Mars - Blog Posts
NASA Langley researchers are experts in modeling and simulations for entry, descent and landing, working on missions since the Viking lander in 1976. In this episode, we explore the challenges of guiding landers like Mars InSight through the Martian atmosphere for a safe landing.



NASA InSight launched on March 5, 2018.
For more, visit https://mars.nasa.gov/insight/
Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage 101

We need the biggest rocket stage ever built for the bold missions in deep space that NASA's Space Launch System rocket will give us the capability to achieve. This infographic sums up everything you need to know about the SLS core stage, the 212-foot-tall stage that serves as the backbone of the most powerful rocket in the world. The core stage includes the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank that hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and the journey to Mars.
Image Credit: NASA/MSFC
Orion Launch Abort System Motor Gets Fired-up About the Journey to Mars
Applause resounded from NASA and its partners as they watched Orion’s jettison motor generate 40,000 pounds of thrust in just a blink of an eye, preparing the spacecraft for its first integrated mission with the Space Launch System rocket.
Onlookers had just witnessed a 1.5-second jettison motor test firing at Aerojet Rocketdyne’s facility in Sacramento, California.
The Orion launch abort system (LAS) is designed to protect astronauts in the unlikely event there is an issue during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from the rocket during a mission. The jettison motor is activated during ascent to separate the launch abort system from the spacecraft after it is no longer needed during a mission.
“This test showed us that the jettison motor can quickly generate the amount of thrust needed to pull the LAS away during an Orion mission,” said Tim Larson, jettison motor principle engineer for Lockheed Martin who has been with the project since inception. “I’m very pleased with how the test went.”
The fifth firing
The jettison motor has now undergone five tests, including two test flights. Each test in the series builds upon each other, moving the nation forward on its journey to Mars.
The motor used for the fifth test was rebuilt from a previous test motor.
“We were able to recycle some of the parts from the second ground test and use it for this test,” said NASA LAS project manager Robert Decoursey. “We not only went green, but we also saved money.”
Inside and around the test motor were instruments that included strain gauges, accelerometers and pressure transducers, which feed engineers high-quality data that show whether the motor design is ready for upcoming flight tests and missions. This motor had more instruments and produced more data than any of the previous tests.
“There are many intricate details in the jettison motor design that are not obvious from the outside, and the consistent orchestration of those details are most important to obtain predictable performance,” said NASA LAS deputy project manager Deborah Crane. “Aerojet Rocketdyne has done an excellent job executing this test on schedule.”
The jettison motor bakery
Creating a jettison motor is like baking two big cakes and making enough batter for some leftover cupcakes, according to Tim Warner, NASA LAS business manager.
The jettison motor being tested in the photo above would be activated during ascent to separate the launch abort system from the spacecraft after it is no longer needed during a mission.Credits: Aerojet Rocketdyne
What’s most exciting for the team, besides the successful test, are the latest upgrades to their baking and mixing tools.
“We were using two mixing batches to make just one motor, but have recently upgraded to a larger mixing bowl, saving us time and money,” Decoursey said.
The new mixing bowl can hold up to 450 whopping gallons of cake batter, or in NASA terms, motor propellant.
The team mixes up the batter in this large mixing bowl and evenly splits the batter into two pots for a perfectly sculpted jettison motor.
Any leftover propellant is used to make small test motors. The smaller motors are used to check the propellant’s combustion capabilities before the motors are accepted for test or flight.
What’s next?
NASA and its partners are expected to perform the last flight test of the launch abort system in 2019 before they begin sending crew to deep space aboard Orion. During the final test, an uncrewed Orion capsule will launch from a modified Peacekeeper missile and demonstrate a successful abort under the highest aerodynamic loads it could experience during a mission.
The jettison motor will be used during Orion’s first integrated mission with SLS, known as Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) in late 2018. The mission will be the second test flight for Orion, and the first for SLS. EM-1 will send Orion on a three-week journey approximately 40,000 miles beyond the moon. The test will demonstrate the integrated performance of the rocket and spacecraft before their second test flight together, Exploration Mission-2, which will carry crew.
The LAS is led out NASA’s Langley Research Center in Virginia in collaboration with NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama.
Sasha Ellis
NASA Langley Research Center

The Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) is one of the largest buildings in the world (525 ft 10 in tall, 716 ft long, and 518 ft wide) . It was originally built for assembly of Apollo/Saturn vehicles and was later modified to support Space Shuttle operations and now, Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission 1.
In this view looking up from the floor of the VAB at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, four levels of new work platforms are now installed on the north and south sides of High Bay 3. The G-level work platforms were most recently installed, at about the 14th floor level. Below them are the H, J and K level platforms.
The G-level work platforms are the fourth of 10 levels of work platforms that will surround and provide access to SLS. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to VAB High Bay 3, including installation of the new work platforms, to prepare for NASA’s journey to Mars.

NASA Langley researchers and engineers are:
Playing key roles in the development of both the Space Launch System and the Orion crew capsule, which will carry astronauts beyond the moon to an asteroid, and eventually to the dusty surface of the Red Planet.
Leading the aerodynamic design of the Space Launch System by doing analysis and extensive testing in facilities such as the Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel and Transonic Dynamics Tunnel.
Performing water impact testing and doing critical aerosciences and structural analyses for the Orion crew capsule. We also assist in analyzing and practicing recovery operations for Orion.
Developing Orion's Launch Abort System, or LAS, which is designed to protect astronauts in the unlikely event a problem arises during launch.
Spearheading work on advanced entry, descent, and landing (EDL) systems for planetary robotic missions and eventual human-scale missions to the surface of Mars. Understanding the aerodynamics and heating of atmospheric entry will enable more precise landing missions, while testing of new technologies will enable much larger missions to reach the Martian surface.
Developing safe and reliable autonomous systems to supplement human operations, including mechanisms that can work in deep space to maneuver, assemble and service structures. In the 2020s, NASA plans to use this kind of technology to retrieve an asteroid.
Leading the development of materials and structures for lightweight and affordable space transportation and habitation systems.
Solving the problems of deep space radiation protection, including leadership of the Human Research Program to develop a better understanding of space radiation on crew health and safety. Langley is also building prototype designs for habitats and storm shelters for use in space.
Working on sensor systems, known as Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology (ALHAT), that will equip future planetary landers with the ability to assess landing hazards and land safely and precisely on many different planetary surfaces, including the moon, Mars and other planetary bodies.
Developing the Hypersonic Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator, or HIAD, a device that could some day help cargo, or even people, land on another planet. HIAD could give NASA more options for future planetary missions, because it could allow spacecraft to carry larger, heavier scientific instruments and other tools for exploration.
NASA Crash-Test Dummies Make A Splash Landing

Engineers drop a NASA’s Orion Spacecraft test capsule with crash-test dummies inside into 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin to simulate what the spacecraft may experience when splashing down in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions.
More: http://www.nasa.gov/feature/langley/nasa-crash-test-dummies-suit-up-for-action

Curiosity Self-Portrait at Martian Sand Dune
This self-portrait of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows the vehicle at "Namib Dune," where the rover's activities included scuffing into the dune with a wheel and scooping samples of sand for laboratory analysis.
The scene combines 57 images taken on Jan. 19, 2016, during the 1,228th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars. The camera used for this is the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) at the end of the rover's robotic arm.
Namib Dune is part of the dark-sand "Bagnold Dune Field" along the northwestern flank of Mount Sharp. Images taken from orbit have shown that dunes in the Bagnold field move as much as about 3 feet (1 meter) per Earth year.
The location of Namib Dune is show on a map of Curiosity's route athttp://mars.nasa.gov/msl/multimedia/images/?ImageID=7640. The relationship of Bagnold Dune Field to the lower portion of Mount Sharp is shown in a map at PIA16064.
The view does not include the rover's arm. Wrist motions and turret rotations on the arm allowed MAHLI to acquire the mosaic's component images. The arm was positioned out of the shot in the images, or portions of images, that were used in this mosaic. This process was used previously in acquiring and assembling Curiosity self-portraits taken at sample-collection sites, including "Rocknest" (PIA16468), "Windjana" (PIA18390) and "Buckskin" (PIA19807).
For scale, the rover's wheels are 20 inches (50 centimeters) in diameter and about 16 inches (40 centimeters) wide.
MAHLI was built by Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover.
More information about Curiosity is online at http://www.nasa.gov/msl andhttp://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl/.
New Gravity Map Gives Best View Yet Inside Mars
A new map of Mars' gravity made with three NASA spacecraft is the most detailed to date, providing a revealing glimpse into the hidden interior of the Red Planet.
"Gravity maps allow us to see inside a planet, just as a doctor uses an X-ray to see inside a patient," said Antonio Genova of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, Massachusetts. "The new gravity map will be helpful for future Mars exploration, because better knowledge of the planet's gravity anomalies helps mission controllers insert spacecraft more precisely into orbit about Mars. Furthermore, the improved resolution of our gravity map will help us understand the still-mysterious formation of specific regions of the planet." Genova, who is affiliated with MIT but is located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, is the lead author of a paper on this research published online March 5 in the journal Icarus.
The improved resolution of the new gravity map suggests a new explanation for how some features formed across the boundary that divides the relatively smooth northern lowlands from heavily cratered southern highlands. Also, the team confirmed that Mars has a liquid outer core of molten rock by analyzing tides in the Martian crust and mantle caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and the two moons of Mars. Finally, by observing how Mars' gravity changed over 11 years – the period of an entire cycle of solar activity -- the team inferred the massive amount of carbon dioxide that freezes out of the atmosphere onto a Martian polar ice cap when it experiences winter. They also observed how that mass moves between the south pole and the north pole with the change of season in each hemisphere.

The map was derived using Doppler and range tracking data collected by NASA's Deep Space Network from three NASA spacecraft in orbit around Mars: Mars Global Surveyor (MGS), Mars Odyssey (ODY), and the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Like all planets, Mars is lumpy, which causes the gravitational pull felt by spacecraft in orbit around it to change. For example, the pull will be a bit stronger over a mountain, and slightly weaker over a canyon.
Slight differences in Mars' gravity changed the trajectory of the NASA spacecraft orbiting the planet, which altered the signal being sent from the spacecraft to the Deep Space Network. These small fluctuations in the orbital data were used to build a map of the Martian gravity field.

The gravity field was recovered using about 16 years of data that were continuously collected in orbit around Mars. However, orbital changes from uneven gravity are tiny, and other forces that can perturb the motion of the spacecraft had to be carefully accounted for, such as the force of sunlight on the spacecraft's solar panels and drag from the Red Planet's thin upper atmosphere. It took two years of analysis and computer modeling to remove the motion not caused by gravity.
"With this new map, we've been able to see gravity anomalies as small as about 100 kilometers (about 62 miles) across, and we've determined the crustal thickness of Mars with a resolution of around 120 kilometers (almost 75 miles)," said Genova. "The better resolution of the new map helps interpret how the crust of the planet changed over Mars' history in many regions."
For example, an area of lower gravity between Acidalia Planitia and Tempe Terra was interpreted before as a system of buried channels that delivered water and sediments from Mars' southern highlands into the northern lowlands billions of years ago when the Martian climate was wetter than it is today. The new map reveals that this low gravity anomaly is definitely larger and follows the boundary between the highlands and the lowlands. This system of gravity troughs is unlikely to be only due to buried channels because in places the region is elevated above the surrounding plains. The new gravity map shows that some of these features run perpendicular to the local topography slope, against what would have been the natural downhill flow of water.

An alternative explanation is that this anomaly may be a consequence of a flexure or bending of the lithosphere -- the strong, outermost layer of the planet -- due to the formation of the Tharsis region. Tharsis is a volcanic plateau on Mars thousands of miles across with the largest volcanoes in the solar system. As the Tharsis volcanoes grew, the surrounding lithosphere buckled under their immense weight.
The new gravity field also allowed the team to confirm indications from previous gravity solutions that Mars has a liquid outer core of molten rock. The new gravity solution improved the measurement of the Martian tides, which will be used by geophysicists to improve the model of Mars' interior.
Changes in Martian gravity over time have been previously measured using the MGS and ODY missions to monitor the polar ice caps. For the first time, the team used MRO data to continue monitoring their mass. The team has determined that when one hemisphere experiences winter, approximately 3 trillion to 4 trillion tons of carbon dioxide freezes out of the atmosphere onto the northern and southern polar caps, respectively. This is about 12 to 16 percent of the mass of the entire Martian atmosphere. NASA's Viking missions first observed this massive seasonal precipitation of carbon dioxide. The new observation confirms numerical predictions from the Mars Global Reference Atmospheric Model – 2010.
The research was funded by grants from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter mission and NASA's Mars Data Analysis Program.
Bill Steigerwald
The wonders of Mars
1,000 Days in Orbit: MAVEN’s Top 10 Discoveries at Mars
On June 17, our MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission) will celebrate 1,000 Earth days in orbit around the Red Planet.

Since its launch in November 2013 and its orbit insertion in September 2014, MAVEN has been exploring the upper atmosphere of Mars. MAVEN is bringing insight to how the sun stripped Mars of most of its atmosphere, turning a planet once possibly habitable to microbial life into a barren desert world.

Here’s a countdown of the top 10 discoveries from the mission so far:
10. Unprecedented Ultraviolet View of Mars

Revealing dynamic, previously invisible behavior, MAVEN was able to show the ultraviolet glow from the Martian atmosphere in unprecedented detail. Nightside images showed ultraviolet “nightglow” emission from nitric oxide. Nightglow is a common planetary phenomenon in which the sky faintly glows even in the complete absence of eternal light.
9. Key Features on the Loss of Atmosphere

Some particles from the solar wind are able to penetrate unexpectedly deep into the upper atmosphere, rather than being diverted around the planet by the Martian ionosphere. This penetration is allowed by chemical reactions in the ionosphere that turn the charged particles of the solar wind into neutral atoms that are then able to penetrate deeply.
8. Metal Ions

MAVEN made the first direct observations of a layer of metal ions in the Martian ionosphere, resulting from incoming interplanetary dust hitting the atmosphere. This layer is always present, but was enhanced dramatically by the close passage to Mars of Comet Siding Spring in October 2014.
7. Two New Types of Aurora

MAVEN has identified two new types of aurora, termed “diffuse” and “proton” aurora. Unlike how we think of most aurorae on Earth, these aurorae are unrelated to either a global or local magnetic field.
6. Cause of the Aurorae

These aurorae are caused by an influx of particles from the sun ejected by different types of solar storms. When particles from these storms hit the Martian atmosphere, they can also increase the rate of loss of gas to space, by a factor of ten or more.
5. Complex Interactions with Solar Wind

The interactions between the solar wind and the planet are unexpectedly complex. This results due to the lack of an intrinsic Martian magnetic field and the occurrence of small regions of magnetized crust that can affect the incoming solar wind on local and regional scales. The magnetosphere that results from the interactions varies on short timescales and is remarkably “lumpy” as a result.
4. Seasonal Hydrogen

After investigating the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet for a full Martian year, MAVEN determined that the escaping water does not always go gently into space. The spacecraft observed the full seasonal variation of hydrogen in the upper atmosphere, confirming that it varies by a factor of 10 throughout the year. The escape rate peaked when Mars was at its closest point to the sun and dropped off when the planet was farthest from the sun.
3. Gas Lost to Space

MAVEN has used measurements of the isotopes in the upper atmosphere (atoms of the same composition but having different mass) to determine how much gas has been lost through time. These measurements suggest that 2/3 or more of the gas has been lost to space.
2. Speed of Solar Wind Stripping Martian Atmosphere

MAVEN has measured the rate at which the sun and the solar wind are stripping gas from the top of the atmosphere to space today, along with details of the removal process. Extrapolation of the loss rates into the ancient past – when the solar ultraviolet light and the solar wind were more intense – indicates that large amounts of gas have been lost to space through time.
1. Martian Atmosphere Lost to Space

The Mars atmosphere has been stripped away by the sun and the solar wind over time, changing the climate from a warmer and wetter environment early in history to the cold, dry climate that we see today.
Maven will continue its observations and is now observing a second Martian year, looking at the ways that the seasonal cycles and the solar cycle affect the system.
For more information about MAVEN, visit: www.nasa.gov/maven
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Happy Martian New Year!

For any planet, a year is the time it takes to make one orbit around the sun. Because Mars is farther away from the sun, it has to travel a greater distance than Earth. It takes Mars about twice as long as it does for Earth to make one circle around the sun…therefore, a year on Mars lasts twice as long.

On May 5, Mars passes solar longitude 0 as the sun crosses the equator on Mars. This is the vernal equinox and was chosen by planetary scientists as the start of a new year.

Mars has four seasons, roughly twice as long as those on Earth, but with more variation given Mars’ eccentric orbit and the fact its orbital speed varies more as a result.

Did you know that there’s a U.S. city named Mars? Mars, PA hosts an annual Mars New Year celebration and we’re participating in this two-day science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) event to inspire young people to pursue innovation and exploration.

More info on Mars, PA: http://www.marsnewyear.com/
Get updated images from the events in Mars, PA here: https://www.flickr.com/photos/nasahqphoto/sets/72157683457751005/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, let us break it down for you. Here are a few things to know this week:
1. The View from the Far Shore

The rugged shores of Pluto’s highlands come into sharp view in a newly released image from our New Horizons spacecraft. This latest view zooms in on the southeastern portion of Pluto’s great ice plains, where they border dark highlands formerly named Krun Macula.
2. Dawn’s Latest Light

Our Dawn mission has now completed more than 1,000 orbital revolutions since entering into Ceres’ gravitational grip in March 2015. The probe is healthy and performing its ambitious assignments impeccably. See what it has revealed lately HERE.
3. Counting Down

Our OSIRIS-REx mission to the asteroid Bennu is now entering the final preparations for its planned launch in September. In a new interview, the mission’s principal investigator reports on the final pre-flight tests happening at our Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
4. Deep Dive

Three successful engine maneuvers to bring the lowest part of the spacecraft’s orbit down to just 74 miles (119 km) above the surface of Mars, the MAVEN mission’s fifth deep dip campaign has begun. MAVEN is studying the planet’s atmosphere up close.
5. Storm Season

Meanwhile, other robotic Mars orbiters have revealed that a pattern of three large regional dust storms occurs with similar timing most Martian years. The seasonal pattern was detected from dust storms’ effects on atmospheric temperatures, which spacecraft have been monitoring since 1997.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Bob Eggleton’s Mars hotel is named “Mars Hotel”
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
There’s even more to Mars.

1. Batten Down the Hatches
Good news for future astronauts: scientists are closer to being able to predict when global dust storms will strike the Red Planet. The winds there don’t carry nearly the same force that was shown in the movie “The Martian,” but the dust lofted by storms can still wreak havoc on people and machines, as well as reduce available solar energy. Recent studies indicate a big storm may be brewing during the next few months.
+ Get the full forecast

2. Where No Rover Has Gone Before
Our Opportunity Mars rover will drive down an ancient gully that may have been carved by liquid water. Several spacecraft at Mars have observed such channels from a distance, but this will be the first up-close exploration. Opportunity will also, for the first time, enter the interior of Endeavour Crater, where it has worked for the last five years. All this is part of a two-year extended mission that began Oct. 1, the latest in a series of extensions going back to the end of Opportunity’s prime mission in April 2004. Opportunity landed on Mars in January of that year, on a mission planned to last 90 Martian days (92.4 Earth days). More than 12 Earth years later, it’s still rolling.
+ Follow along + See other recent pictures from Endeavour Crater

3. An Uphill Climb
Opportunity isn’t the only NASA Mars rover getting a mission extension. On the other side of the planet, the Curiosity rover is driving and collecting samples amid some of the most scenic landscapes ever visited on Mars. Curiosity’s two-year mission extension also began Oct. 1. It’s driving toward uphill destinations, including a ridge capped with material rich in the iron-oxide mineral hematite, about a mile-and-a-half (two-and-a-half kilometers) ahead. Beyond that, there’s an exposure of clay-rich bedrock. These are key exploration sites on lower Mount Sharp, which is a layered, Mount-Rainier-size mound where Curiosity is investigating evidence of ancient, water-rich environments that contrast with the harsh, dry conditions on the surface of Mars today.
+ Learn more

4. Keep a Sharp Lookout
Meanwhile, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter continues its watch on the Red Planet from above. The mission team has just released a massive new collection of super-high-resolution images of the Martian surface.
+ Take a look

5. 20/20 Vision for the 2020 Rover
In the year 2020, Opportunity and Curiosity will be joined by a new mobile laboratory on Mars. In the past week, we tested new “eyes” for that mission. The Mars 2020 rover’s Lander Vision System helped guide the rocket to a precise landing at a predesignated target. The system can direct the craft toward a safe landing at its primary target site or divert touchdown toward better terrain if there are hazards in the approaching target area.
+ Get details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
humanitys journey to mars
post by nasa
Getting to Mars: 4 Things We’re Doing Now
We’re working hard to send humans to Mars in the 2030s. Here are just a few of the things we’re doing now that are helping us prepare for the journey:
1. Research on the International Space Station

The International Space Station is the only microgravity platform for the long-term testing of new life support and crew health systems, advanced habitat modules and other technologies needed to decrease reliance on Earth.

When future explorers travel to the Red Planet, they will need to be able to grow plants for food, atmosphere recycling and physiological benefits. The Veggie experiment on space station is validating this technology right now! Astronauts have grown lettuce and Zinnia flowers in space so far.

The space station is also a perfect place to study the impacts of microgravity on the human body. One of the biggest hurdles of getting to Mars in ensuring that humans are “go” for a long-duration mission. Making sure that crew members will maintain their health and full capabilities for the duration of a Mars mission and after their return to Earth is extremely important.

Scientists have solid data about how bodies respond to living in microgravity for six months, but significant data beyond that timeframe had not been collected…until now! Former astronaut Scott Kelly recently completed his Year in Space mission, where he spent a year aboard the space station to learn the impacts of microgravity on the human body.
A mission to Mars will likely last about three years, about half the time coming and going to Mars and about half the time on the Red Planet. We need to understand how human systems like vision and bone health are affected and what countermeasures can be taken to reduce or mitigate risks to crew members.
2. Utilizing Rovers & Tech to Gather Data

Through our robotic missions, we have already been on and around Mars for 40 years! Before we send humans to the Red Planet, it’s important that we have a thorough understanding of the Martian environment. Our landers and rovers are paving the way for human exploration. For example, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has helped us map the surface of Mars, which will be critical in selecting a future human landing site on the planet.

Our Mars 2020 rover will look for signs of past life, collect samples for possible future return to Earth and demonstrate technology for future human exploration of the Red Planet. These include testing a method for producing oxygen from the Martian atmosphere, identifying other resources (such as subsurface water), improving landing techniques and characterizing weather, dust and other potential environmental conditions that could affect future astronauts living and working on Mars.

We’re also developing a first-ever robotic mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid, collect a multi-ton boulder from its surface and redirect it into a stable orbit around the moon. Once it’s there, astronauts will explore it and return with samples in the 2020s. This Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) is part of our plan to advance new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
3. Building the Ride
Okay, so we’ve talked about how we’re preparing for a journey to Mars…but what about the ride? Our Space Launch System, or SLS, is an advanced launch vehicle that will help us explore beyond Earth’s orbit into deep space. SLS will be the world’s most powerful rocket and will launch astronauts in our Orion spacecraft on missions to an asteroid and eventually to Mars.

In the rocket’s initial configuration it will be able to take 154,000 pounds of payload to space, which is equivalent to 12 fully grown elephants! It will be taller than the Statue of Liberty and it’s liftoff weight will be comparable to 8 fully-loaded 747 jets. At liftoff, it will have 8.8 million pounds of thrust, which is more than 31 times the total thrust of a 747 jet. One more fun fact for you…it will produce horsepower equivalent to 160,000 Corvette engines!

Sitting atop the SLS rocket will be our Orion spacecraft. Orion will be the safest most advanced spacecraft ever built, and will be flexible and capable enough to carry humans to a variety of destinations. Orion will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
4. Making it Sustainable
When humans get to Mars, where will they live? Where will they work? These are questions we’ve already thought about and are working toward solving. Six partners were recently selected to develop ground prototypes and/or conduct concept studies for deep space habitats.

These NextSTEP habitats will focus on creating prototypes of deep space habitats where humans can live and work independently for months or years at a time, without cargo supply deliveries from Earth.

Another way that we are studying habitats for space is on the space station. In June, the first human-rated expandable module deployed in space was used. The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is a technology demonstration to investigate the potential challenges and benefits of expandable habitats for deep space exploration and commercial low-Earth orbit applications.
Our journey to Mars requires preparation and research in many areas. The powerful new Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft will travel into deep space, building on our decades of robotic Mars explorations, lessons learned on the International Space Station and groundbreaking new technologies.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

(via A Knight's Mission to Mars)
Hey everyone! I recently had the opportunity to work on and publish an article about student opportunities in the space industry in the University of Central Florida’s student-run publication Imprint. Please feel free to check out my article and see the other awesome work Imprint has!

Once upon a time, Mars had lakes, or at least wetter conditions than it does today. The latest from NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover shows slabs of rock cross-hatched with shallow ridges that likely originated as cracks in drying mud, evidence of an ancient era when these sediments were deposited were.
Space Scene

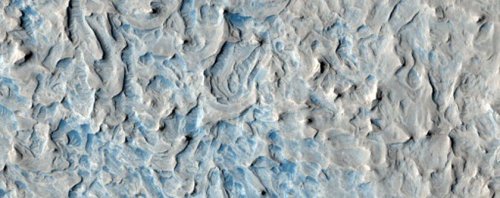
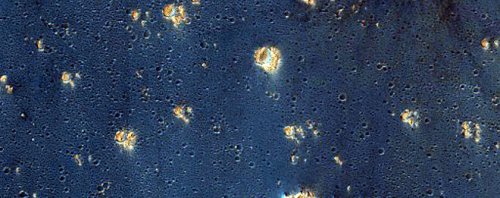
An image of a fresh crater on Mars! The crater spans approximately 30m (100 ft) in diameter and is surrounded by a large, rayed blast zone. Because the terrain where the crater formed is dusty, the fresh crater appears blue in the enhanced colour of the image, due to removal of the reddish dust in that area.
Space Scene

The distinctively fluted surface and elongated hills in this image in Medusae Fossae on Mars are caused by wind erosion of a soft fine-grained rock. Called yardangs, these features are aligned with the prevailing wind direction. This wind direction would have dominated for a very long time to carve these large-scale features into the exposed rock we see today. The image was acquired at 15:25 local Mars time on June 28, 2016, by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Space Scene

They might look like trees on Mars, but they're not. Groups of dark brown streaks have been photographed by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on melting pinkish sand dunes covered with light frost. The above image was taken in 2008 April near the North Pole of Mars. At that time, dark sand on the interior of Martian sand dunes became more and more visible as the spring Sun melted the lighter carbon dioxide ice. When occurring near the top of a dune, dark sand may cascade down the dune leaving dark surface streaks.
Space Scene