Source

source
More Posts from Misscounterfactual and Others







BMW iX Flow featuring E Ink !
With the BMW iX Flow featuring E Ink being presented on the occasion of CES 2022, the Munich-based premium car manufacturer is offering the prospect of a future technology that uses digitisation to adapt the exterior of a vehicle to different situations and individual wishes. The surface of the BMW iX Flow featuring E Ink can vary its shade at the driver’s prompting.

Moonbound: One Year Since Artemis I
On this day last year, the Artemis I rocket and spacecraft lit up the sky and embarked on the revolutionary mission to the Moon and back. The first integrated flight test of the rocket and spacecraft continued for 25.5 days, validating NASA’s deep exploration systems and setting the stage for humanity’s return to the lunar surface.

On Nov. 16, 2022, the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket met or exceeded all expectations during its debut launch on Artemis I. The twin solid rocket booster motors responsible for producing more than 7 million pounds of thrust at liftoff reached their performance target, helping SLS and the Orion spacecraft reach a speed of about 4,000 mph in just over two minutes before the boosters separated.

Quite a few payloads caught a ride aboard the Orion spacecraft on the Artemis I mission: In addition to a number of small scientific satellites called CubeSats, a manikin named Commander Moonikin Campos sat in the commander’s seat. A Snoopy doll served as a zero-gravity indicator — something that floats inside the spacecraft to demonstrate microgravity.

During the mission, Orion performed two lunar flybys, coming within 80 miles of the lunar surface. At its farthest distance during the mission, Orion traveled nearly 270,000 miles from our home planet, more than 1,000 times farther than where the International Space Station orbits Earth. This surpassed the record for distance traveled by a spacecraft designed to carry humans, previously set during Apollo 13.

The Orion spacecraft arrived back home to planet Earth on Dec. 11, 2022. During re-entry, Orion endured temperatures about half as hot as the surface of the Sun at about 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Within about 20 minutes, Orion slowed from nearly 25,000 mph to about 20 mph for its parachute-assisted splashdown.

Recovery teams successfully retrieved the spacecraft and delivered it back to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center for de-servicing operations, which included removing the payloads (like Snoopy and Commander Moonikin Campos) and analyzing the heat shield.

With the Artemis I mission under our belt, we look ahead to Artemis II — our first crewed mission to the Moon in over 50 years. Four astronauts will fly around the Moon inside Orion, practicing piloting the spacecraft and validating the spacecraft’s life support systems. The Artemis II crew includes: NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, and Christina Koch, and CSA astronaut Jeremy Hansen.
As we look ahead to Artemis II, we build upon the incredible success of the Artemis I mission and recognize the hard work and achievements of the entire Artemis team. Go Artemis!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
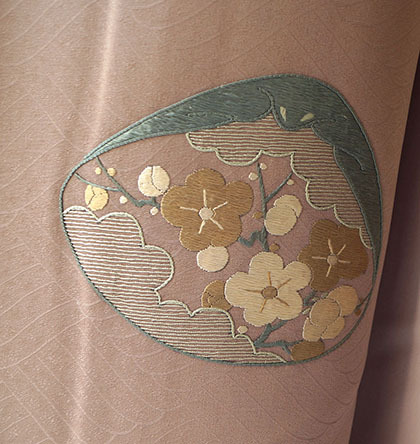





Delicate patterns evocative of ancient palaces for this outfit, pairing a kimono with decorated kaiawase (Heian period shell-matching game) over waves ground, and a beautiful obi depicting tagasode (kimono discarded on ikou/rack)
Adobe steals your color

When a company breaks a product you rely on — wrecking decades of work — it’s natural to feel fury. Companies know this, so they try to deflect your rage by blaming their suppliers. Sometimes, it’s suppliers who are at fault — but other times, there is plenty of blame to go around.
For example, when Apple deleted all the working VPNs from its Chinese App Store and backdoored its Chinese cloud servers, it blamed the Chinese government. But the Chinese state knew that Apple had locked its devices so that its Chinese customers couldn’t install third-party apps.
That meant that an order to remove working VPNs and apps that used offshore clouds from the App Store would lock Apple customers into Chinese state surveillance. The order to block privacy tools was a completely foreseeable consequence of Apple’s locked-down “ecosystem.”
https://locusmag.com/2021/01/cory-doctorow-neofeudalism-and-the-digital-manor/
In 2013, Adobe started to shift its customers to the cloud, replacing apps like Photoshop and Illustrator with “Software as a Service” (“SaaS”) versions that you would have to pay rent on, every month, month after month, forever. It’s not hard to understand why this was an attractive proposition for Adobe!
Adobe, of course, billed its SaaS system as good for its customers — rather than paying thousands of dollars for its software up front, you could pay a few dollars (anywhere from $10-$50) every month instead. Eventually, of course, you’d end up paying more, assuming these were your professional tools, which you expected to use for the rest of your life.
For people who work in prepress, a key part of their Adobe tools is integration with Pantone. Pantone is a system for specifying color-matching. A Pantone number corresponds to a specific tint that’s either made by mixing the four standard print colors (cyan, magenta, yellow and black, AKA “CMYK”), or by applying a “spot” color. Spot colors are added to print jobs after the normal CMYK passes — if you want a stripe of metallic gold or a blob of hot pink, you specify its Pantone number and the printer loads up a separate ink and runs your media through its printer one more time.
Pantone wants to license this system out, so it needs some kind of copyrightable element. There aren’t many of these in the Pantone system! There’s the trademark, but that’s a very thin barrier. Trademark has a broad “nominative use” exception: it’s not a trademark violation to say, “Pantone 448C corresponds to the hex color #4a412a.”
Perhaps there’s a copyright? Well yes, there’s a “thin” database copyright on the Pantone values and their ink equivalents. Anyone selling a RIP or printer that translates Pantone numbers to inks almost certainly has to license Pantone’s copyright there. And if you wanted to make an image-editing program that conveyed the ink data to a printer, you’d best take a license.
All of this is suddenly relevant because it appears that things have broken down between Adobe and Pantone. Rather than getting Pantone support bundled in with your Adobe apps, you must now pay $21/month for a Pantone plugin.
https://twitter.com/funwithstuff/status/1585850262656143360
Remember, Adobe’s apps have moved to the cloud. Any change that Adobe makes in its central servers ripples out to every Adobe user in the world instantaneously. If Adobe makes a change to its apps that you don’t like, you can’t just run an older version. SaaS vendors like to boast that with cloud-based apps, “you’re always running the latest version!”
The next version of Adobe’s apps will require you to pay that $21/month Pantone fee, or any Pantone-defined colors in your images will render as black. That’s true whether you created the file last week or 20 years ago.
Doubtless, Adobe will blame Pantone for this, and it’s true that Pantone’s greed is the root cause here. But this is an utterly foreseeable result of Adobe’s SaaS strategy. If Adobe’s customers were all running their apps locally, a move like this on Pantone’s part would simply cause every affected customer to run older versions of Adobe apps. Adobe wouldn’t be able to sell any upgrades and Pantone wouldn’t get any license fees.
But because Adobe is in the cloud, its customers don’t have that option. Adobe doesn’t have to have its users’ backs because if it caves to Pantone, users will still have to rent its software every month, and because that is the “latest version,” those users will also have to rent the Pantone plugin every month — forever.
What’s more, while there may not be any licensable copyright in a file that simply says, “Color this pixel with Pantone 448C” (provided the program doesn’t contain ink-mix descriptions), Adobe’s other products — its RIPs and Postscript engines — do depend on licensable elements of Pantone, so the company can’t afford to tell Pantone to go pound sand.
Like the Chinese government coming after Apple because they knew that any change that Apple made to its service would override its customers’ choices, Pantone came after Adobe because they knew that SaaS insulated Adobe from its customers’ wrath.
Adobe customers can’t even switch to its main rival, Figma. Adobe’s just dropped $20b to acquire that company and ensure that its customers can’t punish it for selling out by changing vendors.
Pantone started out as a tech company: a way to reliably specify ink mixes in different prepress houses and print shops. Today, it’s an “IP” company, where “IP” means “any law or policy that allows me to control the conduct of my customers, critics or competitors.”
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
That’s likewise true of Adobe. The move to SaaS is best understood as a means to exert control over Adobe’s customers and competitors. Combined with anti-competitive killer acquisitions that gobble up any rival that manages to escape this control, and you have a hostage situation that other IP companies like Pantone can exploit.
A decade or so ago, Ginger Coons created Open Colour Standard, an attempt to make an interoperable alternative to Pantone. Alas, it seems dormant today:
http://adaptstudio.ca/ocs/
Owning colors is a terrible idea and technically, it’s not possible to do so. Neither UPS Brown nor John Deere Green are “owned” in any meaningful sense, but the companies certainly want you to believe that they are. Inspired by them and Pantone, people with IP brain-worms keep trying to turn colors into property:
https://onezero.medium.com/crypto-copyright-bdf24f48bf99
The law is clear that colors aren’t property, but by combining SaaS, copyright, trademark, and other tech and policies, it is becoming increasingly likely that some corporation will stealing the colors out from under our very eyes.
[Image ID: A Pantone swatchbook; it slowly fades to grey, then to black.]
Fancy Mossy Styrofoam

Fancy looking neighborhood....but besides the awful infrastructure maybe the bas reliefs aren’t even real.




Romantic antique attire perfect for kôyô (autumn leaves viewing season) depicting small birds in turning maples trees.
The black silk shusu obi is matched with a lovely sanpogi (lit. ”stroll outfit”). Those were beautiful kimono featuring mirror designs on skirt flaps and all over patterns. I believe they were worn as fashionable day dress and were briefly in fashion in Kansai (Osaka?) pre wwii.
The practicality and ingenuity shown with these radiators is inspiring. I love the multiple use of the heat source.
Could this also be used to dry linens or is that too much humidity?






Radiators with food-warming compartments
GUYS!!!!! IT'S GOING TO LAUNCH IN FIVE MINUTES!!!
I'M BEING SERIOUS

20-12-22
-
 solarpunkbaby liked this · 3 months ago
solarpunkbaby liked this · 3 months ago -
 jessyvivid reblogged this · 3 months ago
jessyvivid reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 diligentriver reblogged this · 3 months ago
diligentriver reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 annasmertina reblogged this · 4 months ago
annasmertina reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 littlepoots reblogged this · 4 months ago
littlepoots reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 scorpionxclub liked this · 5 months ago
scorpionxclub liked this · 5 months ago -
 k-sungyoon liked this · 5 months ago
k-sungyoon liked this · 5 months ago -
 thecatholicseamstress liked this · 6 months ago
thecatholicseamstress liked this · 6 months ago -
 void-flesh reblogged this · 6 months ago
void-flesh reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 simplyghosting liked this · 7 months ago
simplyghosting liked this · 7 months ago -
 urami1080 reblogged this · 7 months ago
urami1080 reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 archer-bro reblogged this · 7 months ago
archer-bro reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 archer-bro liked this · 7 months ago
archer-bro liked this · 7 months ago -
 holbytlanna liked this · 7 months ago
holbytlanna liked this · 7 months ago -
 thagale reblogged this · 7 months ago
thagale reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 flightsoffancyonpaperwings liked this · 7 months ago
flightsoffancyonpaperwings liked this · 7 months ago -
 sojournertales liked this · 7 months ago
sojournertales liked this · 7 months ago -
 rolkientolkien reblogged this · 7 months ago
rolkientolkien reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 shenzi-hemlock reblogged this · 7 months ago
shenzi-hemlock reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 christ-chan-official reblogged this · 7 months ago
christ-chan-official reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 christ-chan-official liked this · 7 months ago
christ-chan-official liked this · 7 months ago -
 geminiagentgreen reblogged this · 7 months ago
geminiagentgreen reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 geminiagentgreen liked this · 7 months ago
geminiagentgreen liked this · 7 months ago -
 whenyoucantsleeepatnight reblogged this · 7 months ago
whenyoucantsleeepatnight reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 kinetikatrue reblogged this · 7 months ago
kinetikatrue reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 qcity-blackbird reblogged this · 7 months ago
qcity-blackbird reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 ma-liin liked this · 8 months ago
ma-liin liked this · 8 months ago -
 sympangala liked this · 8 months ago
sympangala liked this · 8 months ago -
 nebelstreifling liked this · 8 months ago
nebelstreifling liked this · 8 months ago -
 mini-kaiju liked this · 8 months ago
mini-kaiju liked this · 8 months ago -
 14nortenaprincess14 liked this · 9 months ago
14nortenaprincess14 liked this · 9 months ago -
 roseharlaws liked this · 9 months ago
roseharlaws liked this · 9 months ago -
 bluesmileeface liked this · 11 months ago
bluesmileeface liked this · 11 months ago -
 texashippiecowboy liked this · 11 months ago
texashippiecowboy liked this · 11 months ago -
 everythingburritos liked this · 1 year ago
everythingburritos liked this · 1 year ago -
 abnormal-artist reblogged this · 1 year ago
abnormal-artist reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 abnormal-artist liked this · 1 year ago
abnormal-artist liked this · 1 year ago -
 boompopping reblogged this · 1 year ago
boompopping reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lowcountry-gothic liked this · 1 year ago
lowcountry-gothic liked this · 1 year ago -
 ereh-emanresu-tresni reblogged this · 1 year ago
ereh-emanresu-tresni reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ereh-emanresu-tresni liked this · 1 year ago
ereh-emanresu-tresni liked this · 1 year ago -
 oldman55 liked this · 1 year ago
oldman55 liked this · 1 year ago -
 bluerazzjazzhands reblogged this · 1 year ago
bluerazzjazzhands reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 fairy-ganj-mother liked this · 1 year ago
fairy-ganj-mother liked this · 1 year ago

