In Many Ways, Scientific Analyses Of Consciousness Suffer From The Same Limitations And Constraints As


In many ways, scientific analyses of consciousness suffer from the same limitations and constraints as cosmological theories: right right at the outset, certain manipulations and observations cannot be carried out.
More Posts from Csmsdust and Others
Slime Molds and Intelligence

Okay, despite going into a biology related field, I only just learned about slime molds, and hang on, because it gets WILD.
This guy in the picture is called Physarum polycephalum, one of the more commonly studied types of slime mold. It was originally thought to be a fungus, though we now know it to actually be a type of protist (a sort of catch-all group for any eukaryotic organism that isn't a plant, animal, or a fungus). As protists go, it's pretty smart. It is very good at finding the most efficient way to get to a food source, or multiple food sources. In fact, placing a slime mold on a map with food sources at all of the major cities can give a pretty good idea of an efficient transportation system. Here is a slime mold growing over a map of Tokyo compared to the actual Tokyo railway system:

Pretty good, right? Though they don't have eyes, ears, or noses, the slime molds are able to sense objects at a distance kind of like a spider using tiny differences in tension and vibrations to sense a fly caught in its web. Instead of a spiderweb, though, this organism relies on proteins called TRP channels. The slime mold can then make decisions about where it wants to grow. In one experiment, a slime mold was put in a petri dish with one glass disk on one side and 3 glass disks on the other side. Even though the disks weren't a food source, the slime mold chose to grow towards and investigate the side with 3 disks over 70% of the time.

Even more impressive is that these organisms have some sense of time. If you blow cold air on them every hour on the hour, they'll start to shrink away in anticipation when before the air hits after only 3 hours.
Now, I hear you say, this is cool and all, but like, I can do all those things too. The slime mold isn't special...
To which I would like to point out that you have a significant advantage over the slime mold, seeing as you have a brain.
Yeah, these protists can accomplish all of the things I just talked about, and they just... don't have any sort of neural architecture whatsoever? They don't even have brain cells, let alone the structures that should allow them to process sensory information and make decisions because of it. Nothing that should give them a sense of time. Scientists literally have no idea how this thing is able to "think'. But however it does, it is sure to be a form of cognition that is completely and utterly different from anything that we're familiar with.
“Imagine what it would look like if ChatGPT were a lossless algorithm. If that were the case, it would always answer questions by providing a verbatim quote from a relevant Web page. We would probably regard the software as only a slight improvement over a conventional search engine, and be less impressed by it. The fact that ChatGPT rephrases material from the Web instead of quoting it word for word makes it seem like a student expressing ideas in her own words, rather than simply regurgitating what she’s read; it creates the illusion that ChatGPT understands the material. In human students, rote memorization isn’t an indicator of genuine learning, so ChatGPT’s inability to produce exact quotes from Web pages is precisely what makes us think that it has learned something. When we’re dealing with sequences of words, lossy compression looks smarter than lossless compression.”
— Ted Chiang’s essay about ChatGPT is required reading

It is one of the commonest of mistakes to consider that the limit of our power of perception is also the limit of all there is to perceive.
C.W. Leadbeater

Abandoned library, roadside somewhere in Oregon.





Ask yourself at every moment "is this necessary?"

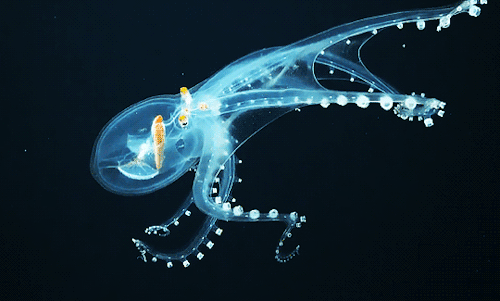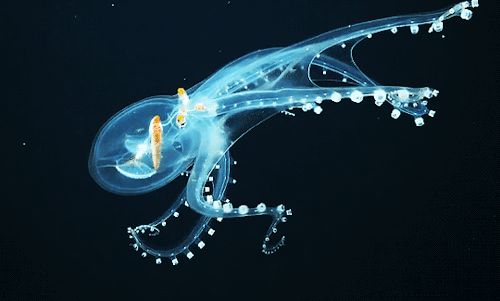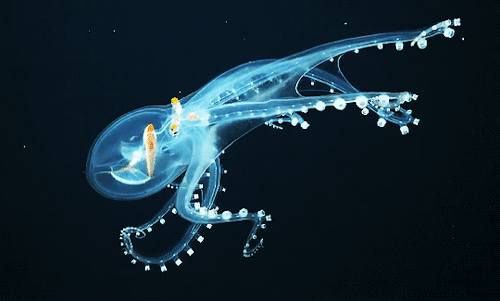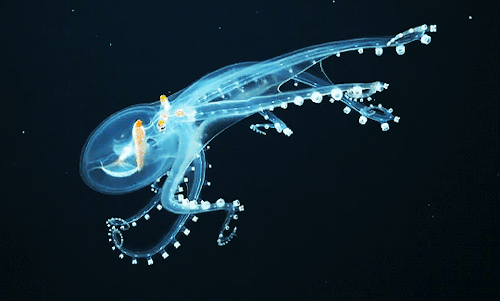


Glass Octopus l Phoenix Islands

The books I'm reading at the moment.

Meditations by Marcus Aurelius - I love this book. It puts you in the perspective of the time and space you occupy, I found a lot of my own thinking and feelings within the pages of this book. A guy born in AD 121 has very clear view on life that is still relevant today.

Great Adaptations by Kenneth Catania - A professor of biological sciences takes you on a journey with him while he studies various animals adaptive abilities. Star nosed moles, electric eels, tentacled snakes... Very interesting insight in how these creatures evolved and adapted.

What we cannot know by Marcus du Sautoy - Explains concepts from the ground up, I like the illustrations that accompany the text and practical examples. Lays foundations to the known and wonders into the future of research and the possibilities that come with it as well as limitations. Covering themes from quantum physics and cosmology to sensory perception and neuroscience.

Labyrinths of reason by William Poundstone - "Blue sky, sunshine, deja vu glazed with dread." How do you know this isn't all a dream? Is anything certain? Ontology, logic, mathematics, deduction, epistemology, memory formation, paradoxes and puzzles.

A brain for numbers by Andreas Nieder - Humans' understanding of numbers is intuitive. How are infants able to perceive numbers even before they learn the words for them? How do our brains process numbers? Can animals count? He shows how it is an adaptive ability and that plenty of animals have the number sense too. There is a variety of research and supporting evidence mentioned which I really like.
-
 kiara-on-the-shore reblogged this · 9 months ago
kiara-on-the-shore reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 thegayanaesthetist liked this · 1 year ago
thegayanaesthetist liked this · 1 year ago -
 komplikacije liked this · 2 years ago
komplikacije liked this · 2 years ago -
 milo-is-queer reblogged this · 2 years ago
milo-is-queer reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 milo-is-queer liked this · 2 years ago
milo-is-queer liked this · 2 years ago -
 shiikid reblogged this · 2 years ago
shiikid reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 virvarium reblogged this · 2 years ago
virvarium reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 nonahbeans reblogged this · 2 years ago
nonahbeans reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 nonahbeans liked this · 2 years ago
nonahbeans liked this · 2 years ago -
 csmsdust reblogged this · 2 years ago
csmsdust reblogged this · 2 years ago
