Er-zico - Leisure







More Posts from Er-zico and Others



Inside the new MTA K-9 training center in Stormville, New York
At a sprawling campus north of New York City, a 3-year-old German Shepherd named Johnny frantically sniffed through seats and luggage bins on an out-of-service commuter rail train trying to catch a whiff of hidden explosive.
When Johnny found a black bag with the faint scent of C-4, commonly used to blow up buildings, he sat statue-still at attention, alerting handler Kevin Pimpinelli of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority police to his discovery. In return, Pimpinelli rewarded him with a prized chew toy.
“In the real world, he can find the explosive before it gets on the train,” Pimpinelli said. "Our job is to try to prevent that device getting in.”
Johnny is one of 50 of the transit authority’s police dogs being trained at its $13 million, 72-acre training center in Stormville, New York, about 70 miles (113 km) north of New York City.
The Metropolitan Transit Authority operates subways, buses, and railroads in New York, New Jersey and Connecticut and provides more than 2.7 billion trips each year to travelers, according to the agency’s website.
The canine training center, the biggest facility of its kind in the United States, begins full operations on June 8, 2016, and will train dogs used by police across the nation.
Amid attacks including the March bombing of a Brussels train station and airport, which killed 32 people, U.S. police agencies see highly trained dogs as key to maintaining security in large public spaces.
Their sharp sense of smell exceeds the ability of humans and machines to detect explosives and track suspects.
“The importance of this facility is growing daily because we get more threats daily,” said MTA Police Lieutenant John Kerwick, who oversees the agency’s police-dog training operations.
The dogs are carefully selected. Only about one in 30 dogs assessed at breeders are chosen for the canine police force. The dogs are mainly German Shepherds like Johnny or Belgian Malinois, high-energy breeds known for a strong desire to work.
HIGHLY TRAINED SNIFFERS
Those handpicked few are trained to detect threats such as explosives or contraband including narcotics, said David Ferland, who heads the United States Police Canine Association (USPCA).
The MTA dog training facility includes rooms modeled after classrooms and bus stations, 26 kennels and a veterinary clinic. Outside, there are nine buses, ponds and train cars at the end of a retired Metro North railroad track. All are used to train the dogs.
While there is no central database tracking the number of police dogs in service in the United States, the USPCA estimates the figure at about 10,000.
Ferland said interest in training police dogs has risen dramatically since the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks on New York and Washington, evidence of a sense of urgency in combating similar threats.
“Before 9/11, there were only a handful of these training sites,” Ferland said. “Now, there are training facilities an hour’s drive from every major city in the U.S.”
The Stormville facility will offer initial 12-week courses where dogs learn to detect explosives and the refresher courses that dogs are required to take each month.
The canines are exposed to heights, loud noises, fumes, moving vehicles and other distractions they would face on the job.
Typically they work until about the age of 10, after which they normally go on to live as pets in their primary handlers’ homes.
“They’re like family,” said Officer Keith Flood with his three-year-old black Shepherd-Malinois mix named Doc, after finishing a training exercise. (Reuters)
See more images of the K-9 training center on Yahoo News!
Chicago task force releases landmark report, calls on Police Chief to acknowledge racism in police force
Yesterday, Chicago’s Police Accountability Task Force released its final report. Historically, the report called on the newly appointed Chicago Police Superintendent to acknowledge the force’s “history of racial disparity and discrimination.” Many believe the report, which many believe forced Mayor Rahm Emanuel to publicly acknowledge the Chicago Police Department’s continued issues with racism and to consider dismantling the city’s widely criticized Internal Police Review Board.
The task force was established in response to the public outcry in the wake of the death of Laquan McDonald, who was shot 16 times while running away from a Chicago Police Officer. The task force “dug deeper into the complaints of so many about the callous and disrespectful way in which they had been treated by some officers” within the CPD, and recommended sweeping changes to what it described as “systemic problems in CPD.”
The source of the current state of mistrust and animosity between the public and the CPD, it found, was the result of
racism
a mentality in CPD that the ends justify the means
a failure to make accountability a core value and imperative within CPD
a significant underinvestment in human capital



Below are the recommendations of the task force:
How We Propose to Empower People.
Create a Community Safety Oversight Board, allowing the community to have a powerful platform and role in the police oversight system.
Implement a citywide Reconciliation Process beginning with the Superintendent publicly acknowledging CPD’s history of racial disparity and discrimination, and making a public commitment to cultural change.
Replace CAPS with localized Community Empowerment and Engagement Districts (CEED) for each of the city’s 22 police districts, and support them accordingly. Under CEED, district Commanders and other leadership would work with local stakeholders to develop tailored community policing strategies and partnerships.
Renew commitment to beat-based policing and expand community patrols so that officers learn about and get to know the communities they serve, and community members take an active role in partnering with the police.
Reinvigorate community policing as a core philosophy and approach that informs actions throughout the department.
Evaluate and improve the training officers receive with respect to youth so that they are prepared to engage in ways that are age-appropriate, trauma-informed and based in a restorative justice model.
Require CPD and the police oversight system to be more transparent and release to the public incident-level information on arrests, traffic and investigatory stops, officer weapon use and disciplinary cases.
Host citywide summits jointly sponsored by the Mayor and the President of the Cook County Board to develop and implement comprehensive criminal justice reform.
Encourage the Mayor and President of the Cook County Board to work together to develop and implement programs that address socioeconomic justice and equality, housing segregation, systemic racism, poverty, education, health and safety.
Adoption of a citywide protocol allowing arrestees to make phone calls to an attorney and/or family member(s) within one hour of arrest.
Implementation of citywide “Know Your Rights” training for youth.
How We Propose to Address the Inadequate Emphasis on Accountability
Create a dedicated Inspector General for Public Safety, which would independently audit and monitor CPD and the police oversight system, including for patterns of racial bias.
Replace the Independent Police Review Authority with a new and fully transparent and accountable Civilian Police Investigative Agency, which will enhance structural protections, powers and resources for investigating serious cases of police misconduct, even in the absence of sworn complaints. The new CPIA should ensure an accessible, professional and supportive complaint process.
Implement a data-driven, best-in-class Early Intervention System for CPD to identify officers with problems before they become problems for the community.
Fundamentally change provisions in the collective bargaining agreements that are impediments to accountability, such as allowing for anonymous complaints, eliminating the ability to change statements after reviewing video and removing the requirement to destroy complaint records.
Fully implement the first-in-the-nation written video release policy for officer-involved shootings.
Expand CPD’s body cam pilot program.
Require that all disciplinary information be provided online so that citizens can track complaints and discipline histories.
How We Propose to Address Other Systemic and Longstanding Problems
Establish for the first time in Chicago a Deputy Chief of Diversity and Inclusion in CPD.
Implement policies to dismantle the institutionalization of the police “code of silence,” including substantial changes to the collective bargaining agreements between the police and the City, ending command channel review, reforming the role of CPD supervisors and pattern and practice analysis.
Establish a smart 911 system for OEMC, allowing residents to pre-enter information on mental health or other issues that would be instantly available to OEMC operators.
Create a multi-layer co-responder system where mental health providers work with OEMC and CPD to link individuals to treatment.
Expand significantly the Crisis Intervention System for CPD and other first responders.
Create a “Mental Health Critical Response Unit” within CPD that is responsible for mental health crisis response functions, training, support, community outreach and engagement, cross-agency coordination and data collection.
Create a hotline for CPD members, whether civilian or sworn, to lodge complaints, and develop a third-party system for the processing and follow-up of all comments and complaints reported to the hotline.







The star of “Grey’s Anatomy”, Jesse Williams, was presented a Humanitarian award at the BET Awards on Sunday, June 26. It’s a well-deserved win since Jesse has been fighting for equal rights for Black people and supporting the Black Lives Matter for a really long time.
If you happened to miss it, watch the full speech here.
#BlackLivesMatter
#BETAwards








Read the full story here.
10 Ways to Look After Your Mental Wellbeing (with added kitties)
1. Talk about your feelings
Talking about your feelings can help you stay in good mental health and deal with times when you feel troubled.

2. Keep active
Regular exercise can boost your self-esteem and can help you concentrate, sleep, and look and feel better. Exercise keeps the brain and your other vital organs healthy, and is also a significant benefit towards improving your mental health.

3. Eat well
Your brain needs a mix of nutrients in order to stay healthy and function well, just like the other organs in your body. A diet that’s good for your physical health is also good for your mental health.

4. Drink sensibly
We often drink alcohol to change our mood. Some people drink to deal with fear or loneliness, but the effect is only temporary.
When the drink wears off, you feel worse because of the way the alcohol has affected your brain and the rest of your body. Drinking is not a good way to manage difficult feelings.

5. Keep in touch
There’s nothing better than catching up with someone face to face, but that’s not always possible. You can also give them a call, drop them a note, or chat to them online instead. Keep the lines of communication open: it’s good for you!

6. Ask for help
None of us are superhuman. We all sometimes get tired or overwhelmed by how we feel or when things don’t go to plan.
If things are getting too much for you and you feel you can’t cope, ask for help. Your family or friends may be able to offer practical help or a listening ear.
Local services are there to help you.

7. Take a break
A change of scene or a change of pace is good for your mental health.
It could be a five-minute pause from cleaning your kitchen, a half-hour lunch break at work, or a weekend exploring somewhere new. A few minutes can be enough to de-stress you. Give yourself some ‘me time’.

8. Do something you’re good at
What do you love doing? What activities can you lose yourself in? What did you love doing in the past?
Enjoying yourself can help beat stress. Doing an activity you enjoy probably means you’re good at it, and achieving something boosts your self-esteem.

9. Accept who you are
We’re all different. It’s much healthier to accept that you’re unique than to wish you were more like someone else. Feeling good about yourself boosts your confidence to learn new skills, visit new places and make new friends. Good self-esteem helps you cope when life takes a difficult turn.

10. Care for others
‘Friends are really important… We help each other whenever we can, so it’s a two-way street, and supporting them uplifts me.’
Caring for others is often an important part of keeping up relationships with people close to you. It can even bring you closer together.

(Source: mentalhealth.org.uk)
Solitude matters, and for some people, it’s the air they breathe
Susan Cain (via fyp-psychology)





Meoww!
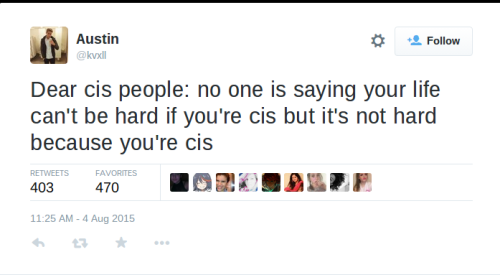
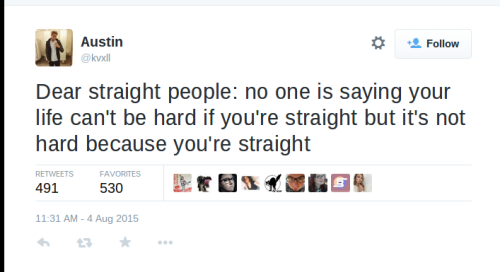
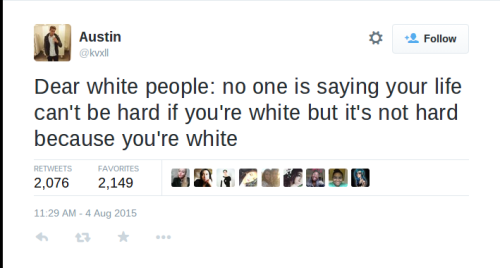
why is this so hard to understand










End the epidemic, end the stigma. Understand the actual risks. Donate to a local HIV organziation. Follow SexEdPlus for more stuff like this.
-
 mymaysworld liked this · 1 year ago
mymaysworld liked this · 1 year ago -
 indian-honey liked this · 6 years ago
indian-honey liked this · 6 years ago -
 wellnessinspired liked this · 6 years ago
wellnessinspired liked this · 6 years ago -
 cold-student-tree liked this · 7 years ago
cold-student-tree liked this · 7 years ago -
 sango-nakamuro liked this · 7 years ago
sango-nakamuro liked this · 7 years ago -
 obsessive-shipper reblogged this · 7 years ago
obsessive-shipper reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 crysmah liked this · 8 years ago
crysmah liked this · 8 years ago -
 adeeburr reblogged this · 8 years ago
adeeburr reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 gargle-floss liked this · 8 years ago
gargle-floss liked this · 8 years ago -
 honeylemony reblogged this · 8 years ago
honeylemony reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 honeylemony liked this · 8 years ago
honeylemony liked this · 8 years ago -
 mr-flamel reblogged this · 8 years ago
mr-flamel reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mr-flamel liked this · 8 years ago
mr-flamel liked this · 8 years ago -
 mdescapes reblogged this · 8 years ago
mdescapes reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mdescapes liked this · 8 years ago
mdescapes liked this · 8 years ago -
 xbittercheri liked this · 8 years ago
xbittercheri liked this · 8 years ago -
 matoradostdaram reblogged this · 8 years ago
matoradostdaram reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 thedreamoracle reblogged this · 8 years ago
thedreamoracle reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 kewpie-pie liked this · 8 years ago
kewpie-pie liked this · 8 years ago -
 zyin reblogged this · 8 years ago
zyin reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 deaddemonsdestruction liked this · 8 years ago
deaddemonsdestruction liked this · 8 years ago -
 myluckyerror liked this · 8 years ago
myluckyerror liked this · 8 years ago -
 naram--sin reblogged this · 8 years ago
naram--sin reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 naram--sin liked this · 8 years ago
naram--sin liked this · 8 years ago -
 bollywood-ishq reblogged this · 8 years ago
bollywood-ishq reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 sugarandscars liked this · 8 years ago
sugarandscars liked this · 8 years ago -
 freekarina reblogged this · 8 years ago
freekarina reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 exhaustediaryofaweeb-blog liked this · 8 years ago
exhaustediaryofaweeb-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 yeahhimchillin liked this · 8 years ago
yeahhimchillin liked this · 8 years ago -
 kappuccinos liked this · 8 years ago
kappuccinos liked this · 8 years ago -
 dragonwriter142 reblogged this · 8 years ago
dragonwriter142 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 misssterious-canadian-empire reblogged this · 8 years ago
misssterious-canadian-empire reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mahomegurlnagini reblogged this · 8 years ago
mahomegurlnagini reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 er-zico reblogged this · 8 years ago
er-zico reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 raindrop-of-love reblogged this · 9 years ago
raindrop-of-love reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 stroonicorn reblogged this · 9 years ago
stroonicorn reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 slide3blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
slide3blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 slide3blog liked this · 9 years ago
slide3blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 thesunisashe reblogged this · 9 years ago
thesunisashe reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 beelord-lordofbees reblogged this · 9 years ago
beelord-lordofbees reblogged this · 9 years ago
Dear Readers,Welcome to my personal blog. I'm Sabyasachi Naik (Zico,24).An Agnostic,deeply NON religious(atheist), and Secular Progressive Civil Engineer . I'm brown and proud to be an Indian tribe. “I want to say a word to the Brahmins: In the name of God, religion, sastras you have duped us. We were the ruling people. Stop this life of cheating us from this year. Give room for rationalism and humanism.” ― Periyar E.V. Ramasamy
198 posts