Evosia Chasing Auroras Is Much Like Living Life: If You Show Up, Always Be Prepared For The Amazing
evosia Chasing auroras is much like living life: if you show up, always be prepared for the amazing to happen.
More Posts from Xyhor-astronomy and Others
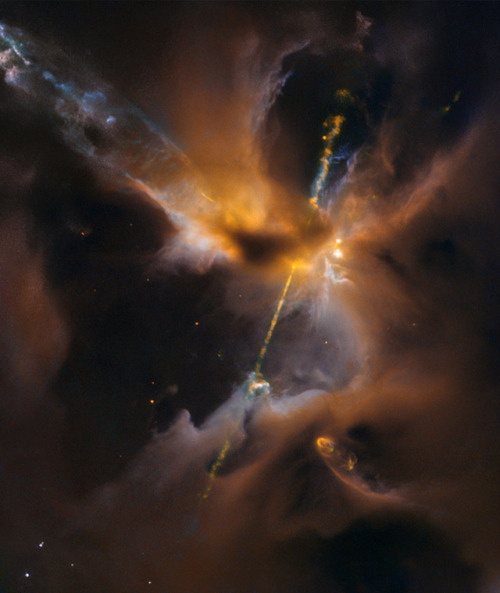

Hubble Sees the Force Awakening in a Newborn Star
This celestial lightsaber does not lie in a galaxy far, far away, but rather inside our home galaxy, the Milky Way. It’s inside a turbulent birthing ground for new stars known as the Orion B molecular cloud complex, located 1,350 light-years away.
In the center of the image, partially obscured by a dark, Jedi-like cloak of dust, a newborn star shoots twin jets out into space as a sort of birth announcement to the universe
Credit: NASA/ESA










Dunes, peaks and craters on Mars obtained by HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment), a camera on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
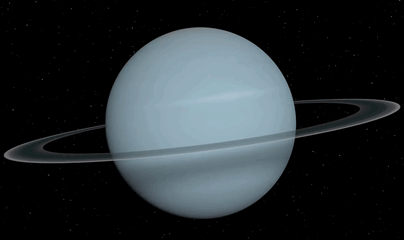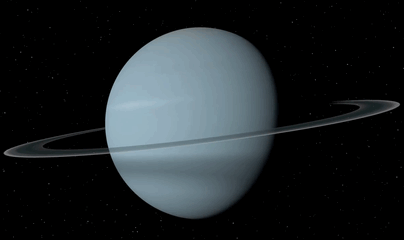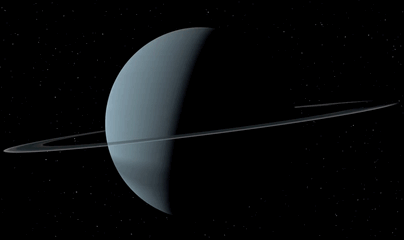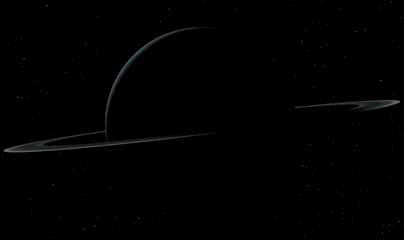
Planet Uranus ♅
Equatorial Diameter: 51.118 km
Satellites: 27
Notable satellites: Oberon, Titania, Miranda, Ariel & Umbriel
Orbit Distance: 2.870.658.186 km (19 AU)
Orbit Period: 84 Earth years
Surface Temperature: -220°C
Discovered Date: March 13th 1781
Discovered By: William Herschel
Image credit: Oscar Malet

Neptune Clouds
This Voyager 2 high resolution color image, taken 2 hours before closest approach, provides obvious evidence of vertical relief in Neptune’s bright cloud streaks.
Credit: NASA / Voyager 2

Shadow Veil by Abi Ashra (Tumblr)

Should there be a holiday called Astronomy Day?
Where lights are to be turned off for the entire night so everyone could see the stars?










The Largest Black Hole Merger Of All-Time Is Coming, And Soon
“Over in Andromeda, the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way, a number of unusual systems have been found. One of them, J0045+41, was originally thought to be two stars orbiting one another with a period of just 80 days. When additional observations were taken in the X-ray, they revealed a surprise: J0045+41 weren’t stars at all.”
When you look at any narrow region of the sky, you don’t simply see what’s in front of you. Rather, you see everything along your line-of-sight, as far as your observing power can take you. In the case of the Panchromatic Hubble Andromeda Treasury, where hundreds of millions of stars were captured in impressive fashion, background objects thousands of times as distant can also be seen. One of them, J0045+41, was originally thought to be a binary star system that was quite tight: with just an 80 day orbital period. Follow-up observations in the X-ray, however, revealed that it wasn’t a binary star system after all, but an ultra-distant supermassive black hole pair, destined to merge in as little as 350 years. If we build the right observatory in space, we’ll be able to observe the entire inspiral-and-merger process for as long as we like!
Come get the full story, and some incredible pictures and visuals, on today’s Mostly Mute Monday!
Eight curiosities about black holes
In this post contains some facts and curiosities about one of the most extreme objects in the universe - Black Holes. Black holes are some of the strangest and most fascinating objects found in outer space. They are objects of extreme density, with such strong gravitational attraction that even light cannot escape from their grasp if it comes near enough.

1° A Massive Star Collapsing In Upon Itself
Say you have a star that’s about 20 times more massive than the Sun. Our Sun is going to end its life quietly; when its nuclear fuel burns out, it’ll slowly fade into a white dwarf. That’s not the case for far more massive stars. When those monsters run out of fuel, gravity will overwhelm the natural pressure the star maintains to keep its shape stable. When the pressure from nuclear reactions collapses, according to the Space Telescope Science Institute, gravity violently overwhelms and collapses the core and other layers are flung into space. This is called a supernova. The remaining core collapses into a singularity — a spot of infinite density and almost no volume. That’s another name for a black hole.

2° Black holes come in a range of sizes.
There are at least three types of black holes, ranging from relative squeakers to those that dominate a galaxy’s center. Primordial black holes are the smallest kinds, and range in size from one atom’s size to a mountain’s mass. Stellar black holes, the most common type, are up to 20 times more massive than our own Sun and are likely sprinkled in the dozens within the Milky Way. And then there are the gargantuan ones in the centers of galaxies, called “supermassive black holes.” They’re each more than one million times more massive than the Sun. How these beasts formed is still being examined.

3° The first black hole wasn’t discovered until X-ray astronomy was used
Cygnus X-1 was first found during balloon flights in the 1960s, but wasn’t identified as a black hole for about another decade. According to NASA, the black hole is 10 times more massive to the Sun. Nearby is a blue supergiant star that is about 20 times more massive than the Sun, which is bleeding due to the black hole and creating X-ray emissions.

4° Black holes are only dangerous if you get too close
Like creatures behind a cage, it’s okay to observe a black hole if you stay away from its event horizon — think of it like the gravitational field of a planet. This zone is the point of no return, when you’re too close for any hope of rescue. But you can safely observe the black hole from outside of this arena. By extension, this means it’s likely impossible for a black hole to swallow up everything in the Universe (barring some sort of major revision to physics or understanding of our Cosmos, of course.)

5° We aren’t sure if wormholes exist
A popular science-fiction topic concerns what happens if somebody falls into a black hole. Some people believe these objects are a sort of wormhole to other parts of the Universe, making faster-than-light travel possible. But as this Smithsonian Magazine article points out, anything is possible since we still have a lot to figure out about physics. “Since we do not yet have a theory that reliably unifies general relativity with quantum mechanics, we do not know of the entire zoo of possible spacetime structures that could accommodate wormholes,” said Abi Loeb, who is with the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.

6° Black holes will spaghettify you and everything else
If a person was able to survive long enough to describe falling into a black hole, he would at first experience weightless as he goes into free fall, but then feel intense “tidal” gravitational forces as he got closer to the center of the black hole. In other words, if his feet were closer to the centre than his head, then they would feel a stronger pull until he eventually is stretched and then ripped apart. As he falls in he may observe distorted images as the light bends around him and he will also still be able to see beyond the black hole as light continues to reach him from the outside.

7° Weird time stuff happens around black holes
This is best illustrated by one person (call them Unlucky) falling into a black hole while another person (call them Lucky) watches. From Lucky’s perspective, Unlucky’s time clock appears to be ticking slower and slower. This is in accordance with Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which (simply put) says that time is affected by how fast you go, when you’re at extreme speeds close to light. The black hole warps time and space so much that Unlucky’s time appears to be running slower. From Unlucky’s perspective, however, their clock is running normally and Lucky’s is running fast.

8° Massive Black Hole in The Center Of Milky Way
It is now thought that most galaxies are held together by supermassive black holes at their centers, which cluster hundreds of solar systems around them. In fact, 30,000 light years away at the centre of our own Milky Way galaxy is a black hole with 30 million times the mass of our own sun.
Source: space.com, universetoday.com, sciencealert.com & astronomytrek.com
Astronomy and Astrophysics: Facts
Here is a list of some curiosities of astronomy and astrophysics. From our solar system to interstellar space.

Rings of Saturn: With an estimated local thickness of as little as 10 m and as much as 1 km, they are composed of 99.9% pure water ice with a smattering of impurities that may include tholins or silicates. The main rings are primarily composed of particles ranging in size from 1 cm to 10 m.

Valhalla (crater): Valhalla is the largest multi-ring impact crater on Jupiter’s moon Callisto and in the Solar System. It is named after Valhalla, the God Odin’s hall in Norse mythology where warriors are taken after death.

Europa (lineae): Europa’s most striking surface features are a series of dark streaks crisscrossing the entire globe, called lineae (English: lines). Close examination shows that the edges of Europa’s crust on either side of the cracks have moved relative to each other. The larger bands are more than 20 km (12 mi) across, often with dark, diffuse outer edges, regular striations, and a central band of lighter material. The most likely hypothesis states that the lineae on Europa may have been produced by a series of eruptions of warm ice as the Europan crust spread open to expose warmer layers beneath. The effect would have been similar to that seen in Earth’s oceanic ridges.

Tartarus Dorsa: The western part of Pluto’s northern hemisphere consists of an extensive, highly distinctive set of 500-meter-high mountains informally named Tartarus Dorsa; the spacing and shape of the mountains looks similar to scales or tree bark.

Mountain in Ceres: Ahuna Mons is the largest mountain on the dwarf planet and asteroid Ceres. It protrudes above otherwise smooth terrain, it is not an impact feature, and it appears to be the only mountain of its kind on Ceres. Bright streaks run top to bottom on its slopes; these streaks are thought to be salt, similar to the better known Cererian bright spots, and likely resulted from cryovolcanic activity from Ceres’s interior. It is named after the traditional post-harvest festival Ahuna of the Sumi Naga people of India.

Pluto has a tenuous atmosphere consisting of nitrogen (N2), methane (CH4), and carbon monoxide (CO), which are in equilibrium with their ices on Pluto’s surface. According to the measurements by New Horizons, the surface pressure is about 1 Pa(10 μbar), roughly one million to 100,000 times less than Earth’s atmospheric pressure. It was initially thought that, as Pluto moves away from the Sun, its atmosphere should gradually freeze onto the surface; studies of New Horizons data and ground-based occultations show that Pluto’s atmospheric density increases, and that it likely remains gaseous throughout Pluto’s orbit.

Sagittarius A*: Sagittarius A* is a bright and very compact astronomical radio source at the center of the Milky Way, near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius. It is part of a larger astronomical feature known as Sagittarius A. Sagittarius A* is thought to be the location of a supermassive black hole, like those that are now generally accepted to be at the centers of most spiral and elliptical galaxies.

Double Pulsar: PSR J0737−3039 is the only known double pulsar. It consists of two neutron stars emitting electromagnetic waves in the radio wavelength in a relativistic binary system. The two pulsars are known as PSR J0737−3039A and PSR J0737−3039B. It was discovered in 2003 at Australia’s Parkes Observatory by an international team led by the radio astronomer Marta Burgay during a high-latitude pulsar survey.

IC 1101: IC 1101 is a supergiant elliptical galaxy at the center of the Abell 2029 galaxy cluster, approximately 320 megaparsecs (1.04 billion light-years) from Earth. IC 1101 is among the largest known galaxies, but there is debate in the astronomical literature about how to define the size of such a galaxy.

A rogue planet (also termed an interstellar planet, nomad planet, free-floating planet, orphan planet, wandering planet, starless planet, sunless planet, or Planemo) is a planetary-mass object that orbits the galaxy center directly. Such objects have been ejected from the planetary system in which they formed or have never been gravitationally bound to any star or brown dwarf. The Milky Way alone may have billions of rogue planets.
souce: wikipedia
Image credit: NASA/JPL/SwRI, Ted Stryk, John Rowe Animations, commons.wikimedia
The NASA Village
Today in the NASA Village… Making More with Less

Stacey Boland works at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) on missions that use remote sensing instruments for Earth observation. From space, we can learn so much about our changing environment here on Earth.
Maximizing science research requires finding creative and cost effective ways to do it! Her team developed the ISS-RapidScat instrument using left over equipment NASA had in storage from a program launched in the 1990’s. ISS-RapidScat is an external payload mounted to the outside of the Columbus module, part of the International Space Station. ISS-RapidScat measures ocean wind speed and direction to help track tropical cyclones and hurricanes. Stacey’s team was able to get a functioning piece of hardware for about a tenth the cost of a traditional “small” Earth science mission.
Stacey said, “It wasn’t easy, but it was worth it! Working in the space program doesn’t require perfection - but it does require passion and hard work! We work as a team here at NASA and everyone’s role is important. We rely on each other to do our best, regardless of what part of the mission is “ours.” All the parts need to work together for it to be a success and that takes teamwork and good communication!”
Stacey’s story represents how being creative in the NASA Village can really make a difference!

Where did Stacey get her hunger for space? “When I was growing up, my dad and I would learn about each shuttle mission and then watch launches on TV together. It was fun learning about science and exploration together. Now, as a parent, I’m continuing on that tradition with my son”
“I was able to watch the SpaceX-4 launch in person with my mom, dad, husband, and son”, Stacy said. “It was absolutely incredible to share that experience with them. My son still talks about it and has been practicing drawing rockets ever since. He often asks when we can go back to Florida to see another one!”
Experiencing a rocket launch in person is amazing. Feeling the sound waves from the engines push against your body is quite a rush. And when it is hardware you helped create, on its way into space, it makes that experience even more special.
Next time on the NASA Village… A visit to the NASA Village inspires a lifelong career.
Do you want more stories? Find our NASA Villagers here!
-
 camarinmpa liked this · 5 years ago
camarinmpa liked this · 5 years ago -
 snowcappedquinceanera liked this · 5 years ago
snowcappedquinceanera liked this · 5 years ago -
 rad-iaant liked this · 6 years ago
rad-iaant liked this · 6 years ago -
 the-future-is-equal liked this · 7 years ago
the-future-is-equal liked this · 7 years ago -
 d3licate-kitten reblogged this · 7 years ago
d3licate-kitten reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 polareyez reblogged this · 7 years ago
polareyez reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lavangarda reblogged this · 7 years ago
lavangarda reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 shuhadaaulmaarakah reblogged this · 7 years ago
shuhadaaulmaarakah reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 crysta-ga-lee reblogged this · 7 years ago
crysta-ga-lee reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 xyhor-physicalgeography reblogged this · 7 years ago
xyhor-physicalgeography reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 blacklighttanuki liked this · 7 years ago
blacklighttanuki liked this · 7 years ago -
 dmitriwilliams reblogged this · 7 years ago
dmitriwilliams reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 fairly-distracted reblogged this · 7 years ago
fairly-distracted reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 aliendiety reblogged this · 7 years ago
aliendiety reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 neverthelessbunpersisted reblogged this · 7 years ago
neverthelessbunpersisted reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 smtfaggot liked this · 7 years ago
smtfaggot liked this · 7 years ago -
 uglyymodelmannequin reblogged this · 7 years ago
uglyymodelmannequin reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 futchfuck reblogged this · 7 years ago
futchfuck reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 f0rever-always reblogged this · 7 years ago
f0rever-always reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 disney-eyes reblogged this · 7 years ago
disney-eyes reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 im-gonna-run-the-world liked this · 7 years ago
im-gonna-run-the-world liked this · 7 years ago -
 parisjackscn liked this · 7 years ago
parisjackscn liked this · 7 years ago -
 peachhyg0gh reblogged this · 7 years ago
peachhyg0gh reblogged this · 7 years ago
For more content, Click Here and experience this XYHor in its entirety!Space...the Final Frontier. Let's boldly go where few have gone before with XYHor: Space: Astronomy & Spacefaring: the collection of the latest finds and science behind exploring our solar system, how we'll get there and what we need to be prepared for!
128 posts