Evo-Devo (Despacito Biology Parody) - A Capella Science
Evo-Devo (Despacito Biology Parody) - A Capella Science
This is how we go from single cells to people.
More Posts from Simplyphytoplankton and Others




North Cascades National Park, Washington
A night in the Cascade Mountains
Phytoplankton (Coccolithophore) bloom!

Phytoplankton bloom in the Bay of Biscay.
The waters off the western coast of France show swirls of green and turquoise as a result of a phytoplankton bloom associated with increasing springtime temperatures.
Keep reading




Baby loggerhead turtle at home in the sargassum in the Gulf Stream current, where it will spend roughly 5 years, finally being large enough that many animals won’t be able to eat! Sea Turtles have a very difficult life, most of which never make it to maturity and reproduce! Our own existence here on earth as a species is responsible for the death of many beautiful creatures including the sea Turtles, due to mistakes of the past! We have the knowledge, technology and some the drive to fix this, but will we make necessary changes to put our beautiful planet into a sustainable direction? I MOST DEFINITELY WILL! Please join me as our planets future and all creatures are dependent on it! Be the change the world needs! @jim_abernethy #beautiful #babyturtle #gorgeous #cute #precious #underwater #saveturtles #saveoceans (at Jim Abernethy’s Scuba Adventures & Marine Life Art Gallery)

Diatoms: Algae in glass houses
Check out my new post!
http://becausephytoplankton.blogspot.com/2018/09/diatoms-algae-in-glass-houses.html

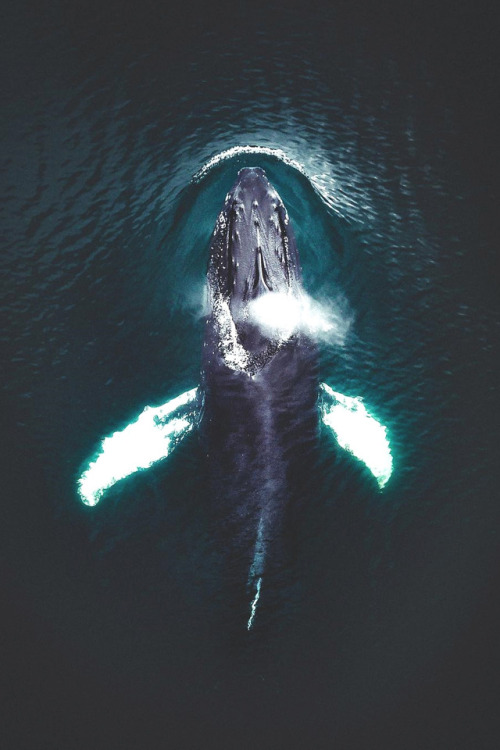
It may be winter in the Northern Hemisphere, but down in Antarctica, it’s currently summertime. This humpback whale migrated south to feast on the plentiful krill along the West Antarctic Peninsula.
Credit: © Ari Friedlaender
What will scientists find in the deep waters off California?
Deep-sea corals and sponges are some of the oldest animals on Earth, living for hundreds of years at depths beyond direct human observation. Coral, sponge, and fish communities thrive in the cold, deep waters off California’s coast, but are rarely – if ever – visited or observed.
In late July and early August, scientists using advanced technology aboard the NOAA Ship Bell M. Shimada will study unexplored seafloor habitats off North-Central California in NOAA’s Greater Farallones and Cordell Bank national marine sanctuaries. Their focus includes coral, sponge, and groundfish communities. What they learn will help inform the management of these special ocean areas, and add to knowledge about deep-sea habitats and the biological communities that live there.

A crinoid and bubblegum coral grow in the deep sea in Cordell Bank National Marine Sanctuary. Photo: OET/NOAA
Using a robot to explore the deep
To survey the seafloor and record images of the habitats as deep as 2,000 feet (600 meters), scientists are using a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), launched from the ship and sent into the depths of the ocean. In addition to sending real-time video and images via a cable connected to the ship, the unmanned ROV will collect geological and biological specimens for identification. Scientists will also conduct seafloor mapping, an important tool for management of marine areas.

A remotely operated vehicle collects a sponge sample. The yellow sponge is a new species that was found on the wreck of the USS Independence. Photo: OET/NOAA
Why journey to the deep?
The deep sea is vastly unknown because it is largely inaccessible by humans. However, it affects us in many ways. A healthy ocean is essential to the health of our planet, and deep-sea communities are an important part of marine ecosystems. The deep sea nurtures fish stocks and hosts life-forms like bacteria and sponges that have contributed to medical discoveries.
Coral and sponge habitats are among the most biodiverse and productive ecosystems throughout the entire ocean. Increasing global human demand for resources has created a need for expanded science and conservation of these deep-ocean ecosystems and the benefits they may yield. Both living and dead corals and sponges are “biogenic habitats,” where the organisms themselves provide habitat for other marine life.
Previous NOAA expeditions off California’s coast have identified several new species of corals and sponges, including Swiftia farallonesica, a slender white coral, in the deep waters of Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary, off the Sonoma County coast. New sponge species were discovered living on the wreck of the USS Independence off the San Mateo County coast. They were also discovered in Cordell Bank National Marine Sanctuary, both in Bodega Canyon and on the deep slope near Cordell Bank to the north. New species discoveries indicate that we still have much to learn about the deep sea.
The ocean supports hundreds of billions of dollars of the U.S. economy through food, jobs, transportation, recreation, and other services. NOAA’s mission is “to understand and predict changes in climate, weather, oceans, and coasts, to share that knowledge and information with others, and to conserve and manage coastal and marine ecosystems and resources.” Assessing the conditions of ocean ecosystems can lead to better management of those areas to support the ocean economy.

Swiftia farallonesica is a new species of coral that was discovered in the deep waters of Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary. Photo: NOAA
Stay tuned for more pictures and information after the expedition!
-
 joyfullyinharmony liked this · 4 years ago
joyfullyinharmony liked this · 4 years ago -
 homesicklinguist liked this · 4 years ago
homesicklinguist liked this · 4 years ago -
 sommerlyrik reblogged this · 6 years ago
sommerlyrik reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 parple reblogged this · 7 years ago
parple reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mediaspecial123blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
mediaspecial123blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thesunwillset4u liked this · 7 years ago
thesunwillset4u liked this · 7 years ago -
 timallenphoto liked this · 7 years ago
timallenphoto liked this · 7 years ago -
 shereallyknowsfam liked this · 7 years ago
shereallyknowsfam liked this · 7 years ago -
 keenheartfire-blog liked this · 7 years ago
keenheartfire-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 quixr reblogged this · 7 years ago
quixr reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mbchumblr liked this · 7 years ago
mbchumblr liked this · 7 years ago -
 scienceandthings reblogged this · 7 years ago
scienceandthings reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 delightfulweaselmakergoth-blog liked this · 7 years ago
delightfulweaselmakergoth-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 panicked-sarcasm liked this · 7 years ago
panicked-sarcasm liked this · 7 years ago -
 no-esc-apricot-butt reblogged this · 7 years ago
no-esc-apricot-butt reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ren-evolve reblogged this · 7 years ago
ren-evolve reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 waywaytoomanythoughts reblogged this · 7 years ago
waywaytoomanythoughts reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 katherine-traylor liked this · 7 years ago
katherine-traylor liked this · 7 years ago -
 henry-p-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago
henry-p-blog1 liked this · 7 years ago -
 jospoon liked this · 7 years ago
jospoon liked this · 7 years ago -
 purexed liked this · 7 years ago
purexed liked this · 7 years ago -
 theadviceowl-blog liked this · 7 years ago
theadviceowl-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 sciencenerd4-blog liked this · 7 years ago
sciencenerd4-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 lastlighthousekeeper liked this · 7 years ago
lastlighthousekeeper liked this · 7 years ago -
 kyle1372-blog liked this · 7 years ago
kyle1372-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 2806-0395-blog liked this · 7 years ago
2806-0395-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 elilont reblogged this · 7 years ago
elilont reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 zombiisnt reblogged this · 7 years ago
zombiisnt reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ser-khallen reblogged this · 7 years ago
ser-khallen reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 frinenarvaez-blog liked this · 7 years ago
frinenarvaez-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 bunniezofdoom liked this · 7 years ago
bunniezofdoom liked this · 7 years ago -
 honeybeesociety-blog liked this · 7 years ago
honeybeesociety-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 panda-poes reblogged this · 7 years ago
panda-poes reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 crabsnctenophores liked this · 7 years ago
crabsnctenophores liked this · 7 years ago -
 morganeilish reblogged this · 7 years ago
morganeilish reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 bellafuga reblogged this · 7 years ago
bellafuga reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 simplyphytoplankton reblogged this · 7 years ago
simplyphytoplankton reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 tilting-planet liked this · 7 years ago
tilting-planet liked this · 7 years ago -
 vennix liked this · 7 years ago
vennix liked this · 7 years ago -
 cessar-diencaeus reblogged this · 7 years ago
cessar-diencaeus reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 cessar-diencaeus liked this · 7 years ago
cessar-diencaeus liked this · 7 years ago -
 brewerbaby liked this · 7 years ago
brewerbaby liked this · 7 years ago -
 prof-honeydew liked this · 7 years ago
prof-honeydew liked this · 7 years ago -
 elvinbiologist reblogged this · 7 years ago
elvinbiologist reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 elvinbiologist liked this · 7 years ago
elvinbiologist liked this · 7 years ago

Blog dedicted to phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that are responsible for half of the photosynthesis that occurs on Earth. Oh, and they look like art... Follow to learn more about these amazing litter critters! Caution: Will share other ocean science posts!Run by an oceanographer and phytoplankton expert. Currently a postdoctoral researcher.Profile image: False Colored SEM image of Emiliania huxleyi, a coccolithophore, and the subject of my doctoral work. Credit: Steve Gschmeissner/ Science Photo Library/ Getty ImagesHeader image: Satellite image of a phytoplankton bloom off the Alaskan Coast, in the Chukchi SeaCredit: NASA image by Norman Kuring/NASA's Ocean Color Web https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/92412/churning-in-the-chukchi-sea
158 posts