Just In Case You Forget This Exists.
Just in case you forget this exists.
It exists.
More Posts from Risingstarling and Others
Writing Antagonists: (Aka, Your Villains and Bad Guys)
The antagonist is often either one of the most fun things to write, or the most dreaded. But either way, they are a key element of the story, and that cannot be ignored. So, let’s talk about how to make a really great antagonist.
You may have in the past met a writer or teacher or whomever who insists on using the words “protagonist and antagonist” over words like “hero and villain.” Personally, I am not so stingy about it, I feel that I know what you mean anyway so it doesn’t really matter- what there is a legitimate reason as to why you should at least try to think of your villain as your antagonist instead.
And that reason is connotation. Well, denotation too, really- villain and antagonist aren’t completely the same thing, but I’m bringing it down to connotation.
Simply said, when you think of the word “villain”, you’ll think something like “that’s the bad guy in the story.” And when you think of the “antagonist”, you probably think “that’s a fancy word for villain, aka the bad guy in the story.”
But antagonist isn’t just a fancy word. It’s a fancy concept. It means “the guy that opposes the good guy.” That can be on any argument or view. When writing your antagonist is to remember that nothing is black/white, good/bad thinking, and that includes your antagonist.
Let’s map out the steps to making a complex villain- aka, an antagonist.
First, remember that your antagonist (usually) is a person, just like your protagonist. It might help to develop them outside of their intentions first, and put a person to the upcoming reputation.
Background:
Chances are, your antagonist didn’t just rise up out of the ground ready to kill. They came from somewhere. Your readers don’t even have to know everything about your antag’s backstory, but you do, if you want to really understand them. It often holds the key reason as to why your antagonist is where they are. The drive behind anger, revenge, change, or pleasing someone else can come from the events in their background.
Why do they hold the beliefs they hold? Were they raised that way? Were they taught by some mentor figure? Were they cover from a reality they couldn’t bear? Are they trying to please someone, or get revenge on someone who displeased them? The answer should be in their background.
Motives/Beliefs:
Remember, every villain is a hero in their own mind. They believe that what they are doing is necessary, even if they recognize that it is unpleasant. What are they fighting for? Why does it matter to them so much, that they are willing to overlook all the harm they do?
“The Greater Good”: This is one of the more common and understandable villain motives. They believe that what they are doing now is paving the way to a better future. But keep in mind that what your antag views as a “better future” may be very, very different than the average opinion. Maybe a “better future” for them is a genocidal purge or the world ending in flames. Who knows.
That’s not the only type of motive. Be creative. Work with the information you established in your character’s background to find the most reasonable motive.
Tipping Point:
This is going to be related to your background and motive in an interesting way. Think of your antagonist as a character who has already completed their Character Arc and reached a negative end. Look at the points of change on the character arc- the ones that push your character farther down their path. What are those events? Those are the tipping points that prompted your character towards becoming they way they are now- those key moments where your character had a choice, and they chose to become bitter, hateful, vengeful, cold, or other negative things.
These could be the deaths of loved ones, the promptings of a mentor, or a moment of injustice that made them realize that the world isn’t always kind.
Personality/Actions:
This is the part where you develop them outside of their intentions. How do they behave?
It’s tempting to just say that your villain is a villain because they torture and kill people. But those are not the only things that make a villain a scary or serious threat. Some characters might jump to violence easier than others. Some might be more into psychological torment. Some might actually seem really charming or persuasive, which is frightening in it’s own way- they might actually be tricky enough to confuse you into making bad decisions on your own. Think about your character’s background again. What makes the most sense for them as a person?
Presentation:
This is how your antagonist comes across to others. Keep in mind that your reader and your other characters don’t know your antagonist like you do. How does this person present to the world?
-Are they open to discussion/negotiation?
-Are they open about their intentions?
-How quick are they to violence?
-What are their methods of war?
-When you meet them, are they charismatic, quiet, charming, vulgar? Do they have a sense of humor, or are they stoic?
-Do they seem to enjoy what they are doing, or do they express regrets even as they do it?
Moral Complexity:
What are they willing to do to achieve their goals? Do they have weaknesses in their personal lives?
1. Do they have noble ends behind their controversial means?
2. Is there a line even they won’t cross?
3. Do they have someone/something that they care about?
4. Do they prefer to do the killing/torturing etc themselves or do they just give the order?
Remember that if your antagonist does have any of these moral weaknesses, they are not going to want to show it. One has to keep up intimidating appearances, after all.
Speaking of appearances…
Appearance:
This part is here to tell you what not to do. There are certain appearances that are getting really old with villains.
1. Dressing in all black. Why do they even do that? It’s time to stop associating black with “bad” and white with “good”. It just isn’t like that, so stop making villains all dark and stuff.
2. Scars. I think scars are pretty cool, don’t get me wrong. But if there is no relevant reason for it to be there, don’t talk about it all the time. That goes for all characters, not just villains. Like the color black, scars are not just a villain thing. Everyone has them. Don’t associate them with “bad.”
3. Sexy. I get the idea that making a villain attractive makes them harder to hate, but that can be kind of a cop out of actual complexity. Again, if there is no legitimate reason to make your villain sexy, then don’t. It’s not necessary.
4. Ugly. I hesitate to call any traits inherently ugly, but if you’re striving to make your character unpleasant looking just because they’re bad, then once again, you are associating feature=evil, which is not creative at best and seriously socially harmful at worst.
Basically, your villains should be just as diverse as anyone else. You don’t need stereotypes to make them scary. Sometimes it’s scarier than anything else to just have an average person. It sort of adds to the idea that anyone could be a villain. And that’s pretty frightening.
Key Point:
- Complicate your villains. They’re not just Evil McEvilpants.
That’s it for now, but like anything else in writing, antagonists have a lot of possibility and exceptions. But that was your basic rundown on the things to consider when making a complicated antagonist.
~Penemue










Japanese learning mistakes… There are TONS. Should you be worried and give up? NO! Because making mistakes and SCREWING UP is a NECESSARY part of learning. Only after you make a mistake and get corrected is when you get better!
So here’s a big list of Japanese Mistakes lesson for you. So that you get better at Japanese. Hope you enjoy!
Source – Taken from
For Learners: Top 52 Japanese Mistakes That Beginners Make
http://www.linguajunkie.com/japanese/japanese-mistakes-by-learners
1. Mistaking Particles Wa & Ga
は・が
This is one of the most common Japanese mistakes that learners make.
It is really hard to suggest a solution for this since even Japanese have moments where they doubt which one of these should be used. You really need to get used to it with time. But, let’s try anyway:
Solution: To put it simply:
は identifies the topic of the sentence
が identifies the subject of the sentence
2. Mistaking Particles Ni & De
に・で
Another common one. Both of these are connected with actions, but to make it a bit simpler let’s say that.
Solution…
に identifies and indicates “existence”, the location of the object.
で on the other hand indicates the location where the action is taking place.
3. Adjectives ending with い in the past tense
Yet another common mistake which pops up even if you’re not a beginner. Let’s take the word 寒い (cold). You see many learners who use 「寒いでした。」It’s wrong.
Solution:
The correct and polite way of saying “It was cold” is 「寒かったです。」.
It is important to pay attention to what type of an adjective you are using な or い.
4. Saying “You” in Japanese
あなた・君
Unlike English, one doesn’t really use the word you while talking to Japanese people.
Solution:
Instead we use the name of the certain person instead of saying you.「今日太郎に会えて良かった。」 is one example. Or, don’t say “you” at all. It’s kind of confrontational.
5. Saying “I” in Japanese
俺 – Ore (masculine)
僕 – Boku (masculine)
私 – Watashi (m/f)
あたし – Atashi (feminine)
There is a large number of personal pronouns in Japanese and the usage also depends on the gender, age, context, and of course your relation and the position of the person you are talking to.
Just be careful to use the gender appropriate pronoun, otherwise you might be frowned at.
Solution:
Say watashi for now. It’s safe and polite. Later, once you understand the full nuances, use them as you wish.
6.The Little Tsu
っ・ッ
Stop! Another one of the common Japanese mistakes here!
Okay this tiny little thing changes the pronunciation of your word and along with it most likely even the meaning. It basically is used to double the sound of the consonant. If you pay attention to your pronunciation, this shouldn’t be a huge problem.
7. Long vowels
Yet another pronunciation mistake pretty similar to the one above. More often than not the meaning of the word will change depending on the length of the vowel, for example:
おばさん (aunt)
おばあさん (grandmother)
8. Iru & Aru in Japanese
いる・ある
Mixing these up is a very common Japanese mistake.
These are words indicating existence of living beings and things respectively. It is common to see learners use ある when talking about animals, but you should keep in your mind that with animals and birds, and everything else that can breathe you use いる.
Solution:
Living Beings: Use いる
Inanimate Objects: Use ある
9. Katakana – カタカナ
For some reason many learners find it harder to remember katakana compared to hiragana and kanji. A
And yet another issue is we never seem to understand what the katakana words mean since they often do not match their English pronunciations. Hence, we too pronounce English words wrongly when we try to change them into katakana.
This would go on the “understandable” Japanese mistakes list. If you make it, I can sympathize.
10. The excessive usage of と
と is pretty much the equivalent of “and” in English. However it cannot be used in every situation. For example when you are connecting adjectives you can’t use と.
Solution:
Instead you will have something like this: 「可愛くて、美しくて、素敵だった」. In other words the form of the word itself changes.
11. Apologizing in Japanese
There are a lot of words in Japanese that can be used for apologizing, and they vary from situation to situation. However let’s concentrate on 「ごめんなさい」 and 「すみません」. They are quite interchangeable but to make it easier for you:
Solution
Let’s say that:
ごめんなさい is equivalent to “sorry”
すみません is “excuse me”.
Keep it simple and use them like that.
12. Japanese Greeting Mistakes
The most common greeting in Japan is 「こんにちは」. However when meeting close friends it is better to avoid this phrase, since it is formal.
Solution
You’d have better chances of bonding with your friends if you use おっす/hello for bye orおつかれ/otsukare for bye.
13. Dakara and Kara
だから・から
And again, learners tend to use だから even when から is supposed to be used. A simple example of this will be 「美味しいだから」.
Solution
だから is usually used with nouns and な type of adjectives, not with verbs or い adjectives.
14. Misusing Desu kara
~ですから
We often use this when we are explaining something, or pointing reasons for this or that. However to most Japanese this will sound like you are trying to find an excuse for your actions.
15. Calling someone “san”
~さん
Now 「さん」 is a suffix that we add when we are talking to somebody, but a lot of Japanese learners seem to add this even to their own names when talking about themselves. Just DO NOT ever do this.
16. Thanking someone in Japanese
ありがとう・ありがとうございます
Well the main difference here is informal/formal.
However you should be careful when using the informal version. If you are talking to somebody who is clearly above you, be it age-wise or position-wise, no matter how close you are there are situations when it’s better to use the formal version. For example, when you have asked them for a favor.
17. Keigo – 敬語 (formal speech)
Now, this is the opposite of the above above. Do not talk to your close friends in 敬語 (unless you have to ask them to do a big favor to you), because this will make them think you are trying to distance yourself from them and all of this can get in the way of your friendship.
18. Sorea, Are, Soko, Asoko
それ – Sore – That
あれ – Are – That (over there – further than sore)
そこ – Soko – Over there
あそこ – Asoko – Way Over there (further than asoko)
These mean that and there if you look for the English equivalents. However as in everything else with Japanese, the nuances matter. To put it simply それ indicates closeness to the person you are talking to, while あれ suggests that the thing is not close to either of you.
19. Gender appropriate
Japanese is a very gender specific language, like it or not. It’s not like you will become a social outcast but people will point out that you sound girly, or that you have a very dirty and boyish vocabulary for a young girl.
20. The Overall Mess of Kanji
We can turn this article into 1,000 Japanese mistakes if we expanded on this.
So!
If you have been learning Japanese for any period of time and do not have Chinese or Korean background, kanji has probably been a pain in the neck for you. You miss one tiny part and the meaning of the word changes. Not to mention there are hundreds and hundreds of them to memories.
21. Confusing words that have the exact same pronunciation
Okay, this might be a bit tricky, but you have to figure out the meaning out of the context or depending on the kanji and intonation. Not much else can be done.
Here are some examples:
地震・自身 – both are “jishin”
橋・箸・端 – all are “hashi”
22. ~してもいいですか・~してもよろしいでしょうか
They both basically mean “can i do this”, however the main difference is in the level of politeness. If you are talking to a senpai, teacher, professor, boss, somebody who is older than you, or somebody who is above you in any way, it is highly recommended to use the latter rather than the former.
23. Kawaiisou vs Kawaisou
可愛いそう – Kawaiisou
可哀そう – Kawaisou
When you try to describe something, you usually add ~そう at the end of your い adjective. To do this you cut the い and replace it with the ~そう. However, even though the difference is clear in written form thanks to kanji, a mistake in pronunciation will change the meaning from “cute” to “pitiful”.
24. Misusing Morau, Ageru, Kureru
もらう・あげる・くれる
I don’t know about you but learning the difference between these was a burning hell to me. もらう means to receive, while the other two mean to give.
However, depending on how you use these, the meaning can get pretty confusing, i.e. 「手伝ってくれてもいいですか。」 is offering your help to someone, so be sure to use もらう instead if you are looking for help!
This is one of those Japanese mistakes even the pros make at times.
25. The Particle No
の
A lot of people seem to misuse 「の」. For example, using a の in between an adjective and noun –「厳しいの先生」– Kibishii no sensei – strict teacher.
The 「の」here is redundant and there is no need to use it at all. Why? Because the adjective already modifies AND belongs to the noun. That’s the job of an adjective, to modify a noun. There’s no need to use の.
http://www.linguajunkie.com/japanese/japanese-mistakes-by-learners

How to burn calories
- Eat yogurt! Studies have shown that people who ate low fat yogurt lost 70% more fat than those who didn’t.
- The more you increase the intensity in your workouts, you’ll burn more fat faster than regular aerobic exercises.
- Iron helps oxygen get to your cells and if your cells aren’t getting enough oxygen, your metabolism will start to slow down.
- Drink water! Water helps your body perform better and increases your metabolism up to 30%. The colder it is, the better it is.
- Alcohol slows down your metabolism, it’s not healthy and you should try to stay away from it.
- Drinking green tea can increase your metabolism and it helps you burn up to 60 calories a day!
—
Please message me any tips you’d like me to post
I took a second the do the proper accents and that is so true 😂

(Via: Instagram.com) 😂👏👌 . Which way do you say it? . I say it like both British and American . . . . . . #louistomlinson #lou #boobear #niallhoran #nialler #harrystyles #hazza #liampayne #leeyum #daddydirectioner #zaynmalik #djmalik #onedirection #upallnight #takemehome #whereweare #thisisus #directionerforever #directioner #larry #lilo #lirry #zarry #zouis #ziall #ziam #nouis #narry #niam - See One Direction Live! http://ow.ly/r72Te
![Pote Usa Loppy Fur Color Plushies (Big) [Pre-order] $24,99](https://64.media.tumblr.com/4940eace99e67a4a4186909a97e1fd36/tumblr_nqy4jbIwj41t1hhoho1_500.jpg)
Pote Usa Loppy Fur Color Plushies (Big) [Pre-order] $24,99
Sign up here for a $5 coupon c;


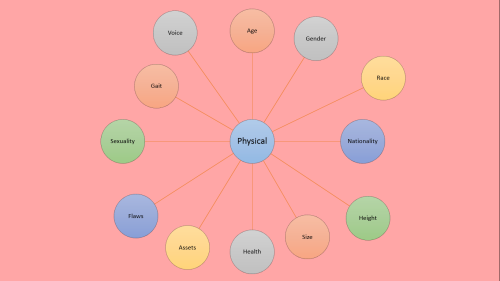

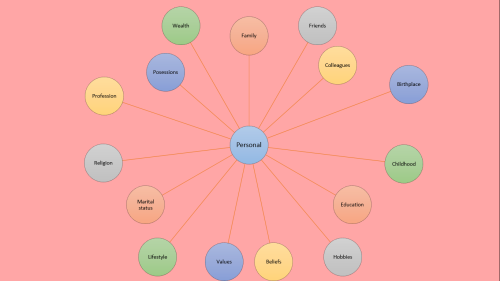
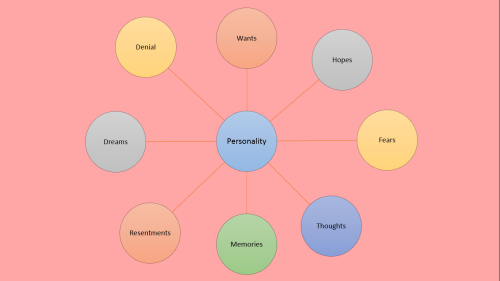
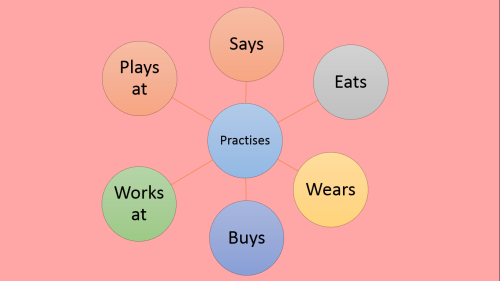

I made a slideshow about how to create a fictional character… I got most of the information from the ‘start writing fiction’ (free) course on the OpenUniversity website and found it incredibly useful so here’s a visual version for you :)

Keep reading

-
 candiegray reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
candiegray reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 everyartreferencepostilleverneed reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
everyartreferencepostilleverneed reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 psybelle-draws liked this · 3 weeks ago
psybelle-draws liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 acidicleafbat liked this · 3 weeks ago
acidicleafbat liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 pen-and-paper-needed liked this · 3 weeks ago
pen-and-paper-needed liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 enjolrasingaround liked this · 3 weeks ago
enjolrasingaround liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 too-late-to-change-the-name-now reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
too-late-to-change-the-name-now reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 too-late-to-change-the-name-now liked this · 3 weeks ago
too-late-to-change-the-name-now liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 luisalecto liked this · 3 weeks ago
luisalecto liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 nebulous-aroace-from-outerspace reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
nebulous-aroace-from-outerspace reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 nebulous-aroace-from-outerspace liked this · 3 weeks ago
nebulous-aroace-from-outerspace liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 sparklingwaterhater liked this · 4 weeks ago
sparklingwaterhater liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 badlifedecisionshotline reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
badlifedecisionshotline reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 badlifedecisionshotline liked this · 4 weeks ago
badlifedecisionshotline liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 necoslav liked this · 4 weeks ago
necoslav liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 savvytwinkle liked this · 4 weeks ago
savvytwinkle liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 cerberus253 reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
cerberus253 reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 write-with-will liked this · 4 weeks ago
write-with-will liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 frozenoverblackballoon liked this · 1 month ago
frozenoverblackballoon liked this · 1 month ago -
 miyabinopenguin liked this · 1 month ago
miyabinopenguin liked this · 1 month ago -
 tetrasealion reblogged this · 1 month ago
tetrasealion reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 tinamisu liked this · 1 month ago
tinamisu liked this · 1 month ago -
 purpleinkdrinker liked this · 1 month ago
purpleinkdrinker liked this · 1 month ago -
 707shappiness reblogged this · 1 month ago
707shappiness reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 indefinitereferences reblogged this · 1 month ago
indefinitereferences reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 nezjazz reblogged this · 1 month ago
nezjazz reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 windyocinspo reblogged this · 1 month ago
windyocinspo reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 shark-time liked this · 1 month ago
shark-time liked this · 1 month ago -
 erraticloners liked this · 1 month ago
erraticloners liked this · 1 month ago -
 maresources reblogged this · 1 month ago
maresources reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 naturaldogoils liked this · 1 month ago
naturaldogoils liked this · 1 month ago -
 eeriealmonds liked this · 1 month ago
eeriealmonds liked this · 1 month ago -
 pyr0bot-art liked this · 1 month ago
pyr0bot-art liked this · 1 month ago -
 onlyhereforturtles reblogged this · 1 month ago
onlyhereforturtles reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 maybelinefox reblogged this · 1 month ago
maybelinefox reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 exhaustedmay-reblogs reblogged this · 1 month ago
exhaustedmay-reblogs reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 exhaustedwriterartist liked this · 1 month ago
exhaustedwriterartist liked this · 1 month ago -
 bowandbrush-the-sequel reblogged this · 1 month ago
bowandbrush-the-sequel reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 a-simple-gremlin reblogged this · 1 month ago
a-simple-gremlin reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 hmmwellok reblogged this · 1 month ago
hmmwellok reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 greybazzy liked this · 1 month ago
greybazzy liked this · 1 month ago -
 snarechan reblogged this · 1 month ago
snarechan reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 best-yet reblogged this · 1 month ago
best-yet reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 best-yet liked this · 1 month ago
best-yet liked this · 1 month ago -
 buckybucananbarnes reblogged this · 1 month ago
buckybucananbarnes reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 toc-the-scrambled liked this · 1 month ago
toc-the-scrambled liked this · 1 month ago -
 fiend-for-culture reblogged this · 1 month ago
fiend-for-culture reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 afrotunada reblogged this · 1 month ago
afrotunada reblogged this · 1 month ago
Right now this is just anything that comes to mind since I'm a complete noob at tumblr. I've been hearing about it for years but I never really felt like I had anything to say. Well all that has changed now and I figured I'd see what all the hype about tumlr is really about. Anyway don't take anything I say too seriously for now...I'll probably change it later when I become more comfortable with this website.
168 posts