Celebrate #BlackHoleFriday With Nurturing Baby Stars
Celebrate #BlackHoleFriday with Nurturing Baby Stars

Are you throwing all your money into a black hole today?
Forget Black Friday — celebrate #BlackHoleFriday with us and get sucked into this recent discovery of a black hole that may have sparked star births across multiple galaxies.
If confirmed, this discovery would represent the widest reach ever seen for a black hole acting as a stellar kick-starter — enhancing star formation more than one million light-years away. (One light year is equal to 6 trillion miles.)
A black hole is an extremely dense object from which no light can escape. The black hole's immense gravity pulls in surrounding gas and dust. Sometimes, black holes hinder star birth. Sometimes — like perhaps in this case — they increase star birth.
Telescopes like our Chandra X-ray Observatory help us detect the X-rays produced by hot gas swirling around the black hole. Have more questions about black holes? Click here to learn more.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Cool Space GIFs from the Internet
There’s a lot of historical and archived space footage on the internet and we’re excited to see that the public (you!) have taken it to create many other products that teach people about exploration, space and our universe. Among those products are GIFs. Those quick videos that help you express what you’re trying to say via text, or make you laugh while surfing the web.
Are space GIFs the new cat videos of the internet? Don’t know, but we sure do like them!
Here are a few neat space GIFs from the internet…
This GIF of the Cat Eye Nebula shows it in various wavelengths…

Followed by a GIF of a cat in space…floating in front of the Antennae galaxies...

One time, a frog actually photobombed the launch of our LADEE spacecraft…someone on the internet gave him a parachute…

Want to see what it’s like to play soccer in space? There’s a GIF for that…

There are also some beautiful GIFs looking through the Cupola window on the International Space Station…


This warped footage from the International Space Station gives us ride around the Earth…

While this one encourages us to explore the unknown...

When our New Horizons spacecraft flew by dwarf planet Pluto in 2015, the internet couldn’t get enough of the Pluto GIFs...

NASA GIFs

Want to dive into a black hole of other fun space GIFs? Check out our GIPHY page HERE.
Want to use our GIFs?! You can! Our GIFs are accessible directly from the Twitter app. Just tap or click the GIF button in the Twitter tool bar, search for NASAGIF, and all NASA GIFs will appear for sharing and tweeting. Enjoy!
GIF Sources
Cat Eye GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/astronomy-cZpDWjSlKjWPm Cat GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/cat-HopYL0SamcCli Frog GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/nasa-photo-rocket-NOsCSDT2rUgfK Soccer GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/yahoo-astronauts-zerogravity-QF1ZomA11zofC Cupola 1 GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/nasa-Mcoxp6TgvQm6A Cupola 2 GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/timelapse-space-11f3o8D2rQWzCM Earth GIF: http://giphy.com/gifs/earth-milky-way-international-space-station-ONC6WgECm5KEw Explore GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/text-timelapse-lapse-Vj7gwAvhgsDYs Pluto 1 GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/l46CzjUnYFfeMXiNO Pluto 2 GIF: https://giphy.com/gifs/pluto-dbV1LkFWWob84
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
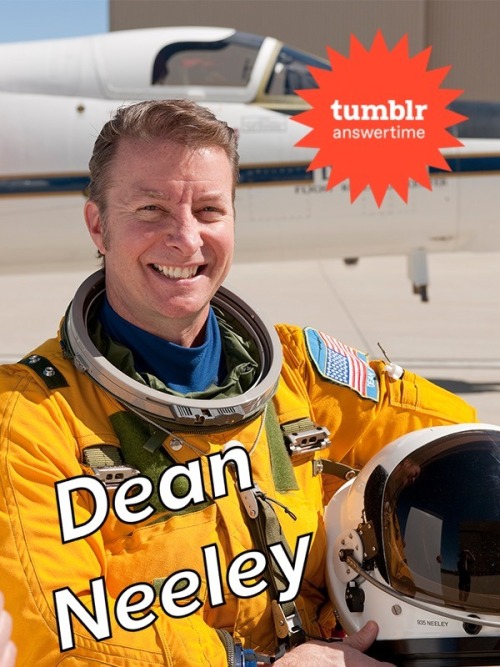

Wonder what it’s like to fly for NASA Earth science expeditions? Ask our research pilot anything!
This January, we’re kicking off five new airborne Earth science expeditions aimed at studying our home planet from the land, sea and air. Here’s your chance to hear what it’s like from the cockpit!
Research pilot Dean “Gucci” Neeley will be taking your questions in an Answer Time session on Friday, January 10 from 12-1pm ET here on NASA’s Tumblr! Find out what it’s like to fly research aircraft that use the vantage point of space to increase our understanding of Earth, improve lives and safeguard our future! Make sure to ask your question now by visiting http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Dean Neeley, retired U.S. Air Force officer and pilot, joined our Armstrong Flight Research Center in 2012 as a research pilot. Neeley flies a diverse array of highly modified airborne science, research and mission support aircraft such as the single-seat Lockheed ER-2 high-altitude science jet. The ER-2 collects information about Earth resources, celestial observations, atmospheric chemistry and dynamics and oceanic processes. Neeley has also flown the Gulfstream G-II mission support aircraft, which explores environmentally friendly aircraft concepts, the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), which observes the solar system and beyond at mid- and far-infrared wavelengths, and the C-20A (G-III) science platform aircraft, which carries our Jet Propulsion Laboratory's synthetic aperture radar.
Dean Neeley Fun Facts
Dean’s call sign Gucci came from flying KC-10 “Gucci Boys” before being hired to fly U-2 aircraft. Some say he spends too much time/money on his hair, clothes, cars. 😂
He played drums in two rock bands in the 80s and 90s; Agent Orange and the Defoliants; The Mod Sky Gods.
He spent his years in the Air Force as a reconnaissance squadron commander, wing chief of safety, stealth fighter squadron director and bomber in multiple worldwide aerial combat campaigns.
Dean holds a Bachelor of Science in Aerospace Engineering and a Master of Aeronautical Science degree.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What has been the best memory you have so far at NASA?

Launch Your Creativity with Space Crafts!
In honor of the completion of our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s spacecraft — the vehicle that will maneuver the observatory to its place in space and enable it to function once there — we’re bringing you a space craft you can complete at home! Join us for a journey across the cosmos, starting right in your own pantry.
Stardust Slime
Ingredients:
1 5 oz. bottle clear glue
½ tablespoon baking soda
Food coloring
1 tablespoon contact lens solution
1 tablespoon glitter
Directions:
Pour the glue into a bowl.
Mix in the baking soda.
Add food coloring (we recommend blue, purple, black, or a combination).
Add contact lens solution and use your hands to work it through the slime. It will initially be very sticky! You can add a little extra contact lens solution to make it firmer and less goopy.
Add glitter a teaspoon at a time, using as much or as little as you like!
Did you know that most of your household ingredients are made of stardust? And so are you! Nearly every naturally occurring element was forged by living or dying stars.
Take the baking soda in this slime recipe, for example. It’s made up of sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. The hydrogen was made during the big bang, right at the start of the universe. But the other three elements were created by dying stars. So when you show your friends your space-y slime, you can tell them it’s literally made of stardust!
Still feeling crafty? Try your hand at more pantry projects or these 3D and paper spacecraft models. If you’re eager for a more advanced space craft, check out these embroidery creations for inspiration! Or if you’re ready for a break, take a virtual tour of an interactive version of the Roman Space Telescope here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!


Tumblr, this is Houston speaking! The flight directors Answer Time with Chloe Mehring and Diane Dailey is live. Stay tuned to learn about what happens in mission control, how to become a flight director, and what Hollywood sometimes gets wrong about the job. View ALL the answers HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Science-Heavy SpaceX Dragon Headed to Space Station
Heads up: a new batch of science is headed to the International Space Station aboard the SpaceX Dragon on April 2, 2018. Launching from Florida's Cape Canaveral Air Force Station atop a Falcon 9 rocket, this fire breathing (well, kinda…) spacecraft will deliver science that studies thunderstorms on Earth, space gardening, potential pathogens in space, new ways to patch up wounds and more.

Let's break down some of that super cool science heading 250 miles above Earth to the orbiting laboratory:
Sprites and Elves in Space
Atmosphere-Space Interactions Monitor (ASIM) experiment will survey severe thunderstorms in Earth's atmosphere and upper-atmospheric lightning, or transient luminous events.

These include sprites, flashes caused by electrical break-down in the mesosphere; the blue jet, a discharge from cloud tops upward into the stratosphere; and ELVES, concentric rings of emissions caused by an electromagnetic pulse in the ionosphere.
Here's a graphic showing the layers of the atmosphere for reference:

Metal Powder Fabrication
Our Sample Cartridge Assembly (MSL SCA-GEDS-German) experiment will determine underlying scientific principles for a fabrication process known as liquid phase sintering, in microgravity and Earth-gravity conditions.

Science term of the day: Liquid phase sintering works like building a sandcastle with just-wet-enough sand; heating a powder forms interparticle bonds and formation of a liquid phase accelerates this solidification, creating a rigid structure. But in microgravity, settling of powder grains does not occur and larger pores form, creating more porous and distorted samples than Earth-based sintering.
Sintering has many applications on Earth, including metal cutting tools, automotive engine connecting rods, and self-lubricating bearings. It has potential as a way to perform in-space fabrication and repair, such as building structures on the moon or creating replacement parts during extraterrestrial exploration.
Plants in space! It's l[a]unch time!
Understanding how plants respond to microgravity and demonstrating reliable vegetable production in space represent important steps toward the goal of growing food for future long-duration missions. The Veggie Passive Orbital Nutrient Delivery System (Veggie PONDS) experiment will test a passive nutrient delivery system in the station's Veggie plant growth facility by cultivating lettuce and mizuna greens for harvest and consumption on orbit.
The PONDS design features low mass and low maintenance, requires no additional energy, and interfaces with the Veggie hardware, accommodating a variety of plant types and growth media.

Quick Science Tip: Download the Plant Growth App to grow your own veggies in space! Apple users can download the app HERE! Android users click HERE!
Testing Materials in Space
The Materials ISS Experiment Flight Facility (MISSE-FF) experiment will provide a unique platform for testing how materials, coatings and components react in the harsh environment of space.

A continuation of a previous experiment, this version's new design eliminates the need for astronauts to perform spacewalks for these investigations. New technology includes power and data collection options and the ability to take pictures of each sample on a monthly basis, or more often if required. The testing benefits a variety of industries, including automotive, aeronautics, energy, space, and transportation.
New Ways to Develop Drugs in Space

Microgravity affects movement and effectiveness of drugs in unique ways. Microgravity studies already have resulted in innovative medicines to treat cancer, for example. The Metabolic Tracking investigation determines the possibility of developing improved drugs in microgravity, using a new method to test the metabolic impacts of drug compounds. This could lead to more effective, less expensive drugs.
Follow @ISS_Research on Twitter for your daily dose of nerdy, spacey goodness.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
I’m sure you’re trained so that nothing in space is really a surprise, but: was there anything about spacewalking that surprised you when you did it for the first time?
What’s Enceladus?
Before we tell you about Enceladus, let’s first talk about our Cassini spacecraft…
Our Cassini mission to Saturn is one of the most ambitious efforts in planetary space exploration ever mounted. Cassini is a sophisticated robotic spacecraft orbiting the ringed planet and studying the Saturnian system in detail.

Cassini completed its initial four-year mission to explore the Saturn System in June 2008. It has also completed its first mission extension in September 2010. Now, the health spacecraft is making exciting new discoveries in a second extension mission!
Enceladus

Enceladus is one of Saturn’s many moons, and is one of the brightest objects in our solar system. This moon is about as wide as Arizona, and displays at least five different types of terrain. The surface is believed to be geologically “young”, possibly less than 100 million years old.
Cassini first discovered continually-erupting fountains of icy material on Enceladus in 2005. Since then, the Saturn moon has become one of the most promising places in the solar system to search for present-day habitable environments.

Scientists found that hydrothermal activity may be occurring on the seafloor of the moon’s underground ocean. In September, it was announced that its ocean –previously thought to only be a regional sea – was global!
Since Cassini is nearing the end of its mission, we are able to make a series of three close encounters with Enceladus, one of Saturn’s moons.
Close Encounters
On Oct. 14, Cassini performed a mid-range flyby of Enceladus, but the main event will take place on Oct. 28, when Cassini will come dizzyingly close to the icy moon. During this flyby, the spacecraft will pass a mere 30 miles above the moon’s south polar region!

This will be the deepest-ever dive through the moon’s plume of icy spray, where Cassini can collect images and valuable data about what’s going on beneath the frozen surface.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Astronaut Journal Entry - The Last Week
Currently, six humans are living and working on the International Space Station, which orbits 250 miles above our planet at 17,500mph. Below you will find a real journal entry, written in space, by NASA astronaut Scott Tingle.
To read more entires from this series, visit our Space Blogs on Tumblr.

I can’t believe that Expedition 55 is already over. Today is Sunday, and we will depart the International Space Station (ISS) next Sunday morning (June 3).
168 days in space.
There have been many challenging moments, but even more positive highlights of our time on ISS. The new crew from the Soyuz MS-08 spacecraft (Oleg Artymyev, Drew Feustel and Ricky Arnold) joined Norishige Kanai (Nemo), Anton Shkaplerov and I last March. Since then, we have completed two spacewalks, captured and released the SpaceX Dragon-14 cargo craft, captured the Cygnus OA-9 cargo craft and completed a myriad of maintenance and science activities.

The team on the ground controlling, monitoring, supporting and planning has been amazing. It is always great to work with them, and especially during the moments where the equipment, tools, procedures or crew need help. It is incredible to see how much a good team can accomplish when methodically placing one foot in front of the other.
I have been lucky in that the first crew (Mark Vande Hei, Joe Acaba and Alexander Misurkin (Sasha)) and the second crew (Drew, Ricky and Oleg) were all amazing to work with. I do believe the planets aligned for my mission onboard ISS.

Drew and Ricky have been friends forever, and listening to them nip at each other provided a ton of great humor for the ground and for us. Their one-liners to each other reminded me of several scenes from the movie Space Cowboys.
This a great example that happened as I was writing this log entry:
Ricky: Hey Maker, is this your smoothie?
Maker: No.
Ricky: It must be Drew’s.
Drew: Hey Ricky, don’t drink my smoothie.
Ricky: What smoothie? This one has my name on it (as he writes his name on it).
Drew: Okay, Grandpa Underpants, hands off my smoothie.
Ricky: Okay, Feustelnaut – we have rules around here, so this is my smoothie now!
All: Much laughing. (To quote my kids: “LOL!”)
One the hardest things to do in space is to maintain positive control of individual items such as tools, spare parts, fasteners, etc. We try very hard not to lose things, but even with all of the attention and positive control, items can still float away and disappear.
We generally hold items in a crew transfer bag (CTB). Inside the CTB are many items for the system that it supports. When the CTB is opened, the items are free floating inside the bag and tend to escape. It is very difficult to maintain control of the items – especially if they are small, do not have Velcro, or when the daily schedule is so tight that we are rushing to stay on time. We always try to close the CTB’s and Ziploc bags after removing or replacing each item to maintain positive control, but this takes much more time to do for individual items, and if the timeline is tight, we absorb more risk by rushing.

The same applies for tools, which we usually keep in a Ziploc bag while working on individual systems and tasks. Last month, I was installing a new low temperature cooling loop pump that had failed a month or two earlier. I gathered the needed tools into my modified (with Velcro) Ziploc bag as I always do and floated over to the work area. When I got there, one of the tools that I had gathered was missing. I looked for 30 minutes, and could not find it. Lost items are very hard to find because the items that escape are usually barely moving and blend in with the environment very quickly. A lost item could be right in front of us and we would never see it.

Our crew, after learning these lessons, decided that when anyone loses something, we would tell the other crew members what we had lost with a general location. This has had a huge impact on finding items. If a different crew member can help within the first minutes of losing an item, the new crew member has an excellent chance of finding the item. We have proven this technique several times during the expedition – and Nemo was the very best at quickly finding lost items. But, in my case, we still could not find the missing tool. Our amazing ground team understood and vectored me to a replacement tool and I finished the job. I spent the next 3 weeks watching, looking and never forgetting about the lost tool. Then, one day last week, Oleg came to the lab and handed us a tool he had found in his Soyuz spacecraft, way on the aft side of the ISS. Amazing. We finally found the tool and I was happy again. This was a lucky ending. ISS has many corners, crevices and hard-to-see areas where missing items could hide and never be found.

We captured a Cygnus cargo craft last Thursday. I was very impressed with the entire team. Our specialists and training professionals in Mission Control did a great job preparing the necessary procedures and making sure we were proficient and ready to conduct operations. The robotic arm is a wonderful system that we could not operate ISS without. Being in space, however, it has some very unique handling qualities. If you think about a spring-mass-damper system just as you did during physics or control theory class, and then remove the damper, you will see a system that is very subject to slow rate oscillations.
In test pilot terms, damping ratio is very low and the latency is well over a half of a second. Also in test pilot terms – this is a pilot-induced oscillations (PIO) generator. These characteristics require crew to “fly” the robotic arm using open-loop techniques, which requires a huge amount of patience. Test pilots are sometimes not very patient, but understanding the system and practicing with the incredible simulators that our ground team built and maintain help keep our proficiency as high as possible. The capture went flawlessly, and I was very impressed with the professionalism across the board – crew, flight controllers and training professionals – what a great job!

Drew, Ricky and I got to play guitar a few times while on ISS. This was fun! Drew connected pickups to the acoustic guitars and then connected the pickups to our tablets for amplification. I’ve never heard an acoustic guitar sound like an electric guitar amped up for heavy metal before. We had a great jam on the song “Gloria”, and a couple others. Rock on!
Last night we had our last movie night. The entire crew gathered in Node 2 and watched Avengers Infinity Wars on the big screen. We enjoy each other’s company, as we did during Expedition 54, and this was a welcome break from the daily grind of trying to complete the required stowage, maintenance and science activities while preparing for departure.
Our last full weekend here on ISS. I gave myself a haircut. We usually clean our spaces each weekend to make sure we can maintain a decent level of organization, efficiency and morale. This weekend is no different, and it is time for me to vacuum out all of our filters and vents. You’d be amazed at what we find!
The top 5 things I will miss when I am no longer in space:
The incredible team that supports ISS operations from our control centers
The camaraderie onboard ISS
The breathtaking view of the Earth, Moon, Sun and Stars
Floating/flying from location to location with very little effort
Operations in the extreme environment of space
Find more ‘Captain’s Log’ entries HERE.
Follow NASA astronaut Scott Tingle on Instagram and Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Everything You Need to Know About the Aug. 21 Eclipse
On Aug. 21, all of North America will experience a solar eclipse.

If skies are clear, eclipse-watchers will be able to see a partial solar eclipse over several hours, and some people – within the narrow path of totality – will see a total solar eclipse for a few moments.
How to Watch
It’s never safe to look at the Sun, and an eclipse is no exception. During a partial eclipse (or on any regular day) you must use special solar filters or an indirect viewing method to watch the Sun.

If you have solar viewing glasses, check to make sure they’re safe and undamaged before using them to look at the Sun. Make sure you put them on before looking up at the Sun, and look away before removing them. Eclipse glasses can be used over your regular eyeglasses, but they should never be used when looking through telescopes, binoculars, camera viewfinders, or any other optical device.
If you don’t have eclipse glasses, you can still watch the eclipse indirectly! You can make a pinhole projector out of a box, or use any other object with tiny holes – like a piece of cardstock with a hole, or your outstretched, interlaced fingers – to project an image of the partially eclipsed Sun onto the ground.

Of course, if it’s cloudy (or you’d just rather stay inside), you can watch the whole thing online with us at nasa.gov/eclipselive. Tune in starting at noon ET.
If you’re in the path of totality, there will be a few brief moments when it is safe to look directly at the eclipse. Only once the Moon has completely covered the Sun and there is no light shining through is it safe to look at the eclipse. Make sure you put your eclipse glasses back on or return to indirect viewing before the first flash of sunlight appears around the Moon’s edge.

Why do eclipses happen?
A solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth, casting its shadow down on Earth’s surface. The path of totality – where the Moon completely covers the Sun – is traced out by the Moon’s inner shadow, the umbra. People within the Moon’s outer shadow, the penumbra, can see a partial eclipse.

The Moon’s orbit around Earth is tilted by about five degrees, meaning that its shadow usually doesn’t fall on Earth. Only when the Moon lines up exactly between the Sun and Earth do we see an eclipse.

Though the Sun is about 400 times wider than the Moon, it is also about 400 times farther away, making their apparent sizes match up almost exactly. This is what allows the Moon to block out the Sun’s bright face, while revealing the comparatively faint, pearly-white corona.
The Science of Eclipses
Eclipses are a beautiful sight to see, and they’re also helpful for our scientists, so we’re funding eleven ground-based science investigations to learn more about the Sun and Earth.

Total solar eclipses reveal the innermost regions of the Sun’s atmosphere, the corona. Though it’s thought to house the processes that kick-start much of the space weather that can influence Earth, as well as heating the whole corona to extraordinarily high temperatures, we can’t study this region at any other time. This is because coronagraphs – the instruments we use to study the Sun’s atmosphere by creating artificial eclipses – must cover up much of the corona, as well as the Sun’s face in order to produce clear images.

Eclipses also give us the chance to study Earth’s atmosphere under uncommon conditions: the sudden loss of solar radiation from within the Moon’s shadow. We’ll be studying the responses of both Earth’s ionosphere – the region of charged particles in the upper atmosphere – and the lower atmosphere.
Learn all about the Aug. 21 eclipse at eclipse2017.nasa.gov, and follow @NASASun on Twitter and NASA Sun Science on Facebook for more. Watch the eclipse through the eyes of NASA at nasa.gov/eclipselive starting at 12 PM ET on Aug. 21.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 filnetwdedoctloc liked this · 1 year ago
filnetwdedoctloc liked this · 1 year ago -
 vexalia liked this · 2 years ago
vexalia liked this · 2 years ago -
 spaceman-of-space reblogged this · 3 years ago
spaceman-of-space reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 sociallyawkwardbirb liked this · 4 years ago
sociallyawkwardbirb liked this · 4 years ago -
 primordialbitch reblogged this · 5 years ago
primordialbitch reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 adiposeclot liked this · 5 years ago
adiposeclot liked this · 5 years ago -
 brickonthemoon liked this · 5 years ago
brickonthemoon liked this · 5 years ago -
 notcouchtato2398 liked this · 5 years ago
notcouchtato2398 liked this · 5 years ago -
 cherryobvious liked this · 5 years ago
cherryobvious liked this · 5 years ago -
 ad-astra-per-aspera-80 reblogged this · 5 years ago
ad-astra-per-aspera-80 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 216-11 liked this · 5 years ago
216-11 liked this · 5 years ago -
 spaciegracie07 liked this · 5 years ago
spaciegracie07 liked this · 5 years ago -
 lotusroyals liked this · 5 years ago
lotusroyals liked this · 5 years ago -
 roogranger liked this · 5 years ago
roogranger liked this · 5 years ago -
 avaant-gaarde liked this · 5 years ago
avaant-gaarde liked this · 5 years ago -
 interdimensionalfractal liked this · 5 years ago
interdimensionalfractal liked this · 5 years ago -
 themostpowerfulmutant liked this · 5 years ago
themostpowerfulmutant liked this · 5 years ago -
 miguelvicentevidal liked this · 5 years ago
miguelvicentevidal liked this · 5 years ago -
 myrathepeach liked this · 5 years ago
myrathepeach liked this · 5 years ago -
 unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago
unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago -
 tenebrobscuro reblogged this · 5 years ago
tenebrobscuro reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 tenebrobscuro liked this · 5 years ago
tenebrobscuro liked this · 5 years ago -
 jungkookstigerlily liked this · 5 years ago
jungkookstigerlily liked this · 5 years ago -
 steadyfisheclipsepaper liked this · 5 years ago
steadyfisheclipsepaper liked this · 5 years ago -
 greatzoologyaestheticartisan liked this · 5 years ago
greatzoologyaestheticartisan liked this · 5 years ago -
 cmonboard liked this · 5 years ago
cmonboard liked this · 5 years ago -
 chickenscratch42 liked this · 5 years ago
chickenscratch42 liked this · 5 years ago -
 draco-sarcastic liked this · 5 years ago
draco-sarcastic liked this · 5 years ago -
 lovingherwasgay liked this · 5 years ago
lovingherwasgay liked this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts