A Hexagonal Storm With A Diameter Of 25,000 Km Raging At The North Pole Of Saturn.

A hexagonal storm with a diameter of 25,000 km raging at the north pole of Saturn.
More Posts from Ad-astra-affecte-spe and Others






Orion, The Great Hunter

The close-up of the Andromeda Galaxy from the Hubble Space Telescope shows how many stars there really are.
source

Andromeda over the Swiss Alps Image Credit: Dzmitry Kananovich
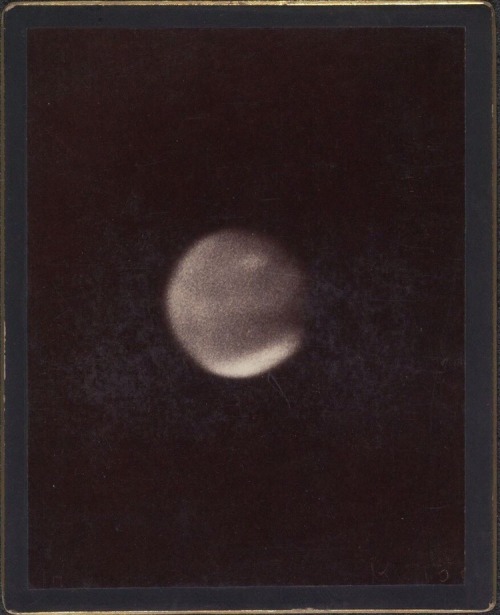


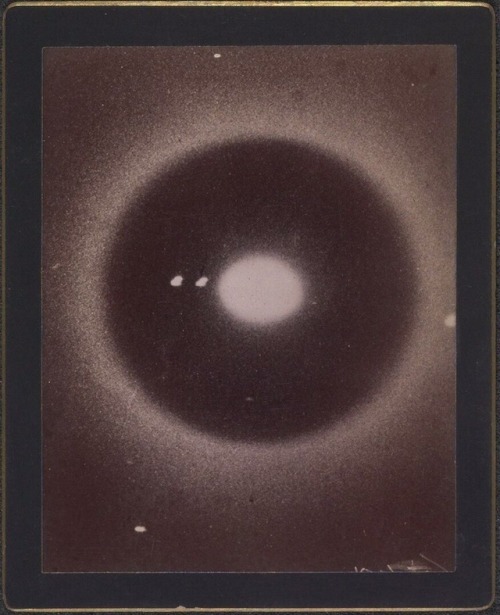
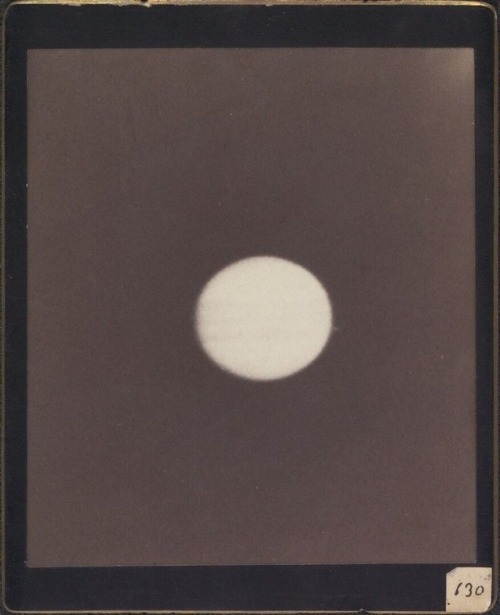
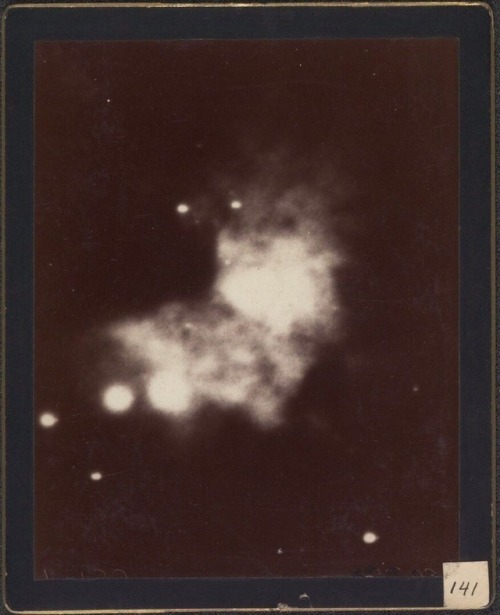
Astronomical photographs, Harvard College Observatory, Cambridge, 1890-1920
Two spiral galaxies, NGC 6040 and NGC 6039, are merging together at the right side of this Hubble image. NGC 6039 is seen face-on and is circular in shape. NGC 6040 seems to lie in front of the first one. In the lower-left corner, cut off by the frame, the elliptical galaxy NGC 6041 — a central member of the galaxy cluster that Arp 122 resides in — appears as light radiating from a point. The color image was made from separate exposures taken in the visible and infrared regions





Jupiter Swirling Storms l NASA Juno

NGC 1365, Heart of the Universe

The glittering globular cluster Terzan 12 — a vast, tightly bound collection of stars — fills the frame of this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. This star-studded stellar census comes from a string of observations that aim to systematically explore globular clusters located towards the centre of our galaxy, such as this one in the constellation Sagittarius. The locations of these globular clusters — deep in the Milky Way galaxy — mean that they are shrouded in gas and dust, which can block or alter the wavelengths of starlight emanating from the clusters.
Here, astronomers were able to sidestep the effect of gas and dust by comparing the new observations made with the razor-sharp vision of Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys and Wide-Field Camera 3 with pre-existing images. Their observations should shed light on the relation between age and composition in the Milky Way’s innermost globular clusters.
[Image Description: The frame is completely filled with bright stars, ranging from tiny dots to large, shining stars with prominent spikes. In the lower-right the stars come together in the core of the star cluster, making the brightest and densest area of the image. The background varies from darker and warmer in colour, to brighter and paler where there are more stars.]Credit:
ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Cohen (Rutgers University)

-
 r4vensong liked this · 1 week ago
r4vensong liked this · 1 week ago -
 plagueyourmind reblogged this · 1 week ago
plagueyourmind reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 fl8faces reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
fl8faces reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 lj-i7 liked this · 3 weeks ago
lj-i7 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 jmdj liked this · 3 weeks ago
jmdj liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 babychurrro reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
babychurrro reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 corpsebridal reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
corpsebridal reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 cafepost liked this · 3 weeks ago
cafepost liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 ladiablesse liked this · 3 weeks ago
ladiablesse liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 flowyello reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
flowyello reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 jukeboxangel liked this · 3 weeks ago
jukeboxangel liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 30-four reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
30-four reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 yves-deruyter reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
yves-deruyter reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 grof-edmont-dantes liked this · 3 weeks ago
grof-edmont-dantes liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 the-riff-compels-me liked this · 3 weeks ago
the-riff-compels-me liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 j1ui reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
j1ui reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 raemora liked this · 3 weeks ago
raemora liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 whowhatwhyyy reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
whowhatwhyyy reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 geekmybride liked this · 3 weeks ago
geekmybride liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 pallacides reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
pallacides reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 clumsy-sky reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
clumsy-sky reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 976-evil reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
976-evil reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 rhymewithme liked this · 3 weeks ago
rhymewithme liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 fizzyday reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
fizzyday reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 arcane3xistence reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
arcane3xistence reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 arjak-mistwalker liked this · 3 weeks ago
arjak-mistwalker liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 cigsafter-coffee reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
cigsafter-coffee reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 neznosrce reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
neznosrce reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 neznosrce liked this · 3 weeks ago
neznosrce liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 flowyello liked this · 3 weeks ago
flowyello liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 laa-solassitude reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
laa-solassitude reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 im-out-with-lanterns reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
im-out-with-lanterns reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 kozonauta reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
kozonauta reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 arewealloststars liked this · 4 weeks ago
arewealloststars liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 roombawithaknife reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
roombawithaknife reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 venusmoon reblogged this · 1 month ago
venusmoon reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 francisofthespook liked this · 1 month ago
francisofthespook liked this · 1 month ago -
 mymanreedus reblogged this · 1 month ago
mymanreedus reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 conceptqbq liked this · 1 month ago
conceptqbq liked this · 1 month ago -
 carnalsuitra liked this · 1 month ago
carnalsuitra liked this · 1 month ago -
 omgitsdana reblogged this · 1 month ago
omgitsdana reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 omgitsdana liked this · 1 month ago
omgitsdana liked this · 1 month ago -
 ancientsong reblogged this · 1 month ago
ancientsong reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 well-within-electric-dreams liked this · 1 month ago
well-within-electric-dreams liked this · 1 month ago -
 bog-bitch liked this · 1 month ago
bog-bitch liked this · 1 month ago -
 thisismyideaofhumor reblogged this · 1 month ago
thisismyideaofhumor reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 cozy-corner liked this · 2 months ago
cozy-corner liked this · 2 months ago -
 honeydew-jam reblogged this · 2 months ago
honeydew-jam reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 fw09 reblogged this · 2 months ago
fw09 reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 the3st reblogged this · 2 months ago
the3st reblogged this · 2 months ago

★•Astronomy, Physics, and Aerospace•★ Original and Reblogged Content curated by a NASA Solar System Ambassador
204 posts



