Dunes, Peaks And Craters On Mars Obtained By HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment), A Camera










Dunes, peaks and craters on Mars obtained by HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment), a camera on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Image credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
More Posts from Xyhor-astronomy and Others
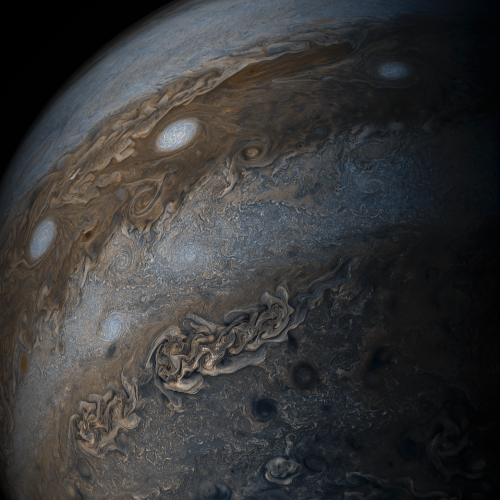

Jupiter’s Bands of Clouds
This enhanced-color image of Jupiter’s bands of light and dark clouds was created by citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran using data from the JunoCam imager on NASA’s Juno spacecraft.
Three of the white oval storms known as the “String of Pearls” are visible near the top of the image. Each of the alternating light and dark atmospheric bands in this image is wider than Earth, and each rages around Jupiter at hundreds of miles (kilometers) per hour. The lighter areas are regions where gas is rising, and the darker bands are regions where gas is sinking.
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Gerald Eichstädt /Seán Doran
The dusty, star-forming galaxy took shape in the first billion years after the Big Bang and is likely to be one of the first galaxies to ever form, says Min Yun, astrophysicist of the University of Massachusetts Amherst.

Located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of our neighbouring dwarf galaxies, this young globular-like star cluster is surrounded by a pattern of filamentary nebulosity that is thought to have been created during supernova blasts. It consists of a main globular cluster in the centre and a younger, smaller cluster, seen below and to the right, composed of extremely hot, blue stars and fainter, red T-Tauri stars. This wide variety of stars allows a thorough study of star formation processes.
Credit: ESA, NASA and Martino Romaniello (ESO, Germany)
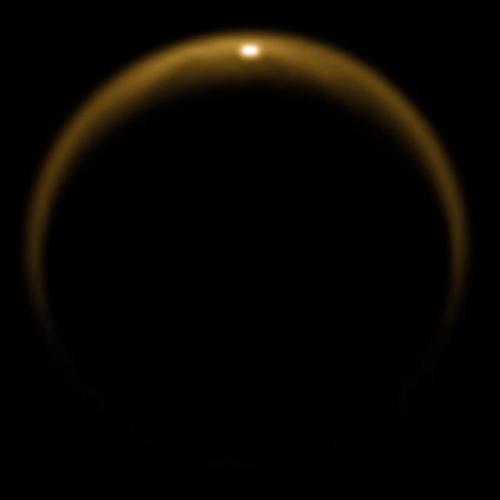




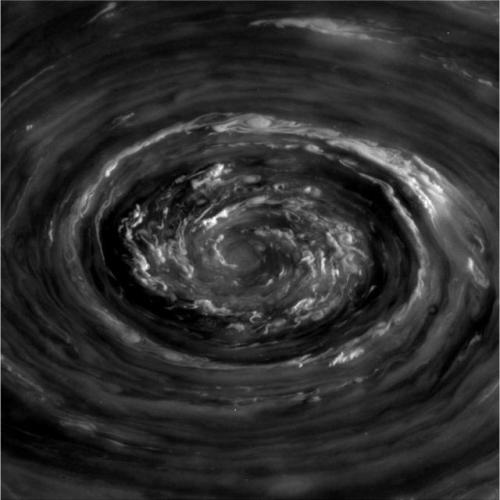




Tomorrow one of the most prolific and beloved spacecraft missions will come to an end when the Cassini spacecraft makes its final plunge into Saturn. After nearly 20 years in space and 13 years orbiting Saturn, the Cassini mission is close to running out of fuel. To prevent the craft from contaminating one of Saturn’s moons – which its mission revealed may harbor the ingredients for life – mission operators are instead sending it on a fatal dive into the gas giant.
Cassini has and will continue to provide a trove of scientific insights about Saturn and its environs. It has given us front-row seats to a storm that wrapped around the entire planet. It shed new light on Saturn’s spectacular hexagonal polar vortex and showed us the beauty of auroras on other planets. Cassini also showed us that Saturn’s moon Titan has stable hydrocarbon lakes at its surface, fed by methane rains and driven by processes unfamiliar to terrestrial ones. It also gave us paths for future exploration by documenting plumes of water ejected from Enceladus’ icebound oceans.
Cassini also holds a special place in my heart. It launched while I was in middle school, reached Jupiter while I was in college, and collected data throughout my postgraduate research career. It was an inspiration for my undergraduate spacecraft mission design projects, and it provided fun and exciting fluid dynamical discoveries throughout my time writing FYFD. It’s my favorite mission (sorry, Mars rovers, New Horizons, Dawn, and Juno!) and likely to remain so for years to come.
So thank you, Cassini, and many thanks to all the scientists, engineers, and operators who’ve worked on the mission during the decades from its conception to completion. You did a hell of a job. Godspeed, Cassini! (Photo credits: NASA/JPL)
P.S. - Tonight I’ll be helping kick off the Ig Nobel Prize ceremony. You can tune into the live webcast here. The ceremony officially starts at 6 PM Eastern time, but I recommend tuning in early, especially if you want to catch my full spiel. - Nicole

NASA’s Juno Probe Returns Stunning New Image of Jupiter
http://www.sci-news.com/space/juno-image-jupiter-05256.html


What are Pulsars?
Pulsars are spherical, compact objects that are about the size of a large city but contain more mass than the sun. Discovered in 1967, pulsars are fascinating members of the cosmic community.
From Earth, pulsars often look like flickering stars. On and off, on and off, they seem to blink with a regular rhythm. But the light from pulsars does not actually flicker or pulse, and these objects are not actually stars.
Pulsars radiate two steady, narrow beams of light in opposite directions. Although the light from the beam is steady, pulsars appear to flicker because they also spin. It’s the same reason a lighthouse appears to blink when seen by a sailor on the ocean: As the pulsar rotates, the beam of light may sweep across the Earth, then swing out of view, then swing back around again. To an astronomer on the ground, the light goes in and out of view, giving the impression that the pulsar is blinking on and off. The reason a pulsar’s light beam spins around like a lighthouse beam is that the pulsar’s beam of light is typically not aligned with the pulsar’s axis of rotation.
Click here to see the animation
Click here to hear the pulsars sound

Ghost Nebula
![Andromeda [x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/aa70ce40e59ba0f9da6e334afac731fe/tumblr_ox11noOQXn1tuy5mao1_500.jpg)
Andromeda [x]
js

Image of the planet Neptune seen by the space probe Voyager 2
Image credit: NASA/JPL

An irregular island
This image, courtesy of the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), captures the glow of distant stars within NGC 5264, a dwarf galaxy located just over 15 million light-years away in the constellation of Hydra (The Sea Serpent).
Dwarf galaxies like NGC 5264 typically possess around a billion stars — just one per cent of the number of stars found within the Milky Way. They are usually found orbiting other, larger, galaxies such as our own, and are thought to form from the material left over from the messy formation of their larger cosmic relatives.
NGC 5264 clearly possesses an irregular shape — unlike the more common spiral or elliptical galaxies — with knots of blue star formation. Astronomers believe that this is due to the gravitational interactions between NGC 5264 and other galaxies nearby. These past flirtations sparked the formation of new generations of stars, which now glow in bright shades of blue.
https://www.spacetelescope.org/images/potw
-
 spacecadetwench liked this · 1 year ago
spacecadetwench liked this · 1 year ago -
 va-lentine liked this · 1 year ago
va-lentine liked this · 1 year ago -
 coololdsoulpoetlove liked this · 1 year ago
coololdsoulpoetlove liked this · 1 year ago -
 liarandascoundrel reblogged this · 1 year ago
liarandascoundrel reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 chibirim reblogged this · 1 year ago
chibirim reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 chibirim liked this · 1 year ago
chibirim liked this · 1 year ago -
 xiadz reblogged this · 1 year ago
xiadz reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 xiadz liked this · 1 year ago
xiadz liked this · 1 year ago -
 nepenthenaeum reblogged this · 1 year ago
nepenthenaeum reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 concephenomenontunidentified liked this · 1 year ago
concephenomenontunidentified liked this · 1 year ago -
 msbrandan reblogged this · 1 year ago
msbrandan reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 msbrandan liked this · 1 year ago
msbrandan liked this · 1 year ago -
 dehautdesert reblogged this · 1 year ago
dehautdesert reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 warriorofdune reblogged this · 1 year ago
warriorofdune reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 emptyanddark reblogged this · 3 years ago
emptyanddark reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 emptyanddark liked this · 3 years ago
emptyanddark liked this · 3 years ago -
 wachsurfer2018 liked this · 5 years ago
wachsurfer2018 liked this · 5 years ago -
 lunaknox liked this · 5 years ago
lunaknox liked this · 5 years ago -
 thefuckisthissshit reblogged this · 5 years ago
thefuckisthissshit reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 jd-glitch reblogged this · 6 years ago
jd-glitch reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 zvixs reblogged this · 6 years ago
zvixs reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 notoriouslyethereal reblogged this · 6 years ago
notoriouslyethereal reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 hablegeny liked this · 6 years ago
hablegeny liked this · 6 years ago -
 bsidejack liked this · 6 years ago
bsidejack liked this · 6 years ago -
 cccdm3 liked this · 6 years ago
cccdm3 liked this · 6 years ago -
 thepitofhell reblogged this · 6 years ago
thepitofhell reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 yoongicherie reblogged this · 6 years ago
yoongicherie reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 theaccidentalartists liked this · 6 years ago
theaccidentalartists liked this · 6 years ago -
 big-friendly liked this · 7 years ago
big-friendly liked this · 7 years ago -
 big-friendly reblogged this · 7 years ago
big-friendly reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 instoresnearyou reblogged this · 7 years ago
instoresnearyou reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 princes-tower liked this · 7 years ago
princes-tower liked this · 7 years ago -
 bromblecomble reblogged this · 7 years ago
bromblecomble reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 holometabolism reblogged this · 7 years ago
holometabolism reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 wolvesofwinterr liked this · 7 years ago
wolvesofwinterr liked this · 7 years ago -
 greyjoylesbian reblogged this · 7 years ago
greyjoylesbian reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 jillandjackalope reblogged this · 7 years ago
jillandjackalope reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thisworldofmine reblogged this · 7 years ago
thisworldofmine reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 soygreentealattes reblogged this · 7 years ago
soygreentealattes reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 soygreentealattes liked this · 7 years ago
soygreentealattes liked this · 7 years ago -
 e-l-e-k-t-r-a reblogged this · 7 years ago
e-l-e-k-t-r-a reblogged this · 7 years ago
For more content, Click Here and experience this XYHor in its entirety!Space...the Final Frontier. Let's boldly go where few have gone before with XYHor: Space: Astronomy & Spacefaring: the collection of the latest finds and science behind exploring our solar system, how we'll get there and what we need to be prepared for!
128 posts