Breathe.

Breathe.
More Posts from Groovyblueworld and Others

Anyake is the highly regarded and mysterious leader of the High Desert mouse tribe. No one knows how old she is and no one would dare ask. She doesn't talk much, and ventures out among her people even less, but they know that she would fight to the death to protect them.
Anyake is a @walloyamorring and svetlanagermanova Granny Mouse Ayra with an Angels Addiction faceup and a Popovy size wig from Fantasydolls on Etsy.
The Granny Mice are currently available for preorder!! I can't recommend them highly enough ❤️❤️❤️.
#bjd #legitbjd #walloyamorring #grannymouseayra #walloyamoringgrannymouse #bjdphoto #fantasybjd
*Instagram repost

Sunrise books, vinyl, cd, buy, sell, trade

It’s been a long stressful day, let’s have a photo of Acacia’s sweet little face. You can see her little mark too. 💜

A Constant Hum (found in a derelict factory)

The data does not support the assumption that all burned out people can “recover.” And when we fully appreciate what burnout signals in the body, and where it comes from on a social, economic, and psychological level, it should become clear to us that there’s nothing beneficial in returning to an unsustainable status quo.
The term “burned out” is sometimes used to simply mean “stressed” or “tired,” and many organizations benefit from framing the condition in such light terms. Short-term, casual burnout (like you might get after one particularly stressful work deadline, or following final exams) has a positive prognosis: within three months of enjoying a reduced workload and increased time for rest and leisure, 80% of mildly burned-out workers are able to make a full return to their jobs.
But there’s a lot of unanswered questions lurking behind this happy statistic. For instance, how many workers in this economy actually have the ability to take three months off work to focus on burnout recovery? What happens if a mildly burnt-out person does not get that rest, and has to keep toiling away as more deadlines pile up? And what is the point of returning to work if the job is going to remain as grueling and uncontrollable as it was when it first burned the worker out?
Burnout that is not treated swiftly can become far more severe. Clinical psychologist and burnout expert Arno van Dam writes that when left unattended (or forcibly pushed through), mild burnout can metastasize into clinical burnout, which the International Classification of Diseases defines as feelings of energy depletion, increased mental distance, and a reduced sense of personal agency. Clinically burned-out people are not only tired, they also feel detached from other people and no longer in control of their lives, in other words.
Unfortunately, clinical burnout has quite a dismal trajectory. Multiple studies by van Dam and others have found that clinical burnout sufferers may require a year or more of rest following treatment before they can feel better, and that some of burnout’s lingering effects don’t go away easily, if at all.
In one study conducted by Anita Eskildsen, for example, burnout sufferers continued to show memory and processing speed declines one year after burnout. Their cognitive processing skills improved slightly since seeking treatment, but the experience of having been burnt out had still left them operating significantly below their non-burned-out peers or their prior self, with no signs of bouncing back.
It took two years for subjects in one of van Dam’s studies to return to “normal” levels of involvement and competence at work. following an incident of clinical burnout. However, even after a multi-year recovery period they still performed worse than the non-burned-out control group on a cognitive task designed to test their planning and preparation abilities. Though they no longer qualified as clinically burned out, former burnout sufferers still reported greater exhaustion, fatigue, depression, and distress than controls.
In his review of the scientific literature, van Dam reports that anywhere from 25% to 50% of clinical burnout sufferers do not make a full recovery even four years after their illness. Studies generally find that burnout sufferers make most of their mental and physical health gains in the first year after treatment, but continue to underperform on neuropsychological tests for many years afterward, compared to control subjects who were never burned out.
People who have experienced burnout report worse memories, slower reaction times, less attentiveness, lower motivation, greater exhaustion, reduced work capability, and more negative health symptoms, long after their period of overwork has stopped. It’s as if burnout sufferers have fallen off their previous life trajectory, and cannot ever climb fully back up.
And that’s just among the people who receive some kind of treatment for their burnout and have the opportunity to rest. I found one study that followed burned-out teachers for seven years and reported over 14% of them remained highly burnt-out the entire time. These teachers continued feeling depersonalized, emotionally drained, ineffective, dizzy, sick to their stomachs, and desperate to leave their jobs for the better part of a decade. But they kept working in spite of it (or more likely, from a lack of other options), lowering their odds of ever healing all the while.
Van Dam observes that clinical burnout patients tend to suffer from an excess of perseverance, rather than the opposite: “Patients with clinical burnout…report that they ignored stress symptoms for several years,” he writes. “Living a stressful life was a normal condition for them. Some were not even aware of the stressfulness of their lives, until they collapsed.”
Instead of seeking help for workplace problems or reducing their workload, as most people do, clinical burnout sufferers typically push themselves through unpleasant circumstances and avoid asking for help. They’re also less likely to give up when placed under frustrating circumstances, instead throttling the gas in hopes that their problems can be fixed with extra effort. They become hyperactive, unable to rest or enjoy holidays, their bodies wired to treat work as the solution to every problem. It is only after living at this unrelenting pace for years that they tumble into severe burnout.
Among both masked Autistics and overworked employees, the people most likely to reach catastrophic, body-breaking levels of burnout are the people most primed to ignore their own physical boundaries for as long as possible. Clinical burnout sufferers work far past the point that virtually anyone else would ask for help, take a break, or stop caring about their work.
And when viewed from this perspective, we can see burnout as the saving grace of the compulsive workaholic — and the path to liberation for the masked disabled person who has nearly killed themselves trying to pass as a diligent worker bee.
I wrote about the latest data on burnout "recovery," and the similarities and differences between Autistic burnout and conventional clinical burnout. The full piece is free to read or have narrated to you in the Substack app at drdevonprice.substack.com
DO NOT DO THIS!!!
If a website has a paywall, like New York Times, DO NOT use the ctrl+A shortcut then the ctrl+c shortcut as fast as you can because then you may accidentally copy the entire article before the paywall comes up. And definitely don't do ctrl+v into the next google doc or whatever you open because then you will accidentally paste the entire article into a google doc or something!!!! I repeat DO NOT do this because it is piracy which is absolutely totally wrong!!!
Hi! I see in your posts that there are names for the different types of hanfu...but i cannot tell the difference...would you be able to make a post on what the different types of hanfu are? If its too complicated thats ok!
Hi, thanks for the question! I covered the basic types of men’s hanfu here and here, so in this post I’ll describe the basic types of women’s hanfu. Resources on identifying different types of hanfu can be found in my reference tag.
- Ruqun/襦裙 - the most basic type of hanfu consisting of a top and a wrap-around skirt. The top is called “ru/襦” and the skirt is called “qun/ 裙”, hence “ruqun”. Sleeves can be narrow or wide. Generally speaking, people divide ruqun into two types based on the height of the skirt: “Qiyao Ruqun/ 齐腰襦裙” (waist-high ruqun) and “Qixiong Ruqun/ 齐胸襦裙” (chest-high ruqun).
“Qiyao Ruqun” is the kind of ruqun in which the waistband is on the waist. Both men and women can wear it. For women, the top’s collar can be parallel (left), crossed (middle), or u-shaped (right). Men’s ruqun are cross-collared only.

“Qixiong Ruqun”, on the other hand, has its waistband above the chest. The top’s collar can be parallel (left) or crossed (right). It’s only worn by women.

As seen in the photos above, ruqun is often accessorized with a long scarf called Pibo/披帛. Originally used to protect against wind and cold air, pibo gradually became an important feature of hanfu.
- Aoqun/袄裙 - a type of ruqun that became fashionable during the Ming Dynasty. It consists of a double-layered top called “ao/袄“ and a waist-high skirt (”qun”), hence “aoqun”. Unlike the “standard” ruqun that has the top tucked inside the skirt, the aoqun’s top is worn untucked, above the skirt. There are two types of “ao” - “short ao” and “long ao”. The “short ao” (left, right) reaches the waist, while the “long ao” (middle) covers the knees. Ao collars can be crossed (left, middle) or upright (right). Only worn by women.

- Unlike ruqun and aoqun which are made of separate top and bottom pieces, the Shenyi/深衣 style of hanfu consists of one-piece robes that wrap around the body once or several times. Quju/曲裾 (curved-hem robe) and Zhiju/直裾(straight-hem robe) are two types of shenyi. The quju (left, middle) is a robe in which the bottom hem of the left lapel spirals its way up to the waist of the wearer. Modern quju can come in a shortened version (middle) that reveals the skirt worn underneath. In contrast to the quju, the bottom hem of the zhiju (right) circles around levelly, creating a straight line. Quju and Zhiju are worn by both men and women.

- Beizi/褙子 - a parallel-collar “jacket” with side slits beginning at the armpit or at the waist. It can be secured at the front either with ties or a metal button. Extremely versatile, it can be long or short, have narrow or wide sleeves, and is worn by both men and women. During the Song Dynasty, it was popular to wear narrow-sleeved beizi over a chest undergarment and skirt/pants (middle). Another name for Ming Dynasty-style beizi is Pifeng/披风 (right). Pifeng collars can also be upright (not shown).

- Banbi/半臂 - a half-sleeve jacket worn by both men and women. It comes in various lengths and is usually worn over ruqun. Its collar can be parallel (left), crossed (middle), or u-shaped (right). When paired with ruqun, it can be worn tucked inside the skirt as well as over the skirt (untucked).

- Bijia/比甲 - a sleeveless jacket, usually worn over aoqun, that comes in various lengths and styles.

- Daxiushan/大袖衫 - large-sleeve robe commonly paired with ruqun. As its name indicates, its main feature is its broad sleeves. The length is at least 78 inches, and the width exceeds 40 inches. The material is generally thin and light, because it was originally created for wear in the summer.

Of course this doesn’t cover everything, but it describes the basic hanfu styles that appear most often on this blog. Hope this helps!

Yahoooooooooo!!!!
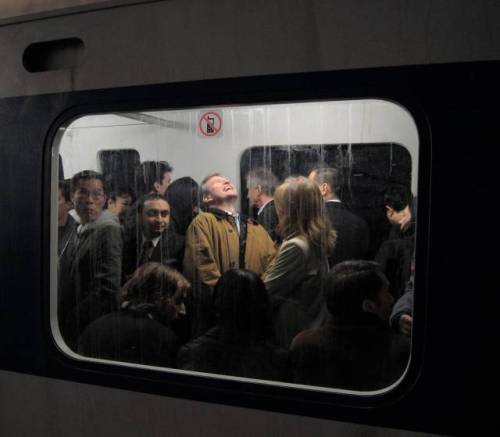






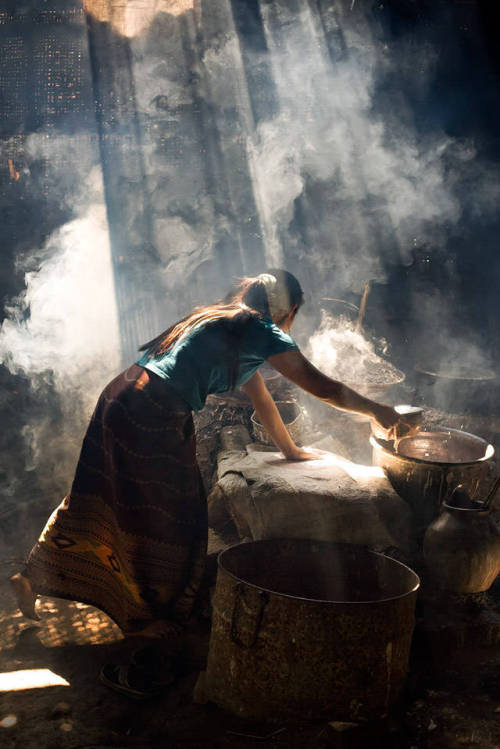

Photos That look Like Renaissance Paintings


The Shining (1980) dir. Stanley Kubrick
-
 jackalopeisaac liked this · 1 year ago
jackalopeisaac liked this · 1 year ago -
 fullyfunctionalminiaturebeehive reblogged this · 1 year ago
fullyfunctionalminiaturebeehive reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 fullyfunctionalminiaturebeehive liked this · 1 year ago
fullyfunctionalminiaturebeehive liked this · 1 year ago -
 curiobjd reblogged this · 1 year ago
curiobjd reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 loststarwarrior liked this · 1 year ago
loststarwarrior liked this · 1 year ago -
 sparrowchute liked this · 1 year ago
sparrowchute liked this · 1 year ago -
 blacknbluengray reblogged this · 1 year ago
blacknbluengray reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 blacknbluengray liked this · 1 year ago
blacknbluengray liked this · 1 year ago -
 cloudragons reblogged this · 1 year ago
cloudragons reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 cloudragons liked this · 1 year ago
cloudragons liked this · 1 year ago -
 jellyfishdungeon liked this · 1 year ago
jellyfishdungeon liked this · 1 year ago -
 catopi reblogged this · 1 year ago
catopi reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 katharynmarie liked this · 1 year ago
katharynmarie liked this · 1 year ago -
 rachels-dollhouse liked this · 1 year ago
rachels-dollhouse liked this · 1 year ago -
 creepydeaddoll liked this · 1 year ago
creepydeaddoll liked this · 1 year ago -
 curiobjd liked this · 1 year ago
curiobjd liked this · 1 year ago -
 denpamoo reblogged this · 1 year ago
denpamoo reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 denpamoo liked this · 1 year ago
denpamoo liked this · 1 year ago -
 godeepestmoonbouquet liked this · 1 year ago
godeepestmoonbouquet liked this · 1 year ago -
 rosslynpaladin reblogged this · 1 year ago
rosslynpaladin reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 rosslynpaladin liked this · 1 year ago
rosslynpaladin liked this · 1 year ago -
 kotilokiki liked this · 1 year ago
kotilokiki liked this · 1 year ago -
 renkorama liked this · 1 year ago
renkorama liked this · 1 year ago -
 sunnwwings-art liked this · 1 year ago
sunnwwings-art liked this · 1 year ago -
 jointed-custody reblogged this · 1 year ago
jointed-custody reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 blithefool liked this · 1 year ago
blithefool liked this · 1 year ago -
 bride-of-bigfoot reblogged this · 1 year ago
bride-of-bigfoot reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 hey-bug liked this · 1 year ago
hey-bug liked this · 1 year ago -
 ponderousorb liked this · 1 year ago
ponderousorb liked this · 1 year ago -
 kingiceburg liked this · 1 year ago
kingiceburg liked this · 1 year ago -
 tenasilvertear reblogged this · 1 year ago
tenasilvertear reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 balljointsandlace reblogged this · 1 year ago
balljointsandlace reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 giraffeseatingcake liked this · 1 year ago
giraffeseatingcake liked this · 1 year ago -
 bitronic liked this · 1 year ago
bitronic liked this · 1 year ago -
 flowerpants-org liked this · 1 year ago
flowerpants-org liked this · 1 year ago -
 sirenhighway liked this · 1 year ago
sirenhighway liked this · 1 year ago -
 sillyartcat liked this · 1 year ago
sillyartcat liked this · 1 year ago -
 queenofsquids reblogged this · 1 year ago
queenofsquids reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 queenofsquids liked this · 1 year ago
queenofsquids liked this · 1 year ago -
 several-flies liked this · 1 year ago
several-flies liked this · 1 year ago -
 zakubabbles liked this · 1 year ago
zakubabbles liked this · 1 year ago -
 the-most-medium-lesbian reblogged this · 1 year ago
the-most-medium-lesbian reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 the-most-medium-lesbian liked this · 1 year ago
the-most-medium-lesbian liked this · 1 year ago -
 fullyfunctionalminiaturebeehive reblogged this · 1 year ago
fullyfunctionalminiaturebeehive reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 groovyblueworld reblogged this · 1 year ago
groovyblueworld reblogged this · 1 year ago

she/her. migrating here from Instagram. Here to look at dolls and have fun. forever pro artist 😎.
231 posts