Possible Case For Fifth Force Of Nature

Possible case for fifth force of nature
A team of physicists at the University of California has uploaded a paper to the arXiv preprint server in which they suggest that work done by a team in Hungary last year might have revealed the existence of a fifth force of nature. Their paper has, quite naturally, caused quite a stir in the physics community as several groups have set a goal of reproducing the experiments conducted by the team at the Hungarian Academy of Science’s Institute for Nuclear Research.
The work done by the Hungarian team, led by Attila Krasznahorkay, examined the possible existence of dark photons - the analog of conventional photons but that work with dark matter. They shot protons at lithium-7 samples creating beryllium-8 nuclei, which, as it decayed, emitted pairs of electrons and positrons. Surprisingly, as they monitored the emitted pairs, instead of a consistent drop-off, there was a slight bump, which the researchers attributed to the creation of an unknown particle with a mass of approximately 17 MeV. The team uploaded their results to the arXiv server, and their paper was later published by Physical Review Letters. It attracted very little attention until the team at UoC uploaded their own paper suggesting that the new particle found by the Hungarian team was not a dark photon, but was instead possibly a protophobic X boson, which they further suggested might carry a super-short force which acts over just the width of an atomic nucleus - which would mean that it is a force that is not one of the four described as the fundamental forces that underlie modern physics.
The paper uploaded by the UoC team has created some excitement, as well as public exclamations of doubt - reports of the possibility of a fifth force of nature have been heard before, but none have panned out. But still, the idea is intriguing enough that several teams have announced plans to repeat the experiments conducted by the Hungarian team, and all eyes will be on the DarkLight experiments at the Jefferson Laboratory, where a team is also looking for evidence of dark photons - they will be shooting electrons at gas targets looking for anything with masses between 10 and 100 MeV, and now more specifically for those in the 17 MeV region. What they find, or don’t, could prove whether an elusive fifth force of nature actually exists, within a year’s time. [Image][Continue Reading→]
More Posts from Science-is-magical and Others

It often seems so quiet after a snowfall because the fresh powder absorbs sound waves. As the snow melts and freezes, it then creates a reflective surface that allows sound to travel farther than normal. Source

Babies don’t just look cute, scientists find
What is it about the sight of an infant that makes almost everyone crack a smile? Big eyes, chubby cheeks, and a button nose? An infectious laugh, soft skin, and a captivating smell? While we have long known that babies look cute, Oxford University researchers have found that cuteness is designed to appeal to all our senses.
They explain that all these characteristics contribute to ‘cuteness’ and trigger our caregiving behaviours, which is vital because infants need our constant attention to survive and thrive. The study is published in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences.
Morten Kringelbach, who together with Eloise Stark, Catherine Alexander, Professor Marc Bornstein and Professor Alan Stein, led the work in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Oxford, said: ‘Infants attract us through all our senses, which helps make cuteness one of the most basic and powerful forces shaping our behaviour.’
Reviewing the emerging literature on how cute infants and animals affect the brain, the Oxford University team found that cuteness supports key parental capacities by igniting fast privileged neural activity followed by slower processing in large brain networks also involved in play, empathy, and perhaps even higher-order moral emotions.
The data shows that definitions of cuteness should not be limited just to visual features but include positive infant sounds and smells. From an evolutionary standpoint, cuteness is a very potent protective mechanism that ensures survival for otherwise completely dependent infants.
Professor Kringelbach said: ‘This is the first evidence of its kind to show that cuteness helps infants to survive by eliciting caregiving, which cannot be reduced to simple, instinctual behaviours. Instead, caregiving involves a complex choreography of slow, careful, deliberate, and long-lasting prosocial behaviours, which ignite fundamental brain pleasure systems that are also engaged when eating food or listening to music, and always involve pleasant experiences.’
The study shows that cuteness affects both men and women, even those without children.
‘This might be a fundamental response present in everyone, regardless of parental status or gender, and we are currently conducting the first long-term study of what happens to brain responses when we become parents.’ said Kringelbach.
Asteroid Terms: Explained
There are interesting asteroid characters in our solar system, including an asteroid that has its own moon and even one that is shaped like a dog bone! Our OSIRIS-REx mission launches at 7:05 p.m. EDT today and will travel to asteroid Bennu.

Scientists chose Bennu as the target of the OSIRIS-REx mission because of its composition, size and proximity to Earth. Bennu is a rare B-type asteroid (primitive and carbon-rich), which is expected to have organic compounds and water-bearing minerals like clays.
Our OSIRIS-REx mission will travel to Bennu and bring a small sample back to Earth for study.

When talking about asteroids, there are some terms scientists use that might not be in your typical vocabulary…but we’ll help with that!
Here are a few terms you should know:
Orbital Eccentricity: This number describes the shape of an asteroid’s orbit by how elliptical it is. For asteroids in orbit around the sun, eccentricity is a number between 0 and 1, with 0 being a perfectly circular orbit and 0.99 being a highly elliptical orbit.
Inclination: The angle, in degrees, of how tilted an asteroid’s orbit is compared to another plane of reference, usually the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
Orbital Period: The number of days it takes for an asteroid to revolve once around the sun. For example, the Earth’s orbital period is 365 days.
Perihelion Distance: The distance between an asteroid and the sun when the asteroid is closest to the sun.
Aphelion Distance: The distance between the asteroid and the sun when the asteroid is farthest away from the sun.
Astronomical unit: A distance unit commonly used to describe orbits of objects around the sun. The distance from the Earth to the sun is one astronomical unit, or 1 AU, equivalent to about 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers.
Diameter: A measure of the size of an asteroid. It is the length of a line from a point on the surface, through the center of the asteroid, extending out to the opposite surface. Irregularly shaped asteroids may have different diameters depending on which direction they are measured.
Rotation Period: The time it takes for an asteroid to complete one revolution around its axis of rotation. For example, the rotation period of the Earth is approximately 24 hours, or 1 day.
Spectral Type: The classification of an asteroid, based on a measurement of the light reflected by the asteroid.

Watch live launch coverage of OSIRIS-REx to asteroid Bennu starting at 5:30 p.m, on NASA TV: http://www.nasa.gov/nasatv
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Birds developed the unique vocal organ that enables them to sing more than 66 million years ago when dinosaurs walked the Earth, a new fossil discovery has shown.
But the earliest syrinx, an arrangement of vibrating cartilage rings at the base of the windpipe, was still a long way from producing the lilting notes of a song thrush or blackbird.
Scientists believe the extinct duck and goose relative that possessed the organ was only capable of making honking noises.
The bird, Vegavis iaai, lived during the Cretaceous era. Although its fossil bones were unearthed from Vega Island in Antarctica in 1992, it was not until three years ago that experts spotted the syrinx.
All birds living today are descended from a particular family of dinosaurs that developed feathers and the ability to fly.
The new discovery suggests the syrinx is another hallmark of birds that was absent from non-avian dinosaurs…
23 science facts we didn't know at the start of 2016
1. Gravitational waves are real. More than 100 years after Einstein first predicted them, researchers finally detected the elusive ripples in space time this year. We’ve now seen three gravitational wave events in total.
2. Sloths almost die every time they poop, and it looks agonising.
3. It’s possible to live for more than a year without a heart in your body.
4. It’s also possible to live a normal life without 90 percent of your brain.
5. There are strange, metallic sounds coming from the Mariana trench, the deepest point on Earth’s surface. Scientists currently think the noise is a new kind of baleen whale call.
6. A revolutionary new type of nuclear fusion machine being trialled in Germany really works, and could be the key to clean, unlimited energy.
7. There’s an Earth-like planet just 4.2 light-years away in the Alpha Centauri star system - and scientists are already planning a mission to visit it.
8. Earth has a second mini-moon orbiting it, known as a ‘quasi-satellite’. It’s called 2016 HO3.
9. There might be a ninth planet in our Solar System (no, Pluto doesn’t count).
10. The first written record demonstrating the laws of friction has been hiding inside Leonardo da Vinci’s “irrelevant scribbles” for the past 500 years.
11. Zika virus can be spread sexually, and it really does cause microcephaly in babies.
12. Crows have big ears, and they’re kinda terrifying.
13. The largest known prime number is 274,207,281– 1, which is a ridiculous 22 million digits in length. It’s 5 million digits longer than the second largest prime.
14. The North Pole is slowly moving towards London, due to the planet’s shifting water content.
15. Earth lost enough sea ice this year to cover the entire land mass of India.
16. Artificial intelligence can beat humans at Go.
17. Tardigrades are so indestructible because they have an in-built toolkit to protect their DNA from damage. These tiny creatures can survive being frozen for decades, can bounce back from total desiccation, and can even handle the harsh radiation of space.
18. There are two liquid states of water.
19. Pear-shaped atomic nuclei exist, and they make time travel seem pretty damn impossible.
20. Dinosaurs had glorious tail feathers, and they were floppy.
21. One third of the planet can no longer see the Milky Way from where they live.
22. There’s a giant, 1.5-billion-cubic-metre (54-billion-cubic-foot) field of precious helium gas in Tanzania.
23. The ‘impossible’ EM Drive is the propulsion system that just won’t quit. NASA says it really does seem to produce thrust - but they still have no idea how. We’ll save that mystery for 2017.
It always creeps me out...
…that no matter
how close
you get
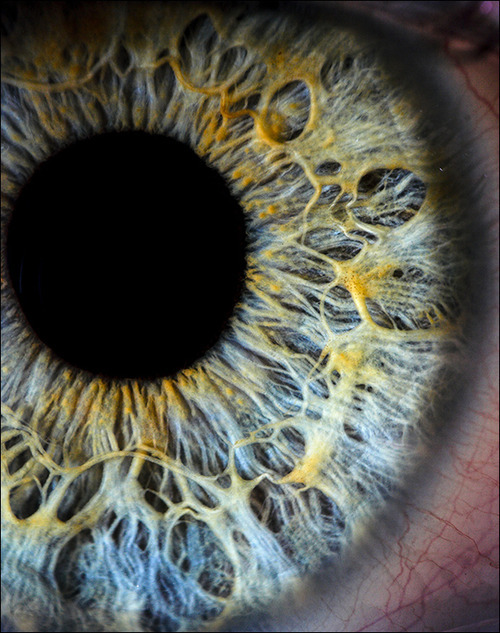
the pupil
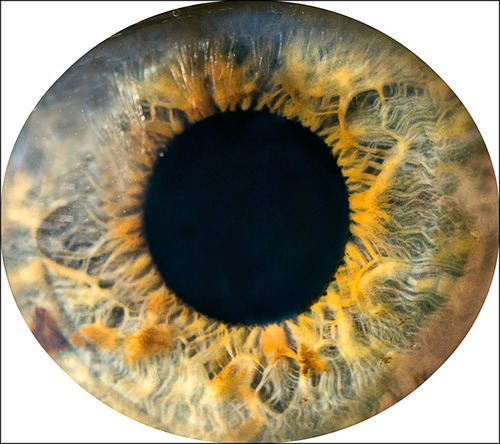
seems to
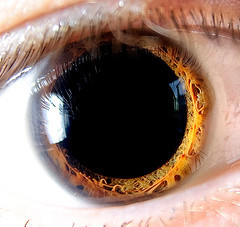
devour light
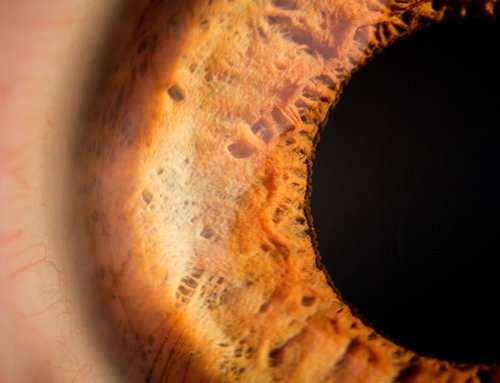
like a black hole
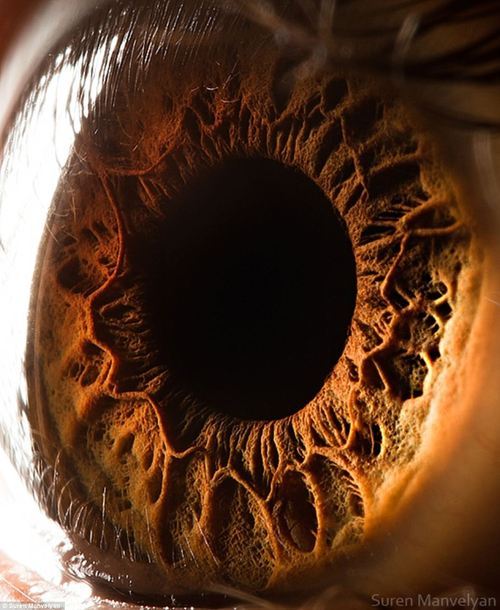
it reflects no light
-
 du-varg-du-varg liked this · 1 year ago
du-varg-du-varg liked this · 1 year ago -
 profanities-of-common-sense reblogged this · 6 years ago
profanities-of-common-sense reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 science-is-magical reblogged this · 6 years ago
science-is-magical reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 whalesandcraftbeers reblogged this · 8 years ago
whalesandcraftbeers reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 stokewillie liked this · 8 years ago
stokewillie liked this · 8 years ago -
 mrvmt liked this · 8 years ago
mrvmt liked this · 8 years ago -
 paradiselostregained-blog liked this · 8 years ago
paradiselostregained-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 no-words-for-iu liked this · 8 years ago
no-words-for-iu liked this · 8 years ago -
 megaomega reblogged this · 8 years ago
megaomega reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 enceoustion reblogged this · 8 years ago
enceoustion reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 logablog reblogged this · 8 years ago
logablog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 troiastar reblogged this · 8 years ago
troiastar reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 collector-of-stuff liked this · 8 years ago
collector-of-stuff liked this · 8 years ago -
 ihasquestions reblogged this · 8 years ago
ihasquestions reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 liamgmartin reblogged this · 8 years ago
liamgmartin reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 redshift-13 liked this · 8 years ago
redshift-13 liked this · 8 years ago -
 iammyfather reblogged this · 8 years ago
iammyfather reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 transroboteeveegirl reblogged this · 8 years ago
transroboteeveegirl reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 transroboteeveegirl liked this · 8 years ago
transroboteeveegirl liked this · 8 years ago -
 mariaozawapics liked this · 8 years ago
mariaozawapics liked this · 8 years ago -
 mahajkhan reblogged this · 8 years ago
mahajkhan reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mahajkhan liked this · 8 years ago
mahajkhan liked this · 8 years ago -
 asamamino reblogged this · 8 years ago
asamamino reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 alan-catlin reblogged this · 8 years ago
alan-catlin reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 alan-catlin liked this · 8 years ago
alan-catlin liked this · 8 years ago -
 cloudynightowl-blog liked this · 8 years ago
cloudynightowl-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 daedalus-crow-blog liked this · 8 years ago
daedalus-crow-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 artperformative-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
artperformative-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 artperformative-blog liked this · 8 years ago
artperformative-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 iwillpetyourdog reblogged this · 9 years ago
iwillpetyourdog reblogged this · 9 years ago