(Image Caption: The Empty Stomach Releases The Hormone Called Ghrelin. By Receiving Ghrelin, The Hypothalamus
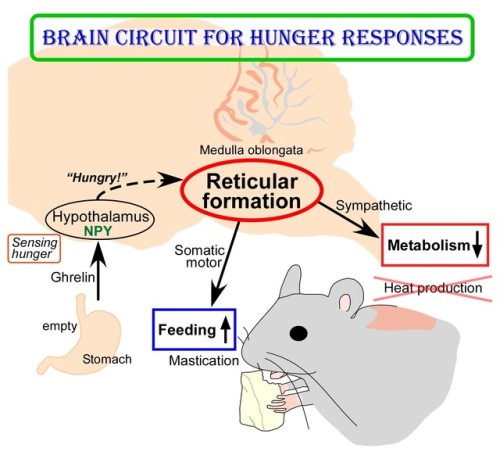
(Image caption: The empty stomach releases the hormone called ghrelin. By receiving ghrelin, the hypothalamus in the brain senses hunger and produces “hunger signaling” through the action of neuropeptide Y (NPY). The hunger signaling activates neurons in the reticular formation of the medulla oblongata, which then inhibit sympathetic output to reduce metabolic heat production and simultaneously provide masticatory motor rhythm to facilitate feeding. Credit: © 2017 Yoshiko Nakamura)
New Insights into Brain Circuit for Hunger Responses during Starvation
The human body responds to starving conditions, such as famine, to promote the chance of survival. It reduces energy expenditure by stopping heat production and promotes feeding behavior. These “hunger responses” are activated by the feeling of hunger in the stomach and are controlled by neuropeptide Y (NPY) signals released by neurons in the hypothalamus. However, how NPY signaling in the hypothalamus elicits the hunger responses has remained unknown.
Sympathetic motor neurons in the medulla oblongata are responsible for heat production by brown adipose tissue (BAT). Researchers centered at Nagoya University have now tested whether the heat-producing neurons respond to the same hypothalamic NPY signals that control hunger responses. They injected NPY into the hypothalamus of rats and tested the effect on heat production. Under normal conditions, blocking inhibitory GABAergic receptors or stimulating excitatory glutamatergic receptors in the sympathetic motor neurons induced heat production in BAT. After NPY injection, stimulating glutamatergic receptors did not produce heat, but inhibiting GABAergic receptors did. The study was reported in Cell Metabolism.
“This indicated that hypothalamic NPY signals prevent BAT thermogenesis by using inhibitory GABAergic inputs to sympathetic motor neurons,” study lead author Yoshiko Nakamura says.
Retrograde and anterograde tracing with fluorescent dyes revealed which brain region provided the inhibitory GABAergic inputs to heat-producing motor neurons.
“Tracing experiments showed that sympathetic motor neurons are directly innervated by GABAergic inputs from reticular nuclei in the medulla oblongata,” corresponding author Kazuhiro Nakamura explains, “selective activation of these GABAergic reticular neurons inhibits BAT thermogenesis.”
The researchers’ further findings showed that GABAergic inputs from medullary reticular neurons are involved in hypothalamic NPY-mediated inhibition of heat production in BAT. This hunger response circuit probably explains why anorexic individuals suffer from hypothermia.
Interestingly, stimulation of these medullary reticular neurons prompted rats to begin chewing and feeding. This effect was similar to injecting NPY into the hypothalamus, suggesting that hypothalamic NPY signaling activates reticular neurons in the medulla oblongata to promote feeding and mastication during the hunger response.
Abnormal activation of these neurons under non-starved conditions may contribute to obesity. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to development of more effective treatments for obesity.
More Posts from Science-is-magical and Others
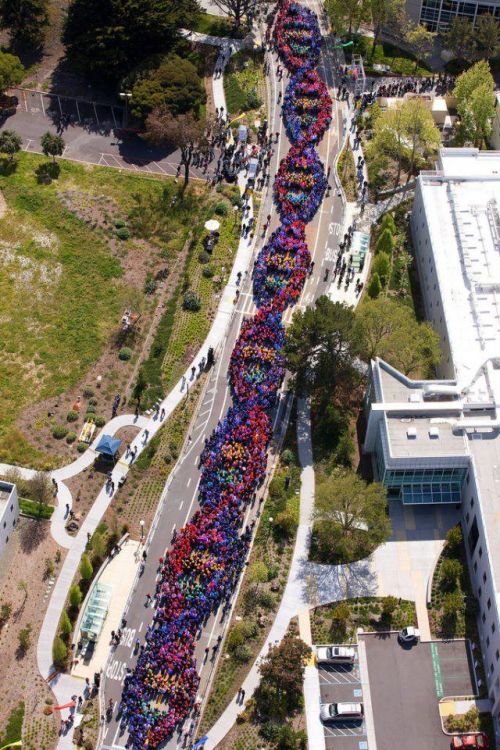

Feb 28, 2013 - By wearing different colored hats, over 2,600 employees at Genentech (in San Francisco) celebrated the 60th anniversary of the discovery of DNA

The existence of large numbers of molecules in winds powered by supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies has puzzled astronomers since they were discovered more than a decade ago. Molecules trace the coldest parts of space, and black holes are the most energetic phenomena in the universe, so finding molecules in black hole winds was like discovering ice in a furnace.
Astronomers questioned how anything could survive the heat of the energetic outflows, but a new theory from researchers in Northwestern University’s Center for Interdisciplinary Research and Exploration in Astrophysics (CIERA) predicts that these molecules are not survivors at all, but brand-new molecules, born in the winds with unique properties that enable them to adapt to and thrive in the hostile environment.
Continue Reading.

A Powerful Solar Flare : It was one of the most powerful solar flares in recorded history. Occurring in 2003 and seen across the electromagnetic spectrum, the Sun briefly became over 100 times brighter in X-rays than normal. The day after this tremendous X 17 solar flare – and subsequent Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) – energetic particles emitted from the explosions struck the Earth, creating auroras and affecting satellites. The spacecraft that took these frames – SOHO – was put in a turtle-like safe mode to avoid further damage from this and subsequent solar particle storms. The featured time-lapse movie condenses into 10 seconds events that occurred over 4 hours. The CME, visible around the central sun-shade, appears about three-quarters of the way through the video, while frames toward the very end are progressively noisier as protons from the explosions strike SOHO’s LASCO detector. One this day in 1859, the effects of an even more powerful solar storm caused telegraphs on Earth to spark in what is known as the Carrington Event. Powerful solar storms such as these may create beautiful aurora-filled skies, but they also pose a real danger as they can damage satellites and even power grids across the Earth. via NASA

About 400 million years ago, before trees were common, the Earth was covered with giant mushrooms. Source
cyanobacterium: i have made Oxygen
chemotrophs: you fucked up a perfectly good planet is what you did. look at it. it’s all rusty
If Earth had Saturn’s Rings
From an excellent post by Jason Davis
From Washington, D.C., the rings would only fill a portion of the sky, but appear striking nonetheless. Here, we see them at sunrise.

From Guatemala, only 14 degrees above the equator, the rings would begin to stretch across the horizon. Their reflected light would make the moon much brighter.

From Earth’s equator, Saturn’s rings would be viewed edge-on, appearing as a thin, bright line bisecting the sky.

At the March and September equinoxes, the Sun would be positioned directly over the rings, casting a dramatic shadow at the equator.

At midnight at the Tropic of Capricorn, which sits at 23 degrees south latitude, the Earth casts a shadow over the middle of the rings, while the outer portions remain lit.

via x
-
 ugga-snarga-arg reblogged this · 7 years ago
ugga-snarga-arg reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 transparentcowboysweetsa9-blog liked this · 7 years ago
transparentcowboysweetsa9-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 science-is-magical reblogged this · 7 years ago
science-is-magical reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 neepsociety reblogged this · 7 years ago
neepsociety reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 revolutionorheroin reblogged this · 7 years ago
revolutionorheroin reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 revolutionorheroin liked this · 7 years ago
revolutionorheroin liked this · 7 years ago -
 lovedovedipndot liked this · 8 years ago
lovedovedipndot liked this · 8 years ago -
 mostsecretfantasies liked this · 8 years ago
mostsecretfantasies liked this · 8 years ago -
 tumblerhasfun liked this · 8 years ago
tumblerhasfun liked this · 8 years ago -
 dmazon-blog liked this · 8 years ago
dmazon-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 iaidcare reblogged this · 8 years ago
iaidcare reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 iaidcare liked this · 8 years ago
iaidcare liked this · 8 years ago -
 enginigger liked this · 8 years ago
enginigger liked this · 8 years ago -
 strangerme11 reblogged this · 8 years ago
strangerme11 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 nirol-blog liked this · 8 years ago
nirol-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 lazynighttyphoon-blog liked this · 8 years ago
lazynighttyphoon-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 1402hijri liked this · 8 years ago
1402hijri liked this · 8 years ago -
 restlessss liked this · 8 years ago
restlessss liked this · 8 years ago -
 littlemiss-chaos liked this · 8 years ago
littlemiss-chaos liked this · 8 years ago -
 daemon-the-pretender liked this · 8 years ago
daemon-the-pretender liked this · 8 years ago -
 landofmazesandinsight liked this · 8 years ago
landofmazesandinsight liked this · 8 years ago -
 thatrenaissanceguy liked this · 8 years ago
thatrenaissanceguy liked this · 8 years ago -
 arlopiro reblogged this · 8 years ago
arlopiro reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 vientoyluna liked this · 8 years ago
vientoyluna liked this · 8 years ago -
 bebop13 liked this · 8 years ago
bebop13 liked this · 8 years ago -
 selenemoonstar liked this · 8 years ago
selenemoonstar liked this · 8 years ago -
 iaminsaan liked this · 8 years ago
iaminsaan liked this · 8 years ago -
 humblenomore reblogged this · 8 years ago
humblenomore reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 klawson5 liked this · 8 years ago
klawson5 liked this · 8 years ago -
 ismellsexandcandies reblogged this · 8 years ago
ismellsexandcandies reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ismellsexandcandies liked this · 8 years ago
ismellsexandcandies liked this · 8 years ago -
 oneapplepiefromscratchplease liked this · 8 years ago
oneapplepiefromscratchplease liked this · 8 years ago -
 luminousradar liked this · 8 years ago
luminousradar liked this · 8 years ago -
 irie--i reblogged this · 8 years ago
irie--i reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 themedicinepage liked this · 8 years ago
themedicinepage liked this · 8 years ago