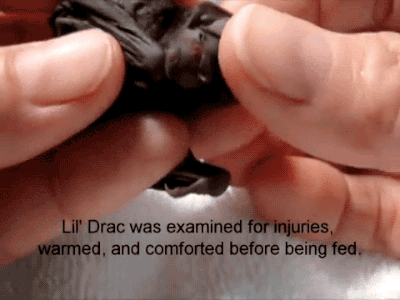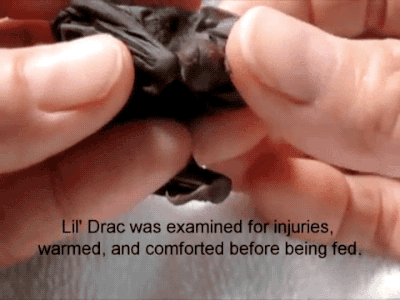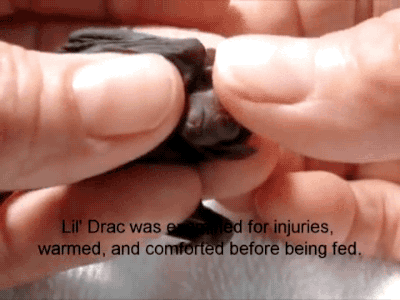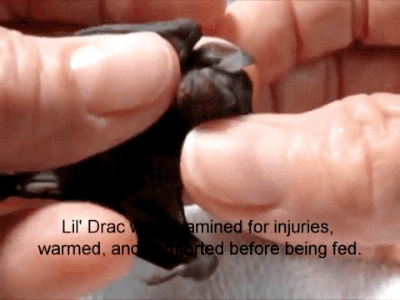
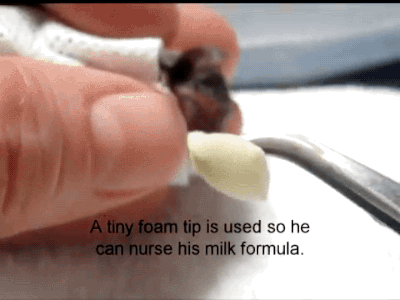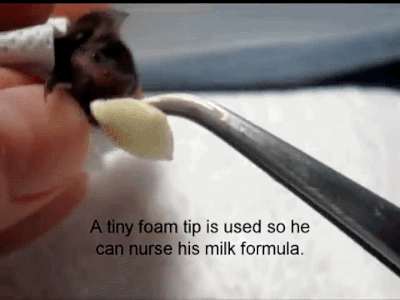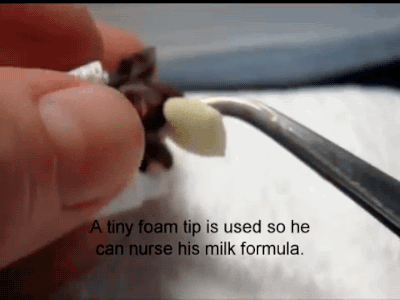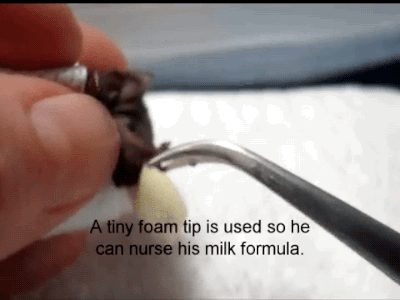
A Reliable Way To Make People Believe In Falsehoods Is Frequent Repetition, Because Familiarity Is Not
A reliable way to make people believe in falsehoods is frequent repetition, because familiarity is not easily distinguished from truth.
Daniel Kahneman, Thinking, Fast and Slow
More Posts from Dotmpotter and Others
#Chocoholic: We sure love our chocolate, but it'd be a lot sweeter if it wasn't coming from child labor.

WATCH the short video here.
+2 million children work in cocoa production in Ghana and the Ivory Coast. This year, Nestlé, Mars Bar, and HERSHEY'S were sued for knowingly partnering with suppliers that use child workers.
DEMAND that these chocolate companies become Made In A Free World here: madeinafreeworld.com/action!
The study authors have calculated the cost of the “lost ecosystem services value” our planet has suffered in the last decade and a half. According to their calculations, the loss due to land degradation averages US $43,400 to $72,000 per square km, some US $870 to $1,450 per person, globally each year. The percentage of the world’s land affected by land degradation has grown a lot in the last decades – it has doubled between the late 1970s and the early 2000s. And the process is far from its end.
“This study by ELD shows the immediate and global impact of land degradation and highlights that actions to tackle it pay off,” Karmenu Vella, European Commissioner for Environment, Fisheries and Maritime Affairs commented on the paper.
“Increased land degradation is also one of the factors that can lead to migration and it is being exacerbated by climate change. On our planet, the area affected by drought has doubled in 40 years. One third of Africa is threatened by desertification. As President Juncker said in his State of the Union speech last week, climate refugees will become a new challenge – if we do not act swiftly.”







On April 26, 1986, a power surge caused an explosion at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant near Pripyat, Ukraine. A large quantity of radioactive material was released.
On May 2, 1986, the Soviet government established a “Zone of Alienation” or “Exclusion Zone” around Chernobyl – a thousand square miles of “radioactive wasteland.” All humans were evacuated. The town of Pripyat was completely abandoned.
But the animals didn’t leave. And a new study, published this month in Current Biology, suggests they are doing fine. “None of our three hypotheses postulating radiation damage to large mammal populations at Chernobyl were supported by the empirical evidence,” says Jim Beasley, one of the researchers.
In fact, some of the populations have grown. These photos (mostly taken by Valeriy Yurko) come from the Belarusian side of the Exclusion Zone, and area called the Polessye State Radioecological Reserve. Kingfisher, elk, boar, baby spotted eagles, wild ponies, moose, rabbits, and wolves all make their home in the park. In some ways, human presence is worse for wildlife than a nuclear disaster.
Image credits:
1986 Chernobyl - ZUFAROV/AFP/Getty Images
Wildlife photos - Valeriy Yurko/Polessye State Radioecological Reserve
Ponies in winter - SERGEI SUPINSKY/AFP/Getty Images
That is the course that world leaders set when they met at the United Nations in New York on September 25 to adopt the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The 17 goals range from ending poverty and improving health to protecting the planet’s biosphere and providing energy for all. They emerged from the largest summit in the UN’s history, the “Rio+20” conference in 2012, followed by the largest consultation the UN has ever undertaken.
We need your help to sustain our not-for-profit mission: ensuring that readers around the world have equal access to ideas and analysis from the world’s leading thinkers.
Unlike their predecessor, the Millennium Development Goals, which focused almost exclusively on developing countries, the new global goals are universal and apply to all countries equally. Their adoption indicates widespread acceptance of the fact that all countries share responsibility for the long-term stability of Earth’s natural cycles, on which the planet’s ability to support us depends.
Johan Rockstrom goes all in on poverty reduction and climate change.
Ifixit repair kits: everything you need to fix everything

Ifixit produce open repair guides for everything imaginable, in a variety of languages, and help sustain a global community of independent repairers who divert electronics from e-waste dumps and keep poor and marginalized people connected to their work, school and families.
The Ifixit repair kits are thoughtful, high-specification, low-cost toolkits designed to work on all modern gadgets, as well as traditional ones (for example, Ifixit manufacture their own drivers for Apple’s bizarre “pentalobe” screws, which Apple had instructed its Genius Bar staff to quietly swap in during routine repairs).
The big daddy of Ifixit kits is the $130 128-bit Universal Bit Kit, which comes in a handsome wooden case and is covered by Ifixit’s lifetime warranty.

But Ifixit makes smaller, more specialized kits, including theSmartphone Repair Kit, priced at $25, specifically aimed at the budgets of enterprising high-school students who want to start their own smartphone repair businesses, using Ifixit’s manuals.
http://boingboing.net/2015/12/02/ifixit-repair-kits-everything.html
AIDS-drug-gouging hedge-douche reneges on promise to cut prices for Daraprim

Martin Shkreli, the hedge-fund douche-bro who hiked the price of an off-patent drug used by AIDS and cancer patients from $13.50 to $750, then promised to lower the prices after becoming the Most Hated Man on the Internet did no such thing, because he is a liar.
http://boingboing.net/2015/11/25/aids-drug-gouging-hedge-douche.html







On April 26, 1986, a power surge caused an explosion at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant near Pripyat, Ukraine. A large quantity of radioactive material was released.
On May 2, 1986, the Soviet government established a “Zone of Alienation” or “Exclusion Zone” around Chernobyl – a thousand square miles of “radioactive wasteland.” All humans were evacuated. The town of Pripyat was completely abandoned.
But the animals didn’t leave. And a new study, published this month in Current Biology, suggests they are doing fine. “None of our three hypotheses postulating radiation damage to large mammal populations at Chernobyl were supported by the empirical evidence,” says Jim Beasley, one of the researchers.
In fact, some of the populations have grown. These photos (mostly taken by Valeriy Yurko) come from the Belarusian side of the Exclusion Zone, and area called the Polessye State Radioecological Reserve. Kingfisher, elk, boar, baby spotted eagles, wild ponies, moose, rabbits, and wolves all make their home in the park. In some ways, human presence is worse for wildlife than a nuclear disaster.
Image credits:
1986 Chernobyl - ZUFAROV/AFP/Getty Images
Wildlife photos - Valeriy Yurko/Polessye State Radioecological Reserve
Ponies in winter - SERGEI SUPINSKY/AFP/Getty Images
Power-pylons that look like looming giants


Choi + Shine, an architecture firm, has proposed modifying Iceland’s existing power-transmission pylons to turn them into looming giants whose arms are poised to reflect their positions – pylons ascending a hill will be posed as though they were scaling its slopes.
The designers claim that it can be made cost-effective through clever engineering, and that the resulting aesthetic experience will be monumental. I agree with the latter statement and am unqualified to assess the former, though Iceland has a weird and cool relationship with power, as it is ia carbon-neutral country whose electricity comes from geothermal sources.
Read the rest
-
 cybergm liked this · 6 years ago
cybergm liked this · 6 years ago -
 aethersea liked this · 6 years ago
aethersea liked this · 6 years ago -
 ihasquestions reblogged this · 6 years ago
ihasquestions reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 yourusernameiswhat liked this · 6 years ago
yourusernameiswhat liked this · 6 years ago -
 princesandpirates liked this · 6 years ago
princesandpirates liked this · 6 years ago -
 aang-the-last-motherfucker reblogged this · 6 years ago
aang-the-last-motherfucker reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 merlinsbeard4332 liked this · 6 years ago
merlinsbeard4332 liked this · 6 years ago -
 im-a-bit-of-a-fire-hazard reblogged this · 6 years ago
im-a-bit-of-a-fire-hazard reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 francesca-disappears liked this · 6 years ago
francesca-disappears liked this · 6 years ago -
 drst reblogged this · 6 years ago
drst reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 morteledraco liked this · 6 years ago
morteledraco liked this · 6 years ago -
 lrthreads liked this · 6 years ago
lrthreads liked this · 6 years ago -
 thayerkerbasy liked this · 6 years ago
thayerkerbasy liked this · 6 years ago -
 welkinalauda reblogged this · 6 years ago
welkinalauda reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 cambriancrew reblogged this · 6 years ago
cambriancrew reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 noninfacies reblogged this · 9 years ago
noninfacies reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 shadow-wasser liked this · 9 years ago
shadow-wasser liked this · 9 years ago -
 237weeks reblogged this · 9 years ago
237weeks reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 dummerhummer reblogged this · 9 years ago
dummerhummer reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 dummerhummer liked this · 9 years ago
dummerhummer liked this · 9 years ago -
 zezlemet reblogged this · 9 years ago
zezlemet reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 lonespektr reblogged this · 9 years ago
lonespektr reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 eightshinyunicorns reblogged this · 9 years ago
eightshinyunicorns reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 dianartemiss reblogged this · 9 years ago
dianartemiss reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 cryptidotter reblogged this · 9 years ago
cryptidotter reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 o-nekosan reblogged this · 9 years ago
o-nekosan reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 o-nekosan liked this · 9 years ago
o-nekosan liked this · 9 years ago -
 artaline liked this · 9 years ago
artaline liked this · 9 years ago -
 teamponytail liked this · 9 years ago
teamponytail liked this · 9 years ago -
 rainonsand reblogged this · 9 years ago
rainonsand reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 rainonsand liked this · 9 years ago
rainonsand liked this · 9 years ago -
 sleepymarmot liked this · 9 years ago
sleepymarmot liked this · 9 years ago -
 kentrakshi liked this · 9 years ago
kentrakshi liked this · 9 years ago -
 cryptidotter liked this · 9 years ago
cryptidotter liked this · 9 years ago -
 youcanchoosefreedom liked this · 9 years ago
youcanchoosefreedom liked this · 9 years ago -
 bettername reblogged this · 9 years ago
bettername reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 eye-of-orion reblogged this · 9 years ago
eye-of-orion reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 meinposhbastard reblogged this · 9 years ago
meinposhbastard reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 21st-century-flapper reblogged this · 9 years ago
21st-century-flapper reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 clickoliver reblogged this · 9 years ago
clickoliver reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ghostsaremyfriends liked this · 9 years ago
ghostsaremyfriends liked this · 9 years ago