Physical Science...In Space!
Physical Science...In Space!
Each month, we highlight a different research topic on the International Space Station. In May, our focus is physical science.

The space station is a laboratory unlike any on Earth; on-board, we can control gravity as a variable and even remove it entirely from the equation. Removing gravity reveals fundamental aspects of physics hidden by force-dependent phenomena such as buoyancy-driven convection and sedimentation.

Gravity often masks or distorts subtle forces such as surface tension and diffusion; on space station, these forces have been harnessed for a wide variety of physical science applications (combustion, fluids, colloids, surface wetting, boiling, convection, materials processing, etc).

Other examples of observations in space include boiling in which bubbles do not rise, colloidal systems containing crystalline structures unlike any seen on Earth and spherical flames burning around fuel droplets. Also observed was a uniform dispersion of tin particles in a liquid melt, instead of rising to the top as would happen in Earth’s gravity.

So what? By understanding the fundamentals of combustion and surface tension, we may make more efficient combustion engines; better portable medical diagnostics; stronger, lighter alloys; medicines with longer shelf-life, and buildings that are more resistant to earthquakes.

Findings from physical science research on station may improve the understanding of material properties. This information could potentially revolutionize development of new and improved products for use in everything from automobiles to airplanes to spacecraft.
For more information on space station research, follow @ISS_Research on Twitter!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Ritasakano and Others
Know your Neurotransmitters

You’ve probably heard about oxytocin in relation to hugging, dopamine in terms of addiction and serotonin in relation to depression. Neurotransmitters are crucial for all sorts of operations in your brain, including mood, appetite and movement. When dysregulated they can lead to undesirable outcomes, including mood disorders like depression and bipolar disorder, addiction and substance use disorders, and psychosis.
You may hear that ‘people with depression have a serotonin shortage’ or ‘addiction is caused by dopamine dysregulation’, and whilst that has some basis in science, the workings of these chemical messengers are somewhat mysterious and definitely more complex than that. Disorders are caused by a number of interactions and neurotransmitters, but for the sake of understanding, let’s keep it simple! In this article we’ll focus on those that are most commonly associated with mood and mental health: serotonin, dopamine, GABA, norepinephrine, oxytocin, and endorphins.
What are neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that communicate between the neurons in your brain. Whenever you think, move, learn, feel, perceive or do pretty much anything at all (even when you think you’re doing nothing), electrochemical impulses are rushing along pathways of neurons to make things happen. There are approximately 86 billion neurons in the brain and they do not actually touch each other! Instead they have small synapses where they ‘connect’, gaps of about 40 nanometres between them. For context, there are one million nanometres in a millimetre! The presynaptic (sending) neuron releases these neurotransmitters into the gap, which are picked up by the postsynaptic (receiving) neuron, triggering a response. All this happens a LOT faster than you can say ‘Give me the happy ones please brain!’
Serotonin: The Moody One
We mostly hear about serotonin with regard to mood, particularly that low levels cause depression. People who take antidepressant drugs, are likely to be taking SSRIs — Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors — which work by preventing presynaptic neurons from taking back the serotonin they release into the synapse so there is more available for the brain to use. As well as mood, serotonin is involved in appetite, sleep, memory, impulse inhibition and sexual desire. If you’re low on it, you might experience depression, anxiety, aggression, irritability, impulsivity, insomnia or poor appetite.

How to get enough
The essential ingredient for serotonin is tryptophan, found in salmon, eggs, spinach and seeds, or available as a supplement. Other players in the synthesis and regulation processes include magnesium, zinc, vitamins D, B6, B12 and L-methionine, and deficiencies in any of these could affect your serotonin availability.
How to ‘hack’ it for happiness
Giving, receiving or even witnessing an act of kindness boosts your serotonin, as does sunlight, exercise, and getting a massage.
Dopamine: The Hedonistic One
Dopamine is most commonly discussed for its role in pleasure, reward and motivation. The neurons in your brain that go crazy when you eat cake, have sex, or take drugs are full of dopamine receptors. It is involved in motivation, satisfaction and reward-driven behaviour, as well as movement, sleep, mood and learning. Too much dopamine is linked to aggression, poor impulse control, binge eating, addiction, and has been linked to psychosis and hallucinations in schizophrenia. Low dopamine is seen in movement disorders like Parkinson’s Disease, and may also result in low motivation, energy and sex drive, brain fog, and mood swings.

How to get enough
Dopamine is made from Tyrosine, which your body creates from phenylalanine, which can be found in meat, fish, eggs, tofu, almonds, avocadoes, milk, nuts and seeds. Tyrosine is also available as a supplement. Other players in the dopamine game that you’ll want to get enough of include copper, iron, and vitamins B3, B6, B9, and C. When you eat food that is high in sugar you’ll get a surge of dopamine, however this can lead to the same kind of desensitisation and tolerance as a drug addiction, with your brain needing more and more to get the same dopaminalicious reward. Poor sleep and chronic stress will also deplete your dopamine.
How to ‘hack’ it for productivity
Dopamine’s main purpose is actually motivation rather than pleasure, making sure you enjoy activities like eating and reproducing so you continue to do them. Think about how enjoyable it is planning a holiday, or clothes shopping for a hot date you’re excited about. Set goals, and use your pleasurable dopamine-surge activities as rewards instead of distractions.
GABA: The Chill One
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) is that neurotransmitter that walks into the chaos and reminds everyone to relax. It is inhibitory, produces a calming effect, reducing anxiety, stress and fear, and helping you sleep. Benzodiazepines like Valium work by enhancing the effect of GABA. If you don’t have enough you may suffer from panic, anxiety and even seizures. GABA is produced naturally in the brain, and low levels can be caused by an inadequate diet, genetics and prolonged stress.

How to get enough
Vitamin B6 is essential for GABA production. You can buy GABA as a food supplement, but scientists aren’t convinced it actually does anything.
How to ‘hack’ it for relaxation
It probably won’t surprise you that yoga, meditation and deep breathing improve your GABA functions. You’ll get the best results if you incorporate them as a regular practice, rather than just when you need them.
Norepinephrine: The Alert One (also known as noradrenaline)
Multitasking norepinephrine functions as a neurotransmitter and a hormone, released into the blood in response to stress. It is involved in attention and alarm response, including the body’s fight or flight response, to help mobilise you for action in the face of danger. It is also implicated in emotions, sleeping, dreaming and is important for memory and learning. Low levels are associated with lethargy, lack of focus and attention, and depression. Overactivity can amplify our normal stress reactions and cause symptoms like anxiety, insomnia, irritability and mood swings.

How to get enough (and regulate it)
Norepinephrine is made from dopamine! It starts with phenylalanine, and goes one step further than dopamine, requiring all the ingredients dopamine requires, and then oxygen and vitamin C to undertake that next transformation. Chronic stress causes prolonged activation of the norepinephrine system, which uses up all your resources, stealing energy from your healing and maintenance systems to prepare for this apparent ongoing threat. Finding ways to reduce stress (see GABA: The Chill One) will regulate your norepinephrine.
How to ‘hack’ it for attention and memory
Coffee’ll do it!
Oxytocin: The Loving One
Oxytocin is both a hormone and a neuropeptide. A neuropeptide is like a large-sized neurotransmitter, and is usually associated with slow, prolonged effects instead of quick ones. Oxytocin is known as ‘the love hormone’ and induces feelings of affection and trust, while inhibiting the brain’s fear response. There you go… this is probably the scientific basis for that hippy notion of fear being the opposite of love! It plays a crucial role in childbirth, breastfeeding, and parental bonding.

How to get enough of it
You can purchase oxytocin as a nasal spray, and it has been shown to promote trust, kindness, emotion recognition and sensitivity. But beware the ‘dark side’ of the cuddle chemical… a 2009 study has shown it can also increase aggression, envy, jealousy and gloating!
How to hack it for those loving feelings
Some studies have shown you can increase oxytocin by meditating, patting your dog or hugging.
Endorphins: The Feelgood One
Most famous for their part in the ‘runner’s high’, endorphins are another neuropeptide. When you feel amazing after a good workout, that’s your endorphins in action. They act as a natural pain reliever, working on the same neuroreceptors as opiates like morphine. They are released as a response to stress or pain, and also during eating, exercising and sex. They improve your mood, lower your stress and boost your self-esteem.

How to get enough of them
Endorphins are produced naturally in the body. We don’t know a lot about endorphin deficiency, but some studies have shown they can become depleted through habitual alcohol use or after traumatic experiences.
How to ‘hack’ them for good feels
You can give yourself a boost of endorphins by eating dark chocolate or something spicy, having a glass of wine, creating music, dancing, doing a workout, meditating, getting a massage, having a sauna or volunteering. Even just having a good laugh will get them working, so watching a good comedy might give you what you need.
Just to reiterate, this is a simplistic explanation and neurotransmitters work in complex ways with each other, with hormones, and with various parts of the body and brain to create different moods and psychological states. We still have a lot to learn about the true nature of these interactions — the brain is a fun and complicated thing to study! But there’s nothing to lose in friending up with your neurotransmitters and giving them the nutrition and stimulus to encourage them. They might even reward you with those oh-so-good brain feels we like so much.
By Larissa Wright (Medium). Gif by AnatomyLearn. Illustration by Compound Interest.
🦋 Borboletas 🦋

Que trabalho maravilhoso!!


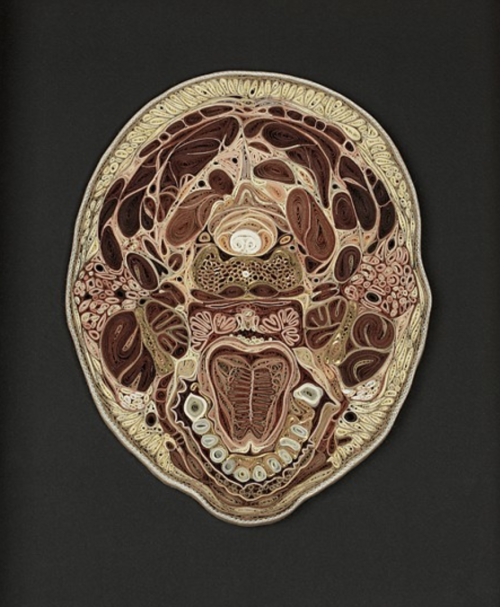

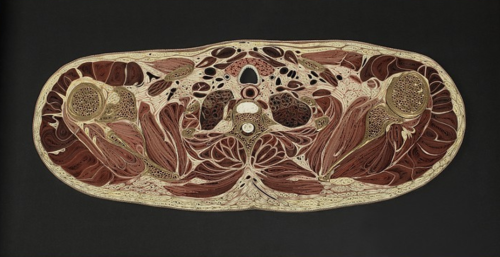
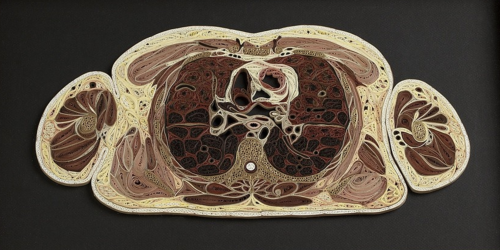
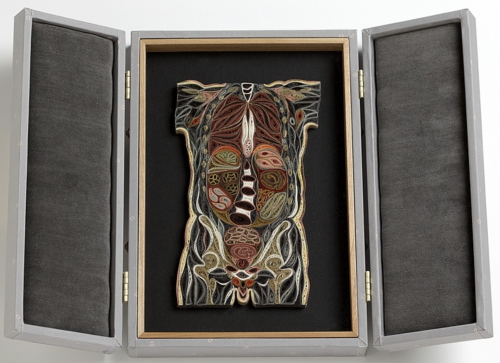

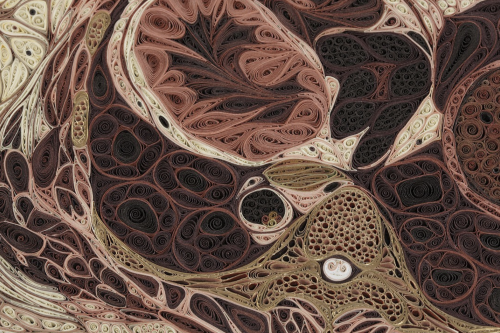

Tissue Series
These pieces are made of Japanese mulberry paper and the gilded edges of old books. They are constructed by a technique of rolling and shaping narrow strips of paper called quilling or paper filigree. Quilling was first practiced by Renaissance nuns and monks who are said to have made artistic use of the gilded edges of worn out bibles, and later by 18th century ladies who made artistic use of lots of free time.
- by Lisa Nilsson




Fire Sprinklers Erupt from Ingeniously Camouflaged Huts to Protect a Historic Japanese Village
A incrível dança do Universo!!
Eclipse Across America
August 21, 2017, the United States experienced a solar eclipse!

An eclipse occurs when the Moon temporarily blocks the light from the Sun. Within the narrow, 60- to 70-mile-wide band stretching from Oregon to South Carolina called the path of totality, the Moon completely blocked out the Sun’s face; elsewhere in North America, the Moon covered only a part of the star, leaving a crescent-shaped Sun visible in the sky.

During this exciting event, we were collecting your images and reactions online.
Here are a few images of this celestial event…take a look:

This composite image, made from 4 frames, shows the International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, as it transits the Sun at roughly five miles per second during a partial solar eclipse from, Northern Cascades National Park in Washington. Onboard as part of Expedition 52 are: NASA astronauts Peggy Whitson, Jack Fischer, and Randy Bresnik; Russian cosmonauts Fyodor Yurchikhin and Sergey Ryazanskiy; and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Paolo Nespoli.
Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls

The Bailey’s Beads effect is seen as the moon makes its final move over the sun during the total solar eclipse on Monday, August 21, 2017 above Madras, Oregon.
Credit: NASA/Aubrey Gemignani

This image from one of our Twitter followers shows the eclipse through tree leaves as crescent shaped shadows from Seattle, WA.
Credit: Logan Johnson

“The eclipse in the palm of my hand”. The eclipse is seen here through an indirect method, known as a pinhole projector, by one of our followers on social media from Arlington, TX.
Credit: Mark Schnyder

Through the lens on a pair of solar filter glasses, a social media follower captures the partial eclipse from Norridgewock, ME.
Credit: Mikayla Chase

While most of us watched the eclipse from Earth, six humans had the opportunity to view the event from 250 miles above on the International Space Station. European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli captured this image of the Moon’s shadow crossing America.
Credit: Paolo Nespoli

This composite image shows the progression of a partial solar eclipse over Ross Lake, in Northern Cascades National Park, Washington. The beautiful series of the partially eclipsed sun shows the full spectrum of the event.
Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
In this video captured at 1,500 frames per second with a high-speed camera, the International Space Station, with a crew of six onboard, is seen in silhouette as it transits the sun at roughly five miles per second during a partial solar eclipse, Monday, Aug. 21, 2017 near Banner, Wyoming.
Credit: NASA/Joel Kowsky
To see more images from our NASA photographers, visit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/nasahqphoto/albums/72157685363271303
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Modesto Carvalhosa on Twitter
-
 retardedcontrollerreading reblogged this · 9 months ago
retardedcontrollerreading reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 hitstun liked this · 1 year ago
hitstun liked this · 1 year ago -
 astronomicalcuber liked this · 2 years ago
astronomicalcuber liked this · 2 years ago -
 lordofshades liked this · 3 years ago
lordofshades liked this · 3 years ago -
 criminally-not-moose liked this · 5 years ago
criminally-not-moose liked this · 5 years ago -
 songweaver reblogged this · 5 years ago
songweaver reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sindysugar reblogged this · 5 years ago
sindysugar reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 barcerona liked this · 5 years ago
barcerona liked this · 5 years ago -
 twowheeltwinkies-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
twowheeltwinkies-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 therandom1234thenorm-blog liked this · 6 years ago
therandom1234thenorm-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 anjonvumije-blog liked this · 7 years ago
anjonvumije-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 roboticforest reblogged this · 7 years ago
roboticforest reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 roboticforest liked this · 7 years ago
roboticforest liked this · 7 years ago -
 icenose liked this · 7 years ago
icenose liked this · 7 years ago -
 thisismyipadsfault liked this · 7 years ago
thisismyipadsfault liked this · 7 years ago -
 t-sci-eng reblogged this · 8 years ago
t-sci-eng reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sleepysneezeydopeydoc-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
sleepysneezeydopeydoc-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sleepysneezeydopeydoc-blog liked this · 8 years ago
sleepysneezeydopeydoc-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 theburningjoint reblogged this · 8 years ago
theburningjoint reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 yodaddy619 reblogged this · 8 years ago
yodaddy619 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 yodaddy619 liked this · 8 years ago
yodaddy619 liked this · 8 years ago -
 andromeda-gay reblogged this · 8 years ago
andromeda-gay reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 andromeda-gay liked this · 8 years ago
andromeda-gay liked this · 8 years ago -
 myshellebellelove reblogged this · 8 years ago
myshellebellelove reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 myshellebellelove liked this · 8 years ago
myshellebellelove liked this · 8 years ago -
 prv-d-maliline reblogged this · 8 years ago
prv-d-maliline reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 magnokabro reblogged this · 8 years ago
magnokabro reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ouraniah reblogged this · 8 years ago
ouraniah reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 stanley869 reblogged this · 8 years ago
stanley869 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 connectedportal liked this · 8 years ago
connectedportal liked this · 8 years ago -
 bibliophilea reblogged this · 8 years ago
bibliophilea reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 d-maliline liked this · 8 years ago
d-maliline liked this · 8 years ago -
 i-got-my-head-checked reblogged this · 8 years ago
i-got-my-head-checked reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 patz30 reblogged this · 8 years ago
patz30 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 cladeoflife reblogged this · 8 years ago
cladeoflife reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 koigikibble liked this · 8 years ago
koigikibble liked this · 8 years ago -
 morohiko16 liked this · 8 years ago
morohiko16 liked this · 8 years ago
