Slime Mold Was Grown On An Agar Gel Plate Shaped Like America And Food Sources Were Placed Where America’s

Slime mold was grown on an agar gel plate shaped like America and food sources were placed where America’s large cities are.
The result? A possible look at how to best build public transportation.
I just really like the idea of slime mold on a map of the US. It’s beautiful.
More Posts from Science-is-magical and Others
Wait, people are mad that it's blurry? Isn't that black hole in another galaxy????
It’s literally like 55 million light years away
Whenever someone tries to claim that evolution is a lie, I send them a picture of platybelodon.

1. It’s an excellent example of transitional evolution.
2. It’s a mess who would intentionally do this and why
3. It makes them piss themselves a little.
“Evolution is just a theory-”

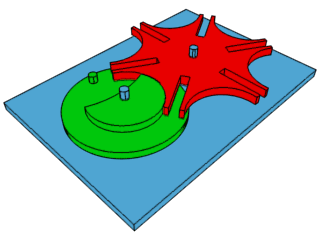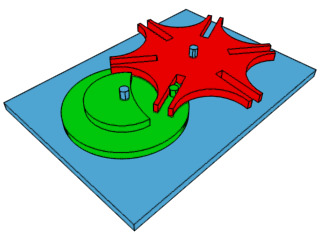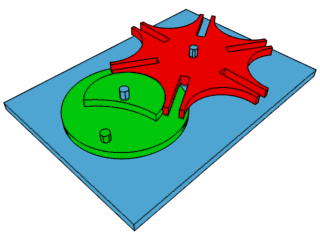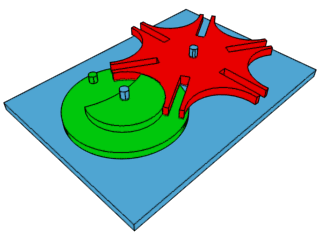
How the Geneva Drive (the mechanical step that makes the second hand on a clock work by turning constant rotation into intermittent motion) works.




Why we need GMOs to survive climate change
Genetically modified organisms get a bad rap for many reasons, but we’ve actually been genetically altering what we eat since the dawn of human history.
“For 10,000 years, we have altered the genetic makeup of our crops,”explains UC Davis plant pathology professor Pamela Ronald.
“Today virtually everything we eat is produced from seeds that we have genetically altered in one way or another.” (You can read more about Ronald’s thoughts on genetically engineered food here.)
Right now her focus is on rice. It’s one of our basic crops and without it, we would struggle to feed much of the world.
With climate change, we’re seeing an increase in flooding in places like India and Bangladesh, which makes it harder to grow this important food staple.
So Ronald and her lab have developed a flood-tolerant strain of rice. It’s known as Sub1a or “scuba rice” and millions of farmers in South Asia are now growing it in their fields.

Today is National Food Day, a day dedicated to hunger awareness. But as we focus on food insecurity, we need to talk more about how global warming will make the problem worse.
As our climate continues to heat up, it has huge impacts on what foods we are able to grow. Will our crops be able to survive droughts and floods? The University of California leads six labs that are working to develop other climate-resilient crops including chickpea, cowpea and millet.
Find out what other scientists are doing to improve our food.
It always creeps me out...
…that no matter
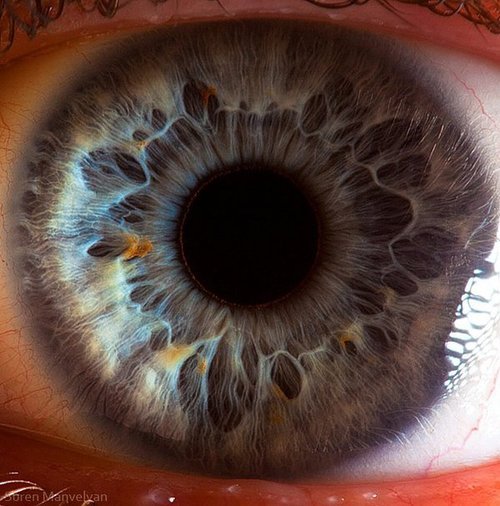
how close
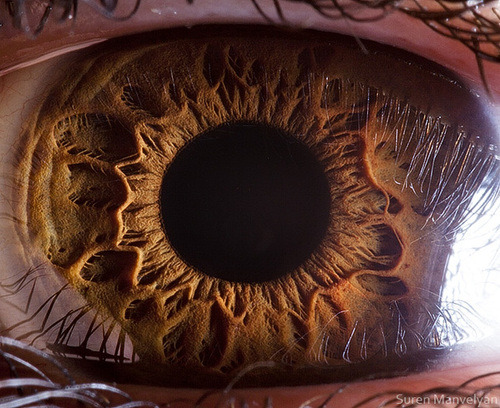
you get
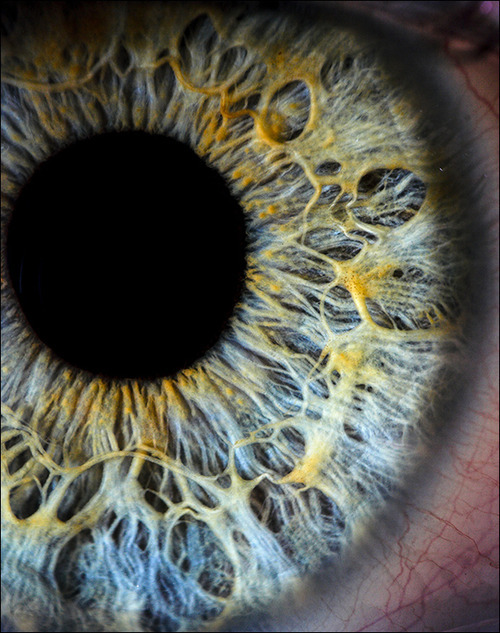
the pupil
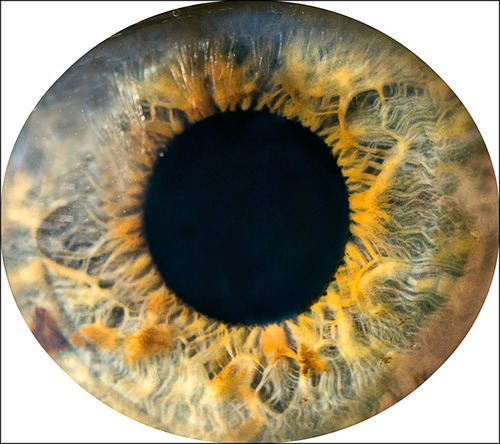
seems to
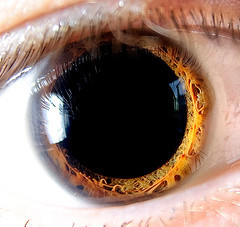
devour light
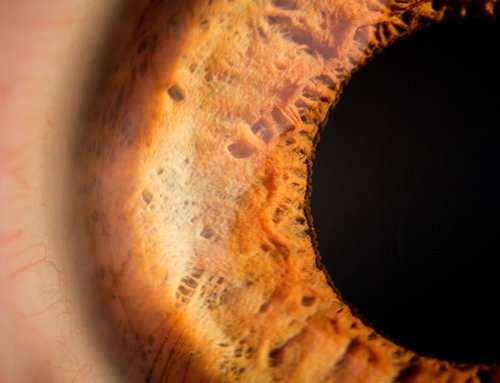
like a black hole
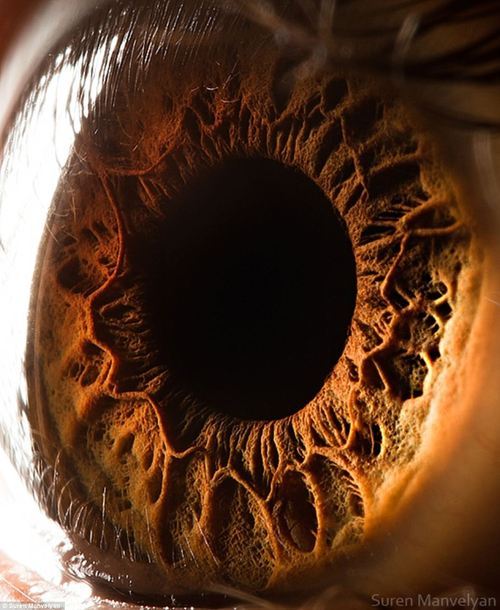
it reflects no light
Blowing Bubbles in the Gamma-ray Sky

Did you know our Milky Way galaxy is blowing bubbles? Two of them, each 25,000 light-years tall! They extend above and below the disk of the galaxy, like the two halves of an hourglass. We can’t see them with our own eyes because they’re only apparent in gamma-ray light, the highest-energy light in the universe.

We didn’t even know these humongous structures were smack in the middle of our galaxy until 2010. Scientists found them when they analyzed the first two years of data from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. They dubbed them the “Fermi bubbles” and found that in addition to being really big and spread out, they seem to have well-defined edges. The bubbles’ shape and the light they give off led scientists to think they were created by a rapid release of energy. But by what? And when?

One possible explanation is that they could be leftovers from the last big meal eaten by the supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy. This monster is more than 4 million times the mass of our own Sun. Scientists think it may have slurped up a big cloud of hydrogen between 6 and 9 million years ago and then burped jets of hot gas that we see in gamma rays and X-rays.

Another possible explanation is that the bubbles could be the remains of star formation. There are massive clusters of stars at very the center of the Milky Way — sometimes the stars are so closely packed they’re a million times more dense than in the outer suburb of the galaxy where we live. If there was a burst of star formation in this area a few million years ago, it could have created the surge of gas needed to in turn create the Fermi bubbles.

It took us until 2010 to see these Fermi bubbles because the sky is filled with a fog of other gamma rays that can obscure our view. This fog is created when particles moving near light speed bump into gas, dust, and light in the Milky Way. These collisions produce gamma rays, and scientists had to factor out the fog to unveil the bubbles.

Scientists continue to study the possible causes of these massive bubbles using the 10 years of data Fermi has collected so far. Fermi has also made many other exciting discoveries — like the the collision of superdense neutron stars and the nature of space-time. Learn more about Fermi and how we’ve been celebrating its first decade in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

In an experiment, two ravens had to simultaneously pull the two ends of one rope to slide a platform with two pieces of cheese into reach. If only one of them pulled, the rope would slip through the loops, leaving them with no cheese. Without any training they solved the task and cooperated successfully.

However, when one of the two birds cheated and stole the reward of its companion, the victims of such cheats immediately noticed and started defecting in further trials with the same individual.

“Such a sophisticated way of keeping your partner in check has previously only been shown in humans and chimpanzees, and is a complete novelty among birds.”

Source








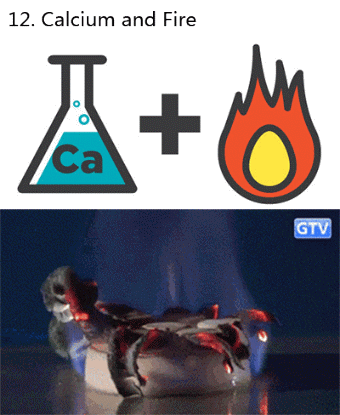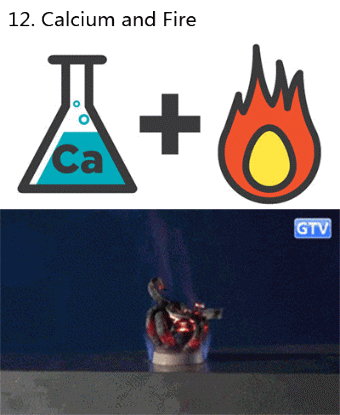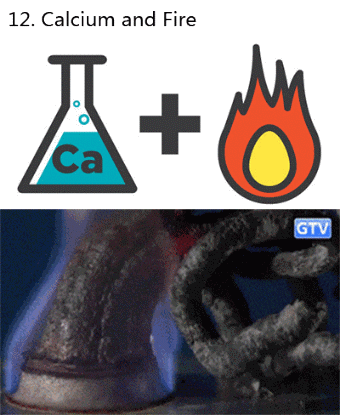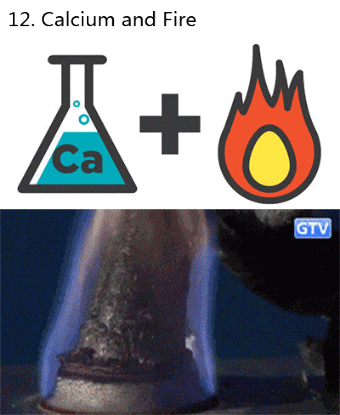
What makes fireworks colorful?
It’s all thanks to the luminescence of metals. When certain metals are heated (over a flame or in a hot explosion) their electrons jump up to a higher energy state. When those electrons fall back down, they emit specific frequencies of light - and each chemical has a unique emission spectrum.
You can see that the most prominent bands in the spectra above match the firework colors. The colors often burn brighter with the addition of an electron donor like Chlorine (Cl).
But the metals alone wouldn’t look like much. They need to be excited. Black powder (mostly nitrates like KNO3) provides oxygen for the rapid reduction of charcoal © to create a lot hot expanding gas - the BOOM. That, in turn, provides the energy for luminescence - the AWWWW.
Aluminium has a special role — it emits a bright white light … and makes sparks!
Images: Charles D. Winters, Andrew Lambert Photography / Science Source, iStockphoto, Epic Fireworks, Softyx, Mark Schellhase, Walkerma, Firetwister, Rob Lavinsky, iRocks.com, Søren Wedel Nielsen
-
 pajulintu reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
pajulintu reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 maggiedeshiboux liked this · 3 weeks ago
maggiedeshiboux liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 riptide-rabbitholes reblogged this · 1 month ago
riptide-rabbitholes reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 h3rs reblogged this · 1 month ago
h3rs reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 cornsnakes-r-cute reblogged this · 1 month ago
cornsnakes-r-cute reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 joanofsharks reblogged this · 1 month ago
joanofsharks reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 ceramicti1e liked this · 1 month ago
ceramicti1e liked this · 1 month ago -
 ceramicti1e reblogged this · 1 month ago
ceramicti1e reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 sensationaltrainreading reblogged this · 1 month ago
sensationaltrainreading reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 whitetiger94things reblogged this · 1 month ago
whitetiger94things reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 pawnsvictory reblogged this · 1 month ago
pawnsvictory reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 saysaraelle liked this · 1 month ago
saysaraelle liked this · 1 month ago -
 obsidian-flame reblogged this · 1 month ago
obsidian-flame reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 weareallkosh liked this · 1 month ago
weareallkosh liked this · 1 month ago -
 thelifeivegot liked this · 1 month ago
thelifeivegot liked this · 1 month ago -
 apeofthedust liked this · 1 month ago
apeofthedust liked this · 1 month ago -
 globalconsciousevolution reblogged this · 1 month ago
globalconsciousevolution reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 globalconsciousevolution liked this · 1 month ago
globalconsciousevolution liked this · 1 month ago -
 felalalieisafeminist reblogged this · 1 month ago
felalalieisafeminist reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 angle0fthegourd reblogged this · 1 month ago
angle0fthegourd reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 sleep-is-my-relationship-status reblogged this · 1 month ago
sleep-is-my-relationship-status reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 yoshifics reblogged this · 1 month ago
yoshifics reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 zippy5080 liked this · 1 month ago
zippy5080 liked this · 1 month ago -
 starry-bi-sky liked this · 2 months ago
starry-bi-sky liked this · 2 months ago -
 rickyspanish133 reblogged this · 2 months ago
rickyspanish133 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 rickyspanish133 liked this · 2 months ago
rickyspanish133 liked this · 2 months ago -
 illryiannightmare liked this · 2 months ago
illryiannightmare liked this · 2 months ago -
 jasontoddisasorceror reblogged this · 2 months ago
jasontoddisasorceror reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 jasontoddisasorceror liked this · 2 months ago
jasontoddisasorceror liked this · 2 months ago -
 saphiraarts liked this · 2 months ago
saphiraarts liked this · 2 months ago -
 dollycravee liked this · 2 months ago
dollycravee liked this · 2 months ago -
 sheepheadfred reblogged this · 2 months ago
sheepheadfred reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 steppentime reblogged this · 2 months ago
steppentime reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 social-justice-raccoon reblogged this · 2 months ago
social-justice-raccoon reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 help-i-need-a-cool-username liked this · 2 months ago
help-i-need-a-cool-username liked this · 2 months ago -
 bioluminescent-obscurity liked this · 2 months ago
bioluminescent-obscurity liked this · 2 months ago -
 jade-dragon555 liked this · 2 months ago
jade-dragon555 liked this · 2 months ago -
 vitamin--s reblogged this · 2 months ago
vitamin--s reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 cha0ticf0x liked this · 2 months ago
cha0ticf0x liked this · 2 months ago -
 aliceelflove reblogged this · 2 months ago
aliceelflove reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 aliceelflove liked this · 2 months ago
aliceelflove liked this · 2 months ago -
 demonic-werewolf reblogged this · 2 months ago
demonic-werewolf reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 demonic-werewolf liked this · 2 months ago
demonic-werewolf liked this · 2 months ago -
 loon-arts liked this · 2 months ago
loon-arts liked this · 2 months ago -
 patchthepirate liked this · 2 months ago
patchthepirate liked this · 2 months ago -
 wine-sluts reblogged this · 2 months ago
wine-sluts reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 wine-sluts liked this · 2 months ago
wine-sluts liked this · 2 months ago -
 kiraistired liked this · 2 months ago
kiraistired liked this · 2 months ago -
 ink-poison-blood reblogged this · 2 months ago
ink-poison-blood reblogged this · 2 months ago