Neptune ♆









Neptune ♆
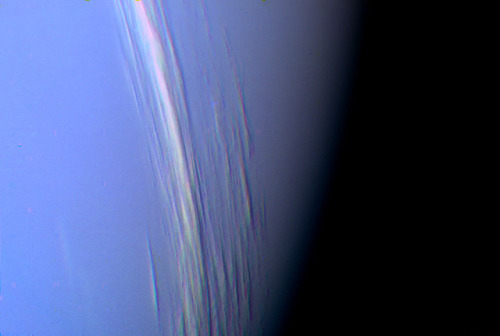
On this day in 1846 was discovered the planet Neptune.
The ice giant Neptune was the first planet located through mathematical predictions rather than through regular observations of the sky. (Galileo had recorded it as a fixed star during observations with his small telescope in 1612 and 1613.) When Uranus didn’t travel exactly as astronomers expected it to, a French mathematician, Urbain Joseph Le Verrier, proposed the position and mass of another as yet unknown planet that could cause the observed changes to Uranus’ orbit. After being ignored by French astronomers, Le Verrier sent his predictions to Johann Gottfried Galle at the Berlin Observatory, who found Neptune on his first night of searching in 1846. Seventeen days later, its largest moon, Triton, was also discovered.
Neptune is invisible to the naked eye because of its extreme distance from Earth. Interestingly, the highly eccentric orbit of the dwarf planet Pluto brings Pluto inside Neptune’s orbit for a 20-year period out of every 248 Earth years. Pluto can never crash into Neptune, though, because for every three laps Neptune takes around the Sun, Pluto makes two. This repeating pattern prevents close approaches of the two bodies.
Nearly 4.5 billion kilometers (2.8 billion miles) from the Sun, Neptune orbits the Sun once every 165 years.
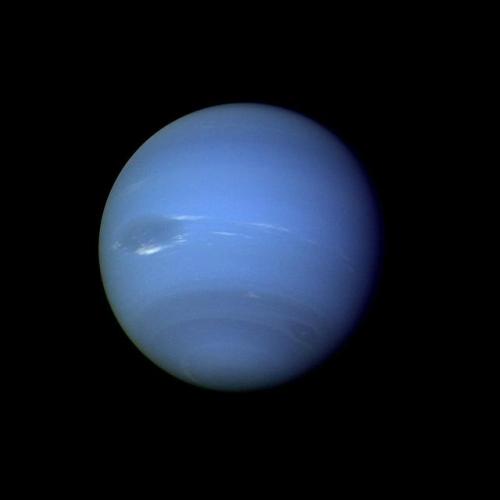
Uranus’ blue-green color is also the result of atmospheric methane, but Neptune is a more vivid, brighter blue, so there must be an unknown component that causes the more intense color.
Despite its great distance and low energy input from the Sun, Neptune’s winds can be three times stronger than Jupiter’s and nine times stronger than Earth’s.
Winds on Neptune travel faster than the speed of sound.
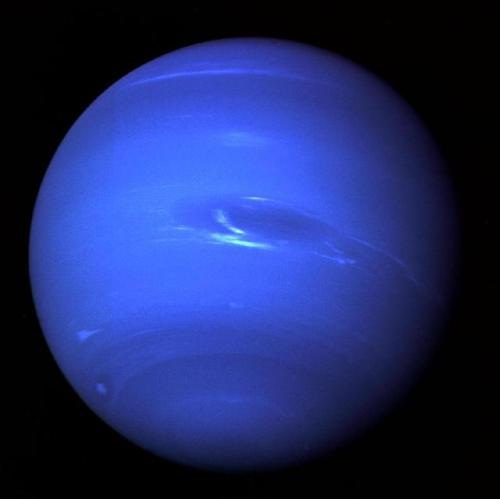
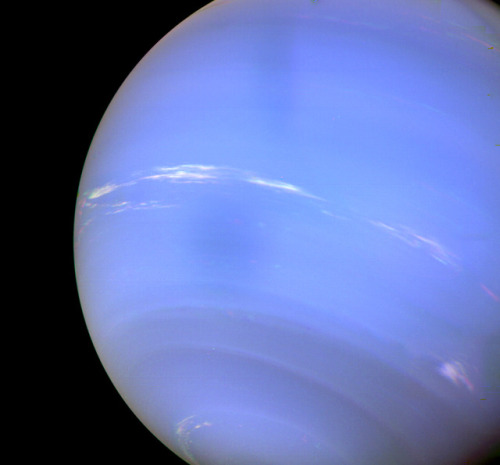
In 1989, Voyager 2 tracked a large, oval-shaped, dark storm in Neptune’s southern hemisphere. This “Great Dark Spot” was large enough to contain the entire Earth.
Neptune has five known rings. Voyager 2’s observations confirmed that these unusual rings are not uniform but have four thick regions (clumps of dust) called arcs. The rings are thought to be relatively young and short-lived.
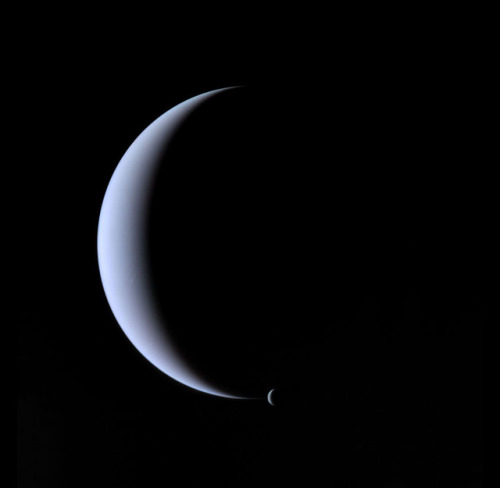
Neptune has 14 known moons, six of which were discovered by Voyager 2.
Triton, Neptune’s largest moon, orbits the planet in the opposite direction compared with the rest of the moons, suggesting that it may have been captured by Neptune in the distant past.
To know more about the planet Neptune click here and here.
Images credit: NASA/JPL- Caltech (some images processed by Kevin M. Gill)
More Posts from Sharkspaceengine and Others

Picture of the Day 2 - November 9, 2018
Narrow sea cuts through the forests of a life supporting world with red-colored vegetation.

Front row seat to a galactic merger.




Evening of the Cosmos. Widescreen Wallpapers 1440 x 900.
Website, Instagram, Facebook, Deviantart, and Artstation
Using All of Our Senses in Space
Today, we and the National Science Foundation (NSF) announced the detection of light and a high-energy cosmic particle that both came from near a black hole billions of trillions of miles from Earth. This discovery is a big step forward in the field of multimessenger astronomy.
But wait — what is multimessenger astronomy? And why is it a big deal?
People learn about different objects through their senses: sight, touch, taste, hearing and smell. Similarly, multimessenger astronomy allows us to study the same astronomical object or event through a variety of “messengers,” which include light of all wavelengths, cosmic ray particles, gravitational waves, and neutrinos — speedy tiny particles that weigh almost nothing and rarely interact with anything. By receiving and combining different pieces of information from these different messengers, we can learn much more about these objects and events than we would from just one.

Lights, Detector, Action!
Much of what we know about the universe comes just from different wavelengths of light. We study the rotations of galaxies through radio waves and visible light, investigate the eating habits of black holes through X-rays and gamma rays, and peer into dusty star-forming regions through infrared light.

The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, which recently turned 10, studies the universe by detecting gamma rays — the highest-energy form of light. This allows us to investigate some of the most extreme objects in the universe.

Last fall, Fermi was involved in another multimessenger finding — the very first detection of light and gravitational waves from the same source, two merging neutron stars. In that instance, light and gravitational waves were the messengers that gave us a better understanding of the neutron stars and their explosive merger into a black hole.

Fermi has also advanced our understanding of blazars, which are galaxies with supermassive black holes at their centers. Black holes are famous for drawing material into them. But with blazars, some material near the black hole shoots outward in a pair of fast-moving jets. With blazars, one of those jets points directly at us!
Multimessenger Astronomy is Cool

Today’s announcement combines another pair of messengers. The IceCube Neutrino Observatory lies a mile under the ice in Antarctica and uses the ice itself to detect neutrinos. When IceCube caught a super-high-energy neutrino and traced its origin to a specific area of the sky, they alerted the astronomical community.
Fermi completes a scan of the entire sky about every three hours, monitoring thousands of blazars among all the bright gamma-ray sources it sees. For months it had observed a blazar producing more gamma rays than usual. Flaring is a common characteristic in blazars, so this did not attract special attention. But when the alert from IceCube came through about a neutrino coming from that same patch of sky, and the Fermi data were analyzed, this flare became a big deal!

IceCube, Fermi, and followup observations all link this neutrino to a blazar called TXS 0506+056. This event connects a neutrino to a supermassive black hole for the very first time.

Why is this such a big deal? And why haven’t we done it before? Detecting a neutrino is hard since it doesn’t interact easily with matter and can travel unaffected great distances through the universe. Neutrinos are passing through you right now and you can’t even feel a thing!
The neat thing about this discovery — and multimessenger astronomy in general — is how much more we can learn by combining observations. This blazar/neutrino connection, for example, tells us that it was protons being accelerated by the blazar’s jet. Our study of blazars, neutrinos, and other objects and events in the universe will continue with many more exciting multimessenger discoveries to come in the future.
Want to know more? Read the story HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Earth-Like World

Picture of the Day 2 - October 16, 2018
Here I come across the most Earth-like planet to date. The planet is covered in green vegetation, blue oceans and ice caps at the poles. This planet is located near the galactic core; therefore, the sky is full of bright stars, even more so than globular clusters.






First pictures from the M59 galaxy. Here I come across a 7 planet system orbiting an orange giant. All the planets in this system are experiencing the effects of the expanding sun, and orbit relatively close to the sun. The outer-most ice giant orbits just 3.62 AU from the sun.
Space Engine System ID: RS-5581-21-3-270-585
I just unfortunately found out that Tumblr does not allow posts with links in them to show up on searches. This is very problematic for me since I like posting 4K resolution pics on here. Anyone have any suggestions on how to keep Tumblr from reducing image sizes so I do not have to add links to my posts?
High Resolution Pics
Partially molten moon
Galaxy NGC 4429 photo bombs this moon shot.
Molten world
Rising giant
Burnt desert
Solar Atmosphere






These will be the last pics from the Large Magellanic Cloud Galaxy. I will have my next galaxy picked out soon.
High Resolution Pictures
Pale green titan-like world
Three suns
Cratered world with a thin atmosphere
White sun
Binary sunset
Two airless worlds






Pictures of the day - November 26, 2018
A system of 6 planet’s orbiting a rare dim carbon star that has swelled into a red giant. All of the planet’s have been roasted by the star. The star has a very low surface temperature; therefore, all of the planets have a red-tint due to the lack of blue colored light.
The outer-most planets form a double planet system which consist of a Mars-like world orbited by an ocean world. The ocean world once being a frozen ice-covered world melted the by expanded sun.
Space Engine System ID: RS 5581-42-4-1201-1122
High Resolution Pictures:
Inner-most world
Massive giant covering the sky
Roasted Ice-giant and its moons
Another burnt world
Outer-most Double Planets
Hurricane
Glowing Sky

Picture of the Day 2 - November 4, 2018
Auroras glow brilliantly over a lunar sky with the Milky way Galaxy looming large.
-
 poofagenius liked this · 2 weeks ago
poofagenius liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 diallokenyatta liked this · 2 weeks ago
diallokenyatta liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 sotsogm liked this · 2 weeks ago
sotsogm liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 briefly-noted reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
briefly-noted reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 1rh2nxoz reblogged this · 2 months ago
1rh2nxoz reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 i-iii-iii-vii liked this · 3 months ago
i-iii-iii-vii liked this · 3 months ago -
 stellarseeming reblogged this · 8 months ago
stellarseeming reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 stellarseeming liked this · 8 months ago
stellarseeming liked this · 8 months ago -
 cernunnos1990 reblogged this · 10 months ago
cernunnos1990 reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 cernunnos1990 liked this · 10 months ago
cernunnos1990 liked this · 10 months ago -
 allarounddivinity reblogged this · 11 months ago
allarounddivinity reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 sailorviii liked this · 11 months ago
sailorviii liked this · 11 months ago -
 yassygoth liked this · 1 year ago
yassygoth liked this · 1 year ago -
 demichrising liked this · 1 year ago
demichrising liked this · 1 year ago -
 spiritualitysalad liked this · 1 year ago
spiritualitysalad liked this · 1 year ago -
 ravexandxlust liked this · 1 year ago
ravexandxlust liked this · 1 year ago -
 starryfishbonesoup liked this · 1 year ago
starryfishbonesoup liked this · 1 year ago -
 spacetism liked this · 1 year ago
spacetism liked this · 1 year ago -
 iwillhaveamoonbase liked this · 2 years ago
iwillhaveamoonbase liked this · 2 years ago -
 erikaalvaradoblog liked this · 2 years ago
erikaalvaradoblog liked this · 2 years ago -
 thy420 liked this · 2 years ago
thy420 liked this · 2 years ago -
 wisent15 liked this · 2 years ago
wisent15 liked this · 2 years ago -
 wisent15 reblogged this · 2 years ago
wisent15 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 not-posting-anymore liked this · 2 years ago
not-posting-anymore liked this · 2 years ago -
 mizar2 reblogged this · 2 years ago
mizar2 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 ttscz liked this · 2 years ago
ttscz liked this · 2 years ago -
 kitapokuyormuhtemelen liked this · 2 years ago
kitapokuyormuhtemelen liked this · 2 years ago -
 rastronomicals liked this · 2 years ago
rastronomicals liked this · 2 years ago -
 christabelq liked this · 2 years ago
christabelq liked this · 2 years ago -
 burtkilljoy liked this · 2 years ago
burtkilljoy liked this · 2 years ago -
 groupwest liked this · 2 years ago
groupwest liked this · 2 years ago -
 nomvdsoul liked this · 2 years ago
nomvdsoul liked this · 2 years ago -
 dark----blue reblogged this · 2 years ago
dark----blue reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 gh0stblonde reblogged this · 2 years ago
gh0stblonde reblogged this · 2 years ago
My Space Engine Adventures, also any space related topic or news. www.spaceengine.org to download space engine. The game is free by the way. Please feel free to ask me anything, provide suggestions on systems to visit or post any space related topic.Check out my other blog https://bunsandsharks.tumblr.com for rabbit and shark blog.
294 posts









