This Is What Happens When A Carrot Is Fired At 300 Km/hour At An Egg, Through Two Sheets Of Cardboard.

This is what happens when a carrot is fired at 300 km/hour at an egg, through two sheets of cardboard.
This is what happens if you separate out the two sheets:

The egg survives! This shows how a Whipple shield works, and is what spacecraft use to protect themselves from micrometeoroid impacts in space. When the projectile (in this case a carrot, but in space it could be a speck of paint, a piece of an old satellite, or a bit of space rock) hits the first layer, it’s moving so fast that it starts to vaporise, because the energy of the collision is enough to break almost every bond in the substance.
It then sprays outwards, spreading the force of impact across a much wider area, meaning the second layer can stop it going any further, keeping your egg (or astronauts) safe.
Watch the full video on our YouTube channel.
More Posts from Philosophical-amoeba and Others







Fuji-Ya Restaurant, Second to None
In 1968, Reiko Weston opened her new Fuji-Ya restaurant built atop the limestone foundation of a 19th-century flour mill overlooking the Mississippi River and the Stone Arch Bridge. The original Fuji-Ya restaurant operated near 8th St. and LaSalle beginning almost a decade earlier, in 1959, and served fine Japanese food including Charcoal-Broiled Teri-Yaki dinners, seafood dishes, soups, rice plates, and more. Fuji-Ya translates to “second to none” and the new restaurant offered a dining experience like no other in the Twin Cities.
Weston’s restaurant business expanded over the years with Taiga, a Chinese Szechwan restaurant in St. Anthony Main, and The Fuji International in Cedar-Riverside neighborhood, which featured Korean, Chinese, and East Indian food in addition to Japanese food. Her restaurants received numerous awards and Weston herself was named Minnesota Small Business Person of the Year in 1979.
After Reiko Weston passed away in 1988, her daughter Carol stepped in to manage. But in 1990, the City of Minneapolis bought out the historic restaurant in order to make way for the newly designed parkway. About a decade later, Fuji Ya was brought to life again in Uptown in the trendy Lyn-Lake area, where it remains today.
Recently, Fuji-Ya has gained renewed attention as the Park Board makes plans for a $12 million riverfront refresh. Plans include the teardown of the old Fuji-Ya building, expansion of green space, improved pedestrian crossings, and the addition of a new riverfront restaurant. It was announced last week that Sioux Chef owners Sean Sherman and Dana Thompson will open Owamni: An Indigenous Kitchen on the site.
Menu from the original Fuji-Ya restaurant at 814 LaSalle Ave. from the Minneapolis History Collection Menu Collection. Photos from the Star Tribune Photograph Collection at the James K. Hosmer Special Collections, Hennepin County Library.

Black Holes are not so Black (Part 3) - Gravitational Waves
The existence of Gravitational Waves have been confirmed. But you probably have heard that. In this post, we will break down this profound discovery into comprehend-able chunks.
This is going to be a amazing journey. Ready ?
Redefining Gravity
When we usually talk of Gravitation we are bound to think like Newton, where objects are assumed to exerting a force upon each other.
Like imaginary arrows of force in space. But this picture, although good for high school crumbled, with the advent of Einstein’s theory of Relativity.
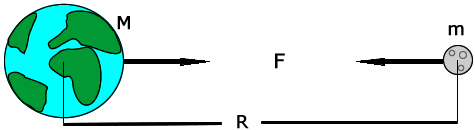
What is the Space-Time Fabric?
Think of space-time fabric as an actual cloth of fabric. ( An analogy )

When you place an object on the fabric, the cloth curves. This is exactly what happens in the solar system as well.

The sun with such a huge mass bends the space-time fabric. And the earth and all the planets are kept in orbit by following this curvature that has been made by the sun.
Attributing to the various masses of objects, the way they bend this fabric also varies.
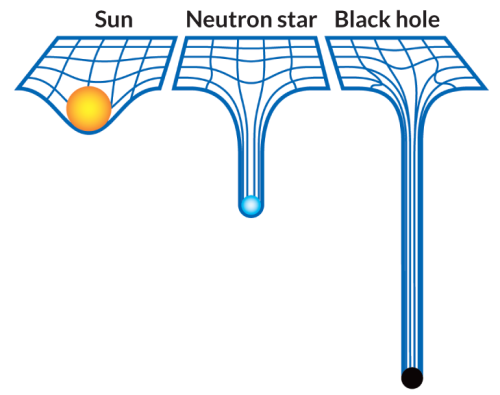
What are Gravitational Waves?
If you drop an object in a medium such as water, they produce ripples that propagate as waves through the medium.

Similarly, Gravitational waves are ripples in space-time fabric produced when you drag heavy objects through space time.
And the nature of these waves is that they don’t require a medium to propagate.
How do you make one?
Everything with mass/energy can create these waves.

Source
Two persons dancing around each other in space too can create gravitational waves. But the waves would be extremely faint.
You need something big and massive accelerating through space-time in order to even detect them.

And orbiting binary stars/black holes are valuable in this retrospect.
How can you detect them?
Let’s turn to the problem to detecting them assuming you do find binary stars/black-holes in the wondrous space to suite your needs.
Well, for starters you cannot use rocks/ rulers to measure them because as the space expands and contracts, so do the rocks. ( the distances will remain same in both the cases )

Here’s where the high school fact that the speed of Light is a constant no matter what plays an important and pivotal role.
If the space expands, the time taken for light to reach from A to B would be longer. And if it contracts, the time taken for it to reach from A to B would be smaller.

PC: PHDComics
By allowing the light waves from the contraction and expansion to interfere with each other, such as done in any interferometry experiment we can detect the expansion or contraction. Voila!
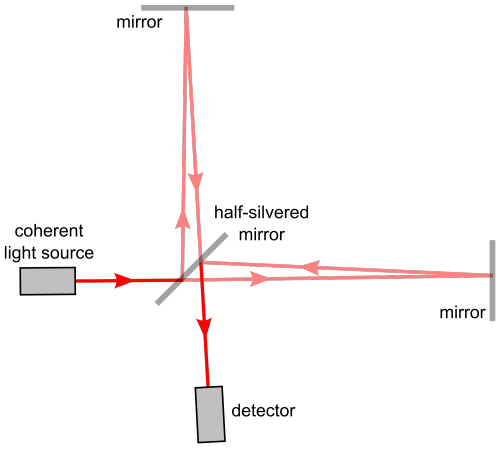
And this is exactly what they did! ( on a macroscopic level ) at LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory)
14 September 2015

Two Black Holes with masses of 29 and 36 solar masses merged together some 1.3 Billion light years away.
Two Black Holes colliding is the header animation of the ‘Black Holes are not so Black Series’, in case if you haven’t noticed.

The merger of these two black holes results in the emission of energy equivalent to 3 solar masses as Gravitational Waves.
This signal was seen by both LIGO detectors, in Livingston and Hanford, with a time difference of 7 milliseconds.
And with the measurement of this time difference, physicists have pronounced the existence of Gravitational Waves.

Source
All this is most certainly easily said than done and requires meticulous and extensive research, not to mention highly sensitive instruments.
Had they not have measured this time difference, we might have had to wait for the merger for more massive black holes to collide and maybe even build more sensitive instruments to detect these waves.
And Einstein predicted this a 100 years back!

Mind Blown!
Note: Hope you are able to understand and appreciate the profundity of the discovery done by mankind.
** All animations used here are merely for Educational purposes. If you have any issues, please write to us at : 153armstrong@gmail.com

I am pretty sure that this cannot be true because I saw an ad from the corn industry that said high fructose corn syrup is good for you…
Fructose alters hundreds of brain genes, which can lead to a wide range of diseases
A range of diseases – from diabetes to cardiovascular disease, and from Alzheimer’s disease to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder – are linked to changes to genes in the brain. A new study by UCLA life scientists has found that hundreds of those genes can be damaged by fructose, a sugar that’s common in the Western diet, in a way that could lead to those diseases.
However, the researchers discovered good news as well: An omega-3 fatty acid known as docosahexaenoic acid, or DHA, seems to reverse the harmful changes produced by fructose.
“DHA changes not just one or two genes; it seems to push the entire gene pattern back to normal, which is remarkable,” said Xia Yang, a senior author of the study and a UCLA assistant professor of integrative biology and physiology. “And we can see why it has such a powerful effect.”
Qingying Meng, Zhe Ying, Emily Noble, Yuqi Zhao, Rahul Agrawal, Andrew Mikhail, Yumei Zhuang, Ethika Tyagi, Qing Zhang, Jae-Hyung Lee, Marco Morselli, Luz Orozco, Weilong Guo, Tina M. Kilts, Jun Zhu, Bin Zhang, Matteo Pellegrini, Xinshu Xiao, Marian F. Young, Fernando Gomez-Pinilla, Xia Yang. Systems Nutrigenomics Reveals Brain Gene Networks Linking Metabolic and Brain Disorders. EBioMedicine, 2016; DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.04.008
Americans get most of their fructose in foods that are sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup, an inexpensive liquid sweetener made from corn starch, and from sweetened drinks, syrups, honey and desserts. The Department of Agriculture estimates that Americans consumed an average of about 27 pounds of high-fructose corn syrup in 2014. Credit: © AlenKadr / Fotolia
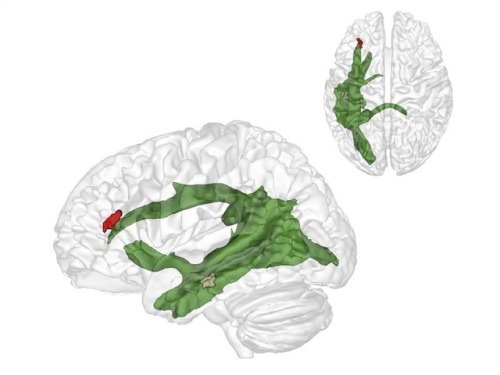
(Image caption: The maturation of fibres of a brain structure called the arcuate fascicle (green) between the ages of three and four years establishes a connection between two critical brain regions: a region (brown) at the back of the temporal lobe that supports adults thinking about others and their thoughts, and a region (red) in the frontal lobe that is involved in keeping things at different levels of abstraction and, therefore, helps us to understand what the real world is and what the thoughts of others are. Credit: © MPI CBS)
The importance of relating to others: why we only learn to understand other people after the age of four
When we are around four years old we suddenly start to understand that other people think and that their view of the world is often different from our own. Researchers in Leiden and Leipzig have explored how that works. Publication in Nature Communications on 21 March.
At around the age of four we suddenly do what three-year-olds are unable to do: put ourselves in someone else’s shoes. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences (MPI CBS) in Leipzig and at Leiden University have shown how this enormous developmental step occurs: a critical fibre connection in the brain matures. Senior researcher and Leiden developmental psychologist Nikolaus Steinbeis, co-author of the article, took part in the research. Lead author, PhD candidate Charlotte Grosse-Wiesmann, worked under his supervision.
Little Maxi
If you tell a 3-year-old child the following story of little Maxi, they will most probably not understand: Maxi puts his chocolate on the kitchen table, then goes to play outside. While he is gone, his mother puts the chocolate in the cupboard. Where will Maxi look for his chocolate when he comes back? A 3-year-old child will not understand why Maxi would be surprised not to find the chocolate on the table where he left it. It is only by the age of 4 years that a child will correctly predict that Maxi will look for his chocolate where he left it and not in the cupboard where it is now.
Theory of Mind
The researchers observed something similar when they showed a 3-year-old child a chocolate box that contained pencils instead of chocolates. When the child was asked what another child would expect to be in the box, they answered “pencils”, although the other child would not know this. Only a year later, around the age of four years, however, will they understand that the other child had hoped for chocolates. Thus, there is a crucial developmental breakthrough between three and four years: this is when we start to attribute thoughts and beliefs to others and to understand that their beliefs can be different from ours. Before that age, thoughts don’t seem to exist independently of what we see and know about the world. That is, this is when we develop a Theory of Mind.
Independent development
The researchers have now discovered what is behind this breakthrough. The maturation of fibres of a brain structure called the arcuate fascicle between the ages of three and four years establishes a connection between two critical brain regions: a region at the back of the temporal lobe that supports adult thinking about others and their thoughts, and a region in the frontal lobe that is involved in keeping things at different levels of abstraction and, therefore, helps us to understand what the real world is and what the thoughts of others are. Only when these two brain regions are connected through the arcuate fascicle can children start to understand what other people think. This is what allows us to predict where Maxi will look for his chocolate. Interestingly, this new connection in the brain supports this ability independently of other cognitive abilities, such as intelligence, language ability or impulse control.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Add to your electronic bookshelf with these free e-books from NASA!
1. The Saturn System Through the Eyes of Cassini

This work features 100 images highlighting Cassini’s 13-year tour at the ringed giant.
2. Earth as Art

Explore our beautiful home world as seen from space.
3. Meatballs and more

Emblems of Exploration showcases the rich history of space and aeronautic logos.
4. Ready for Our Close Up

Hubble Focus: Our Amazing Solar System showcases the wonders of our galactic neighborhood.
5. NASA’s First A

This book dives into the role aeronautics plays in our mission of engineering and exploration.
6. See More

Making the Invisible Visible outlines the rich history of infrared astronomy.
7. Ready for a Deeper Dive?

The NASA Systems Engineering Handbook describes how we get the job done.
8. Spoiler Alert

The space race really heats up in the third volume of famed Russian spacecraft designer Boris Chertok memoirs. Chertok, who worked under the legendary Sergey Korolev, continues his fascinating narrative on the early history of the Soviet space program, from 1961 to 1967 in Rockets and People III.
9. Take a Walk on the Wild Side

The second volume of Walking to Olympus explores the 21st century evolution of spacewalks.
10. No Library Card Needed
Find your own great read in NASA’s free e-book library.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.







LJS 433 is a 17th century Japanese illustrated treatise on the diagnosis of abscesses and tumors and their treatment. Most of the treatments involve acupuncture or burning different substances near the skin. This manuscript, titled Yoso Zusetsu, is made with paper and written in Chinese script.
When comparing the manuscripts that we’ve looked at this week, it’s interesting to note all of the differences - from the manner in which a body is depicted (size, shape, hair style, details) to the medium and script that is used for the manuscript. Even considering how medical practices differ from culture to culture forms many implications!
I highly recommend checking out other illustrated diagrams in the full digitized version of LJS 433 on Openn: http://openn.library.upenn.edu/Data/0001/html/ljs433.html
or Penn In Hand: http://hdl.library.upenn.edu/1017/d/medren/4827745
*This week, we were taking a look at manuscripts having to do with health, medicine, and human physiology specifically focusing on how bodies are displayed in manuscript illuminations or diagrams across different cultures.
I hope you enjoyed this segment!

How many did you know? All worth reading more about!!
11 New Facts Science Has Revealed About The Body
1. Hundreds of genes spring to life after you die - and they keep functioning for up to four days.
2. Livers grow by almost half during waking hours.
3. The root cause of eczema has finally been identified.
4. We were wrong - the testes are connected to the immune system after all.
5. The causes of hair loss and greying are linked, and for the first time, scientists have identified the cells responsible.
6. A brand new human organ has been classified - the mesentery - an organ that’s been hiding in plain sight in our digestive system this whole time.
7. An unexpected new lung function has been found - they also play a key role in blood production, with the ability to produce more than 10 million platelets (tiny blood cells) per hour.
8. Your appendix might actually be serving an important biological function- and one that our species isn’t ready to give up just yet.
9. The brain literally starts eating itself when it doesn’t get enough sleep. brain to clear a huge amount of neurons and synaptic connections away.
10. Neuroscientists have discovered a whole new role for the brain’s cerebellum - it could actually play a key role in shaping human behaviour.
11. Our gut bacteria are messing with us in ways we could never have imagined. Neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s might actually start out in the gut, rather than the brain, and there’s mounting evidence that the human microbiome could be to blame for chronic fatigue syndrome.


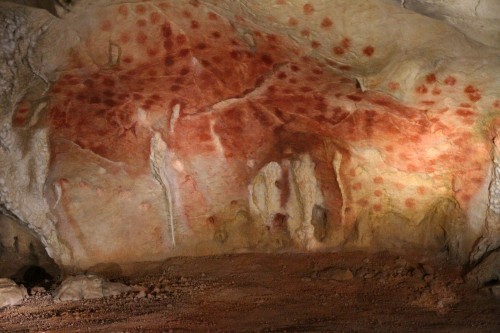



CHAUVET CAVE:
THE Chauvet Cave (also known as the Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc Cave) is a Palaeolithic cave situated near Vallon-Pont-d’Arc in the Ardèche region of southern France that houses impeccably preserved, exquisite examples of prehistoric art.
Now reliably dated to between c. 33,000 and c. 30,000 years ago, the numerous and diverse animals that dot the interior walls of the cave – both painted and engraved – show such high artistic quality that they were initially thought to have been closer in age to the similarly stunning, but much younger art in caves such as the Lascaux Cave. Its age and artistry have made us reconsider the story of art as well as the capabilities of these humans. The cave has been granted UNESCO World Heritage status.
Read More
Article by Emma Groeneveld on AHE

Researchers can identify you by your brain waves with 100 percent accuracy
Your responses to certain stimuli – foods, celebrities, words – might seem trivial, but they say a lot about you. In fact (with the proper clearance), these responses could gain you access into restricted areas of the Pentagon.
A team of researchers at Binghamton University, led by Assistant Professor of Psychology Sarah Laszlo and Assistant Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Zhanpeng Jin, recorded the brain activity of 50 people wearing an electroencephalogram headset while they looked at a series of 500 images designed specifically to elicit unique responses from person to person – e.g., a slice of pizza, a boat, Anne Hathaway, the word “conundrum.” They found that participants’ brains reacted differently to each image, enough that a computer system was able to identify each volunteer’s “brainprint” with 100 percent accuracy.
“When you take hundreds of these images, where every person is going to feel differently about each individual one, then you can be really accurate in identifying which person it was who looked at them just by their brain activity,” said Laszlo.
In their original study, titled “Brainprint,” published in 2015 in
Neurocomputing
, the research team was able to identify one person out of a group of 32 by that person’s responses, with only 97 percent accuracy, and that study only incorporated words, not images
Maria V. Ruiz-Blondet, Zhanpeng Jin, Sarah Laszlo. CEREBRE: A Novel Method for Very High Accuracy Event-Related Potential Biometric Identification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016; 11 (7): 1618 DOI: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2543524
Woman wearing an EEG headset.Credit: Jonathan Cohen/Binghamton University
-
 somegirlblr reblogged this · 3 years ago
somegirlblr reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 myrrhhymns reblogged this · 3 years ago
myrrhhymns reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 aubribubble liked this · 4 years ago
aubribubble liked this · 4 years ago -
 deus-phoenix reblogged this · 4 years ago
deus-phoenix reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 papier-blr reblogged this · 5 years ago
papier-blr reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 papier-blr liked this · 5 years ago
papier-blr liked this · 5 years ago -
 i-know-im-smart reblogged this · 5 years ago
i-know-im-smart reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 i-know-im-smart liked this · 5 years ago
i-know-im-smart liked this · 5 years ago -
 therealfallenangel liked this · 5 years ago
therealfallenangel liked this · 5 years ago -
 marmalade-studies liked this · 5 years ago
marmalade-studies liked this · 5 years ago -
 theinquisitivereceptacle liked this · 5 years ago
theinquisitivereceptacle liked this · 5 years ago -
 letsthathatgirluniverse reblogged this · 6 years ago
letsthathatgirluniverse reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 letsthathatgirluniverse liked this · 6 years ago
letsthathatgirluniverse liked this · 6 years ago -
 cristalblade reblogged this · 6 years ago
cristalblade reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 cristalblade liked this · 6 years ago
cristalblade liked this · 6 years ago -
 piratesangel liked this · 6 years ago
piratesangel liked this · 6 years ago -
 theirishgun liked this · 6 years ago
theirishgun liked this · 6 years ago -
 hamstria liked this · 6 years ago
hamstria liked this · 6 years ago -
 mildlytired-blog liked this · 6 years ago
mildlytired-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 sherif713 liked this · 6 years ago
sherif713 liked this · 6 years ago -
 raeonthearoace reblogged this · 6 years ago
raeonthearoace reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 raeonthearoace liked this · 6 years ago
raeonthearoace liked this · 6 years ago -
 gageblackwood reblogged this · 6 years ago
gageblackwood reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 amoebab liked this · 6 years ago
amoebab liked this · 6 years ago -
 boi-parts reblogged this · 6 years ago
boi-parts reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 willisnt liked this · 7 years ago
willisnt liked this · 7 years ago -
 mydinojustdied liked this · 7 years ago
mydinojustdied liked this · 7 years ago -
 eunillul liked this · 7 years ago
eunillul liked this · 7 years ago -
 approximately27ninjas liked this · 7 years ago
approximately27ninjas liked this · 7 years ago -
 not-racist-gurl liked this · 7 years ago
not-racist-gurl liked this · 7 years ago -
 autoxoiras liked this · 7 years ago
autoxoiras liked this · 7 years ago -
 th3g0dc0mp13x reblogged this · 7 years ago
th3g0dc0mp13x reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ineverland reblogged this · 7 years ago
ineverland reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 shittygeminibitch-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
shittygeminibitch-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 shittygeminibitch-blog liked this · 7 years ago
shittygeminibitch-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 howlittledidiknow reblogged this · 7 years ago
howlittledidiknow reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 robinhood199718 reblogged this · 7 years ago
robinhood199718 reblogged this · 7 years ago
A reblog of nerdy and quirky stuff that pique my interest.
291 posts
