A Complete Beginner’s Guide To Moodboards
A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Moodboards
Please note that this is a guide for complete beginners who have no idea how to get started on making moodboards. Only the very basics will be covered here.
Have you ever wanted to make a moodboard but didn’t know where to start? You have ideas but you have never edited a picture before? Can’t afford photoshop and don’t know how to use it? Look here, this guide is for you!
This guide includes: Free photoshop alternatives, where to find images, and basic tips and tricks to make your moodboard. Click the Read More below :)
Afficher davantage
More Posts from Lune-versatile and Others
For all you worldbuilders out there, I don't know if you know, but r/worldbuilding on Reddit made this Google Doc with a ton of resources they gathered. Thought that might help some of you.
Pls make a list of books you recommend to aspiring writers<3
Ok. Aspiring/burgeoning writer starter kit:
In writing anything you officially become a writer so that’s step one haha, no need to aspire too much. BUT. I’m going to soapbox for a bit using this ask as an excuse love u kissing u etc. So. This will barely be about books, but sort of the recipe of what I (personally and subjectively) think will help anyone who wants to grow their craft. (I know because I've been writing seriously for 14 years)
The act of writing is the best practice you can get but having a well from which to draw on creatively and skill wise in order to DO that practice is the trickier part. And sometimes we can be found lacking because we’re either NOT refilling that well enough, consciously enough, or only with the same sorts of things so it gets stagnant. This is a long one so I’ll shove it under the cut haha.
The recipe:
Study craft
Broaden horizons
Diversify consumption
Consume with intention
Apply with reference
1) Study craft: this is the easiest to make sense of, right? I want to get good at writing so I read books about writing yada yada. Whatever you’re writing, it’s made up of a lot of moving parts, and you can dedicate time studying EACH PART, but figure out what you have the least experience with, or the most difficulty with, and start there. Also, before I go on to preach about why you shouldn’t solely stake your growth on some dusty old books, here’s some dusty old books I recommend:
The Elements of Style (strunk/white/kalman) (really quick and abbreviated advice, read every bit of this but remember: rules are important to know so you can decide which are worth following and which are in need of breaking for the pursuit of your goals. And nobodies perfect, or editors wouldn’t have a job)
Bird by Bird (Anne Lamott) (excellent work about fostering a process, important for everyone who finds themselves a little lost on how to just. Start)
Wonderbook (Jeff Vandermeer) (I haven’t read this one but knowing Vandermeers work this is on my TBR and I KNOW it’s going to be enlightening)
How to Read Literature like a Professor (Thomas C. Foster) (perfect for those who can see others stories working but unsure how to make their own work, I personally didn’t read much of this one but this will help people to more critically engage with what they’re consuming)
Save the Cat Writes a Novel/Joseph Campbells Hero’s Journey/On Writing and Worldbuilding/etc (all of these are on structure and craft in a concrete sense), I would recommend either choose one OR getting the abbreviated/digestible versions through YouTube because a lot of these can repeat themselves. I’m working on a playlist of writing craft/structure videos that I found helpful, so keep an eye out for that)
So. Studying craft should be a multidisciplinary process. Articles online, videos on niche media, books on craft or copying things from your favorites, looking for yourself in the movies you watch or fiction you read. Punctuation, prose, structure, rhetoric, character, world building, pacing, etc. Unfortunately, no matter how seasoned you become as a writer, you will always be learning new things about the craft itself.
It should be fun and I honestly feel like an enlightened little scientist when I see something that really cracks the open the magic for me (ex: scenes that serve more than one purpose are OF COURSE going to be more engaging that scenes with only one purpose- duh) (of COURSE magic systems should have a cost) (of COURSE the characters cant always win OR always lose)
2) Broaden horizons: consuming fiction and studying it is key to knowing how to reproduce it. We start with the training wheels of imitation before we ride away full speed into truly unique original storytelling. But the most impactful and thought-provoking stories are more than just fiction, so you need to know more than stories. Science, history, art, craft, math, music, cooking, psychology, religion, whatever!
Everyone always parrots “write what you know”, but what you KNOW can expand to influence what you write- so keep learning new things all the time and for fun, because you never know what could help your story. Your knowledge is not limited to experience alone, and research is your best friend. ASOIAF was so loved because George RR Martin loved not only fantasy, but British history. The Folk of the Air series is so loved because Holly Blacks special interest is faeries.
Note: this does not mean the study of OTHER PEOPLES trauma and experiences in an appropriative way, rather, become worldly. Because sure, knowing what a gunshot feels like adds realism, but I don’t care about realism if I don’t care about your characters or world. Science fiction is the best example of this: so many of those stories stick with us generationally because they’re pointing a lens back at humanity, asking big philosophical questions with science, which is something that touches us all.
But it doesn’t even need to be Big and Thematic like that. My dear friend @chaylattes has a project where she’s applied her love of plants to the world building AND plot, and has INVENTED whole plant species that enriched their work with something so exclusively Chay. No one else could write Andromeda Rogue because Chay, with specific interests and knowledge, put that specificity into the story.
3) Diversify consumption: surrounding yourself with more of the same means you’re going to regurgitate the same, derivatively. To be a hater for a moment: I can tell within the first chapter if someone only reads/watches one kind of media (m*rvel, fairy smut, grim dark nonsense, etc), and it’s distracting. When I read that derivative work, I’m not thinking about THEIR story. All I can think of is the people who did it first, and better.
Alternatively, the best work draws on the unexpected. Fantasy work taking notes from horror, science fiction including humanistic romance, romance with elements of mystery. RF Kuangs work feels so smart because she’s literally a PHD candidate who’s reading of academic writing. Cassandra Clares work is so interpersonally messy and hard to look away from because she watches a lot of reality television.
Genre is less a set of cages to lock yourself inside of and more so the sections of a great big fictional playground- and you need to start playing. Rules, again, are guidelines that can be bent for the sake of your stories. I predominantly write scifi/fantasy/horror but some of my favorite stuff is literary fiction, historical nonfiction, thrillers, and poetry.
And if you can’t bring yourself to read different genres, it takes significantly less effort to WATCH different genres. Television and film are stories too, and can absolutely be learned from.
4) Consume with intention: this is easier said than done. I, embarrassingly, admit that I did not have any reading comprehension skills until I was at least 19. I was consuming, but I wasn’t thinking a damn critical thought, just spitting it back out in a way that sounded smart.
Critical thinking skills (I say, on the website that historically lacks such a thing) are a muscle that needs to be exercised just as often as your writing muscle. Reading new work, studying craft, learning new shit- none of it matters if you can’t APPLY it all to a story. One can take a clock apart to learn how exactly it ticks, but it won't tell time like a watch until you put it back together.
The key is asking questions, all of the time about everything. That whole “why the curtains were blue” nonsense comes to mind, but if you want to be a good writer, (edit: a writer that cares about whether or not their work is vapid imitation of better work) learning to ask WHY the curtains are blue really does matters.
Ask why in ALL stories you consume, including your own. Why do Ghibli films make me feel calm? (Motifs of undisturbed nature, low stakes plots and quiet scenes of reprieve between action, characters that care about one another and aren’t afraid to show it) Why do I fly through a Gillian Flynn novel but take 8,000 years to read other books? (Concise descriptions, realistic but evocative premise, witty voice, contained and fast paced plot, an abundance of questions driving the mystery leading up to a satisfying crash of answers at the end) Why were the curtains blue, the coffee cup chipped, and the lipstick stain on the rim red instead of purple or pink? And why did the colors matter at all when the scene is about a father at a kitchen table? (You tell me!) Answers may vary.
You can put the work into learning the answer at the source (ie: listening to authors talk about their own work), or through the external interpretations of a critic (proceed with caution here), sure. These are even good when learning HOW to think critically if you don’t even know where to start. But your growth as a writer depends on your ability to answer your OWN questions.
(Why do I feel tense in this scene? Is it because the character says they’re sweating and struggling to breathe? Is it because I’ve been told the monsters close? Is it because the sentences are getting shorter and the author keeps repeating descriptions of that monsters massive bloody teeth coming closer? Or is it because I know the gun in her hands has no bullets because another character already tried what she’s about to try?)
(Why do I feel sad in this scene? Is it because the characters mom just died? Is it because the character can’t even verbalize that sadness to others? Is it because none of the other characters seem to care enough to ask? Is it because of the wilted flowers in the corner? Or is it because there are daisies in the bouquet, and those were the moms favorite?)
I can nod and smile at 1000 opinions about “why X did Y and the end of Z” or “why X is Y and not Z” but how I felt when I consume something, how I was affected and how it made ME PERSONALLY answer my critical questions, that’s what’s important. That’s how we manufacture gay subtext in everything, because sometimes gay is a feeling as opposed to a fact.
Also, if those subjective answers are inconsistent among readers/viewers, the writer likely had their own intentions a little muddled. So, and I know I’m getting tangential but stay with me: romance. You know how you’re supposed to feel happy or convinced that the people falling in love are like, in love? And want to put yourself in that position or whatever? I CANNOT consume most romance media because it all comes off as categorically terrifying to me. I ask myself why the characters are doing what they do, reacting the way they react, saying way they say, and none of it feels romantic. I want to file a restraining order, and that’s the failing of the author, who did not make enough conscious choices in their work and accidentally created horror while writing their color by numbers trope slop of a “romance” novel.
5) Apply with reference: is like taking all your ingredients and finally cooking. You want people to notice and respect when you add certain literary devices, descriptions, character choices, but not to the detriment of your work. Shows like stranger things are popular but divisive because their intertextuality and reliance on nostalgia bolster an otherwise unoriginal idea. They weren’t trying to reinvent the wheel, they were writing a love letter to Stephen Spielberg, and are riding that wave into the ground. But the fairy dick renaissance doesn’t feel nearly as palatable as season one of stranger things did because a lot of times they aren’t using the ingredients in their own way, rather, following the recipe to a T and selling it as new. Food really is the perfect metaphor and sorry in advance because I’m really going to run with it here lol.
When I eat a meal, first of all I know I'm eating food, so don't try and trick me into thinking otherwise or I'll only get annoyed. I want to be able to taste all of what’s in front of me, spice, salt, sweet, bitter, etc and know what what you said you've fed me is really actually truly what I've eaten. One ingredient, or writing choice, shouldn’t overpower another, or surprise me so much I can’t take another bite. I shouldn’t try something you call “sauced and baked yeast patty garnished with fermented milk and smoked meat” and think “this shits pizza” because you didn’t even try to jazz it up more than what the instructions on the digiorno box said. I also shouldn’t bite into something you call a pizza and only taste bread because you really like bread and forgot that a pizza is more than just bread.
But inversely, avoiding all ingredients gets you weird, nary inedible shit like charred milk reduction with lamb mist or whatever. Show me you have knowledge in your genre by referencing it AND remixing it, show me that you studied craft by foreshadowing properly or pacing well, show me you’re more than an AI writerbot by deepening your work with your unique and human influence, show me you read broadly by adding surprising ingredients, and show me that you mean every word you write because you made the curtains blue instead of yellow, and topped your pizza with pepperoni instead of pineapple.
Congrats on making it all the way through my rambling, hope I made sense and that this helped!
I hate to say this, and like, rain on everyone’s parade, but after scrolling past three posts about it on a writing tag …
If you are looking up synonyms to exchange words out in your story with the purpose of sounding smarter, more sophisticated, or complicated to your reader, you are probably abusing the thesaurus.
Now, if you *want* to do this, I mean, you can write whatever or however you want! But I just want you to know that this is frowned upon if you are trying to write at a professional level.
I have an old article on this somewhere …



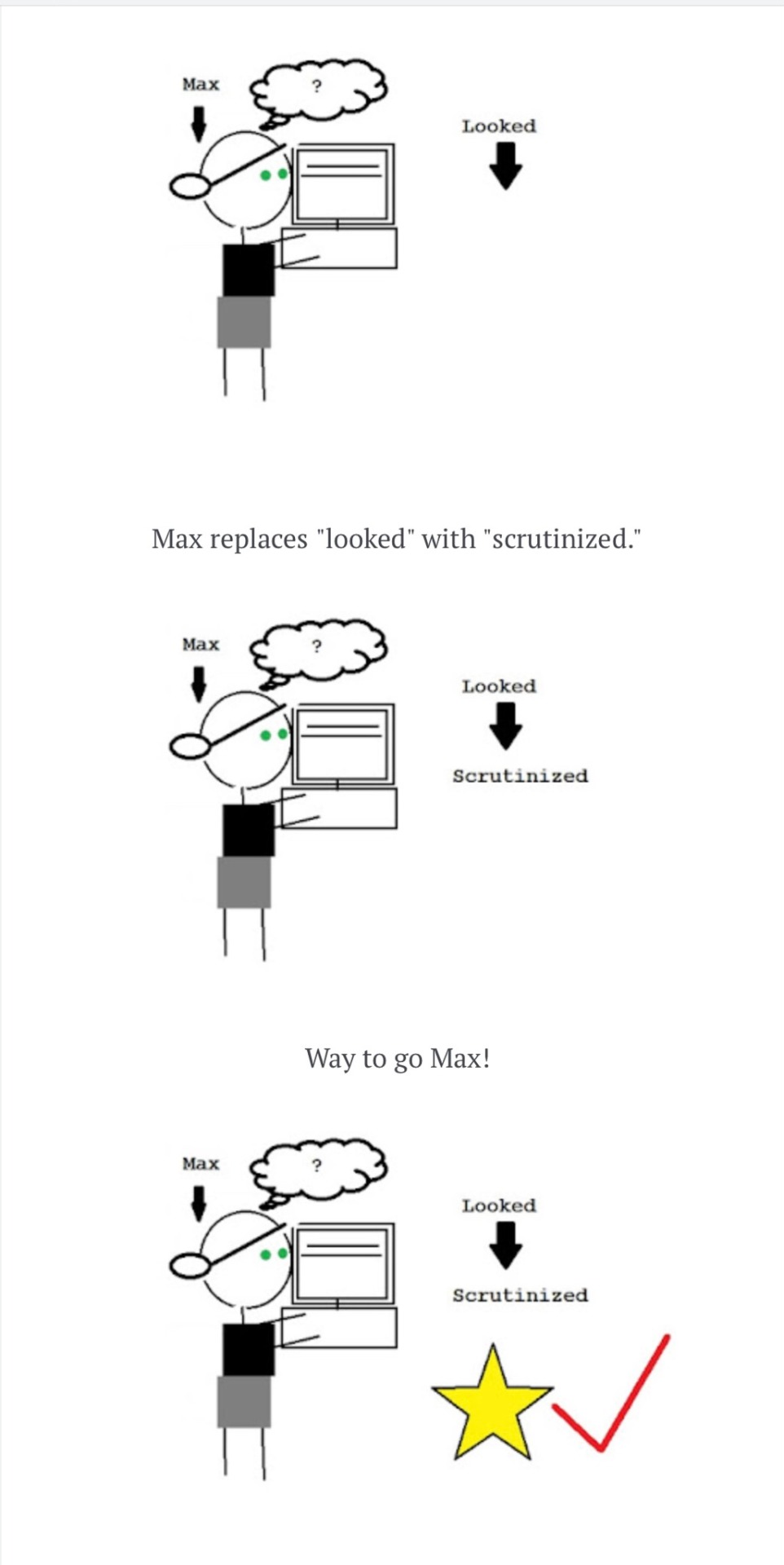


If you want to look at the original article…
https://www.septembercfawkes.com/2018/08/how-to-use-thesaurus-properly.html

Writing Tip!
An easy way to tell if you’re showing instead of telling is how much you’re using is/was. My English professor explained this to me a few semesters ago, and while he just wanted varied sentence structure in my papers, it also works very well for creative writing.
This isn’t to say that is and was are bad verbs, but rather that they are very basic and do not express anything beyond the fact that something exists. Sometimes, that’s all you need to know in a sentence, but often, the writer can make the story or the characters more engaging by explaining who someone is, what something is, where something is, when something is, why something is, or how something or someone is more powerfully by using one of a few tactics.
The first method is to use strong verbs. “Strong verbs” is a term that gets thrown around a lot, but a strong verb is simply a verb that explains what action is happening as clearly as possibly. For instance, when one “jumps” off the diving board, the reader doesn’t know how the person jumped, but the reader will be able to more clearly see the action if you write “she dove” or “he cannonballed” or “she belly-flopped.” Be aware of who is reading your writing and who the narrator is. In general, if your target demographic probably doesn’t know the word or if your narrator wouldn’t know the word, use a simpler, less precise verb and use adverbs to make it specific.
Another way is to show why the narrator was saying “it is/she was/there is” in the first place. Think of the is/was statement as the disease. You want your reader to guess the disease, so you start describing symptoms. For instance, “She is mourning her husband.” vs. “She stared at the empty seat at the table, unfazed by her mother’s repeated attempts to get her attention.” This way is more rambly than just swapping boring verbs for strong verbs, but it is a good way to show the narrator’s experience in life, the narrator’s biases, the narrator’s emotional state, etc.
One other way is to make the object of the sentence the subject instead. This just means that whatever “is/was” is now what the sentence is about. This is a simple fix in cases when the object is doing something in the sentence. Instead of “There was a ball rolling past her feet.” write “A ball rolled past her feet.”
Let me illustrate:
How you can use varied word choice to show who is being talked about:
Bland: Jason’s dad was standing in front of Jason.
Engaging: His dad loomed over him.
By using a stronger verb, the more hostile loomed, the reader gets a better idea of who Jason’s dad is and how Jason feels about him.
How you can use varied word choice to show who is talking:
Bland: Macy was sitting at the edge of her seat.
Engaging: Macy balanced very carefully at the very edge of the seat so her feet could touch the floor, because Macy was a very big girl now.
The POV character is a young girl at an age where she wants to be perceived as older than the height of chair legs and the lack of height of her own legs will let her be. She also refers unironically to herself as a big girl in her own thoughts, something grownups generally do not do. By expanding on the reason for the action instead of the action itself and with careful word choice, you can set the tone of the character and of the story.
How you can use varied word choice to show what something is:
Bland: That is a tree branch blowing against the window.
Still bland but better: A tree branch blew against the window.
Engaging: The branch smacked against the window.
This is an example of taking the object (the thing in the sentence that the verb is happening to) in this case “branch” and make it the subject. In the still bland but better version of the sentence, the fact that the tree branch is blowing against the window is obvious, but that doesn’t tell us anything about how the narrator feels about what the tree branch is doing. That tells us what, but it does not tell us what the character feels about this thing. Smacked is a more violent, sudden, startling verb that communicates suddenness, surprise, and unease.
How you can use varied word choice to show where something is:
Bland: The phone was on the far side of the nightstand.
Engaging: She flopped an arm blindly across the nightstand, but her fingers hit empty air just shy of the faint glow of her phone.
The engaging version of this sentence tells you more about the character’s mental state, fatigued, while also communicating where the phone is. Also, using a more descriptive word like flopped gives the reader a clearer mental image of what is physically happening in the scene.
How you can use varied word choice to show when something is set:
Bland: It was the early two thousands.
Engaging: Jana looked around the room and saw many a teenage male heinie, but not a belt among them.
Noting fashion trends, like sagging pants or hoop skirts, can reinforce the time period that you’re writing in and how the narrator fits or does not fit into that time period.
How you can use varied word choice to show when (what time) something is:
Bland: It was seven P.M. on a summer night.
Engaging: He watched the sun dip below the far reaches of the ocean as he wiped the sweat from his brow.
The engaging version of this sentence uses a few details to show about what time and when in the year this sentence takes place: it is sunset, so the exact time isn’t stated, but the rough time is implied; the ocean does exist at times of the year when humans aren’t on it as much (and here I though the entire state of Hawaii disappeared between September and April) but most readers will associate the beach with summer; and if the reader didn’t get the clue about the traditionally seasonal location, it is hot enough to make the main character sweat.
How you can use varied word choice to show why the narrator believes something:
Bland: Kai is a good friend.
Engaging: Kai held her hair away from her face as she threw up into the toilet bowl for the fourth time that night.
Anyone can say anything about anyone else, but the best way to get a reader to like a character, an idea, or a thing is to show them why they should like that thing. Instead of making bland moral claims like “Love is stronger than hate.” tell me how the Samaritan stopped to save the Jew, or how the enemies put aside their differences to protect what they care about. Instead of saying “He was scared of his dad.” show me the beer cans and the slurred speech, show me the belt falling and the voice yelling. Show the reader why.
How you can use varied word choice to show how something is:
Bland: The woman was looking at him.
Engaging: The woman ogled him.
Strong verbs again! Use strong verbs that are emotionally charged when you’re talking about emotionally charged situations! Being ogled is an uncomfortable sensation for the person being ogled, and it also shows disrespect on the part of the person ogling.
Keep in mind that these are guidelines! Sometimes is is the best word for the job, and don’t stress if you have a lot of is/was in your stories. Just because they’re bland doesn’t mean that sometimes you need bland verbs to communicate what you want to communicate. Still, you don’t want vagueness to be your crutch, either. Practice showing instead of telling when showing is more important, but have fun with it! Besides, you can always edit whatever you hate or are unsure of now sometime later.
Don’t sweat! Go write awesome papers and stories!
The “What-If” Writing Method
Sometimes when I’m writing, brain just....stops. No more ideas. No more words. Nothing. Sometimes, the solution to this problem is to simply take a break from writing and let your brain relax. Other times, though, you really are just at a block for ideas. This happened to me significantly more often than I would like, but thankfully, I’ve developed a solution that works well for me, and it’s uncreativly titled the “what-if” method.
Get a piece of paper and pen. Or a Google doc, or whatever works best for you.
Start brainstorming questions about your story, or possible “what-if” scenarios. (Ex: What if my character got framed for a crime they didn’t commit?)
Write down every single idea that comes to your head. Even if it doesn’t really work for your story. Even ones that deviate from your existing plot. Even the stupid ones. Especially the stupidest ones.
Cross out the ideas you don’t like, circle the ones that you do like.
Start coming up with answers for the questions you circled, or expand in the by coming up with more questions. (Ex: They would have to prove they didn’t commit the crime to regain their freedom. How do they prove it?)
Repeat until you have a full idea that you can work on/write with.
That’s it. That’s the whole strategy. I’ve used this a million times, and it’s gotten me out of a million cases of writers block, so hopefully it can work well for you too! Happy writing!
How do I write a dream sequence that actually feels dreamy and not just confusing or random? I want it to make sense in the story but still have that weird, surreal vibe dreams have.
Before writing a dream sequence, ask yourself: Why is this dream important?
A strong dream sequence serves a narrative purpose. It either reveals something critical about the character or moves the plot forward. For example, it might:
Highlight a character’s inner conflict, such as self-doubt or guilt.
Offer insight into a character’s fears, desires, or memories.
Foreshadow future events.
Explore the story’s themes.
Present an epiphany or realisation that changes the narrative direction.
When you define the purpose of the dream, you give it meaning and ensure it doesn’t feel like a random, disconnected scene.
Vivid imagery and sensory details
Dreams are often hyper-real or surreal. To truly immerse readers, fill your sequences with vivid imagery. Describe not just what the character sees, but also what they hear, smell, and feel. For example:
The air might feel oppressively heavy, as if the character is moving through water.
Colours could be unnaturally bright or pulsing, creating a sense of unease or wonder.
Sounds may echo strangely, or voices may change tones mid-sentence.
Sensory details are your best friend when crafting dreams. They help you draw readers into the scene, making the dream feel almost tangible without being constrained to what is possible.
The power of symbolism
Dreams are often symbolic, reflecting a character’s subconscious thoughts and emotions. A dream sequence offers a fantastic opportunity to use metaphors and symbols to deepen your narrative. For instance:
A crumbling staircase may represent a character’s feelings of insecurity.
A recurring image, like a locked door, could hint at a secret the character is repressing.
Objects or people in the dream might represent aspects of the character’s personality or unresolved relationships.
By embedding symbols, you can subtly communicate deeper layers of meaning to your readers while building suspense without having to state things outright.
Heightened emotion
In dreams, emotions are often exaggerated. A minor embarrassment can swell into overwhelming shame, and a fleeting joy might feel like euphoria. Use this to your advantage to explore your character’s emotional state. For instance:
A character struggling with grief might dream of a loved one, only for them to disappear when approached.
A character racked with guilt could find themselves pursued by shadowy figures.
Striking a balance between disorientation and logic
Dreams are naturally disorienting because they don’t follow the logical flow of reality. You can introduce elements like sudden scene changes, nonsensical dialogue, or impossible physics to create a truly dreamlike experience. For example:
A character might start at a family dinner, only to inexplicably swimming in an ocean of stars.
A trusted friend might appear with the face of a stranger.
Despite the inherent chaos of dreams, your sequence should still have some degree of narrative coherence. A good rule of thumb is to maintain a logical thread that allows the dream to fulfil its narrative purpose, even if the details are illogical.
Establishing atmosphere
The tone and atmosphere of your dream sequence should align with its purpose. Focus on creating a specific emotional response:
For a nightmare, use eerie, oppressive details, like a pulsating fog or distorted, echoing voices.
For a whimsical dream, evoke wonder with surreal and magical details, such as floating landscapes and shimmering light.
Choose your atmosphere carefully to enhance the emotional impact of the scene.
Types of dream sequences to explore
There are many types of dream sequences, and each serves a unique purpose. Here are some of the most common:
Foreshadowing dreams: These hint at future events, creating suspense or intrigue.
Nightmares: These reveal a character’s fears or anxieties.
Fantasy dreams: These involve magical or surreal elements, and are often used to explore themes, symbols, or metaphors.
Recurring dreams: These underscore unresolved issues or patterns in a character’s life.
Lucid dreams: These allow the dreamer to be aware they’re dreaming and possibly influence the dream’s outcome.
Realisation dreams: These provide moments of clarity or epiphany for the character.
Internal conflict dreams: These visually showcase a character’s inner turmoil, providing a unique way to “show, not tell.”
Linked dreams: These connect two or more characters through shared dreamscapes.
Keep it brief and meaningful
Dream sequences should enhance your story, not derail it. While they offer a chance to be wildly creative, keep them concise and focused. Avoid overloading readers with too much detail or overly prolonged scenes. Your audience should leave the dream sequence full or curiosity, not overwhelmed.
Seamlessly transition in and out
Transitions are crucial for dream sequences. Start with subtle hints, like a sound, a sensation, or a surreal visual that cues readers into the shift from reality to dream. Similarly, exit the dream gracefully, creating a smooth return to the waking world. This ensures that readers are not jarred out of the story.
Writing tips for a dreamlike feel
Use narrative distance to create a floaty, disconnected feeling that mirrors the sensation of dreaming.
Experiment with stream-of-consciousness writing for portions of the dream to mimic the fluid and unpredictable nature of thoughts in sleep.
Pay attention to pacing. Dreams often feel both slow and rapid—a contradiction you can reflect by alternating between drawn-out descriptions and sudden, abrupt moments.
Dream sequences are a space where your imagination can truly run free while still serving the story’s deeper purpose. When done well, they are memorable and meaningful, and leave a lasting impact. It’s a technique well worth exploring.
u know what, even if my writing isnt the BEST, i still made it all on my own. like there was a blank word doc and i filled it up with my own words, my own story. i took what was in my head and i made it a real thing. idk i feel like that alone is something to be proud of.
Finish Your Drafts (please)
I have this really bad habit of getting most the way through a draft, seeing how it needs to change structurally and… starting a new one. I have countless unfinished drafts and shorts and written out ideas that haunt me with their cut off sentences and half paragraphs.
Here’s the part that sucks. Finishing a draft is always worth it. Always. No matter how messed up your beginning may be, how much you need to rework or change, how much just isn’t coming together. Get through to the end, even if you have to write a bunch of stuff you aren’t proud of to get there, get through to the end.
I learned more about my novel from one finished draft than I did from the five unfinished ones after it. You need to explore your ending, because your ending is the most important part of the entire piece.
This month we explored outlining and character arcs—all of that planning, all of that work we’ve put into this project leads up to the ending. The ending will tell you more about your direction and how the pieces you’ve tried to put together are working than anything else. It’s the one place you can’t hide. Either the ending wraps up how you want it to, or you need to go back to the drawing board.
I almost didn’t finish that one draft. I knew there was a huge gaping problem I hadn’t noticed before right in the middle and that I had to rework some stuff. I nearly stopped there, but I pushed forward instead. It was there that I discovered a large part of that problem was the ending I had planned. I was working towards the wrong thing, so of course the middle would fall apart.
You’ll be able to see your character arcs, your theme, your subplots, all of it needs to be addressed in the ending, so your ending is going to tell you what is working and what isn’t.
Push through to the finish line. Best case scenario you understand your work and process on a deeper level. Worst case, you have a finished draft—and that’s always something to be proud of.
Good luck! Happy end of February. Next month we’ll be talking about some other ways to create characters and voice, amongst other things. I’m looking forward to it!
Character Charts
One thing that always gets me excited to start a new writing project is creating a character. Creating a new character is a sure-fire way to amp your self up about your new story.
There is no write or wrong way to create them, you just do!
However, creating a new name and face for a story can be daunting, particularly when it comes to naming the character! I like to choose a name with a special meaning or connection to the story I have in mind.
I find it very helpful to refer to a ‘character development’ chart or ‘character features’ charts.
I'll post some helpful charts down below! I hope this helps :)




-
 thecelestialprince liked this · 1 month ago
thecelestialprince liked this · 1 month ago -
 hounddogmoment liked this · 1 month ago
hounddogmoment liked this · 1 month ago -
 sanddfalcon reblogged this · 2 months ago
sanddfalcon reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 arc-angel-o reblogged this · 2 months ago
arc-angel-o reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 arc-angel-o liked this · 2 months ago
arc-angel-o liked this · 2 months ago -
 otoshi-lady reblogged this · 2 months ago
otoshi-lady reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 otoshi-lady liked this · 2 months ago
otoshi-lady liked this · 2 months ago -
 cristalda liked this · 2 months ago
cristalda liked this · 2 months ago -
 winthropsghostkitten liked this · 3 months ago
winthropsghostkitten liked this · 3 months ago -
 tsunderestorming liked this · 3 months ago
tsunderestorming liked this · 3 months ago -
 octopus-atelier liked this · 3 months ago
octopus-atelier liked this · 3 months ago -
 miss-worldddd liked this · 3 months ago
miss-worldddd liked this · 3 months ago -
 sun-the-shattered reblogged this · 5 months ago
sun-the-shattered reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 gaybonesforivy reblogged this · 5 months ago
gaybonesforivy reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 thatoneweird014 reblogged this · 6 months ago
thatoneweird014 reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 thatoneweirdo14 liked this · 6 months ago
thatoneweirdo14 liked this · 6 months ago -
 thatoneweirdo14 reblogged this · 6 months ago
thatoneweirdo14 reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 dentixvoxel liked this · 6 months ago
dentixvoxel liked this · 6 months ago -
 faeking-it reblogged this · 6 months ago
faeking-it reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 faeking-it liked this · 6 months ago
faeking-it liked this · 6 months ago -
 cloudycomforts liked this · 6 months ago
cloudycomforts liked this · 6 months ago -
 streetlightsflicker liked this · 6 months ago
streetlightsflicker liked this · 6 months ago -
 nt1274 liked this · 6 months ago
nt1274 liked this · 6 months ago -
 en-busca-de-mi-ikigai-blog reblogged this · 8 months ago
en-busca-de-mi-ikigai-blog reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 en-busca-de-mi-ikigai-blog liked this · 8 months ago
en-busca-de-mi-ikigai-blog liked this · 8 months ago -
 thatcassieblake liked this · 8 months ago
thatcassieblake liked this · 8 months ago -
 alohaangels liked this · 8 months ago
alohaangels liked this · 8 months ago -
 anarchistabsol liked this · 9 months ago
anarchistabsol liked this · 9 months ago -
 in-ardent-longing liked this · 9 months ago
in-ardent-longing liked this · 9 months ago -
 grandgothpandabagel liked this · 10 months ago
grandgothpandabagel liked this · 10 months ago -
 go-setyoursoulonfire reblogged this · 10 months ago
go-setyoursoulonfire reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 go-setyoursoulonfire liked this · 10 months ago
go-setyoursoulonfire liked this · 10 months ago -
 baby-kittys-stuff liked this · 10 months ago
baby-kittys-stuff liked this · 10 months ago -
 galacticquiltsystem liked this · 10 months ago
galacticquiltsystem liked this · 10 months ago -
 fl-oralfawnarchive reblogged this · 10 months ago
fl-oralfawnarchive reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 srngarden liked this · 10 months ago
srngarden liked this · 10 months ago -
 halfagonyhalfalsoagony liked this · 11 months ago
halfagonyhalfalsoagony liked this · 11 months ago -
 newengland-alligator liked this · 11 months ago
newengland-alligator liked this · 11 months ago -
 helenvader liked this · 11 months ago
helenvader liked this · 11 months ago -
 thereaperisabitch reblogged this · 1 year ago
thereaperisabitch reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 thereaperisabitch liked this · 1 year ago
thereaperisabitch liked this · 1 year ago -
 fumble-femur liked this · 1 year ago
fumble-femur liked this · 1 year ago -
 mentallyhotpenguin liked this · 1 year ago
mentallyhotpenguin liked this · 1 year ago -
 thebooknerd6 liked this · 1 year ago
thebooknerd6 liked this · 1 year ago -
 sherlock-starker liked this · 1 year ago
sherlock-starker liked this · 1 year ago -
 dani-elaine liked this · 1 year ago
dani-elaine liked this · 1 year ago

