I’m Never Leaving This Website
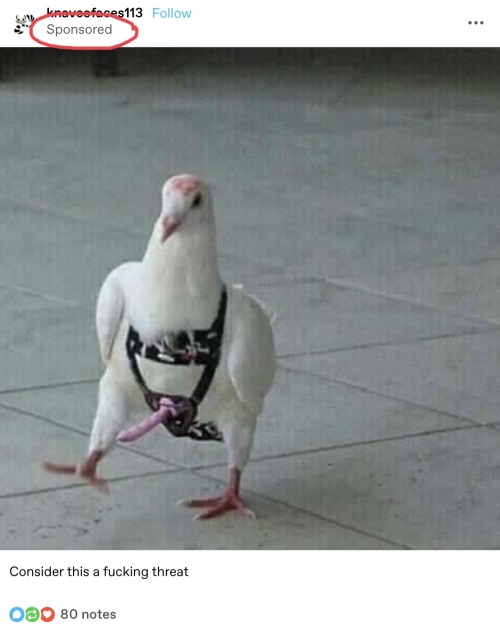

I’m never leaving this website
More Posts from Eggxecutive-dysfunction and Others

The Colorful Clouds of Rho Ophiuchi : The many spectacular colors of the Rho Ophiuchi (oh’-fee-yu-kee) clouds highlight the many processes that occur there. The blue regions shine primarily by reflected light. Blue light from the Rho Ophiuchi star system and nearby stars reflects more efficiently off this portion of the nebula than red light. The Earth’s daytime sky appears blue for the same reason. The red and yellow regions shine primarily because of emission from the nebula’s atomic and molecular gas. Light from nearby blue stars - more energetic than the bright star Antares - knocks electrons away from the gas, which then shines when the electrons recombine with the gas. The dark brown regions are caused by dust grains - born in young stellar atmospheres - which effectively block light emitted behind them. The Rho Ophiuchi star clouds, well in front of the globular cluster M4 visible here on the upper right, are even more colorful than humans can see - the clouds emits light in every wavelength band from the radio to the gamma-ray. via NASA

Saturn and Jupiter in Summer 2020 : During this northern summer Saturn and Jupiter were both near opposition, opposite the Sun in planet Earth’s sky. Their paired retrograde motion, seen about every 20 years, is followed from 19 June through 28 August in this panoramic composite as they wander together between the stars in western Capricornus and eastern Sagittarius. But this December’s skies find them drawing even closer together. Jupiter and Saturn are now close, bright celestial beacons in the west after sunset. On solstice day December 21 they will reach their magnificent 20 year Great Conjunction. Then the two largest worlds in the Solar System will appear in Earth’s sky separated by only about 1/5 the apparent diameter of a Full Moon. via NASA

Barn swallow … Cupola Park, Millsboro, Delaware … 7/11/21

Arches Across an Arctic Sky : What are these two giant arches across the sky? Perhaps the more familiar one, on the left, is the central band of our Milky Way Galaxy. This grand disk of stars and nebulas here appears to encircle much of the southern sky. Visible below the stellar arch is the rusty-orange planet Mars and the extended Andromeda galaxy. For a few minutes during this cold artic night, a second giant arch appeared to the right, encircling part of the northern sky: an aurora. Auroras are much closer than stars as they are composed of glowing air high in Earth’s atmosphere. Visible outside the green auroral arch is the group of stars popularly known as the Big Dipper. The featured digital composite of 18 images was captured in mid-December over the in Norway. via NASA
( <= green bean

if i could turn into an eel. well that’d be ideal.
the plot chickens

Star Cluster R136 Breaks Out : In the center of nearby star-forming region lies a huge cluster containing some of the largest, hottest, and most massive stars known. These stars, known collectively as star cluster R136, part of the Tarantula Nebula, were captured in the featured image in visible light in 2009 through the Hubble Space Telescope. Gas and dust clouds in the Tarantula Nebula, have been sculpted into elongated shapes by powerful winds and ultraviolet radiation from these hot cluster stars. The Tarantula Nebula lies within a neighboring galaxy known as the Large Magellanic Cloud and is located a mere 170,000 light-years away. via NASA



Щегол черноголовый (Carduelis carduelis) - European Goldfinch - Птица 2018 года в Беларуси!, Film Studio Aves
-
 flairina reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
flairina reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 demonfaggotfurry reblogged this · 1 month ago
demonfaggotfurry reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 grazihilario6 liked this · 1 month ago
grazihilario6 liked this · 1 month ago -
 fish3d liked this · 1 month ago
fish3d liked this · 1 month ago -
 clowderofcloudies reblogged this · 1 month ago
clowderofcloudies reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 seesmuffin liked this · 2 months ago
seesmuffin liked this · 2 months ago -
 kitharion reblogged this · 2 months ago
kitharion reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 jamboreeguy reblogged this · 2 months ago
jamboreeguy reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 onyx-the-rat liked this · 2 months ago
onyx-the-rat liked this · 2 months ago -
 amor-vivere liked this · 3 months ago
amor-vivere liked this · 3 months ago -
 manofworm liked this · 3 months ago
manofworm liked this · 3 months ago -
 obertheffect liked this · 3 months ago
obertheffect liked this · 3 months ago -
 whorcerous-origin reblogged this · 3 months ago
whorcerous-origin reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 flairina reblogged this · 3 months ago
flairina reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 nnandmm-archived-hard liked this · 3 months ago
nnandmm-archived-hard liked this · 3 months ago -
 morally-grey-mind reblogged this · 4 months ago
morally-grey-mind reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 iwanttobepersephone liked this · 4 months ago
iwanttobepersephone liked this · 4 months ago -
 reblogagainandagain liked this · 4 months ago
reblogagainandagain liked this · 4 months ago -
 lordhavemercyyyyy liked this · 5 months ago
lordhavemercyyyyy liked this · 5 months ago -
 dinosaursock liked this · 5 months ago
dinosaursock liked this · 5 months ago -
 circo-atayde-hermanos reblogged this · 5 months ago
circo-atayde-hermanos reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 this-is-supposed-to-be-a-blog reblogged this · 5 months ago
this-is-supposed-to-be-a-blog reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 7-a-m liked this · 5 months ago
7-a-m liked this · 5 months ago -
 cemeterygrace liked this · 5 months ago
cemeterygrace liked this · 5 months ago -
 transunicorn reblogged this · 6 months ago
transunicorn reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 what-in-gay-nation liked this · 6 months ago
what-in-gay-nation liked this · 6 months ago -
 didi-on-the-side liked this · 6 months ago
didi-on-the-side liked this · 6 months ago -
 its-always-the-witching-hour liked this · 6 months ago
its-always-the-witching-hour liked this · 6 months ago -
 nomorepainwithslash reblogged this · 6 months ago
nomorepainwithslash reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 sagamivulpix liked this · 6 months ago
sagamivulpix liked this · 6 months ago -
 theynipulation liked this · 6 months ago
theynipulation liked this · 6 months ago -
 tonguingthegods reblogged this · 6 months ago
tonguingthegods reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 paperheartinaglasschest liked this · 7 months ago
paperheartinaglasschest liked this · 7 months ago -
 kozmoglitch reblogged this · 7 months ago
kozmoglitch reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 kozmoglitch liked this · 7 months ago
kozmoglitch liked this · 7 months ago -
 alexagaricwithalittlebitofspice reblogged this · 7 months ago
alexagaricwithalittlebitofspice reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 merakiq liked this · 7 months ago
merakiq liked this · 7 months ago -
 louisthiccsexyglitteryass liked this · 7 months ago
louisthiccsexyglitteryass liked this · 7 months ago -
 123212321 liked this · 7 months ago
123212321 liked this · 7 months ago -
 local-lesbrarian liked this · 7 months ago
local-lesbrarian liked this · 7 months ago -
 serephimboys liked this · 7 months ago
serephimboys liked this · 7 months ago -
 finndly reblogged this · 7 months ago
finndly reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 finndly liked this · 7 months ago
finndly liked this · 7 months ago -
 spootz-spootie-spootify reblogged this · 7 months ago
spootz-spootie-spootify reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 ghibli22 reblogged this · 7 months ago
ghibli22 reblogged this · 7 months ago
