What Would Have Once Sounded Like A Far-fetched Feminist Fantasy – Women Forming The Majority Of A

What would have once sounded like a far-fetched feminist fantasy – women forming the majority of a parliament – is a reality in one country in the world, Rwanda.
In fact, women are making gains throughout all of Africa, but these achievements have been met with a loud silence from the western feminist movement.
African women are blazing a feminist trail - why don’t we hear their voices? (The Guardian)
More Posts from Dotmpotter and Others

We often take our surroundings for granted. This is an excellent piece that outlines some of the problems and proposes a cool way to keep our forests going.


Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a key building block for next-generation devices. It takes features from diamonds, one of the toughest materials in the world, and combines them with features of silicon, our ubiquitous semiconductor technology in electronics to make a very new kind of material for power electronics. SiC can more efficiently handle higher voltage and three times the amount of energy compared to silicon chips, allowing us to run everything from locomotives to planes and wind farms faster and more efficiently.










Brand: Christie Brown
Designer: Aisha Obuobi
Coupe de Classe Winter 2015 Collection
Tumblr: cutfromadiffcloth.tumblr.com | Twitter: @IAM_CFDC | Instagram: @IAMCFDC | Facebook: CUT FROM A DIFFERENT CLOTH | Website: www.cutfromadiffcloth.com
The study authors have calculated the cost of the “lost ecosystem services value” our planet has suffered in the last decade and a half. According to their calculations, the loss due to land degradation averages US $43,400 to $72,000 per square km, some US $870 to $1,450 per person, globally each year. The percentage of the world’s land affected by land degradation has grown a lot in the last decades – it has doubled between the late 1970s and the early 2000s. And the process is far from its end.
“This study by ELD shows the immediate and global impact of land degradation and highlights that actions to tackle it pay off,” Karmenu Vella, European Commissioner for Environment, Fisheries and Maritime Affairs commented on the paper.
“Increased land degradation is also one of the factors that can lead to migration and it is being exacerbated by climate change. On our planet, the area affected by drought has doubled in 40 years. One third of Africa is threatened by desertification. As President Juncker said in his State of the Union speech last week, climate refugees will become a new challenge – if we do not act swiftly.”

UAV Will Determine Best Locations for Wind Energy
Citizen Maths: free/open adult math education for practical real-world numeracy

Without scientific understanding, we don’t run the government, the government runs us” -Carl Sagan, in his final interview.
Last week we released a big batch of new CC-BY licensed content for Citizen Maths a free online course for adults who want to improve their grasp of maths at what in the UK is known as Level 2 (the level that 16 year old school leavers are expected to reach, though many do not).
(Image: Jonathan Worth, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The new course content covers the powerful ideas in maths of “uncertainty” and “representation”. It sits alongside the content for “proportion” which was published last year.
Learning about each idea is supported by a mix of short video tutorials, practical exercises, and quizzes. The practical exercises use a range of approaches including:
* tools like spreadsheets;
* purpose-built self-standing “apps” of various kinds;
* coding in Scratch.
Each powerful idea is shown in action in several different contexts. For example, “uncertainty” involves the following situations:
* Making decisions — value of insurance, risk comparisons;
* Judging — the meaning of cancer screening results;
* Gaming — appreciating odds in roulette, dice, horse-racing;
* Modelling — the uncertain prediction of the weather.
The powerful ideas and the situations in which they are shown in action have been selected in consultation with maths teachers, and with organisations familiar with the learning needs of adults.
http://boingboing.net/2015/11/03/citizen-maths-freeopen-math.html
Meet Hannah Herbst, a 15-year-old from Boca Raton, Florida, who just might be the nation’s top young scientist. Earlier this month, Herbst won a $25,000 prize with a very cheap invention: a prototype probe that converts the movement of the ocean’s currents into energy and costs just $12 to make. Out of nine other middle-school finalists, Herbst was awarded first place in the 2015 Discovery Education 3M Young Scientist Challenge.
This 15-Year-Old’s Invention Converts Ocean Currents Into Energy—for Cheap | GOOD
Greenland is Melting Away
This river is one of a network of thousands at the front line of climate change.
By NYTimes: Coral Davenport, Josh Haner, Larry Buchanan and Derek Watkins
On the Greenland Ice Sheet — The midnight sun still gleamed at 1 a.m. across the brilliant expanse of the Greenland ice sheet. Brandon Overstreet, a doctoral candidate in hydrology at the University of Wyoming, picked his way across the frozen landscape, clipped his climbing harness to an anchor in the ice and crept toward the edge of a river that rushed downstream toward an enormous sinkhole.
If he fell in, “the death rate is 100 percent,” said Mr. Overstreet’s friend and fellow researcher, Lincoln Pitcher.
But Mr. Overstreet’s task, to collect critical data from the river, is essential to understanding one of the most consequential impacts of global warming. The scientific data he and a team of six other researchers collect here could yield groundbreaking information on the rate at which the melting of the Greenland ice sheet, one of the biggest and fastest-melting chunks of ice on Earth, will drive up sea levels in the coming decades. The full melting of Greenland’s ice sheet could increase sea levels by about 20 feet. [bold/itals mine]
“We scientists love to sit at our computers and use climate models to make those predictions,” said Laurence C. Smith, head of the geography department at the University of California, Los Angeles, and the leader of the team that worked in Greenland this summer. “But to really know what’s happening, that kind of understanding can only come about through empirical measurements in the field.”
For years, scientists have studied the impact of the planet’s warming on the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets. But while researchers have satellite images to track the icebergs that break off, and have created models to simulate the thawing, they have little on-the-ground information and so have trouble predicting precisely how fast sea levels will rise.
Dire report by three excellent Times journalists covering a team of researchers camped out on the icesheets of Greenland. The conclusion is that glaciers and land ice are melting at rates far higher than scientists anticipated, or that climate models have shown. This means that sea levels are rising faster than projected, and many coastal communities are in grave danger.
The economic impacts are incalculable.


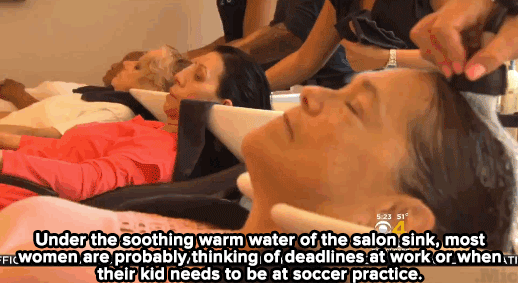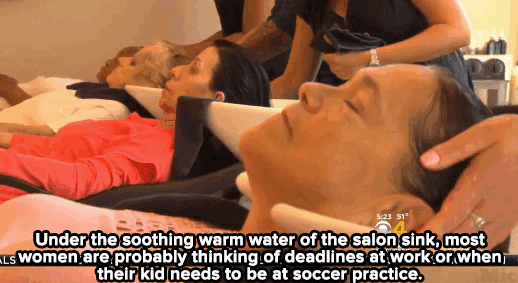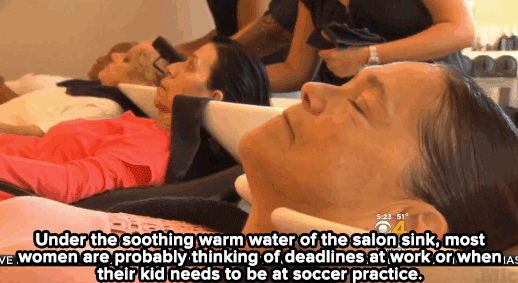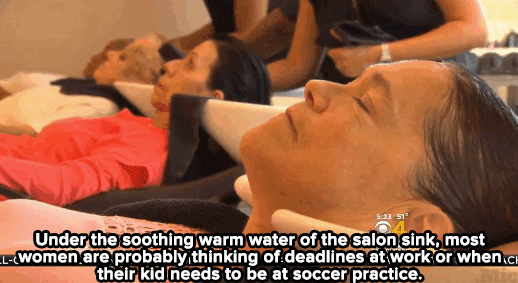
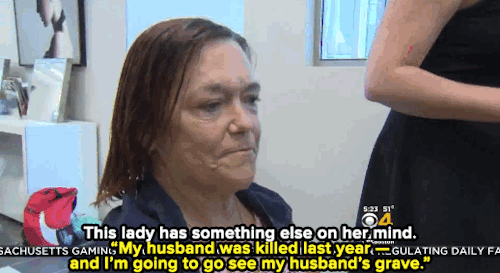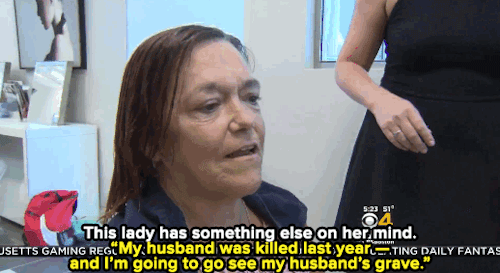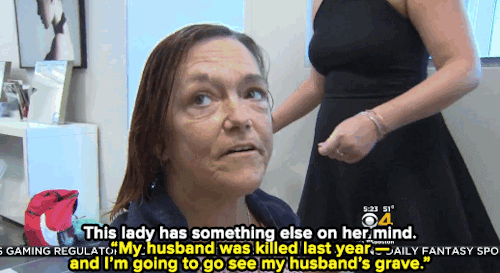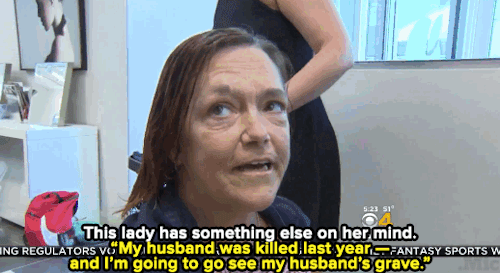






Watch: A haircut may not solve homelessness — but it can make all the difference for these women.
Follow @stylemic
-
 youllneverseemerelax liked this · 1 month ago
youllneverseemerelax liked this · 1 month ago -
 hephastia reblogged this · 10 months ago
hephastia reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 hephastia liked this · 10 months ago
hephastia liked this · 10 months ago -
 captainmarvelously liked this · 1 year ago
captainmarvelously liked this · 1 year ago -
 majokkomaimun reblogged this · 1 year ago
majokkomaimun reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 birdmenmanga liked this · 1 year ago
birdmenmanga liked this · 1 year ago -
 bitemeilovewaffles reblogged this · 1 year ago
bitemeilovewaffles reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 thatoneperson1967 reblogged this · 3 years ago
thatoneperson1967 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 thatoneperson1967 liked this · 3 years ago
thatoneperson1967 liked this · 3 years ago -
 ellynneversweet liked this · 3 years ago
ellynneversweet liked this · 3 years ago -
 bubbledot liked this · 3 years ago
bubbledot liked this · 3 years ago -
 gatorlandqueen liked this · 3 years ago
gatorlandqueen liked this · 3 years ago -
 adriennegabriella reblogged this · 4 years ago
adriennegabriella reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 adriennegabriella liked this · 4 years ago
adriennegabriella liked this · 4 years ago -
 thelaughingdoughnut liked this · 4 years ago
thelaughingdoughnut liked this · 4 years ago -
 marq-winks1067 reblogged this · 4 years ago
marq-winks1067 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 marq-winks1067 liked this · 4 years ago
marq-winks1067 liked this · 4 years ago -
 afk-brb reblogged this · 4 years ago
afk-brb reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 afk-brb reblogged this · 4 years ago
afk-brb reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 tomioneer reblogged this · 4 years ago
tomioneer reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 tomioneer liked this · 4 years ago
tomioneer liked this · 4 years ago -
 designatedlover liked this · 4 years ago
designatedlover liked this · 4 years ago -
 afk-brb reblogged this · 4 years ago
afk-brb reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 doyourworkdamnit reblogged this · 4 years ago
doyourworkdamnit reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 doyourworkdamnit liked this · 4 years ago
doyourworkdamnit liked this · 4 years ago -
 ash-hamiltrash liked this · 4 years ago
ash-hamiltrash liked this · 4 years ago -
 forrestorrest liked this · 4 years ago
forrestorrest liked this · 4 years ago -
 somni-omni liked this · 4 years ago
somni-omni liked this · 4 years ago -
 veryhairdohumancalzone liked this · 4 years ago
veryhairdohumancalzone liked this · 4 years ago -
 13thnomad liked this · 5 years ago
13thnomad liked this · 5 years ago -
 whyamistillonthishellsite13 reblogged this · 6 years ago
whyamistillonthishellsite13 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 cookiedoodle01 liked this · 6 years ago
cookiedoodle01 liked this · 6 years ago -
 cookiedoodle01 reblogged this · 6 years ago
cookiedoodle01 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 achangelingtale liked this · 6 years ago
achangelingtale liked this · 6 years ago -
 kalopyrgos reblogged this · 6 years ago
kalopyrgos reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 victoryfroststarlight liked this · 6 years ago
victoryfroststarlight liked this · 6 years ago -
 kiss-me-sober liked this · 6 years ago
kiss-me-sober liked this · 6 years ago -
 a-storm-of-nightengales liked this · 6 years ago
a-storm-of-nightengales liked this · 6 years ago -
 aronredd reblogged this · 6 years ago
aronredd reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 my-little-secret-cr liked this · 6 years ago
my-little-secret-cr liked this · 6 years ago -
 korraction reblogged this · 6 years ago
korraction reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 elphamejourdemayne liked this · 6 years ago
elphamejourdemayne liked this · 6 years ago
![Map Of The Humongous Fungus: The Largest Living Organism On Earth [1936x1310][OC] CLICK HERE FOR MORE](https://64.media.tumblr.com/db929150f86f0c503804f329c0244a28/tumblr_nyulclrmRz1s6c1p2o1_500.jpg)
