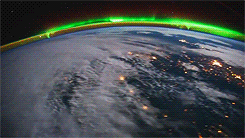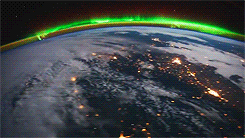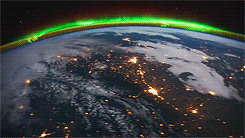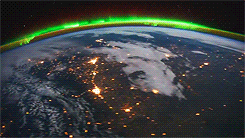
Galactic Poetry



Galactic Poetry
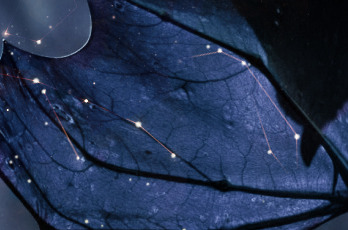
The downfall of living in an urban center, is that all we get to see during the night are blankets of cloud (possibly smog), and if we’re lucky, a few stars. What artist Sanjeev Sivarulrasa is trying to show in his work, Night Light, is what we are missing out on; a magical world, swimming through space, with galaxies and nebulae bejeweling the cosmos.
It is visual poetry.
The artist uses astrophotography to capture the various forms and colours of the stars and planets outside of an observatory setting. According to journalist Becky Rynor, it is as if he is capturing the great masterpieces that our ancestors would see; a natural art. Space does not have to be sacred scientific ground; it can also be merely another aesthetic aspect of our lives, that inspires people to think about the greater world around us. The simple observer plays as big of a role, as the great scientist. When this right to observe is taken away from us, via artificial city lights, we have to make the effort to go to the sources such as countryside’s, forests, lakes, and mountains. We must go to the nature, to connect back to ancient ideas of aesthetic beauty, and renew the senses. Sanjeev’s astrophotographs are to be seen as meditative, bringing awareness to our daily surroundings, and that sometimes, we need to take a step back, and see the bigger picture.
Night Light is currently exhibited at Karsh-Masson Gallery, until the 5th of May, 2013, and there will be an artist talk on the 24th of March, 2013 -Anna Paluch
More Posts from Outofambit and Others

"Eavesdropping on whale songs over the last six years is providing new information vital to answering questions about these giants of the ocean.
The number of whale songs detected is associated with shifting food sources, according to the California scientists—and the number of days humpbacks have been singing has nearly doubled.
When monitoring baleen whale songs in the Pacific Ocean, researchers found year-to-year variations correlated with changes in the availability of the species they forage on.
In vast oceans, monitoring populations of large marine animals can be a “major challenge” for ecologists, explained Dr. John Ryan, a biological oceanographer at the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute in California (MBARI).
Their team deployed underwater microphones called hydrophones to study and track baleen whales, which communicate over long distances through sound.
“Surprisingly, the acoustic behavior of baleen whales provides insights about which species can better adapt to changing ocean conditions,” said Dr. Ryan, a lead author of the study.
They also monitored songs from blue, fin, and humpback whales off the West Coast of the U.S. to see what the song data could reveal about the health of their ecosystem.
The findings, published in the journal PLOS One, showed “large” year-to-year variations in whale song detection.
“The amount of humpback whale song continually increased, with their songs being detected on 34% of days at the beginning of the study and rising to 76% of days after six years,” said Dr. Ryan.
“These increases consistently tracked improved foraging conditions for humpback whales across all study years—large increases in krill abundance, followed by large increases in anchovy abundance.
“In contrast, blue and fin whale song rose primarily during the years of increasing krill abundance.
“This distinction of humpback whales is consistent with their ability to switch between dominant prey. An analysis of skin biopsy samples confirmed that changes had occurred in the whales’ diets.”
He explained that other factors, including the local abundance of whales, may have contributed to patterns in song detections observed in some years, but changes in foraging conditions were the most consistent factor.
“Overall, the study indicates that seasonal and annual changes in the amount of baleen whale song detected may mirror shifts in the local food web.”
WHALES ON THE COMEBACK TRAIL: • Gray Whale, Extinct for Centuries in Atlantic, Is Spotted in Cape Cod • Sighting of Many Blue Whales Around Seychelles is First in Decades – ‘Phenomenal’ • Majestic Sei Whales Reappear in Argentine Waters After Nearly a Century
“The results suggest that an understanding of the relationship between whale song detection and food availability may help researchers to interpret future hydrophone data, both for scientific research and whale management efforts”, which could better protect endangered species."
-via Good News Network, March 1, 2025

Finally! A black hole that you can visit and survive!
Want a trip through a black hole without having to experience that pesky death? You’re in luck. There’s a special kind of black hole that’s not just survivable, but might get you to another time, or another universe.
Black holes are, traditionally, the scariest things in the universe. Huge, mysterious, inescapable, they wander through the universe and eat everything that gets too close. “Too close” is defined by their event horizon. This is the point at which they go dark, because it requires so much energy to escape them that not even light can get away. Since not even a photon can cross the barrier, no event that happens inside the horizon can ever have an effect on people outside.
Unless, something very odd was going on in the center of the black hole. Most black holes spin - this is something that was discovered way back in the 1960s by physicist Roy Kerr. It wasn’t exactly a shock, because most of the material that collapses into a black hole was already spinning. Sometimes, however, the spin on Kerr black holes goes a little above and beyond. Ever spun a glass of water, or soda bottle, so that the liquid inside swirls? Sometimes, if you spin it enough, the liquid actually parts, leaving a clear center and a spinning ring of water around it. The same kind of thing can happen in Kerr black holes. Instead of a singularity at the center, there’s a ring. And you can go through the open portion of that ring without touching the gravitational crush.
What’s on the other side? A lot of people have wondered. Some people think that these kind of black holes might be our key to time travel. They might be wormholes that let us hop between different points of the universe. Or they might be portals to different universes entirely. First we’ll have to find a few, and then we’ll need a few volunteers to go through. Preferably ones that haven’t seen Event Horizon.
Top Image: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Second Image: Dana Berry/NASA
Via NASA, Astrophysics Spectator, Discovery.
theres a giant burning orb in the sky and it can burn your flesh, it can give you diseases, it can kill you, looking directly at it causes physical pain, and we all think this is okay. we like this orb. we like to go outside and lie around on our backs when this orb is in the sky. children draw cute pictures of this levitating death orb with a smiley face on it. what is wrong with us
Rebloggable-d by request: Names in the Speech
So this may be an odd question, and not one you’ve thought about much — but how would the Speech interact with someone who uses/identifies as a different name than their birth/legal name? I don’t mean like Kit — presumably his name in the Speech would include a phrase along the lines of ‘Christopher, called Kit’ — but a case where the birth name has been ‘rejected’, and isn’t part of the wizard’s identity at all.
intheafterlight
Fuck It, Let's Talk About Wizards
I currently view this blog as a way for me to rant about math and stories without anyone being forced to be my audience. So let’s get on with it!
I am going to rant about my all-time favorite book series: The Young Wizards Series by Diane Duane.
SHUT UP. I know what you are thinking, imaginary reader, and YOU ARE WRONG. This is totally not a Harry Potter knockoff. The series was actually started way before Harry Potter. But to assuage your worries, I will list all the things this series has in common with Harry Potter:
It’s about people between the ages of 11 and 17.
Said people have some sort of supernatural powers that could be deemed ‘magical.’
That’s it. That’s the only ways they’re similar.
Weirdly enough, Young Wizards actually has way more in common with Doctor Who than Harry Potter. Even though it’s basically fantasy, the stories feel much more like science fiction.
All right, let’s get on with this. I know what you’re thinking, because I can read the minds of all my imaginary readers.
SO WHAT IS IT ALL ABOUT ANYWAYS?
Basically, magic is real. It’s given out by “The Powers That Be,” basically the gods, to a bunch of people around the Universe. So that they can fight “The Lone Power,” who is basically Satan.
Yes, Satan. Voldemort doesn’t seem so scary now, does he?
Our protagonists, Kit and Nita, are kids that are both chosen for this. “Chosen” actually makes it sound a lot more organized than it really is. Basically, you find a book that tells you how to do magic and what it’s supposed to be used for. If you take the Wizard’s Oath, you now have magical powers. And as a sort of “welcome to the magical powers club” gift, you now have to immediately go fight Satan in a terrifying Ordeal. It’s fucking awesome.
So the first book, So You Want to be a Wizard, chronicles this Ordeal. After that, things get a bit more varied. The protagonists mainly just travel around the Universe, going on dangerous missions, and fighting Satan.
Yes, the Universe. Being basically the warriors of the gods, they are not confined to Earth. This is a fantasy book with aliens in it. Awesome aliens. Some of them are bad, some of them are good, some of them are also wizards. This is, in short, the books you have been waiting for: the books where MAGIC KIDS AND ALSO MAGIC ALIENS FIGHT SATAN oh shit that sounds kind of like Homestuck.
The reason these books are my favorites of all time is because they never get old. Most kids’ books are awesome as a kid and kind of lame as an adult. I have loved these no matter how old I am. I loved them in elementary school and I still do now, in college. And not nostalgic love either, where I just like them because I used to. They’re still exactly as good.
It’s not even in the Harry Potter ‘they grow up with you’ way. Like, when you read The Philosopher’s Stone now, it’s not as good as it was when you were a kid. The first couple Young Wizards books are slightly more childish than the others. Slightly. The series starts off fairly dark and stays that way. Shit gets real. People die. Sacrifices are made. Difficult moral questions are confronted.
One of my favorite parts of this setup is that it’s still our universe. The kids have to hide their powers from the world at large and still show up to school and do normal kid stuff. They have to cope with all that crap while constantly risking their lives to fight evil. And the magic isn’t easy either.
All right, this rant is getting kind of ridiculously long, so I’ll leave you with one last comment. This is the kind of series where you are constantly fistpumping and yelling “HOLY SHIT” (and terrifying the people around you) because crazy awesome stuff goes down a lot.
Here is the list of the books so far, in case you want to read them (you should):
So You Want to be a Wizard (Kids get powers, go on their ordeal)
Deep Wizardry (There’s no way I can describe this without it sounding stupid, but it’s awesome, trust me)
High Wizardry (One of the ones where a lot of crazy awesome shit goes down)
A Wizard Abroad
A Wizard’s Dilemma
A Wizard Alone
Wizard’s Holiday
Wizards at War (HOLY SHIT GUYS THIS ONE IS AWESOME)
A Wizard of Mars

Kepler-62 Has Two Water Worlds Circling in its Habitable Zone
NASA’s Kepler spacecraft has discovered two planets that are the most similar in size to Earth ever found in a star’s habitable zone — the temperate region where water could exist as a liquid.
The finding, reported online today in Science1, demonstrates that Kepler is closing in on its goal of finding a true twin of Earth beyond the Solar System, says theorist Dimitar Sasselov of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts, who is a member of the Kepler discovery team.
Both planets orbit the star Kepler-62, which is about two-thirds the size of the Sun and lies about 1,200 light years (368 parsecs) from the Solar System. The outermost planet from the star, Kepler-62f, has a diameter that is 41% larger than Earth’s and takes 267 days to circle its star. The inner planet, Kepler-62e, has a diameter 61% larger than Earth’s and a shorter orbit of 122 days.
Kepler detected the planets by recording the tiny decrease in starlight that occurs when either of them passes in front of their parent star. Astronomers used those measurements to calculate the planets’ relative size compared to that star.
Continue: Worlds Apart









-
 vaderslocker liked this · 10 years ago
vaderslocker liked this · 10 years ago -
 parental-bear liked this · 10 years ago
parental-bear liked this · 10 years ago -
 teetasse-love-blog liked this · 10 years ago
teetasse-love-blog liked this · 10 years ago -
 a-not-an-e liked this · 10 years ago
a-not-an-e liked this · 10 years ago -
 givememypants reblogged this · 10 years ago
givememypants reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 theartmatrix liked this · 10 years ago
theartmatrix liked this · 10 years ago -
 mandyposey reblogged this · 10 years ago
mandyposey reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 purest-stone reblogged this · 10 years ago
purest-stone reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 infinitehostofheaven reblogged this · 10 years ago
infinitehostofheaven reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 waterfalls-in-space liked this · 10 years ago
waterfalls-in-space liked this · 10 years ago -
 junkyard-gd reblogged this · 10 years ago
junkyard-gd reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 insearchofperfectionn reblogged this · 10 years ago
insearchofperfectionn reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 xcyberdaemon liked this · 10 years ago
xcyberdaemon liked this · 10 years ago -
 godsbasement-blog reblogged this · 10 years ago
godsbasement-blog reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 ivory-rainbow-blog liked this · 10 years ago
ivory-rainbow-blog liked this · 10 years ago -
 jalensaxon liked this · 10 years ago
jalensaxon liked this · 10 years ago -
 the-best-of-space-blog reblogged this · 10 years ago
the-best-of-space-blog reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 kabosha liked this · 10 years ago
kabosha liked this · 10 years ago -
 mymindbetraysme liked this · 10 years ago
mymindbetraysme liked this · 10 years ago -
 mymindbetraysme reblogged this · 10 years ago
mymindbetraysme reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 tomkewin reblogged this · 10 years ago
tomkewin reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 tomkewin liked this · 10 years ago
tomkewin liked this · 10 years ago -
 blog-neko liked this · 10 years ago
blog-neko liked this · 10 years ago -
 imtheswordinthedarkness reblogged this · 10 years ago
imtheswordinthedarkness reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 tyushokigyotushin liked this · 10 years ago
tyushokigyotushin liked this · 10 years ago -
 likebrads liked this · 11 years ago
likebrads liked this · 11 years ago -
 shesyah reblogged this · 11 years ago
shesyah reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 ohmyihaveablog reblogged this · 11 years ago
ohmyihaveablog reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 justsickit reblogged this · 11 years ago
justsickit reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 joshwathecreated reblogged this · 11 years ago
joshwathecreated reblogged this · 11 years ago -
 immortalvivian liked this · 11 years ago
immortalvivian liked this · 11 years ago -
 alekskya liked this · 12 years ago
alekskya liked this · 12 years ago -
 daydreams-and-wishes reblogged this · 12 years ago
daydreams-and-wishes reblogged this · 12 years ago -
 nicotine101 liked this · 12 years ago
nicotine101 liked this · 12 years ago -
 nicotine101 reblogged this · 12 years ago
nicotine101 reblogged this · 12 years ago -
 distant-station reblogged this · 12 years ago
distant-station reblogged this · 12 years ago -
 distant-station liked this · 12 years ago
distant-station liked this · 12 years ago
A personal temporospatial claudication for Young Wizards fandom-related posts and general space nonsense.
288 posts