptibility to psoriasis and PsA.
d) Enteropathic Arthritis (EnA)
Symptoms
Enteropathic arthritis is linked to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and joint swelling and pain.
Causes
The precise cause of EnA is unclear, but it is associated with chronic inflammation in the bowel. This inflammation may allow bacteria to penetrate the bowel wall, triggering an immune response that leads to joint inflammation. The HLA-B27 gene is also linked to EnA.
d) Juvenile Spondyloarthritis (JSpA)
Symptoms
Juvenile spondyloarthritis begins in individuals aged 16 or younger and typically affects the leg joints. Symptoms include joint pain, tenderness, and bowel inflammation.
Causes
Similar to adult spondylitis, JSpA is often associated with the HLA-B27 gene. The exact cause remains unknown, but genetic and environmental factors likely play a role.
e)Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis (USpA)
Symptoms
USpA is characterized by a variety of symptoms that do not fit neatly into a specific rheumatoid disorder. Symptoms may include persistent lower back pain, joint pain in small and large joints, heel pain, swelling in hands and feet, general stiffness, eye inflammation, rash, urinary tract symptoms, and intestinal inflammation.
Causes
The causes of USpA are diverse and not fully understood. It encompasses a range of symptoms that do not meet the criteria for other specific types of spondylitis.
Newer Spondylitis Categorizations
Peripheral Spondyloarthritis (pSpA)
Peripheral spondyloarthritis affects joints and tendons outside the spine and sacroiliac joints, such as the hands, wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, ankles, and feet. It includes forms of spondylitis such as reactive arthritis, enteropathic arthritis, and undifferentiated arthritis.
2. Axial Spondyloarthritis (AxSpA)
Axial spondyloarthritis involves inflammation and pain in the pelvis and spine. This category covers a broad range of spondylitis types and includes individuals with and without sacroiliac joint fusion. AxSpA is further subdivided into non-radiographic AxSpA (without visible joint damage on X-rays) and radiographic AxSpA (visible joint damage).
Diagnosis
Diagnosing spondylitis involves abroad approach, combining physical examination, medical history, and various diagnostic tests. There is no single definitive test for spondylitis, making a comprehensive evaluation essential.
a) Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and family history of autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and spondyloarthritis. The examination may include evaluating joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
b) Diagnostic Tests
Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation, such as elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP). Testing for the presence of the HLA-B27 gene can also provide valuable information, although not all individuals with spondylitis carry this gene.
Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques are crucial for diagnosing spondylitis and assessing the extent of joint and bone damage.
X-rays: X-rays can reveal changes in the spine and sacroiliac joints, such as joint fusion and bone spurs.
MRI Scans: MRI scans provide detailed images of soft tissues and can detect early signs of inflammation and joint damage that may not be visible on X-rays.
Ultrasound Scans: Ultrasound scans can be used to assess inflammation in peripheral joints and tendons.
Genetic Testing: Testing for the HLA-B27 gene can support the diagnosis, particularly in cases where clinical symptoms and imaging findings are inconclusive.
Treatment
While there is no cure for spondylitis, various treatments can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and disease severity.
Medications
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs are commonly used to reduce inflammation and pain in spondylitis patients. Examples include ibuprofen and naproxen.
Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can be prescribed for short-term use to control severe inflammation and pain.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs, including methotrexate and sulfasalazine, can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression in some types of spondylitis.
Biologic Agents: Biologic agents, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (e.g., adalimumab, etanercept) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitors (e.g., secukinumab), target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage.
Analgesics: Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, may be used to manage pain when inflammation is not the primary issue.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing spondylitis by improving and maintaining spine flexibility and overall mobility. Techniques may include:
Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain.
Spinal Manipulation: Performed by a trained physical therapist or chiropractor, spinal manipulation can enhance mobility and reduce pain.
Exercises: Tailored exercise programs can help strengthen muscles, improve posture, and enhance flexibility. Stretching exercises are particularly beneficial for maintaining spine and joint flexibility.
Breathing Exercises: Breathing exercises are essential for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis, as the condition can affect chest expansion and respiratory function. These exercises help maintain normal lung function and prevent restrictive lung disease.
Surgery: Surgery is generally considered a last resort and is reserved for severe cases where conservative treatments have failed. Surgical options include:
Joint Replacement: For patients with severe joint damage, joint replacement surgery (e.g., hip or knee replacement) can restore function and relieve pain.
Spinal Surgery: In cases of severe spinal deformity or nerve compression, spinal surgery may be necessary to correct curvature and alleviate pressure on nerves.
Complementary Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, complementary therapies can provide additional symptom relief and improve overall well-being. These therapies are often used alongside standard medical treatments.
Massage Therapy: Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension, improve blood circulation, and alleviate pain and stiffness in the affected areas.
Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can help manage stress and reduce pain perception.
Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to improve flexibility, strength, and relaxation. Yoga can be particularly beneficial for maintaining spine flexibility and reducing pain.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system and promote natural pain relief and healing.
Cupping: Cupping is a traditional therapy that involves placing suction cups on the skin to improve blood flow and reduce muscle tension. It can be used to alleviate pain and stiffness in the back and other affected areas.
Summary
Spondylitis encompasses a range of chronic inflammatory diseases that affect the spine and sacroiliac region. It is characterized by autoimmune-driven inflammation, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and potential bone fusion. Spondylitis is distinct from spondylosis, a degenerative condition associated with aging. Medical professionals classify spondylitis into various types based on symptoms and affected body regions. Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, blood tests, imaging, and genetic testing. While there is no cure, treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and complementary therapies can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected by spondylitis. By understanding the nature of spondylitis and the available management strategies, individuals can better navigate their condition and maintain an active, fulfilling life.
Medical students and healthcare professionals need to stay informed about the latest advancements in diagnosing and treating spondylitis. Continuous education and expert guidance are crucial for managing these complex conditions. For additional support with challenging medical units, clinical studies, research projects, assignments, and exam preparation, Expert Academic Assignment Help offers professional resources and online classes. For personalized assistance, contact expertassignment46@gmail.com Accessing expert guidance can significantly enhance your understanding and proficiency in medical education.
What is The Process Of Sleep?

Introduction
Sleep is a complex physiological process that encompasses more than merely closing one’s eyes and drifting into unconsciousness. It is an active state of unconsciousness in which the brain, while relatively at rest, remains responsive primarily to internal stimuli. Despite extensive research, the precise purpose of sleep remains incompletely understood. Several prominent theories attempt to elaborate the purpose of sleep, including the Inactivity Theory, Energy Conservation Theory, Restoration Theory, and Brain Plasticity Theory.
Inactivity Theory involves that inactivity during nighttime reduces the risk of predation, offering an evolutionary advantage. This theory suggests that creatures that remained inactive during the night were less likely to fall victim to predators, thereby enhancing survival and reproductive success.
Energy Conservation Theory proposes that the primary function of sleep is to decrease energy demand during periods when it is less efficient to procure food, supported by evidence of a 10% reduction in metabolism during sleep. This theory aligns with the observation that many species exhibit lower metabolic rates during sleep, thereby conserving energy.
Restorative Theory asserts that sleep facilitates the repair and replenishment of cellular components, as evidenced by processes such as muscle repair, tissue growth, protein synthesis, and hormone release occurring predominantly during sleep. This theory is supported by findings that various restorative functions are activated during sleep, promoting physical health and well-being.
Brain Plasticity Theory suggests that sleep is essential for neural reorganization and brain development, particularly in infants and children who require extensive sleep. This theory underscores the role of sleep in cognitive functions, learning, and memory consolidation.
These theories collectively indicate that sleep serves multiple functions, and a combination of these concepts likely explains the necessity of sleep.
Function

Sleep follows a cyclical pattern, alternating between two major phases: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is subdivided into stages 1 through 3, each representing different depths of sleep characterized by unique brain wave patterns, muscle tone, and eye movement patterns. NREM sleep comprises approximately 75–80% of total sleep time, while REM sleep accounts for the remaining 20–25%.
The sleep cycle begins with a short NREM stage 1 phase, progresses through NREM stages 2 and 3, and culminates in REM sleep. This cycle repeats throughout the night, with initial cycles lasting 70–100 minutes and subsequent cycles 90–120 minutes. As the night progresses, the duration of REM sleep increases, eventually comprising up to 30% of the sleep cycle later in the night. Typically, an individual undergoes 4 to 5 sleep cycles per night.
NREM Stage 1: A shallow sleep stage lasting 1–7 minutes, characterized by rhythmical alpha waves (8–13 Hz). This stage represents the transition from wakefulness to sleep, during which the individual can be easily awakened.
NREM Stage 2: A deeper sleep state lasting 10–25 minutes initially, progressing to encompass 50% of the total sleep cycle. EEG recordings during this stage show sleep spindles and K-complexes. Memory consolidation is believed to occur primarily in this stage.
NREM Stage 3: Lasting 20–40 minutes initially, characterized by high-voltage, slow-wave frequency on EEG. This stage, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), is crucial for restorative processes.
REM Sleep: Responsible for dreaming, characterized by muscle paralysis (except for the extraocular muscles) and sawtooth waveforms on EEG. REM sleep involves increased brain activity and is essential for cognitive functions such as learning, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation.
Mechanism

The regulation of sleep involves a delicate balance between homeostatic processes and circadian rhythms.
a) Homeostatic Processes
These processes reflect the body’s need for sleep, increasing the pressure to sleep the longer one stays awake. Sleep generation is initiated within the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO) of the anterior hypothalamus, which inhibits arousal regions in the brain, including the tuberomammillary nucleus, lateral hypothalamus, locus coeruleus, dorsal raphe, laterodorsally segmental nucleus. Hypocretin (orexin) neurons in the lateral hypothalamus facilitate this process synergistically.
b) Circadian Rhythm
The circadian rhythm, or the internal body clock, regulates the sleep-wake cycle and is influenced by light levels detected by the retina. The hypothalamus, particularly the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN),initiates this rhythm. Melatonin, produced by the pineal gland, modulates the circadian rhythm, with levels peaking at night and decreasing during the day. The circadian rhythm typically spans approximately 24.2 hours, and variations in body temperature also play a role, with lower temperatures in the morning and higher temperatures in the evening.
NREM sleep involves a functional disconnection between the brain stem, thalamus, and cortex, maintained by hyperpolarizing GABA neurons. During this phase, corticothalamic neurons signal the thalamus, causing hyperpolarization of thalamic reticular neurons, resulting in delta waves from both thalamic reticular and cortical pyramidal sources.
REM sleep is generated by “REM-on neurons” in the mesencephalic and pontine cholinergic neurons. The pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus and lateral dorsal tegmental neurons trigger desynchronized cortical waveforms. The tonic component of REM sleep is parasympathetically mediated, while the phasic component is sympathetically mediated.
Related Testing
Polysomnography is the primary modality used to study sleep. It is a comprehensive test that includes an electrocardiogram (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), electrooculography (EOG), electromyography (EMG), and oxygen saturation monitoring.
ECG: Measures the electrical activity of the heart to detect cardiac anomalies such as arrhythmias.
EEG: Non-invasively records brain wave activity to determine sleep stages and detect neurological abnormalities.
EOG: Measures eye movements to differentiate between NREM and REM sleep.
EMG: Assesses muscle activity, particularly in the respiratory muscles and peripheral limbs, to detect excessive movement or muscle tension during sleep.
Oxygen Saturation: Monitors respiratory function to ensure adequate oxygenation during sleep.
Clinical Significance

a) .Insomnia
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep and is the most common sleep disorder. It is often related to psychological stressors, poor sleep environments, irregular sleep schedules, or excessive mental, physical, or chemical stimulation. Treatment typically involves cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), sleep hygiene practices, and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions.
b) .Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
OSA is marked by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep due to airway obstruction, often caused by obesity or weak pharyngeal muscles. This condition leads to hypoxia and frequent awakenings, preventing restful sleep. OSA is classified into mild, moderate, and severe based on the frequency of apneic episodes per hour. Treatment options include Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) therapy, mandibular advancement devices, and surgical interventions such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, adenotonsillectomy, and maxillomandibular advancement.
c) .Central Sleep Apnea
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) results from a failure in the central respiratory drive, leading to diminished breathing effort during sleep. Conditions such as congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (Ondine’s curse) or congestive heart failure can cause CSA. Treatment includes CPAP, BiPAP, Adaptive-servo-ventilation, and medications like acetazolamide or theophylline.
d) .Mixed Sleep Apnea
Mixed Sleep Apnea, also known as Complex Sleep Apnea, involves symptoms of both OSA and CSA. This condition typically manifests when patients with OSA develop CSA symptoms upon treatment with CPAP. Treatment often involves low-pressure CPAP therapy.
d) .Ghrelin-Leptin Abnormalities
Sleep duration significantly influences hunger-regulating hormones, with reduced sleep linked to lower levels of leptin and higher levels of ghrelin. Leptin, produced by adipose cells, inhibits hunger, while ghrelin, produced in the gastrointestinal tract, stimulates appetite. Imbalances in these hormones due to inadequate sleep can increase appetite and contribute to higher body mass index (BMI), potentially leading to obesity. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in patients with OSA, where increased BMI is a risk factor.
e) .Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is characterized by a loss of orexin (hypocretin) neurons, leading to unstable transitions between sleep and wakefulness. Symptoms include excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, sleep paralysis, and hypnagogic hallucinations. Narcolepsy type 1 involves a significant loss of orexin neurons, while type 2 is less severe. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with medications such as stimulants, sodium oxybate, and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs and SNRIs), along with lifestyle modifications.
f) .Somnambulism (Sleepwalking)
Somnambulism, or sleepwalking, involves performing activities while in a state of combined sleep and wakefulness. Sleepwalking is associated with increased slow-wave sleep and sleep deprivation, and there is evidence of a genetic predisposition. Treatment includes ensuring a safe sleep environment, improving sleep hygiene, and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions such as benzodiazepines.
Conclusion
Sleep is a physiological process essential for various bodily functions, including energy conservation, cellular repair, brain development, and cognitive function. The precise mechanisms and purposes of sleep remain areas of active research. Understanding the complexities of sleep and its disorders is crucial for promoting overall health and addressing various medical conditions. Ongoing research aims to fully understand the mechanisms of sleep and its broad implications for human health..
Navigating the rigorous demands of medical studies requires support and collaboration. Whether you’re a nursing student, medical doctor, clinical student, pharmacist, or any other medical practitioner, don’t hesitate to seek assistance. Utilize available resources and value teamwork and mentorship.
For personalized support, expert advice, and comprehensive resources, contact Expert Academic Assignment Help at expertassignment46@gmail.com With the right support and dedication, you can achieve your goals and make significant contributions to healthcare.
How Does The Brain Work?

The brain stands as a marvel of biological engineering, Composing of a multitude of bodily functions ranging from cognition and memory to emotions and sensory perception. Together with the spinal cord, it constitutes the central nervous system (CNS), the command center of the human body.
Composition of the Brain

Weighing approximately 3 pounds in adults, the brain’s main structure comprises about 60% fat, interspersed with water, protein, carbohydrates, and salts. Unlike muscles, it houses a complex network of blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
a) Gray and White Matter
Within the central nervous system, gray matter and white matter occupies distinct regions. In the brain, gray matter forms the outer layer, rich in neuron somas, while white matter constitutes the inner section, primarily composed of axons unsheathed in myelin. Conversely, in the spinal cord, this arrangement is reversed.
b) Brain Functionality
The brain operates by transmitting and receiving chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. These signals regulate a myriad of processes, with the brain disseminating each input. Some signals remain confined within the brain, while others traverse the spinal cord and nerves, disseminating information across the body’s expanse. This composes neural network relies on billions of interconnected neurons.
Major Brain Regions and Their Functions

1.Cerebrum
Dominating the brain’s landscape, the cerebrum encompasses the cerebral cortex and underlying white matter. It governs a spectrum of functions, including motor coordination, temperature regulation, language processing, emotional regulation, and sensory perception.
2. Brainstem
Serving as the bridge between the cerebrum and spinal cord, the brainstem comprises the midbrain, pons, and medulla. It regulates vital autonomic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and reflexive responses.
3. Cerebellum
Nestled at the posterior aspect of the brain, the cerebellum coordinates voluntary muscle movements, posture, balance, and motor learning.
Brain Coverings

a) Meninges
Three layers of protective membranes, collectively known as meninges, enshroud the brain and spinal cord. These layers — dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater — shield the delicate neural tissue from physical trauma and infection.
b) Lobes of the Brain
Each hemisphere of the brain comprises four lobes, each harboring distinct functional domains:
Frontal Lobe: Governing executive functions, motor control, and higher cognitive processes.
Parietal Lobe: Integrating sensory information, spatial awareness, and perception of pain and touch.
Occipital Lobe: Specialized for visual processing and perception.
Temporal Lobe: Involved in auditory processing, language comprehension, and memory consolidation.
Deeper Brain Structures
These encompass important structures such as the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and pineal gland, orchestrating hormone secretion, emotional regulation, memory consolidation, and circadian rhythms.
Blood Supply
The brain receives its oxygenated blood supply through the vertebral and carotid arteries, ensuring adequate perfusion of neural tissue. The main network of blood vessels, including the Circle of Willis, safeguards against ischemic insults and facilitates intraarterial communication.
Cranial Nerves

The twelve pairs of cranial nerves, originating from the brainstem, mediate a diverse array of sensory and motor functions, encompassing olfaction, vision, facial expression, and auditory perception.
Comprehending the anatomy and functionality of the brain fosters a deeper appreciation of its complexity and facilitates advances in neuroscientific research and therapeutic interventions aimed at diminishing neurological disorders.
Understanding the detailed anatomy and functionality of the brain is crucial for medical students embarking on their journey of study. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers invaluable assistance in navigating the complexities of neuroscience and related subjects. By leveraging expert guidance and support, students can excel in their medical education and contribute to advancements in the field of Medicine. Email us at expertassignment46@gmail.com to embark on your path to scholarly excellence and professional competency.
How Does The Drug Got Excreted / Eliminated From The Body?

Drug excretion is an important process in pharmacology, encompassing the elimination of pharmaceutical substances from the body. While the ultimate elimination of all drugs is inevitable, the specific pathways involved can vary significantly. Some drugs undergo extensive metabolic transformations before being excreted, while others are expelled from the body in their original form.
The kidneys play a central role in excreting water-soluble substances, effectively filtering them from the bloodstream. Meanwhile, the biliary system handles drugs that remain unabsorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, providing an alternative route for elimination. Although excretion through auxiliary channels such as the intestines, saliva, sweat, breast milk, and lungs is typically minimal, certain volatile anesthetics and residual drug traces in breast milk can have notable impacts, particularly on vulnerable populations such as infants.
Renal excretion constitutes a significant portion of drug elimination, accounting for approximately 20% of the plasma that is filtered through the glomeruli. While most water and electrolytes are reabsorbed back into circulation, polar compounds like drug metabolites are excreted predominantly in urine. However, it’s important to note that renal excretion tends to decrease with age, necessitating careful dosage adjustments for elderly patients to mitigate potential adverse effects.
Numerous factors influence the process of renal excretion, including the extent of protein binding, the degree of drug ionization affecting reabsorption rates, fluctuations in urine pH that can alter excretion dynamics, and the impact of metabolic inhibitors on tubular secretion mechanisms.
Biliary elimination, on the other hand, occurs when drugs traverse the biliary epithelium via active transport mechanisms. However, this process is not without limitations, as transporter saturation can impose constraints on drug excretion rates. Typically, larger molecules containing polar and lipophilic groups are excreted through bile, while smaller molecules tend to favor renal elimination pathways.
In addition to renal and biliary routes, drugs may also be eliminated to varying extents through auxiliary pathways such as saliva, tears, feces, sweat, and exhalation. While the quantities eliminated through these routes are generally minimal, drug excretion in breast milk can pose significant concerns for lactating mothers, potentially exposing nursing infants to pharmacological agents.
Understanding the pharmacokinetic parameters governing drug excretion is paramount for optimizing therapeutic regimens and minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Key parameters include the rate of elimination, clearance, elimination rate constant, and biologic half-life for drugs undergoing first-order elimination kinetics.
In conclusion, drug excretion represents a broad process influenced by a myriad of factors, necessitating comprehensive consideration to ensure the safe and efficacious use of pharmacotherapy.
For medical students navigating the complexities of their studies, Expert Academic Assignment Help serves as a beacon of professionalism and expertise. With a steadfast dedication to excellence and competency, our team provides invaluable support and guidance tailored to your academic needs. Do not hesitate to reach out to us for assistance on your academic journey, email: expertassignment46@gmail.com
Your excellence our pride.
What Is Pulmonary Embolism?

Introduction
Pulmonary embolism (PE) stands as a formidable medical concern, defined by the sudden obstruction of pulmonary arteries by blood clots or other substances. This obstruction poses a grave threat to life if not promptly addressed. In this comprehensive journey , we indulge into the technicality of PE, exploring its profound origins, clinical manifestations, predisposing factors, potential complications, and avenues for prevention.
A. Definition Pulmonary Embolism

Pulmonary embolism manifests when a blood clot, typically originating from deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the lower extremities, migrates to the lungs, precipitating arterial blockage.
B. Significance
PE emerges as a critical condition, triggering significant impairment of pulmonary function and predisposing individuals to severe complications, including mortality, in the absence of timely intervention.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism

A. Common Symptoms encompass acute dyspnea, chest pain, and syncope, often manifesting abruptly and varying in intensity.
B. Additional Symptoms: Patients may also present with hemoptysis, tachycardia, dizziness, diaphoresis, pyrexia, lower limb edema, and cyanosis, reflective of diverse physiological perturbation.
Causes and Risk Factors

a. Venous Thromboembolism
Predominantly, PE ensues from embolic occlusion secondary to thrombi originating in the deep venous system of the lower extremities.
b. Diverse Etiologies
PE may arise from fat emboli, tumor emboli, or air emboli, presenting a spectrum of etiological paradigms.
C. Predisposing Factors:
Notable risk factors encompass antecedent , underlying medical conditions (e.g., cardiovascular diseases, malignancies), surgical interventions, coagulopathies, prolonged immobility, and the prothrombotic milieu associated with COVID-19 infection
Complications of Pulmonary Embolism

a). Mortality:
Untreated PE poses a grave threat to life, with mortality rates approximating one-third of cases, underscoring the exigency of timely intervention.
b). Pulmonary Hypertension
Chronic embolic burden culminates in pulmonary hypertension, engendering elevated pulmonary arterial pressures and consequent cardiac strain.
C. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Persistent emboli precipitate vascular remodeling, culminating in a debilitating condition marked by enduring pulmonary hypertension and associated morbidities.
Prevention of Pulmonary Embolism
A. Pharmacological Prophylaxis
Anticoagulant prophylaxis stands as a cornerstone intervention in high-risk cohorts, mitigating thrombotic propensity perioperatively and during hospitalization.
B. Mechanical Modalities
Mechanical prophylaxis modalities encompass compression stockings, limb elevation, early mobilization, and pneumatic compression devices, fostering venous return and thwarting stasis-induced thrombogenesis.
C. Travel Recommendations
Travelers predisposed to thromboembolic events are counselled on hydration maintenance, periodic ambulation during prolonged periods of immobility, and the judicious utilization of compression garments to mitigate venous stasis during protracted journeys.
Conclusion
Pulmonary embolism emerges as a formidable adversary, demanding expeditious recognition and intervention to forestall catastrophic signal .A comprehensive grasp of its pathophysiological under happenings, clinical hallmarks, predisposing factors, complications, and preventive strategies is paramount for optimal management. Through concerted efforts encompassing risk mitigation and vigilant surveillance, individuals can navigate the perilous terrain of PE with greater resilience, minimizing morbidity and mortality associated with this grave condition.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
How To Select The Appropriate Editor For The Dissertation ?

Crafting a dissertation represent a major academic milestone, requiring meticulous attention to detail and unwavering scholarly precision. A crucial aspect of this endeavor is selecting the right editor, capable of refining and enhancing the quality of your scholarly work. Let’s explore each topic outlined in the guide in detail:
Understanding Your Needs

Before embarking on the search for an editor, it’s essential to assess your specific requirements thoroughly. Determine whether you need comprehensive editing services covering proofreading, formatting, and content refinement, or if you require assistance with specific aspects like structural coherence and grammatical correctness. By clearly defining your needs, you can focus your search on editors whose expertise aligns with your expectations.
Seeking Expertise in Dissertation Editing
Dissertation editing requires a unique skill set that not all editors possess. It’s crucial to seek professionals with specialized experience in academic dissertation editing. Look for editors who demonstrate a deep understanding of scholarly writing conventions, proficiency in navigating various citation styles, and familiarity with academic discourse. Prioritizing such expertise ensures the refinement of your dissertation to meet scholarly standards.
Credentials and Experience

When evaluating potential editors, consider their credentials and experience in the field. Look for editors or services with a strong reputation and a proven track record of successful collaborations with doctoral candidates. Request samples of previous work and client testimonials to gauge the quality of their editing services. Additionally, inquire about their familiarity with your discipline or subject area, as this can significantly impact the effectiveness of their editing.
Quality Assurance Measures
A reputable editing service will have robust quality assurance measures in place to ensure the highest standards of editing. Inquire about the editor’s editing process, including the steps taken to review and refine your dissertation. Look for editors who offer multiple rounds of editing and revisions to address any feedback or concerns. Transparent communication throughout the editing process is indicative of professionalism and dedication to quality.
Customized Editing Solutions
Recognize that every dissertation is unique, with varying editing needs. Seek editors who offer tailored editing solutions customized to your specific requirements. Whether you need assistance with language refinement, structural organization, or adherence to formatting guidelines, choose an editor who can provide targeted support to enhance the clarity, coherence, and scholarly rigor of your dissertation.
Cost and Affordability

While cost is a consideration, prioritize the quality and credibility of the editing service. Compare pricing structures and services offered by different editing providers to find a balance between quality and affordability. Investing in professional editing services is a worthwhile investment in the quality and credibility of your dissertation. Consider the value of the expertise provided by Expert Academic Assignment Help in handling dissertations, ensuring that your academic work meets the highest standards of excellence.
Timeliness and Availability
Meeting deadlines is crucial in academia, so select an editor who can accommodate your timeline and provide timely feedback and revisions. Inquire about their availability and turnaround times to ensure that your editing stays on schedule. Partnering with an editor who demonstrates punctuality and availability ensures a productive and efficient editing collaboration.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate editor for your dissertation is a significant decision that can profoundly impact the quality and effectiveness of your research. By understanding your needs, seeking expertise in dissertation editing, evaluating credentials and experience, ensuring quality assurance measures, opting for customized editing solutions, considering cost and affordability, and prioritizing timeliness and availability, you can make an informed choice that enhances the scholarly rigor and impact of your dissertation.
For professional assistance and guidance with your thesis, dissertation, or PhD studies, email us at expertassignment46@gmail.com Expert Academic Assignment Help offers comprehensive dissertation editing services tailored to meet the unique needs of doctoral candidates, ensuring that your dissertation meets the highest standards of excellence.
Professional Email Etiquette

Email etiquette, often referred to as the ‘code of conduct’ for email communication, encompasses a comprehensive set of principles and guidelines that dictate appropriate behavior when writing or responding to emails. In today’s digital age, characterized by the widespread use of email for both personal and professional communication, understanding and adhering to proper email etiquette are paramount for effective communication and the maintenance of professional relationships.
At its core, effective email etiquette serves several crucial purposes. Firstly, it ensures that communication remains clear, respectful, and devoid of misunderstandings or confusion. By adhering to established etiquette standards, individuals can convey their messages in a professional manner while also demonstrating respect for the recipient’s time and attention. Furthermore, proper email etiquette contributes to the cultivation of a positive and professional image, both for the sender and the organization they represent. This is particularly critical in professional settings, where email communication often serves as the primary means of interaction with clients, colleagues, and stakeholders.
When students are tasked with assignments or projects related to email etiquette, they frequently seek assistance from Expert academic writing services to navigate the complexities of email communication. These services, such as Expert Academic Assignment Help, provide invaluable support and guidance to students, offering expertise and experience in email etiquette principles and their practical application. From understanding the fundamental principles of email etiquette to applying them effectively in various contexts, students benefit from the insights and expertise of professional writers and educators.
A key aspect of email etiquette is being mindful of the tone and style of communication. Emails should be crafted with care, ensuring they are clear, concise, and tailored to the intended audience. Whether communicating with a supervisor, colleague, or friend, it is essential to consider the recipient’s expectations and preferences. Maintaining professionalism in all email correspondence is crucial, as it reflects positively on the sender and enhances the credibility of their message.
In addition to tone and style, the content of emails should also be carefully considered to avoid common pitfalls, such as the use of inappropriate language or tone. While email may appear to be an informal mode of communication, it is essential to remember that emails are a written form of correspondence and should be treated with the same level of professionalism as any other form of communication. Emotionally charged or confrontational emails should be avoided, as they can strain relationships and undermine the sender’s credibility.
The significance of email etiquette extends beyond personal interactions and has significant implications for professional communication. Unprofessional email behavior can have adverse effects on individuals and organizations, ranging from damage to professional reputations to legal liabilities. Conversely, adherence to proper email etiquette enhances professionalism, fosters positive relationships, and promotes efficiency in communication.
Organizations that prioritize email etiquette stand to benefit in several ways. Firstly, by promoting proper email language and behavior, organizations can cultivate a professional image that inspires confidence and trust among clients, partners, and stakeholders. Moreover, awareness of the risks associated with email communication can help shield organizations from potential legal liabilities, such as defamation or breach of confidentiality. Additionally, clear and concise emails facilitate more efficient communication and faster response times, ultimately enhancing productivity and effectiveness in the workplace.
When students seek assistance with email etiquette assignments from services like Expert Academic Assignment Help, they gain access to a wealth of knowledge and expertise in the field. These services offer comprehensive guidance on topics ranging from basic email etiquette principles to advanced strategies for effective communication. By leveraging the insights and support provided by expert writers and educators, students can enhance their understanding of email etiquette and develop the skills necessary to excel in their academic and professional endeavors.
Expert Academic Assignment Help distinguishes itself through several key features that make it a preferred choice for students seeking assistance with email etiquette assignments. Firstly, its 24/7 helpdesk ensures that students can access support and guidance whenever they need it, regardless of their time zone or schedule. Additionally, the service prides itself on delivering plagiarism-free work, ensuring that every assignment is original and unique. Moreover, its reasonable fees make it accessible to students from diverse backgrounds, without compromising on the quality of service or expertise provided. Lastly, Expert Academic Assignment Help offers emergency services for students facing tight deadlines or unexpected challenges, ensuring that they receive timely assistance and support when they need it most.
In conclusion, mastering email etiquette is essential for effective communication in both personal and professional contexts. By understanding and practicing proper email etiquette, individuals can enhance their communication skills, build positive relationships, and achieve success in their academic and professional endeavors. With the guidance and support of expert academic writing services like Expert Academic Assignment Help, students can develop the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in the complex and dynamic world of email communication.
Reach out to us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for assistance in navigating of email communication and ensuring professionalism in your message
10 Strategies For Handling Online Exams.

Online examinations have emerged as a reliable method for evaluating students in today’s digital era. However, navigating through these virtual assessments can present challenges, particularly for individuals new to the format or struggling to adapt. Fortunately, online exam assignment assistance services like Expert Academic Assignment Help provide invaluable guidance to students, empowering them not only to approach examinations with confidence but also to excel in them. Let’s focuses into ten effective strategies recommended by assignment assistance experts to successfully ace online examinations.
1. Familiarize Yourself With The Exam Format
Understanding the structure and format of the examination is paramount. By comprehending what to anticipate, students can better prepare their study approach and manage their time effectively during the examination.
2. Create A Study Schedule
Effective time management is imperative. Establishing a study schedule that encompasses dedicated time for reviewing course materials, practicing sample questions, and undertaking mock examinations ensures comprehensive preparation.
3. Utilize Online Resources
Exploit the varieties of online resources available to supplement learning. Websites, forums, and educational platforms offer a treasure trove of information, including study guides and interactive quizzes, augmenting students’ understanding of the examination material.
4. Practice Regularly
Practice breeds perfection. Allocating time each day to tackle examination questions under timed conditions not only enhances speed and accuracy but also diminishes anxiety by acquainting students with the examination interface.
5. Seek Clarification
Do not hesitate to seek clarification from instructors or peers when encountering difficulties or questions about the examination material. Engaging in discussions through online forums or study groups can enrich understanding and boost confidence.
6. Minimize Distractions
Cultivating a conducive study environment by minimizing distractions is imperative. Identifying a tranquil, well-lit space and disabling electronic device notifications optimize concentration and information retention.
7. Take Regular Breaks
Striking a balance between study sessions and short breaks is crucial for sustaining focus and preventing burnout. Rejuvenating the mind with stretching and relaxation exercises ensures optimal performance.
8. Develop Exam Strategies
Mastery of effective examination strategies can significantly enhance performance. Learning to prioritize questions, manage time efficiently, and utilize available resources enriches examination outcomes.
9. Review And Revise
Thoroughly reviewing course materials in the days leading up to the examination reinforces comprehension and aids retention. Crafting summary notes and mnemonic devices facilitates the recall of key concepts and definitions.
10. Stay Calm And Confident

On the day of the examination, maintaining composure and confidence is paramount. Trusting in one’s preparation, staying focused, and approaching each question methodically are important contributors to success.
In conclusion, mastering online examinations necessitates thorough preparation, consistent practice, and strategic thinking. By adhering to these ten strategies and availing themselves of support from online exam assignment assistance services like Expert Academic Assignment Help, students can elevate their performance, surmount challenges, and attain academic success. With dedication, perseverance, and the right support system in place, excelling in online examinations is entirely attainable.
The strategies for handling online exams is essential for achieving academic success in the digital era. If you’re aiming to enhance your performance and ensure success in your online examinations, don’t hesitate to reach out to Expert Academic Assignment. Connect with us via email: expertassignment46@gmail.com to explore how our specialized assistance can elevate your exam preparation and performance. Remember, seeking support when needed is a wise decision, particularly when it comes to excelling in challenging assessments like online exams.
How to Write a Compelling Blog Post

Crafting captivating headlines is an art that can make or break a blog post. Your headline serves as the gateway to your content, enticing readers indulging deeper into your article. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll involve into the ways and methods of crafting irresistible headlines that not only grab attention but also keep readers engaged from start to finish.
Craft a Great Headline That Readers Can’t Resist

The headline sets the stage for your entire post, acting as a beacon to guide readers towards the valuable insights and information you have to offer. To create a headline that truly resonates with your audience, consider the following strategies:
1.Promise a Solution: Your headline should address a specific problem or need that your target audience has. By promising a solution or benefit, you immediately capture their interest and encourage them to keep reading.
2.Know Your Audience: Conduct thorough research to understand the pain points and interests of your target audience. Tailor your headline to speak directly to their needs and desires, ensuring maximum relevance and engagement.
3.Utilize Proven Templates: Tried-and-tested headline formulas like “How to” and list posts are effective for grabbing attention and driving clicks. Experiment with different templates to see what resonates best with your audience.
4.Engage the Senses: Use sensory words and vivid language to evoke emotions and create a tangible experience for your readers. Engaging multiple senses can make your headline more compelling and memorable.
5.Avoid Over-Promising: While it’s important to make your headline enticing, avoid exaggeration or over-promising. Be truthful and transparent in your messaging to maintain trust and credibility with your audience.
Write an Introduction That Grabs and Seduces

Once you’ve crafted a compelling headline, the introduction serves as the gateway to your content. It should build upon the promise made in the headline and draw readers in with captivating storytelling, thought-provoking questions, or intriguing facts. Consider the following tips for writing an irresistible introduction:
1.Hook Your Readers: Capture readers’ attention from the very first sentence with a compelling hook that intrigues and entices.
2.Set the Tone: Establish the tone and style of your post in the introduction, giving readers a glimpse of what to expect.
3.Preview the Content: Provide a brief overview of what readers can expect to learn or gain from reading your post. This sets clear expectations and encourages readers to continue reading.
Deliver Advice That’s Easy to Consume and Impossible to Ignore
The main body of your post is where you deliver on the promise made in the headline and introduction. Here’s how to ensure your content is both valuable and engaging:
1.Provide Valuable Insights: Offer practical advice, valuable insights, or informative content that fulfills the promise made in your headline.
2. Organize Your Content: Break down complex ideas into digestible chunks and use subheadings to guide readers through your content. This makes it easier for readers to consume and retain information.
3.Incorporate Visuals: Use visuals such as images, infographics, or videos to enhance comprehension and engagement. Visual elements can break up text-heavy content and make your post more visually appealing.
4.Keep it Engaging: Maintain a conversational tone and engage readers with relatable examples, or case studies. Encourage interaction by asking questions or prompting readers to share their experiences.
Close with a Motivational B
The conclusion of your post is your final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s how to end your post on a high note:
Summarize Key Points: Recap the main points or takeaways from your post to reinforce the message you’ve conveyed
Provide a Call to Action: Encourage readers to take the next step, whether it’s sharing the post, leaving a comment, or implementing the advice you’ve provided. A clear call to action motivates readers to engage with your content beyond the initial reading.
3.Leave a Memorable Impression: End your post with a memorable closing statement or thought-provoking question that leaves readers thinking long after they’ve finished reading.
Polish Your Post So It’s Smoother Than a Slip ‘n Slide
Before you hit publish, it’s essential to thoroughly edit and polish your post to ensure it’s error-free and polished to perfection. Consider the following tips for polishing your post:
1.Edit for Clarity and Coherence: Review your content for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Ensure that your ideas are presented in a clear and organized manner.
2.Check for Grammar and Spelling Errors: Proofread your post carefully to catch any grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, or typos. Use grammar-checking tools or enlist the help of a peer to ensure your writing is error-free.
3.Format for Readability: Pay attention to formatting elements such as headings, paragraphs, and bullet points to enhance readability. Break up long blocks of text and use formatting techniques to make your post visually appealing.
4.Seek Feedback: Consider seeking feedback from peers or beta readers to get an outside perspective on your post. Fresh eyes can help identify areas for improvement and ensure your content resonates with your target audience.
By following these steps, you can create blog posts that captivate readers, provide valuable insights, and leave a lasting impression. Crafting compelling headlines is just the first step in creating engaging content that resonates with your audience, but by mastering the art of headline writing, you can set your posts up for success from the very beginning.
In conclusion, mastering the art of blog writing is crucial for creating engaging content that resonates with your audience. If you’re looking to enhance your blogging skills and ensure your posts are set up for success, consider seeking assistance from Expert Academic Assignment. Get in touch via email at expertassignment46@gmail.com to discover how our expertise can elevate your writing game. Remember, it’s okay to seek help when you need it, especially when it comes to crafting compelling content.
Professional Guidance On The Best Thesis Writing Service

Introduction
In the academic journey of a student pursuing higher education, the thesis holds significant importance. It is a culmination of years of study, research, and analysis, representing a student’s expertise in a particular subject. However, crafting a thesis that meets academic standards and fulfills research objectives requires dedication, time, and proficiency in writing. This is where professional thesis writing services come into play, offering assistance and guidance to students in their thesis writing endeavors.
Professional Guidance
Thesis paper writing help services play a crucial role in providing students with the necessary support and resources to produce high-quality theses. These services aid students at various stages of their thesis writing process, from topic selection to final editing. However, with a plethora of thesis writing services available online, choosing the best one can be a daunting task. To help students navigate this challenge effectively, here is a comprehensive guide on selecting the best thesis writing services.
1. Evaluate Reputation and Credibility
The first step in choosing a thesis writing service is to assess its reputation and credibility. Look for reviews, testimonials, and ratings from previous clients to gauge the quality of service offered. A reputable service provider will have positive feedback and a track record of delivering well-researched and professionally written theses.
2. Expertise and Experience
Go for a service that has a team of experienced writers with expertise in your field of study. Thesis writing requires subject-specific knowledge and research skills, so ensure that the writers have relevant qualifications and experience in your area of interest.
3. Customization and Personalization
Every thesis is unique, and it’s essential to choose a writing service that offers customized solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Look for services that allow you to communicate directly with the writer to discuss your ideas, preferences, and expectations.
4. Plagiarism-Free Guarantee
Plagiarism is a serious academic offense, and a reliable thesis writing service should guarantee 100% originality in their work. Ensure that the service provides plagiarism reports and conducts thorough checks using reputable plagiarism detection tools.
5. Timely Delivery
Meeting deadlines is crucial in academic writing, and you should choose a service that prioritizes timely delivery. Discuss the timeline with the service provider and ensure that they can deliver the completed thesis within your specified deadline.
6. Affordability and Transparency
While cost should not be the sole determining factor, it’s essential to consider your budget when choosing a thesis writing service. Look for services that offer transparent pricing with no hidden fees and provide value for your money in terms of quality and service.
7. Customer Support
Effective communication and support are vital throughout the thesis writing process. Choose a service that offers responsive customer support to address any queries or concerns promptly.
Expert Academic Assignment Help: Your Trusted Partner in Thesis Writing

Expert Academic Assignment Help is a reputable academic writing service that has earned a stellar reputation for delivering high-quality thesis writing services across various disciplines. Here’s how Expert Academic Assignment Help fulfills the essential criteria for choosing the best thesis writing services:
Reputation and Credibility
Expert Academic Assignment Help boasts a strong reputation backed by numerous positive reviews and testimonials from satisfied clients. Its credibility is further reinforced by a team of experienced writers who are well-versed in different subjects and academic standards.
Expertise and Experience
The writers at Expert Academic Assignment Help are experts in their respective fields, including finance, Medicine which is a popular area for thesis topics. Whether you need assistance with topics for master thesis in finance or any other subject, Expert Academic Assignment Help has the expertise to deliver outstanding results.
Customization and Personalization
Expert Academic Assignment Help offers personalized thesis writing services tailored to each client’s unique requirements. You can collaborate directly with the assigned writer to discuss your thesis objectives, research findings, and writing style preferences.
Plagiarism-Free Guarantee
Expert Academic Assignment Help prioritizes originality and guarantees plagiarism-free content in all its deliverables. The writers conduct thorough research and cite sources accurately to ensure academic integrity.
Timely Delivery
Expert Academic Assignment Help understands the importance of meeting deadlines and strives to deliver completed theses within the agreed-upon timeframe. You can rely on their punctuality and professionalism throughout the writing process.
Affordability and Transparency
Expert Academic Assignment Help offers competitive pricing with transparent rates and no hidden charges. They provide flexible payment options and ensure that you get value for your investment.
Customer Support
Expert Academic Assignment Help customer support team is available 24/7 to address any queries or concerns you may have. You can reach out to us via live chat, email, or phone for prompt assistance.
In conclusion, choosing the best thesis writing services requires careful consideration of various factors such as reputation, expertise, customization, plagiarism policy, timeliness, affordability, and customer support. Expert Academic Assignment Help stands out as a trusted partner for students seeking top-notch thesis paper writing help services, especially Health Sciences and other academic disciplines. With Expert Academic Assignment Help, you can rest assured that your thesis will be handled with professionalism, dedication, and expertise, leading to academic success and recognition.
In conclusion, I urge students to consider seeking guidance and assistance for their thesis, research, dissertation, essays, and online classes. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers professional support tailored to your academic needs. Don’t hesitate to reach out via email at expertassignment46@gmail.com for expert help and guidance. Your academic success is our priority.
The Best Approach to Writing a Research Paper

1. Understanding the Terrain: Exploratory Research
Before embarking on the journey of writing a research paper, it’s crucial to understand the foundational concept of exploratory research. This preliminary phase serves as a compass, guiding researchers through the complex landscape of scholarly inquiry. Exploratory research helps in delineating the scope, objectives, and methodology of the study.
Exploratory research help provides invaluable insights and guidance in refining research questions, identifying relevant literature, and establishing a solid foundation for the inquiry. Through expert assistance, researchers can navigate through the initial phase with clarity and precision, setting the stage for a robust research endeavor.
2. Charting Your Course

Once researchers have a clear understanding of the research landscape, the next step is to chart a coherent course for the paper. Expert Academic writing solution provider play a pivotal role in this phase by assisting in structuring the research paper, organizing ideas, and formulating a compelling thesis statement.
We offer guidance in selecting suitable research methodologies and refining argumentative frameworks to enhance the quality of the paper. By leveraging their expertise, researchers can ensure that their paper follows a logical progression and effectively communicates their scholarly contributions.
3. Navigating the Seas of Literature
A well-crafted research paper relies heavily on scholarly literature to support its arguments and findings. Navigating the vast seas of academic literature can be a daunting task, but Expert Academic writing guidance services offer invaluable assistance in this regard.
These services help researchers identify relevant sources, critically evaluate existing literature, and synthesize key findings to support their arguments. By leveraging their expertise, researchers can ensure that their paper is anchored in rigorous scholarship and contributes meaningfully to the advancement of knowledge in their field.
4. Plotting Your Course: Developing a Methodological Framework

Central to the success of any research paper is the development of a robust methodological framework. Whether researchers are conducting empirical research or engaging in theoretical inquiry, selecting the appropriate research methods is paramount.
Expert Academic writing solution providers offer invaluable guidance in designing research methodologies that align with the objectives of the study and provide credible evidence to support its claims. By collaborating with experts in the field, researchers can navigate the complexities of research design and execute their studies with precision and vigor.
5. Weaving the Narrative: Crafting Compelling Arguments

At the heart of every research paper lies the art of persuasive argumentation. Effectively weaving together disparate strands of evidence into a cohesive narrative requires fines and precision.
Expert Academic writing solution providers play a crucial role in this phase by aiding researchers in owning their argumentative skills, refining their prose, and crafting compelling arguments that resonate with their readers. Through expert guidance, researchers can elevate the clarity and persuasiveness of their paper, leaving a lasting impression on their audience.
6. Sailing into New Horizons: Embracing Iterative Revision

As researchers navigate the tubulation waters of research paper writing, it’s essential to embrace the iterative nature of the process. Revision is not merely a perfunctory task but rather a transformative journey that enables researchers to refine their ideas, strengthen their arguments, and elevate the overall quality of their paper.
Expert Academic writing guidance services provide constructive feedback, identify areas for improvement, and guide researchers through the revision process with precision and expertise. By embracing feedback and engaging in iterative revision, researchers can sail confidently into new horizons of scholarly inquiry, leaving a lasting impact on their field of study.
Conclusion
In summary, writing a research paper is a noble endeavor that demands diligence, perseverance, and scholarly consistency. By leveraging the expertise of research paper writing services, exploratory research paper assignment help, Expert academic writing solution providers, and writing guidance services, researchers can navigate the complexities of the research process with confidence and precision.
With strategic planning, execution, and iterative revision, researchers can craft a research paper that not only meets the rigorous standards of academic inquiry but also contributes meaningfully to the advancement of knowledge in their field.
This comprehensive approach ensures clarity, precision, and impact in scholarly writing, guiding researchers through each phase of the process towards academic excellence.
For more Enquiries and Further Guidance during the Study process
Email us at: expertassignment46@gmail.com
What Makes a PhD Dissertation Different from a Masters Thesis?

Introduction
In the realm of academia, pursuing advanced degrees such as a Master’s or a PhD involves rigorous research and scholarly endeavors. Central to this academic journey are the culminating projects — the Master’s thesis and the PhD dissertation. While often used interchangeably, these two academic works possess distinct characteristics that set them apart. In this comprehensive discussion, we will major into the differences between a PhD dissertation and a Master’s thesis, exploring various aspects including the depth of research, original contribution to knowledge, duration and intensity of study, evaluation and defense process, as well as career implications and academic prestige.
Depth of Research

One of the fundamental disparities between a PhD dissertation and a Master’s thesis lies in the depth of research. A Master’s thesis typically explores a specific topic within a field of study, offering a comprehensive analysis but within a more confined framework. In contrast, a PhD dissertation delves into original research, contributing novel insights or advancing existing knowledge within the chosen discipline. The depth of investigation required for a dissertation is considerably greater, often involving extensive data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
Original Contribution to Knowledge

Building upon the notion of originality, a PhD dissertation is expected to make a significant contribution to the body of knowledge within the respective field. It must demonstrate a unique perspective, innovative methodology, or novel findings that add value to the academic discourse. On the other hand, while a Master’s thesis also involves original research, its contribution may be more incremental or focused on synthesizing existing literature rather than forging new paths of inquiry.
Duration and Intensity of Study

Another factor that distinguishes a PhD dissertation from a Master’s thesis is the duration and intensity of study involved. Pursuing a PhD typically entails a more prolonged and immersive engagement with the research topic, spanning several years of dedicated study and inquiry. The process of conducting original research, analyzing data, and drafting a dissertation demands a substantial commitment of time and effort. In contrast, a Master’s thesis can often be completed within a shorter timeframe, typically ranging from one to two years, depending on the program’s requirements.
Evaluation and Defense Process
The evaluation and defense process also differ between a PhD dissertation and a Master’s thesis. For a PhD dissertation, the candidate must present their research findings to a committee of faculty members or experts in the field. This oral defense involves a rigorous examination of the dissertation’s methodology, results, and conclusions, as well as the candidate’s ability to articulate and defend their research. In contrast, while some Master’s programs may require a thesis defense, the level of scrutiny and formality is often less intense compared to a PhD dissertation defense.
Career Implications and Academic Prestige

Furthermore, the completion of a PhD dissertation carries significant career implications and academic prestige. Attaining a PhD is often regarded as the highest level of academic achievement, opening doors to advanced research positions, teaching opportunities, and leadership roles within academia and industry. A PhD dissertation serves as a hallmark of expertise and scholarly rigor, signaling to the academic community and potential employers the candidate’s ability to conduct independent research at a high level. On the other hand, while a Master’s thesis is a commendable accomplishment in its own right, it may not carry the same weight in terms of career advancement or academic recognition as a PhD dissertation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison between a PhD dissertation and a Master’s thesis reveals the intricate differences that exist between these two academic endeavors. While both represent significant milestones in academic scholarship, they embody distinct attributes that reflect the depth of research, originality of contribution, and level of academic achievement. Whether seeking thesis vs. dissertation writing help or PhD dissertation assistance, students embarking on these scholarly endeavors can benefit from the guidance and support offered by dissertation writing services. With expert assistance, aspiring scholars can navigate the complexities of research, writing, and presentation, ensuring their academic work meets the highest standards of excellence and scholarly rigor
Understanding the differences between a PhD dissertation and a Master’s thesis is crucial for students embarking on academic research. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers personalized support at every stage of the process, ensuring academic excellence. Reach out at expertassignment46@gmail.com to benefit from expertise and guidance in navigating the complexities of research, writing, and presentation.
6 Simple Steps To Score ‘A’ Grade On Your Research Paper

1. Building Your Thesis
Your thesis serves as the bedrock of your research paper, providing a central focus and guiding principle for your investigation. It’s imperative to construct your thesis around a clear and concise idea, premise, or claim that you intend to explore and defend throughout your paper. In the introduction, articulate precisely what your thesis aims to address, ensuring clarity and coherence from the start outlining the scope and significance of your thesis, you not only distinguish your paper from others but also establish a compelling rationale for your research. Moreover, show case to your readers the insights they stand to gain by engaging with your thesis, thereby enhancing the relevance and impact of your work.
2. Preparing an Outline

Crafting a comprehensive outline is an indispensable organizational tool in the research paper writing process. It functions as a strategic roadmap, enlightening the structure and content of your paper while facilitating coherence and logical progression. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to outlining, it is essential to consider several key elements:
Content and Presentation Style: Determine the thematic framework and narrative structure for each section of your paper, ensuring alignment with your thesis.
Supporting Arguments and Evidence: Incorporate pertinent supporting arguments and empirical evidence to substantiate your thesis and bolster your overrating argument.
Cohesion and Conclusion: Ensure that your outline fosters cohesion by integrating disparate ideas and perspectives, culminating in a definitive conclusion that reinforces the significance of your research.
By vividly crafting an outline that contains these elements, you can streamline the writing process and maintain a cohesive and compelling narrative throughout your paper.
3. Conducting Research

Robust and thorough research is the cornerstone of a successful research paper, providing the empirical foundation and scholarly context necessary to substantiate your thesis. Begin by identifying a diverse array of potential sources that align with the theme focus and research objectives of your paper. With your outline serving as a strategic guide, embark on a systematic exploration of relevant literature, primary sources, and empirical data, prioritizing depth and breadth of coverage over superficiality. While evaluating sources, prioritize relevance and scholarly vigor over perfection, recognizing that the synthesis of diverse perspectives and methodologies can enrich your analysis and deepen the intellectual resonance of your paper.
4 . Writing Your Thesis

Armed with a comprehensive outline and an extensive body of research, it is time to translate your insights and arguments into a cognitive and compelling thesis. Drawing upon the scaffolding provided by your outline, into details craft each section of your paper, maintaining specificity to your thesis statement and overrated argument. Whether elucidating theoretical frameworks, analyzing empirical data, or synthesizing disparate perspectives, strive for consistency and coherence in your writing, ensuring that each subsection contributes meaningfully to the specific narrative of your paper. By adhering to the theme contours mentioned in your outline and showing the resilience of your thesis, you can construct a persuasive and intellectually rigorous argument that resonates with your readers.
5. Editing and Revision

The editing and revision process is an indispensable stage in refining the coherence, clarity, and scholarly rigor of your research paper. Upon completing the initial draft of your paper, undertake a comprehensive review and analysis, focusing on several key areas:
Structural Coherence: Evaluate the organizational coherence and logical progression of your paper, identifying opportunities to streamline transitions and enhance narrative flow.
Clarity and Precision: Scrutinize the clarity and precision of your prose, refining language and syntax to elucidate complex ideas and facilitate reader comprehension.
Scholarly Rigor: Verify the accuracy and integrity of your citations, ensuring adherence to established conventions of academic citation and attribution.
Grammar and Mechanics: Attend to grammatical errors, typographical inconsistencies, and syntactical ambiguities, rectifying any lapses in mechanics that deter from the scholarly integrity of your paper.
By subjecting your paper to rigorous scrutiny and revision, you can elevate the quality and scholarly resonance of your research, enhancing its capacity to engage and persuade your audience.
6. Creating a Checklist

As a culminating step, it is essential to create a comprehensive checklist to ensure that your research paper adheres to the highest standards of scholarly rigor and integrity. This checklist should encompass several key dimensions:
Content: Verify that your paper addresses all requisite components, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, discussion, and conclusion.
Structure: Assess the structural coherence and narrative progression of your paper, ensuring that each section contributes meaningfully to the overarching argument.
Citation and Attribution: Confirm the accuracy and completeness of your citations, adhering to established conventions of academic citation and attribution.
Presentation: Review the formatting and presentation of your paper, attending to stylistic considerations such as font, spacing, and margins.
Proofreading: Conduct a final proofreading of your paper, scrutinizing for any lingering errors or oversights in grammar, syntax, or mechanics.
By rigorously adhering to this checklist, you can ensure that your research paper meets all necessary criteria for scholarly excellence and academic integrity, thereby maximizing its impact and credibility within the academic community.
By specifically following these six steps, you can consistently produce research papers of exceptional quality and academic rigor, irrespective of your current skill level or disciplinary background. Each step represents a critical juncture in the research paper writing process, providing a strategic framework for conceptualizing, organizing, and presenting your research in a compelling and intellectually rigorous manner. By embracing these principles and methodologies, you can elevate the caliber and excellent resonance of your research papers, thereby enhancing your academic proficiency and contributing meaningfully to the advancement of knowledge within your chosen field of study.
Crafting a top-notch research paper demands careful planning, thorough research, and diligent editing. Following the outlined steps can boost students’ writing skills and consistently lead to ‘A’ grades. Yet, academic writing complexities can overwhelm newcomers or those short on time.
Remember, seeking help isn’t weakness but a proactive strategy to ensure work quality. By utilizing available resources and seeking aid when necessary, students can ease academic writing stress and enrich their learning journey.
Therefore, I strongly encourage students to consider seeking assistance from Expert Academic Assignment Help by emailing expertassignment46@gmail.com With their expertise and support, students can receive tailored guidance, feedback, and assistance throughout the research paper writing process. By leveraging the expertise of academic professionals, students can overcome challenges, refine their writing skills, and achieve academic success more effectively.
H. pylori Infection

Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a significant global health concern, affecting a substantial portion of the world’s population. The discussion aims to provide an in-depth exploration of various aspects of H. pylori infection, including its prevalence, transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, complications, prevention strategies, and future research directions.
Prevalence and Transmission

H. pylori infection is widespread, with approximately two-thirds of the world’s population harboring the bacterium in their gastrointestinal tract. Various factors contribute to its prevalence, including socioeconomic status, living conditions, hygiene practices, and geographic location. The discussion indulges into the epidemiological trends of H. pylori infection across different populations and regions, highlighting disparities in prevalence rates and associated risk factors.
Transmission of H. pylori occurs primarily through interpersonal contact and ingestion of contaminated food or water. Saliva, fecal-oral transmission, and oral-oral transmission, including through kissing, are significant modes of spread. Poor sanitation and overcrowded living conditions facilitate the transmission of the bacterium, particularly in resource-limited settings. The discussion explores the mechanisms of H. pylori transmission and the implications for public health interventions aimed at reducing its spread.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

While many individuals with H. pylori infection remain asymptomatic, others experience a range of gastrointestinal symptoms, including stomach pain, bloating, nausea, and weight loss. The discussion elucidates the spectrum of clinical manifestations associated with H. pylori infection, emphasizing the importance of recognizing atypical presentations and considering differential diagnoses.
Diagnosing H. pylori infection presents several challenges due to the variability of symptoms and the limitations of available diagnostic tests. We critically evaluates the utility of different diagnostic modalities, including stool antigen tests, urea breath tests, and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, in detecting H. pylori infection. It also examines the role of serological tests and molecular techniques in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and guiding clinical management decisions.
Treatment Options

The standard treatment regimens for H. pylori infection typically involve a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). However, rising rates of antibiotic resistance pose significant challenges to effective eradication therapy. It explores the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in H. pylori and the implications for treatment outcomes.
Alternative treatment approaches, such as sequential therapy, concomitant therapy, and bismuth-based quadruple therapy, are also examined in the context of their efficacy and tolerability. Highlighting the importance of individualizing treatment regimens based on antibiotic susceptibility testing and patient-specific factors to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Complications

Peptic ulcers are a common complication of H. pylori infection, resulting from the bacterium’s ability to disrupt the gastric mucosal barrier and induce inflammation. The discussion elucidates the pathophysiology of peptic ulcer formation and the factors contributing to ulcer recurrence and complications.
In addition to peptic ulcers, H. pylori infection is associated with an increased risk of more serious complications, such as gastric cancer and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. The discussion explores the molecular mechanisms underlying H. pylori-induced carcinogenesis and the strategies for early detection and management of gastric neoplasms.
Prevention

Preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the burden of H. pylori infection and its associated complications. The discussion emphasizes the importance of promoting good hygiene practices, including handwashing and sanitation, to minimize the risk of transmission.
Furthermore, dietary factors may influence the risk of H. pylori infection and its clinical outcomes. The discussion evaluates the evidence regarding the impact of dietary habits, such as consumption of fruits, vegetables, and probiotics, on H. pylori colonization and disease progression. It also addresses the potential role of vaccination in preventing H. pylori infection and its complications, highlighting ongoing research efforts in vaccine development.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research efforts are focused on advancing our understanding of H. pylori pathogenesis, identifying novel therapeutic targets, and developing effective preventive strategies. The discussion highlights recent advancements in H. pylori research, including insights into bacterial virulence factors, host immune responses, and microbial interactions within the gastric microbiota.
Future directions in H. pylori research encompass a multidisciplinary approach, integrating molecular biology, epidemiology, immunology, and clinical medicine. The discussion outlines key areas for future investigation, such as the development of targeted antimicrobial agents, the role of host genetics in H. pylori susceptibility, and the impact of microbial dysbiosis on disease outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, H. pylori infection remains a significant public health challenge, with implications for gastrointestinal health and disease worldwide. A comprehensive understanding of the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of H. pylori infection is essential for guiding clinical practice and informing public health policies. By addressing the complexities of H. pylori infection through interdisciplinary research and collaborative efforts, we can strive towards reducing its global burden and improving patient outcomes.
In managing H. pylori infection, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are crucial alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice enables us to advance gastroenterology and improve patient outcomes.
As we address H. pylori infection and its broader implications on gastrointestinal health, let’s remain dedicated to providing optimal patient care. By working collaboratively and embracing interdisciplinary approaches, we can positively impact lives and contribute to a healthier future.
Email expertassignment46@gmail.com to explore how we can assist you in achieving your academic and professional aspirations. Wishing you continued success in your medical journey.
Pneumonia In Children And Adults

Introduction
Pneumonia stands as a prevalent respiratory infection, exerting a significant burden on global public health. Its impact extends beyond mere morbidity, contributing to substantial healthcare costs and socioeconomic consequences. This discussion aims to elucidate the general nature of pneumonia, encompassing its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities, treatment strategies, complications, and preventive measures. By indulging into these factors, we aim to provide a better understanding of pneumonia’s complexity and underscore the importance of timely recognition and management.
Pathophysiology

Pneumonia ensues from the infiltration of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and less commonly, parasites, into the lower respiratory tract. Upon inhalation or aspiration of these pathogens, they gain access to the alveoli, where they incite an inflammatory response. This inflammatory cascade triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, recruiting immune cells to the site of infection. Neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes converge to eradicate the invading pathogens, leading to the characteristic consolidation and exudate formation within the affected lung tissue. As the infection progresses, alveolar edema, impaired gas exchange, and parenchymal damage ensue, culminating in the clinical manifestations of pneumonia.
Clinical Presentation

The clinical presentation of pneumonia encompasses a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild respiratory complaints to life-threatening respiratory failure. Common symptoms include cough, productive sputum production, fever, chills, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, and systemic manifestations such as malaise and fatigue. The severity of symptoms varies depending on factors such as the underlying pathogen, the extent of lung involvement, the host’s immune status, and comorbidities. In pediatric populations, pneumonia may present with nonspecific symptoms such as feeding difficulties, lethargy, and irritability, posing diagnostic challenges. Conversely, elderly individuals may exhibit atypical presentations characterized by confusion, hypothermia, and exacerbations of underlying chronic conditions.
Diagnostic Modalities

The diagnosis of pneumonia hinges on a comprehensive clinical assessment, augmented by various diagnostic modalities to confirm the presence of pulmonary infection and reveal its etiology. A thorough history and physical examination provide invaluable insights into the patient’s symptomatology, risk factors, and clinical trajectory. Symptomatic findings such as crackles, wheezes, and diminished breath sounds may aid in localizing the site of infection and assessing disease severity. Radiographic imaging, notably chest X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, serves as the cornerstone of pneumonia diagnosis, revealing characteristic radiographic findings such as airspace opacities, lobar consolidation, and interstitial infiltrates. Laboratory investigations, including complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin levels, may corroborate the clinical suspicion of pneumonia and guide therapeutic decisions. Additionally, microbiological testing of respiratory specimens through techniques such as sputum culture, blood cultures, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays facilitates pathogen identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing, thereby informing targeted therapy.
Treatment Strategies

The management of pneumonia hinges on prompt initiation of empiric antimicrobial therapy tailored to the likely causative pathogen(s) and disease severity. Antibiotics represent the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia, with the choice of agent dictated by factors such as local antimicrobial resistance patterns, patient age, comorbidities, and recent antibiotic exposure. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include beta-lactam agents (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins), macrolides, fluoroquinolones, and combination regimens for severe or healthcare-associated infections. Conversely, viral pneumonia necessitates supportive care measures, given the limited efficacy of antiviral agents in most cases. Influenza-associated pneumonia may benefit from neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir, while respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia may warrant ribavirin therapy in select cases. Adjunctive therapies such as oxygen supplementation, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids may mitigate respiratory distress and improve clinical outcomes, particularly in severe or hypoxemic patients. The duration of antimicrobial therapy varies depending on factors such as the causative pathogen, clinical response, radiographic resolution, and the presence of complications. Close monitoring of clinical parameters and serial imaging studies guide the decision-making process, enabling clinicians to tailor therapy to individual patient needs.
Complications

Pneumonia harbors the potential for various complications, ranging from mild to life-threatening sequelae, necessitating vigilant monitoring and timely intervention. Common complications include pleural effusion, empyema, lung abscess, respiratory failure, septic shock, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pleural effusion denotes the accumulation of fluid within the pleural space, secondary to inflammation or impaired lymphatic drainage, manifesting as dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, and dullness to percussion on physical examination. Empyema represents a purulent collection within the pleural cavity, often complicating bacterial pneumonia and necessitating drainage via thoracentesis or chest tube placement. Lung abscesses manifest as circumscribed cavities containing necrotic debris and pus within the lung parenchyma, triggered by persistent fever, productive cough, and hemoptysis. Respiratory failure ensues from impaired gas exchange and alveolar hypoventilation, caused by worsening hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, necessitating mechanical ventilation and intensive care support. Septic shock represents a life-threatening complication of severe pneumonia, characterized by systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and end-organ dysfunction, requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. ARDS denotes a severe form of acute lung injury, characterized by diffuse alveolar damage, refractory hypoxemia, and bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging, necessitating lung-protective ventilation and supportive care in the intensive care unit (ICU). The occurrence of complications portends a poor prognosis and underscores the need for early recognition and intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Preventive Measures

Preventing pneumonia entails a broad approach encompassing vaccination, infection control measures, and health promotion strategies aimed at reducing the risk of respiratory infections and their sequelae. Vaccination stands as a cornerstone of pneumonia prevention, targeting common bacterial and viral pathogens implicated in pneumonia pathogenesis. Vaccines such as the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) confer protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae, the leading bacterial cause of pneumonia, particularly in high-risk populations such as young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals. Influenza vaccination remains paramount in mitigating influenza-associated pneumonia and reducing disease transmission, underscoring the importance of annual vaccination campaigns targeting vulnerable populations. Additionally, adherence to infection control measures, including hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and environmental sanitation, plays a pivotal role in reducing the spread of respiratory pathogens in healthcare settings and the community at large. Health promotion efforts aimed at smoking cessation, optimizing nutrition, and addressing underlying comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and immunodeficiency bolster immune resilience and mitigate pneumonia risk. Furthermore, early identification and management of predisposing factors such as malnutrition, homelessness, and overcrowded living conditions attenuate pneumonia susceptibility and enhance overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumonia emerges as a formidable respiratory infection, posing significant challenges to global public health. Its diverse etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, treatment modalities, complications, and preventive measures underscore the nature of pneumonia management. Timely recognition and intervention are imperative in mitigating the morbidity and mortality associated with pneumonia, necessitating a collaborative approach among healthcare providers, public health authorities, and policymakers. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of pneumonia’s manifest and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can strive towards reducing its burden and improving patient outcomes. Through ongoing research, education, and advocacy efforts, we can envision a future where pneumonia-related morbidity and mortality are substantially diminished, paving the way for enhanced respiratory health and well-being worldwide.
In managing pneumonia, compassion, empathy, and a holistic approach are essential alongside clinical expertise. Striving for excellence in knowledge and practice allows us to enhance respiratory medicine and patient outcomes.
As we address pneumonia and broader cardiovascular health complexities, let’s remain committed to optimal patient care. Together, we can impact lives positively and foster a healthier future.
Email expertassignment46@gmail.com to discover how we can support your academic and professional goals. Wishing you ongoing success in your medical journey.
12 Key Factors On How To Choose the Best Assignment Writing Service

Search the web
Begin your quest by thoroughly exploring the internet to discover a multitude of assignment help services. By conducting comprehensive research, you gain insight into the array of options available and the unique offerings of each provider. Take note of the diverse services and features offered by different platforms to compare and evaluate them effectively.
2. Look for good reviews
Positive reviews and star ratings serve as valuable indicators of a service provider’s reliability and quality. When scouring through reviews, prioritize platforms with favorable feedback from previous clients. Compile a list of providers with exemplary reviews to further scrutinize their offerings and assess their suitability for your requirements.
3. Discuss with others
Leverage the wisdom of your peers by seeking advice from classmates or senior students who have availed themselves of online assignment help services. Their firsthand experiences and recommendations can provide invaluable insights to guide your decision-making process. Engage in open discussions to gather diverse perspectives and gain clarity on the strengths and weaknesses of various service providers.
4. Go through blogs and forums
Explore student-centric blogs and forums to engage with individuals from diverse academic backgrounds and institutions. By participating in discussions within these online communities, you can glean valuable insights and opinions regarding different assignment help providers. Take advantage of this platform to gather anecdotal evidence and gather nuanced perspectives to inform your decision.
5. Experienced assignment writing experts
Prioritize assignment help providers with a team of experienced writers who possess the requisite expertise to comprehend and fulfill the requirements of your assignments. Thoroughly assess the credentials and track record of the experts associated with each service provider to ensure their competency and proficiency. Opt for platforms that emphasize the qualifications and experience of their writers as a testament to their commitment to delivering high-quality solutions.
6. Use review websites
Harness the power of independent review websites that specialize in evaluating assignment help services. These platforms offer impartial assessments and unbiased insights into the performance and reputation of different providers. Rely on these credible sources to identify reputable service providers and discern between reliable options and subpar alternatives. Utilize the comprehensive reviews and ratings available on these websites to streamline your selection process and make well-informed decisions.
7. Look for samples
Authentic assignment help providers often showcase samples of their work to demonstrate the caliber and proficiency of their writers. Take advantage of these samples to evaluate the quality of writing, adherence to academic standards, and effectiveness in addressing assignment requirements. By scrutinizing these samples, you can gain valuable insights into the writing style, depth of research, and overall competence of the company’s writers. Use this firsthand evidence to assess the suitability of each provider and make informed choices based on tangible evidence.
8. Originality
Prioritize assignment help providers that prioritize originality and authenticity in their solutions. Plagiarism can have severe repercussions on your academic performance and integrity, making it essential to choose providers that guarantee 100% authentic assignment solutions. Look for platforms that offer complimentary plagiarism reports alongside their final deliverables to reassure you of the originality and uniqueness of the content. Verify the provider’s commitment to upholding academic integrity and ethical standards to safeguard your academic reputation and success.
9. Assurance of top grades
Seek out assignment help providers that offer assurances of achieving top grades for your assignments. While it’s essential to approach such claims with a degree of skepticism, reputable providers often back their promises with tangible evidence and guarantees. Look for platforms that offer transparent communication channels, such as valid contact information and 24/7 support services, to facilitate ongoing dialogue and address any concerns or queries promptly. Exercise discernment when evaluating assurances of top grades and prioritize providers that demonstrate accountability, reliability, and a commitment to excellence.
10. Reasonable charges
When selecting an assignment writing service, prioritize platforms that offer reasonable and transparent pricing structures. Avoid succumbing to exorbitant fees and hidden charges that can strain your financial resources and undermine the value proposition of the service. Instead, opt for providers that offer competitive pricing without compromising on the quality or integrity of their solutions. Look for platforms that offer flexible payment options, discounts, and money-back guarantees to enhance affordability and mitigate financial risks.
11. Customized services
Emphasize the importance of personalized and tailored services when evaluating assignment help providers. Opt for platforms that demonstrate a willingness to accommodate your specific requirements and preferences, ensuring a bespoke approach to addressing your academic needs. Verify that the provider can adhere to formatting guidelines, citation styles, and other academic specifications relevant to your assignments. Prioritize platforms that prioritize customization and adaptability to deliver solutions that align seamlessly with your academic objectives and expectations.
12. Qualified writers
Place a premium on the expertise and qualifications of the writers associated with each assignment help provider. Look for platforms that boast a team of highly qualified experts with advanced degrees, preferably at the Master’s or Ph.D. level, in their respective fields. Prioritize providers that emphasize the rigorous vetting and selection process for their writers to ensure the highest standards of competency and professionalism. Choose platforms that foster ongoing professional development and training initiatives to empower their writers with the latest knowledge, skills, and methodologies. By prioritizing qualified writers, you can access expert guidance, insights, and assistance tailored to your academic discipline and requirements.
In conclusion,
selecting the best assignment writing service entails a meticulous and systematic evaluation of various factors, ranging from the reputation and reliability of the provider to the expertise and qualifications of its writers. By adopting a discerning and comprehensive approach to the selection process, you can identify reputable and trustworthy platforms that align with your academic objectives and expectations. Prioritize transparency, authenticity, and quality in your decision-making process to ensure a rewarding and enriching academic experience.
Wishing you well with your education journey! For further guidance and assistance with your assignments, email us at williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com