Wanted: Shredder For Five Million Tires Dumped In Spain



Wanted: Shredder for five million tires dumped in Spain
Spanish authorities are struggling to dispose of five million tires dumped on a site close to a housing development north of Toledo. The 90,000 tons’ worth of tires have been dumped there since 2002.
Environmentalists say that should a fire break out, it could not be extinguished with water and would have to be smothered with earth. In the event of a fire, Madrid’s main airport would likely have to be shut down and an estimated 11,000 homes evacuated. | Read more
More Posts from Dotmpotter and Others

Turns out, in addition to leaving our mark on surfaces, we’re also emitting a bacterial signature into the air—what scientists call a “microbial cloud.” And according to a new study conducted by the Biology and the Built Environment Center at the University of Oregon, this invisible aura is so specific that it can be used to distinguish between individual people.
Our Bodies, Our Microbial Clouds
[Graphic: Viputheshwar Sitaraman/Draw Science]

Dust, stars, and cosmic rays swirling around Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, captured by the Rosetta probe. (Source)



Earthprints: Aletsch Glacier
One of Europe’s biggest glaciers, the Great Aletsch, coils 14 miles through the Swiss Alps - and yet this mighty river of ice could almost vanish in the lifetimes of people born today because of climate change. The glacier, 900 meters (2,950 feet) thick at one point, has retreated about 3 km (1.9 miles) since 1870 and that pace is quickening, as with many other glaciers around the globe.
That is feeding more water into the oceans and raising world sea levels. It was only after I got down onto the ice, with spikes on my boots for grip and often roped to my guide for safety, that I appreciated the full scale of the glacier, on the south side of the Jungfraujoch railway station.
And yet even the Great Aletsch glacier, the biggest in the Alps and visible from space, is under threat from the build-up of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere from factories, power plants and cars that are blamed for global warming. (REUTERS) Photography by Denis Balibouse/REUTERS Read: Vast Alpine glacier could almost vanish by 2100 due to warming See more photos of the Great Aletsch and our other slideshows on Yahoo News.


Emily, a process engineer at GE Aviation in Auburn, AL is all suited up to remove a print from a Direct Metal Laser Melting machine. These machines additively manufacture metal components for CFM’s best-selling LEAP jet engine, printing in 20 micron layers — roughly 1/3 the width of a human hair.

Algorithm predicts and prevents train delays two hours in advance
Transport apps such as Ototo make it easier than ever for passengers to stay informed about problems with public transport, but real-time information can only help so much — by the time users find out about a delayed service, it is often too late to take an alternative route. Now, Stockholmstag — the company that runs Sweden’s trains — have found a solution in the form of an algorithm called ‘The Commuter Prognosis’, which can predict network delays up to two hours in advance, giving train operators time to issue extra services or provide travelers with adequate warning. READ MORE…
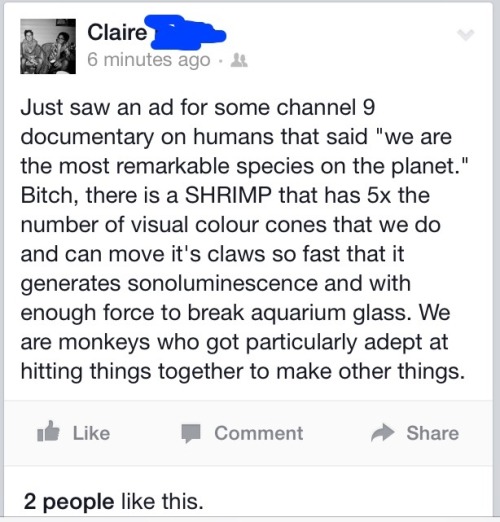
I am not here for the idea that humans > everything else.

“A bus map you often see is the same thickness and same color line for the whole network: It makes [agencies] look like they’ve got the whole place covered,” says Wiggins. “That’s to the benefit of them and not to the rider.”
Wiggins thinks transit maps designed around coverage ultimately harm the system as a whole. Instead of using the map to find a bus route that works for a particular trip, riders stick to one specific line whose schedule they know—avoiding the map altogether. The result is a ridership that ends up taking a car more than it otherwise might, and one that objects loudly when the agency proposes a system change that would force them to learn a new route.
“I think with a better map, it actually might facilitate people being able to let go a little bit,” he says. “It stops becoming ‘this is my route and this is what I cling to’ and more of a network you can relate to.”
How San Francisco Got Its New Rider-Friendly Transit Map
When’s the last time you thought about the revolving door? This modest invention—something you likely encounter with a sense of dread while rushing off to the office or airport—is something of a modern miracle. Every time a revolving door rotates, it generates enough electricity to power a 60-watt light bulb for 23 minutes, equalizes indoor temperatures, and reduces carbon output—ultimately slowing climate change.
Revolving Doors Are an Energy Powerhouse. Why Don’t We Use Them? | GOOD
-
 ttlygay liked this · 9 years ago
ttlygay liked this · 9 years ago -
 perfuscos reblogged this · 9 years ago
perfuscos reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 dezznuttyvibes-blog liked this · 9 years ago
dezznuttyvibes-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 themans--man-blog liked this · 9 years ago
themans--man-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 vanilla-villella reblogged this · 9 years ago
vanilla-villella reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 oceanspirits liked this · 9 years ago
oceanspirits liked this · 9 years ago -
 yearofthefreaks liked this · 9 years ago
yearofthefreaks liked this · 9 years ago -
 droopyhazeleyes reblogged this · 9 years ago
droopyhazeleyes reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 moodysaint reblogged this · 9 years ago
moodysaint reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 dun3bugg7 liked this · 9 years ago
dun3bugg7 liked this · 9 years ago -
 itsemjay16-blog liked this · 9 years ago
itsemjay16-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 itsemjay16-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
itsemjay16-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 mmarshall25-blog liked this · 9 years ago
mmarshall25-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 tavgenius reblogged this · 9 years ago
tavgenius reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 lalasbella liked this · 9 years ago
lalasbella liked this · 9 years ago -
 run-hide-blog-blog liked this · 9 years ago
run-hide-blog-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 flyonthewallmedstudent reblogged this · 9 years ago
flyonthewallmedstudent reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 within-without-philosophy reblogged this · 9 years ago
within-without-philosophy reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 butimpicasso liked this · 9 years ago
butimpicasso liked this · 9 years ago -
 dotmpotter reblogged this · 9 years ago
dotmpotter reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 urbanoceanix reblogged this · 9 years ago
urbanoceanix reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 lionelfaucher reblogged this · 9 years ago
lionelfaucher reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 teremi-hc reblogged this · 9 years ago
teremi-hc reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 alilmagic reblogged this · 9 years ago
alilmagic reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 reticent-y reblogged this · 9 years ago
reticent-y reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 earthchildmaeve liked this · 9 years ago
earthchildmaeve liked this · 9 years ago -
 zquwil liked this · 9 years ago
zquwil liked this · 9 years ago -
 professorsatan reblogged this · 9 years ago
professorsatan reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 teremi-hc liked this · 9 years ago
teremi-hc liked this · 9 years ago -
 haciendaespanola reblogged this · 9 years ago
haciendaespanola reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 juggaluggarumproast reblogged this · 9 years ago
juggaluggarumproast reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 zyxzy liked this · 9 years ago
zyxzy liked this · 9 years ago -
 amyntrox liked this · 9 years ago
amyntrox liked this · 9 years ago -
 gabrielrain liked this · 9 years ago
gabrielrain liked this · 9 years ago -
 maaarine reblogged this · 9 years ago
maaarine reblogged this · 9 years ago
