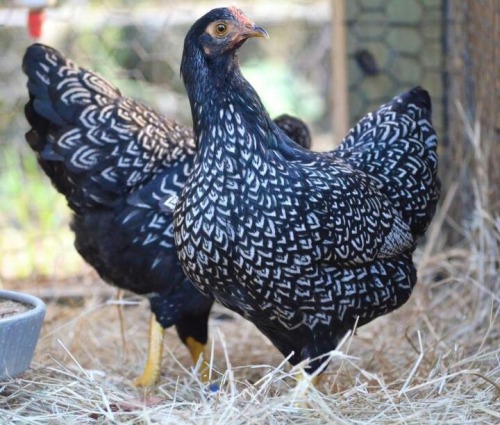
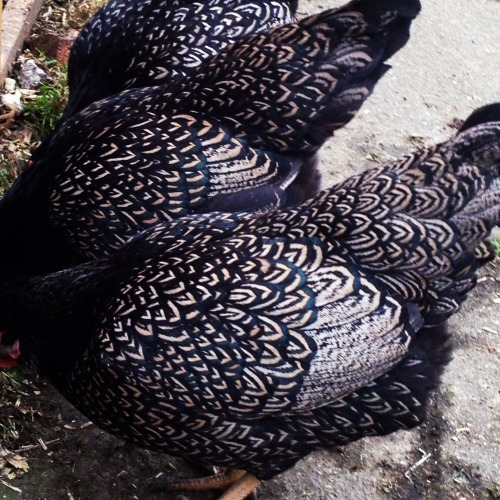
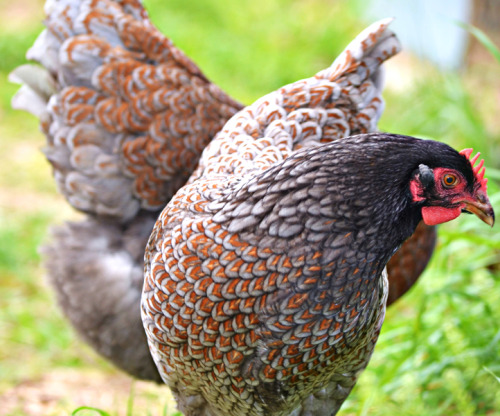
Dazed In Space Is A Wonderful 80’s Sci-Fi Adventure Where three Kids Get Lost In A Weird Dimension!
Dazed in Space is a wonderful 80’s Sci-Fi adventure where three kids get lost in a weird dimension!
Read More & Play The Beta Demo, Free (Windows)
Gameplay Video:
More Posts from Thejunkdrawers and Others
Hanfu in Components: Structure Conventions (pt2)
navigation: hanfu in components 1 2 3.1 3.2 ...
Thanks for the love on the last post, I’ve been motivated to continue writing LOL Anyway: Construction/sewing pattern/structure is very important to hanfu!
There are a few important structure conventions when it comes to hanfu—almost all traditional-cut hanfu follow these rules; you could call them the defining characteristics of hanfu. There are exceptions to every rule of course (I will go over some caveats at the end of this post), but generally if a hanfu design ignores these rules we might consider it to be ‘incorrect.'
(There will be a longer follow-up pt. 3 post to this explaining the anatomy of a hanfu top/robe, where there will be more detailed in-context illustrations and descriptions. I just figured I should list these ‘rules’ somewhere separately.)
中縫/中缝/zhong1 feng4/Center Seam


Take a look at your shirts. Is there a shoulder seam between the front of the shirt and the back of the shirt? Western clothing tends to consist of a front piece + back piece sewn together to create a space for your body to sit in:

Hanfu doesn’t work like that. Traditionally, the garment isn’t separated into a front piece and back piece: it’s separated into a right piece and left piece, which are joined together at the vertical center seam. Why? Traditional fabric has a narrower width than the standard ~145cm that we have today, so a long, narrow piece is less wasteful to cut out from a bolt of silk than a wide one.

Therefore there is always a center seam, one running vertically down the front and one down the back. 中 = center, 縫 = seam, so 中縫 means center seam. There’ll be a front center seam (前中縫) and a back center seam (後中縫).


不破肩/不破肩/bu2 po4 jian1/No Broken Shoulder
Kind of an addendum onto the previous point? Additionally since the body pieces are separated into left/right rather front/back, there’s no seam at the top of the shoulder here. The fabric is simply draped over the arm/shoulder to hang down, covering the torso on both sides.*


*Caveat: Some modified hanfu that vendors sell today will have a shoulder seam, especially thicker winter garments or short-sleeved garments. This is a design choice made to prevent the fabric from looking too stiff, known as 破肩/破肩/po4 jian1,literally “broken shoulder.” It can look great, lots of hanfu makers do it! But just to be clear, that is a MODIFICATION.
接袖/接袖/jie1 xiu4/Sleeve Connection


Western clothing patterns tend to have something where the fabric of the sleeve gets connected to the fabric of the garment’s body at the shoulder/armpit, often with a concave arm hole shape to help with the contours of the garment when it’s worn.

Hanfu sleeves, on the other hand, are never connected at the armpit—they are connected halfway down the arm. In other words, the piece of fabric that forms the body extends to also cover the upper arm part of the sleeve. The actual sleeve piece is connected to the body at the bicep/elbow area via a flat seam. (In the case of half- or no- sleeve garments there might just not be a separate sleeve piece.)


右衽/右衽/you4 ren4/"Right Over Left" Rule


Applies to cross-collar, some varieties of round collar, and some varieties of standing collar tops. In the case that the front of the garment crosses over itself, the flap coming from the wearer’s left goes OVER the flap coming from the wearer’s right. Easiest way to make sense of this is, if you’re looking at someone wearing a cross-collar hanfu top, the cross will look like a lowercase y.


Caveats
NO RULE EXISTS WITHOUT EXCEPTION!!! These rules exist because a majority of hanfu follow them and they are a standard that people agree on right now. However, there are ALWAYS cases—historically or otherwise—where these rules may be broken. For example, there are several Ming Dynasty cross collar robes that happen to be left over right, and the location of the sleeve seam can differ based on what garment you're looking at.
Also, many modern hanfu manufacturers will deliberately choose to break these 'rules' in favor of aesthetics. This is a purposeful design choice—not one that's done out of ignorance or disrespect. It's easy for common modifications to get mistaken for 'historically accurate.' To be clear, it is 100% okay and super common for modifications to exist! Just don't go around claiming that it was historically that way.
My advice is that if you're starting out with hanfu, try to stick to these rules in the back of your head as closely as possible. Once you've built your foundational knowledge, then you can start exploring the exceptions to the rules. These rules may not be foolproof, but they are a useful tool to help you understand the commonalities and trends within hanfu without overwhelming you.
Last note: it is generally more of a taboo for seams that should exist to not exist in a piece of clothing (i.e. no center back seam) than for extra seams to exist. If you go look in museums for the artifacts that hanfu is based off of, you'll notice that a lot of them—especially the ones from earlier dynasties—are a chaotic patchwork of a bunch of random piece of fabric sewn together to create the garment. Fabric is expensive, people don't want to waste it! So it's not all that weird to have seams in random places.
Happy 除夕 everyone! 有蛇有得 :>
navigation: hanfu in components 1 2 3.1 3.2 ...
Pro Tip: The Way You End a Sentence Matters
Here is a quick and dirty writing tip that will strengthen your writing.
In English, the word at the end of a sentence carries more weight or emphasis than the rest of the sentence. You can use that to your advantage in modifying tone.
Consider:
In the end, what you said didn't matter.
It didn't matter what you said in the end.
In the end, it didn't matter what you said.
Do you pick up the subtle differences in meaning between these three sentences?
The first one feels a little angry, doesn't it? And the third one feels a little softer? There's a gulf of meaning between "what you said didn't matter" (it's not important!) and "it didn't matter what you said" (the end result would've never changed).
Let's try it again:
When her mother died, she couldn't even cry.
She couldn't even cry when her mother died.
That first example seems to kind of side with her, right? Whereas the second example seems to hold a little bit of judgment or accusation? The first phrase kind of seems to suggest that she was so sad she couldn't cry, whereas the second kind of seems to suggest that she's not sad and that's the problem.
The effect is super subtle and very hard to put into words, but you'll feel it when you're reading something. Changing up the order of your sentences to shift the focus can have a huge effect on tone even when the exact same words are used.
In linguistics, this is referred to as "end focus," and it's a nightmare for ESL students because it's so subtle and hard to explain. But a lot goes into it, and it's a tool worth keeping in your pocket if you're a creative writer or someone otherwise trying to create a specific effect with your words :)
Foods Humanity Figures Out Everywhere
soup: Boil The Food To Make Food Water
stew? gravy? curry?: like soup but less water more food
porridge: add water to the starch but not so much. warm and mushy yum
pancake/flatbread: make the starch wet and flat, then put on hot surface.
fried starch thing: Use hot oil to make starch crispy yum++
dumpling: put the not starch in the starch thing and cook it.
alt dumpling: ball of starch added to soup or stew. makes chewy starch ball yum yum
filled portable food: starch wrapper of some kind to make it so you can eat the messy food with your hands.

1) Risus Monkey Fantasy Language Cypher
This is amazing!!!!!!!!!!
Are you creating a fictional language? Do you need help coming up with words that sound like they fit with what you’ve come up with so far?
Just put your fictional language in the model text, type some words in the translation text, and click “translate”. It’ll “translate” whatever words you put in using patterns from your sample text.
2) Speed Distance Calculator
These calculators aren’t perfect, but they can help you figure out:
How long it will take your characters to get somewhere based on how fast they’re going,
how far your characters moved based on how fast they were going and on how long they were moving,
how fast your characters need to move to reach a certain distance in a specified time
The calculator was meant for cyclists, but you can use it to get estimates for other things too.
3) Fantasy Calendar Generator
Another amazing resource!
This can create a random calendar for you or you can input the year, the number of months, the name of the months, the number of moons, the number of days in a week, the names of each day, and more.
You can even save the data for your calendar so that when you go back to the generator, all you have to do to get to your calendar is paste the data.
4) Inkarnate Map Maker
This is a new resource that’s still in beta, so it’ll probably be updated in the coming months.
This map maker is easy to use and free. You can add different climates, mountains, trees, towns, cities, text, and notes. For an example of these maps, look at the quick map I made for this post’s header.
A random assortment of archaic/disused English words that should still be used:
brust (bristled or bristly)
coolth (coolness. We still have 'warmth' so why did this one disappear????)
ambiloquent (using ambiguous language)
downsteepy (steeply descending)
mazeful (confusing)
evulgate (to send out among the people, to publish or distribute)
toploftical (haughty)
hazardry (risk-taking)
dizzard (a fool, jester, or stupid person)
againster (someone who is habitually opposed to things or 'against' things)
loselry (behavior characteristic of a losel, which is similar to a 'loser,' except the connotation encompasses "profligate" or "scoundrel")
plaguey
malengine (evil intent, fraud, deceit)
beasten (of or pertaining to beasts)
wranglesome (contentious and prone to quarreling)
dwine (to waste away)









Necropolis of Cerveteri
A major centre of Etruscan civilisation that was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2004, the Necropolis stretches for more than two kilometres. This certainly makes it the most imposing in all Etruria and one of the most magnificent monuments of its kind anywhere in the Mediterranean basin. These monumental tombs are located inside tumuli, partly cut into the tufa rock and partly built over it. The purpose of these edifices was to illustrate the desire of a handful of aristocratic families to make a statement about their wealth and to perpetuate a lifestyle of the highest quality also after death.
Images and text via, additional images via + via
People, especially games, get eldritch madness wrong a lot and it’s really such a shame.
An ant doesn’t start babbling when they see a circuit board. They find it strange, to them it is a landscape of strange angles and humming monoliths. They may be scared, but that is not madness.
Madness comes when the ant, for a moment, can see as a human does.
It understands those markings are words, symbols with meaning, like a pheromone but infinitely more complex. It can travel unimaginable distances, to lands unlike anything it has seen before. It knows of mirth, embarrassment, love, concepts unimaginable before this moment, and then…
It’s an ant again.
Echoes of things it cannot comprehend swirl around its mind. It cannot make use of this knowledge, but it still remembers. How is it supposed to return to its life? The more the ant saw the harder it is for it to forget. It needs to see it again, understand again. It will do anything to show others, to show itself, nothing else in this tiny world matters.
This is madness.
-
 thejunkdrawers reblogged this · 2 months ago
thejunkdrawers reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 ssolvix reblogged this · 11 months ago
ssolvix reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 wonderer125blog liked this · 1 year ago
wonderer125blog liked this · 1 year ago -
 b1uhh liked this · 2 years ago
b1uhh liked this · 2 years ago -
 banan-p liked this · 2 years ago
banan-p liked this · 2 years ago -
 transparentjpg liked this · 2 years ago
transparentjpg liked this · 2 years ago -
 rizblogs reblogged this · 2 years ago
rizblogs reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 majicarpmon liked this · 2 years ago
majicarpmon liked this · 2 years ago -
 nikoonaroomba reblogged this · 2 years ago
nikoonaroomba reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 cthulhutheater liked this · 2 years ago
cthulhutheater liked this · 2 years ago -
 bobert-07 liked this · 2 years ago
bobert-07 liked this · 2 years ago -
 doctor-ciel liked this · 2 years ago
doctor-ciel liked this · 2 years ago -
 justinforprez liked this · 2 years ago
justinforprez liked this · 2 years ago -
 daftpunkinstein liked this · 2 years ago
daftpunkinstein liked this · 2 years ago -
 radfireshoeegg liked this · 2 years ago
radfireshoeegg liked this · 2 years ago -
 thispistolsmokes reblogged this · 2 years ago
thispistolsmokes reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 roguecritter liked this · 2 years ago
roguecritter liked this · 2 years ago -
 clowncakesss liked this · 2 years ago
clowncakesss liked this · 2 years ago -
 cinnamolmorten liked this · 2 years ago
cinnamolmorten liked this · 2 years ago -
 mocchoisacutie reblogged this · 2 years ago
mocchoisacutie reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 sokerikeiju liked this · 2 years ago
sokerikeiju liked this · 2 years ago -
 katiemonz liked this · 2 years ago
katiemonz liked this · 2 years ago -
 unmecha liked this · 2 years ago
unmecha liked this · 2 years ago -
 goldgargoyles liked this · 2 years ago
goldgargoyles liked this · 2 years ago -
 grandmasickomode reblogged this · 2 years ago
grandmasickomode reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 squishloveme reblogged this · 2 years ago
squishloveme reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 art-trocious liked this · 2 years ago
art-trocious liked this · 2 years ago -
 downloadcuteness reblogged this · 2 years ago
downloadcuteness reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 aninspiredartist liked this · 2 years ago
aninspiredartist liked this · 2 years ago -
 mystic-fairy-tame liked this · 2 years ago
mystic-fairy-tame liked this · 2 years ago -
 superswooshy liked this · 2 years ago
superswooshy liked this · 2 years ago -
 my-intrests liked this · 2 years ago
my-intrests liked this · 2 years ago -
 laforgegeordi liked this · 2 years ago
laforgegeordi liked this · 2 years ago -
 yah-boi-sarah liked this · 2 years ago
yah-boi-sarah liked this · 2 years ago -
 gay-and-random-shit-i-can-find reblogged this · 2 years ago
gay-and-random-shit-i-can-find reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 gay-and-random-shit-i-can-find liked this · 2 years ago
gay-and-random-shit-i-can-find liked this · 2 years ago -
 malhw reblogged this · 2 years ago
malhw reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 malhw liked this · 2 years ago
malhw liked this · 2 years ago -
 melle-d liked this · 2 years ago
melle-d liked this · 2 years ago -
 ampharosstan liked this · 2 years ago
ampharosstan liked this · 2 years ago -
 3diario liked this · 2 years ago
3diario liked this · 2 years ago -
 sweetcookie301 liked this · 2 years ago
sweetcookie301 liked this · 2 years ago -
 ultimate-motherfucker9 liked this · 2 years ago
ultimate-motherfucker9 liked this · 2 years ago -
 bingsearchengine liked this · 2 years ago
bingsearchengine liked this · 2 years ago -
 cleffalover173 reblogged this · 2 years ago
cleffalover173 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 cleffalover173 liked this · 2 years ago
cleffalover173 liked this · 2 years ago -
 blaze-art reblogged this · 2 years ago
blaze-art reblogged this · 2 years ago

A side blog where I'll *try* to keep things organised.yeahthatsnotgoingtolastlong
241 posts