A Home Library.




A home library.
More Posts from Purpletelescope and Others









Eight Ways to Remember Anything by Alex Lickerman M.D.
Reference: Research-based strategies to boost your memory and keep it strong via psychology today

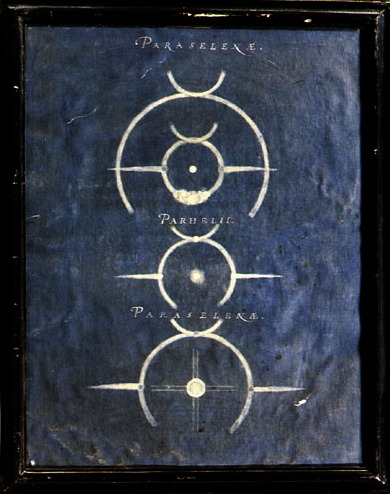

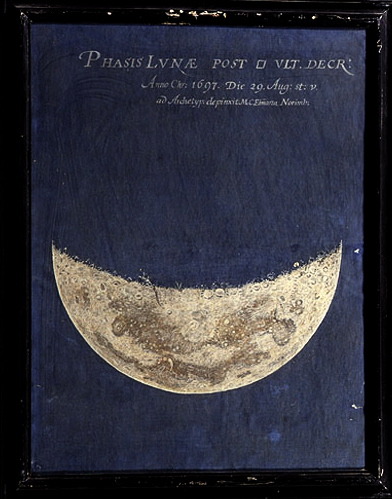



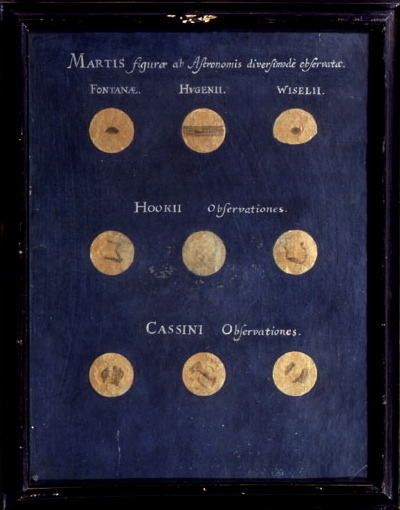



sunday, september 20th, 2020 | this morning was nice! I had a smoothie and did my planning for the week, then I worked on some physics notes. the weather is finally starting to cool down and I am so, so happy about it :D
OKAY CAN SOMEBODY EXPLAIN TO ME HOW THE FUCK YOU SHIP A PACKAGE OF COOKIES TO A FRIEND WHO LIVES IN NEW JERSEY, ONLY TO HAVE IT NOT GET THERE ON TIME BECAUSE IT SOMEHOW ENDED UP IN GUAM?
I JUST
GUAM?
Do you have any advice for how not to get overwhelmed when reading scientific literature, mainly primary research articles? I have to present one at the end of this month for in order to graduate from University and I'm trying to read through and understand it, but every couple of lines I start having a miniature panic attack because I feel as if I don't understand ANYTHING that I am reading
BOY HAVE YOU COME TO RIGHT PLACE BC I READ SCIENTIFIC PAPERS EVERY. SINGLE. DAY. /cries a bit
Don’t read the abstract first thing. I know a lot of people do, but that’s a big mistake if you’re not a super duper level 100 science genius. If you read the abstract without knowing the science really well, it’s going to sound like gibberish soon. Read the abstract last, because it serves as a good summary.
Instead, start with the introduction. This will give you the background information you need, and it always starts out very broad.
Skip the methods part for now. Read the Results after you read the intro, and refer back to the Methods section if you don’t know what some assay is, how the mice were fed, etc. But sometimes the methods section isn’t very helpful since they go into too much detail. That leads me to..
Don’t know something? Look it up! So you come across something like “aneuploidy”, and you have no idea what it means. Don’t try to gather information from context clues; just straight up Google it, or ask someone who knows. This is the most important thing. No one is ever going to understand everything in a paper (unless they wrote it, of course). Even the top scientists have to Google stuff all the time when reading other papers. Sometimes, you can even refer back to the references in the back of the paper for answers.
Jot down notes. Once you find out what aneuploidy is, write it down on the margin of the paper so you can refer back to it. Maybe even draw a small diagram too as an example.
Annotate the figures. The figures are very very very important. They’re what tells the story. If you understand everything in the figure–the question asked, the method used, what the x- and y-axes mean, etc, what the result was–then you will understand the entire paper. So scribble away. Draw arrows. Write notes. Circle things. Define acronyms. Color code stuff. This is what all the primary papers I read look like when it comes to figures:

(Also pay attention to the Figure legends. Sometimes they’ll tell you extra information)
Explain the figures out loud. If you can explain it in your own words, you’ve got it down! You’re going to have to do this for your presentation anyway.
If it helps, write down important observations/figure summaries on a separate piece of paper so you have something you can quickly reference when putting together your presentation.
As far as the presentation goes, I like to create my slides in this order: Title, Background, Hypothesis, Questions Asked (basically a summary of what they wanted to find), Question #1 (which is essentially what Figure 1 should be about), (Additional background if necessary), Method(s) used to answer Question #1, Figures that answer Question #1, Question #1 conclusion, Question #2, etc, etc, until finally, Conclusion, Future Goals. You may have a different format, but just throwing out the one I use.
You can do it! The trick to reading scientific literature is really… Google/ask questions for things you don’t know, and really understand the figures. And with anything that’s hard at first, practice will soon make it easier :) Good luck! If you need help with the specific paper, you can send me the first author’s name, title, and year published and I can see if I can help you with anything :)
The only acceptable solar system diagram!

Some idioms and phrases you should know about part I
Salt of the earth: a very good or worthy person.
Gut-wrenching: making you feel very upset or worried.
Make a spectacle of yourself: to do something that makes you look stupid and attracts people’s attention.
Pass muster: be accepted as adequate or satisfactory.
Putty in someone’s hands: easily influenced by someone else, excessively willing to do what someone else wishes.
Look before you leap: carefully consider the possible consequences before taking action.
Set the wheels in motion : to do something that will cause a series of actions to start.
Off the books: without being included on official records.
A long Haul: something that takes a lot of time and energy.
An end in itself: a goal that is pursued in it’s own right to the exclusion of others.
Night owl: a person who prefers to be awake late at night.
Kick the Bucket: to die.
Alter Ego: a person’s secondary or alternative personality immediately or extremely quickly; at once.
Freak of Nature: something or someone that is unusual, rare, or abnormal in some way / To avoid attracting attention to yourself.









May study challenge day 23!
What type of learner are you (visual, kinetic, etc.)? How does this translate to your study methods?
I’ve never really had one particular learning type that works for me more than others - I try to study in different ways, but I guess my study style fits with a visual learning method more than others?
Today - a photo from a chemistry experiment, reviewing English, chemistry homework, violin practice, piano practice, making chemistry notes, music homework, Latin lit revision, and my cute little productivity tracker with a flower for each day 🌷🌟
Planets i learned about via youtube while procrastinating my english essay
Planet 55 Cancri e is basically a giant diamond. like the planet is a diamond. and it would be worth $26.9 nonillion
Planet Gliese 436 b is an ice planet that is constantly on fire do to its close proximity to its parent star. the ice doesn’t melt bc the planet’s gravity is so strong it physically prevents the ice from melting
Planet HD 189733b rains sideways glass…. constantly
Planet J1407-B has planetary rings that are 200x the size of saturn. if saturn’s ring were as big as J1407-B’s we’d be able to see them with our naked eye from earth AND they would dominate our sky and look larger than a full moon
Planet Wasp-12b rotates so close to its parent star that its slowly being consumed by the it
Planet Gliese 581c is one of the candidates for a planet that can support life however it orbits a tiny dwarf star and is tidally locked so one side is constantly subject to immense sunlight while the other is constantly in darkness. there’s a small area of the planet however, that is just the right temp to support life. u just can’t step out of said area. the skies are red and the plants would have be a black color instead of a green bc they would use infrared light for photosynthesis. (a message was actually sent to the planet in 2008 in hopes that there’s life on the planet but the message wont reach the planet until 2029).
Planet GJ 1214b is a water planet nicknamed “water world” is has no land at all and the water is so deep it goes down miles all the way to the planet’s core.
Planet Wasp-17b is the largest planet discovered thus far. its so large its existence contradicts our understanding of how planets are formed. and it has a retrograde orbit, so it orbits in the opposite direction of its parent star.
Planet HD 188753 has 3 suns you should have triple shadows and there would be almost daily eclipses. and no matter which direction u face on the planet u would always see a sunset
Planet HD106906b is the loneliest planet discovered thus far. its known as “super jupiter” bc its 11x bigger than jupiter. it orbits its parent star at a distance of 60 billion miles (which is v strange) hence why its the loneliest planet.
Planet Tres 2b is the darkest planet known. it reflects less than 1% of light (it reflects less light than coal and black acrylic paint). the tiny part of the planet that does reflect light is red making the planet glow a dim red.
-
 pagesandkayla liked this · 2 weeks ago
pagesandkayla liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 h0spi7idk1 liked this · 2 months ago
h0spi7idk1 liked this · 2 months ago -
 dandylandon liked this · 3 months ago
dandylandon liked this · 3 months ago -
 shes4real liked this · 4 months ago
shes4real liked this · 4 months ago -
 lat3bl00mer liked this · 4 months ago
lat3bl00mer liked this · 4 months ago -
 griffinxgallo liked this · 5 months ago
griffinxgallo liked this · 5 months ago -
 mo-the-gremlin-dandelion liked this · 6 months ago
mo-the-gremlin-dandelion liked this · 6 months ago -
 vodka-latte-library liked this · 6 months ago
vodka-latte-library liked this · 6 months ago -
 timidreamer liked this · 6 months ago
timidreamer liked this · 6 months ago -
 bbp35 reblogged this · 6 months ago
bbp35 reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 bbp35 liked this · 6 months ago
bbp35 liked this · 6 months ago -
 indy-housebeautiful reblogged this · 6 months ago
indy-housebeautiful reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 4am-bangtan liked this · 6 months ago
4am-bangtan liked this · 6 months ago -
 tily-c liked this · 7 months ago
tily-c liked this · 7 months ago -
 lovetakingpics liked this · 7 months ago
lovetakingpics liked this · 7 months ago -
 less-sad liked this · 7 months ago
less-sad liked this · 7 months ago -
 ranispersonalblog liked this · 7 months ago
ranispersonalblog liked this · 7 months ago -
 superstarfighter liked this · 8 months ago
superstarfighter liked this · 8 months ago -
 heavynights reblogged this · 8 months ago
heavynights reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 atlas-affogato liked this · 8 months ago
atlas-affogato liked this · 8 months ago -
 merzbuilds liked this · 8 months ago
merzbuilds liked this · 8 months ago -
 hassliebe8 liked this · 9 months ago
hassliebe8 liked this · 9 months ago -
 billgavemeextrachips liked this · 9 months ago
billgavemeextrachips liked this · 9 months ago -
 holder-of-destiny reblogged this · 9 months ago
holder-of-destiny reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 bratty-little-fairy liked this · 9 months ago
bratty-little-fairy liked this · 9 months ago -
 occasionallyclever liked this · 9 months ago
occasionallyclever liked this · 9 months ago -
 m-a-salter reblogged this · 9 months ago
m-a-salter reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 purplewolfbitch liked this · 9 months ago
purplewolfbitch liked this · 9 months ago -
 pattypatty3 liked this · 9 months ago
pattypatty3 liked this · 9 months ago -
 abatefaria reblogged this · 9 months ago
abatefaria reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 gobluerose70 liked this · 10 months ago
gobluerose70 liked this · 10 months ago -
 nicole-annette reblogged this · 10 months ago
nicole-annette reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 nicole-annette liked this · 10 months ago
nicole-annette liked this · 10 months ago -
 hidefromeveryone liked this · 10 months ago
hidefromeveryone liked this · 10 months ago -
 eduurun liked this · 10 months ago
eduurun liked this · 10 months ago -
 magiccereal reblogged this · 10 months ago
magiccereal reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 afawnintheforest reblogged this · 10 months ago
afawnintheforest reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 afawnintheforest liked this · 10 months ago
afawnintheforest liked this · 10 months ago -
 venusvondrackova liked this · 10 months ago
venusvondrackova liked this · 10 months ago -
 nikinu69 liked this · 10 months ago
nikinu69 liked this · 10 months ago -
 ambrmlw reblogged this · 10 months ago
ambrmlw reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 ambrmlw liked this · 10 months ago
ambrmlw liked this · 10 months ago -
 bizarre-jojo liked this · 11 months ago
bizarre-jojo liked this · 11 months ago -
 keebiekneebiez reblogged this · 11 months ago
keebiekneebiez reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 mundoturco liked this · 11 months ago
mundoturco liked this · 11 months ago -
 serenedys liked this · 11 months ago
serenedys liked this · 11 months ago -
 danceportal liked this · 11 months ago
danceportal liked this · 11 months ago

