If The Earth Was Flat, Cats Would Have Pushed Everything Off Of It By Now.
If the Earth was flat, cats would have pushed everything off of it by now.
More Posts from Dragons-barb and Others
Insidious

The myth that panic, looting, and antisocial behavior increases during the apocalypse (or apocalyptic-like scenarios) is in fact a myth—and has been solidly disproved by multiple scientific studies. The National Earthquake Hazards Reduction Program, a research group within the United States Federal Emergency Management Administration (FEMA), has produced research that shows over and over again that “disaster victims are assisted first by others in the immediate vicinity and surrounding area and only later by official public safety personnel […] The spontaneous provision of assistance is facilitated by the fact that when crises occur, they take place in the context of ongoing community life and daily routines—that is, they affect not isolated individuals but rather people who are embedded in networks of social relationships.” (Facing Hazards and Disasters: Understanding Human Dimensions, National Academy of Sciences, 2006). Humans do not, under the pressure of an emergency, socially collapse. Rather, they seem to display higher levels of social cohesion, despite what media or government agents might expect…or portray on TV. Humans, after the apocalypse, band together in collectives to help one another—and they do this spontaneously. Disaster response workers call it ‘spontaneous prosocial helping behavior’, and it saves lives.
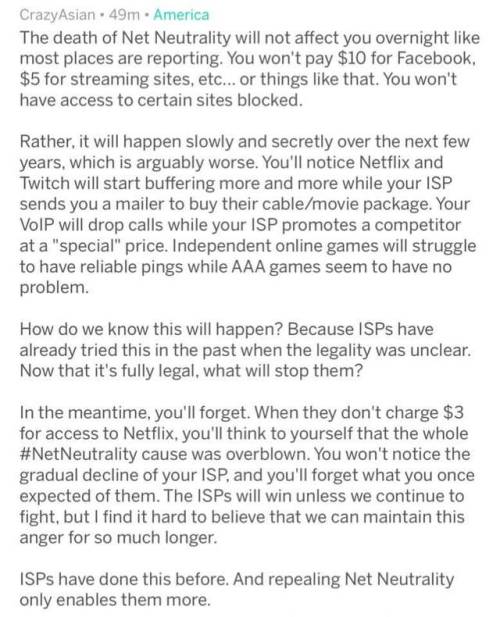
We're Just Having Sandwiches for Dinner, So You Won't Miss Anything: Identifying Identity Through a Critical Lens
Sounds legit

Mine is “Activating forms of oppression as performance: the phenomenology of tunglr.hell.”
Hand-fasting sash I made for my son's and daughter-in-law's wedding. It's the first time I've done embroidery and I'm quite happy with it ( they are, too!)
- Green, white, and silver were their chosen wedding colors.
- Blue and red are the colors representing the words each/both choose for what marriage means to them (mostly based on Druidic and Wicca traditions).
- Circles throughout symbolizing the Summer Solstice, their wedding date.
- On the white side, the flowers around their names and wedding date are traditional Bohemian designs in honor of Tya's heritage.
- The style on the green side is generally Celtic (a good portion of Nathan's heritage and a style that resonates with both of them - the music list was amazing!).
- Tree of Life and endless knots represent the intertwining of their lives and growth / nurturing / life (Celtic and Norse traditions, although I couldn't fit all 9 roots of Yggdrasil).
- On either end are the masculine (sun) and feminine (moon) with one "protecting" the other, allowing the other the freedom from a safe place to explore, create, and become their best selves.


Black Holes: Seeing the Invisible!
Black holes are some of the most bizarre and fascinating objects in the cosmos. Astronomers want to study lots of them, but there’s one big problem – black holes are invisible! Since they don’t emit any light, it’s pretty tough to find them lurking in the inky void of space. Fortunately there are a few different ways we can “see” black holes indirectly by watching how they affect their surroundings.

Speedy stars
If you’ve spent some time stargazing, you know what a calm, peaceful place our universe can be. But did you know that a monster is hiding right in the heart of our Milky Way galaxy? Astronomers noticed stars zipping superfast around something we can’t see at the center of the galaxy, about 10 million miles per hour! The stars must be circling a supermassive black hole. No other object would have strong enough gravity to keep them from flying off into space.

Two astrophysicists won half of the Nobel Prize in Physics last year for revealing this dark secret. The black hole is truly monstrous, weighing about four million times as much as our Sun! And it seems our home galaxy is no exception – our Hubble Space Telescope has revealed that the hubs of most galaxies contain supermassive black holes.
Shadowy silhouettes
Technology has advanced enough that we’ve been able to spot one of these supermassive black holes in a nearby galaxy. In 2019, astronomers took the first-ever picture of a black hole in a galaxy called M87, which is about 55 million light-years away. They used an international network of radio telescopes called the Event Horizon Telescope.

In the image, we can see some light from hot gas surrounding a dark shape. While we still can’t see the black hole itself, we can see the “shadow” it casts on the bright backdrop.
Shattered stars
Black holes can come in a smaller variety, too. When a massive star runs out of the fuel it uses to shine, it collapses in on itself. These lightweight or “stellar-mass” black holes are only about 5-20 times as massive as the Sun. They’re scattered throughout the galaxy in the same places where we find stars, since that’s how they began their lives. Some of them started out with a companion star, and so far that’s been our best clue to find them.

Some black holes steal material from their companion star. As the material falls onto the black hole, it gets superhot and lights up in X-rays. The first confirmed black hole astronomers discovered, called Cygnus X-1, was found this way.
If a star comes too close to a supermassive black hole, the effect is even more dramatic! Instead of just siphoning material from the star like a smaller black hole would do, a supermassive black hole will completely tear the star apart into a stream of gas. This is called a tidal disruption event.
Making waves
But what if two companion stars both turn into black holes? They may eventually collide with each other to form a larger black hole, sending ripples through space-time – the fabric of the cosmos!

These ripples, called gravitational waves, travel across space at the speed of light. The waves that reach us are extremely weak because space-time is really stiff.
Three scientists received the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics for using LIGO to observe gravitational waves that were sent out from colliding stellar-mass black holes. Though gravitational waves are hard to detect, they offer a way to find black holes without having to see any light.
We’re teaming up with the European Space Agency for a mission called LISA, which stands for Laser Interferometer Space Antenna. When it launches in the 2030s, it will detect gravitational waves from merging supermassive black holes – a likely sign of colliding galaxies!

Rogue black holes
So we have a few ways to find black holes by seeing stuff that’s close to them. But astronomers think there could be 100 million black holes roaming the galaxy solo. Fortunately, our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will provide a way to “see” these isolated black holes, too.

Roman will find solitary black holes when they pass in front of more distant stars from our vantage point. The black hole’s gravity will warp the starlight in ways that reveal its presence. In some cases we can figure out a black hole’s mass and distance this way, and even estimate how fast it’s moving through the galaxy.
For more about black holes, check out these Tumblr posts!
⚫ Gobble Up These Black (Hole) Friday Deals!
⚫ Hubble’s 5 Weirdest Black Hole Discoveries
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Let's mash up Frederic Brown's "Knock" a bit and tell me who's at the door...
The last person in the universe sat alone in a room. There was a knock on the door...
It's the Veiled Woman who's finally going to explain to me what the fuck.
So chill....
and I have no idea why...despite mayo jars being way more practical, and yet I still have cookie tins full of buttons.
A whole generation of women collectively decided, without the help of the internet, to use cookie tins for storing sewing supplies.

Second picture of the book illustration. This time the chapter is about Melanin. Big topic in the text are ravens, so… why not ravens in the illustration too. It is 7 in the morning now and I am tired.
-
 whostolemygoldfish liked this · 2 years ago
whostolemygoldfish liked this · 2 years ago -
 whynotwhenyoucould reblogged this · 2 years ago
whynotwhenyoucould reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 endoyamato reblogged this · 3 years ago
endoyamato reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 kazeot reblogged this · 3 years ago
kazeot reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 hemi-demi-semiquaver liked this · 3 years ago
hemi-demi-semiquaver liked this · 3 years ago -
 postpostskriptum reblogged this · 3 years ago
postpostskriptum reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 singingrainbows reblogged this · 3 years ago
singingrainbows reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 crustybreadrolls reblogged this · 5 years ago
crustybreadrolls reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 cunnilingusdingus reblogged this · 5 years ago
cunnilingusdingus reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 cunnilingusdingus liked this · 5 years ago
cunnilingusdingus liked this · 5 years ago -
 skinnyswallow reblogged this · 6 years ago
skinnyswallow reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 skinnyswallow liked this · 6 years ago
skinnyswallow liked this · 6 years ago -
 minnie-the-bee liked this · 6 years ago
minnie-the-bee liked this · 6 years ago