Saturn And Its Amazing Rings, Observed By The Cassini Probe On This Day In 2004.

Saturn and its amazing rings, observed by the Cassini probe on this day in 2004.
More Posts from Ad-astra-affecte-spe and Others


Lunar halo
@picabuzz

2023 February 22
Our Increasingly Active Sun Image Credit & Copyright: Mehmet Ergün
Explanation: Our Sun is becoming a busy place. Only two years ago, the Sun was emerging from a solar minimum so quiet that months would go by without even a single sunspot. In contrast, already this year and well ahead of schedule, our Sun is unusually active, already nearing solar activity levels seen a decade ago during the last solar maximum. Our increasingly active Sun was captured two weeks ago sporting numerous interesting features. The image was recorded in a single color of light called Hydrogen Alpha, color-inverted, and false colored. Spicules carpet much of the Sun’s face. The brightening towards the Sun’s edges is caused by increased absorption of relatively cool solar gas and called limb darkening. Just outside the Sun’s disk, several scintillating prominences protrude, while prominences on the Sun’s face are known as filaments and show as light streaks. Magnetically tangled active regions are both dark and light and contain cool sunspots. As our Sun’s magnetic field winds toward solar maximum over the next few years, whether the Sun’s high activity will continue to increase is unknown.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap230222.html

The glittering globular cluster Terzan 12 — a vast, tightly bound collection of stars — fills the frame of this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. This star-studded stellar census comes from a string of observations that aim to systematically explore globular clusters located towards the centre of our galaxy, such as this one in the constellation Sagittarius. The locations of these globular clusters — deep in the Milky Way galaxy — mean that they are shrouded in gas and dust, which can block or alter the wavelengths of starlight emanating from the clusters.
Here, astronomers were able to sidestep the effect of gas and dust by comparing the new observations made with the razor-sharp vision of Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys and Wide-Field Camera 3 with pre-existing images. Their observations should shed light on the relation between age and composition in the Milky Way’s innermost globular clusters.
[Image Description: The frame is completely filled with bright stars, ranging from tiny dots to large, shining stars with prominent spikes. In the lower-right the stars come together in the core of the star cluster, making the brightest and densest area of the image. The background varies from darker and warmer in colour, to brighter and paler where there are more stars.]Credit:
ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Cohen (Rutgers University)


M85 (center right) and NGC 4394 (center left) // Bart Delsaert
M85 is an elliptical galaxy, but one that has a complex series of shells and ripples. These features are thought to have been created some 4-7 billion years ago when it merged with another galaxy. It is currently interacting with the barred spiral galaxy NGC 4394, which might be supporting the shells' structure.
This galaxy was an original discovery of Méchain's in 1781 and is an isolated member of the Virgo Cluster, about 60 million light years away.

Over 800 terrestrial exoplanets visualized and arranged according to their equilibrium temperature and size.
chart by u/mVargic



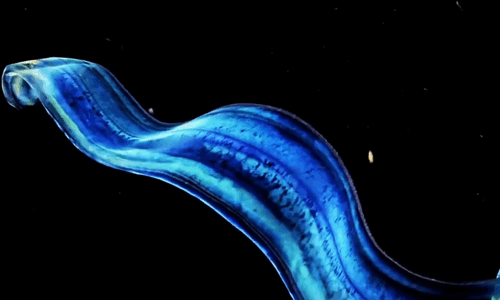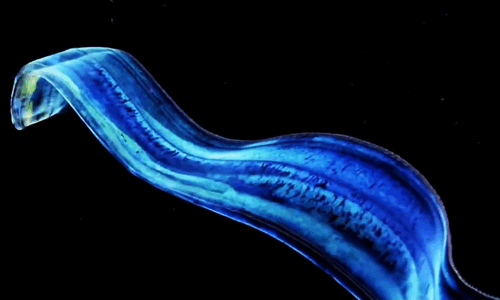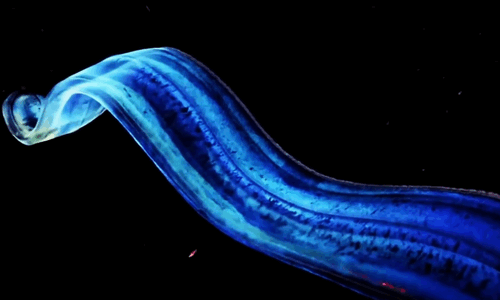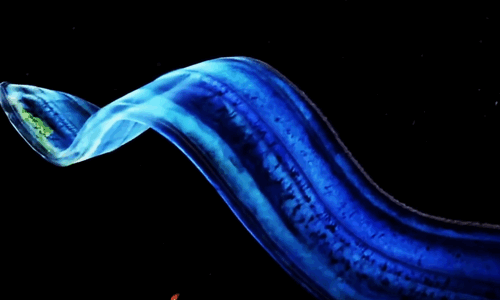




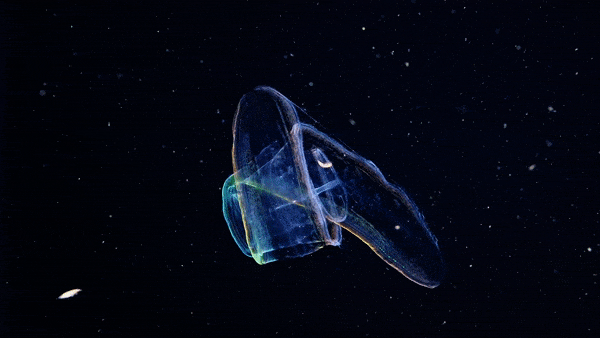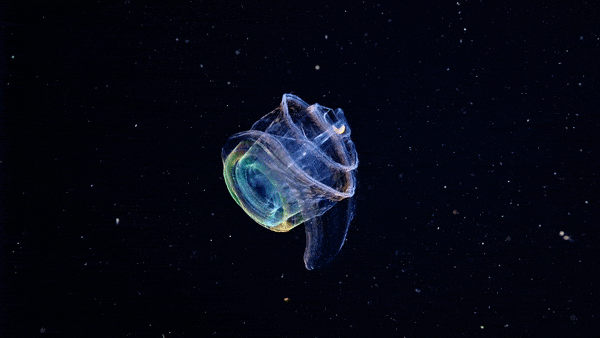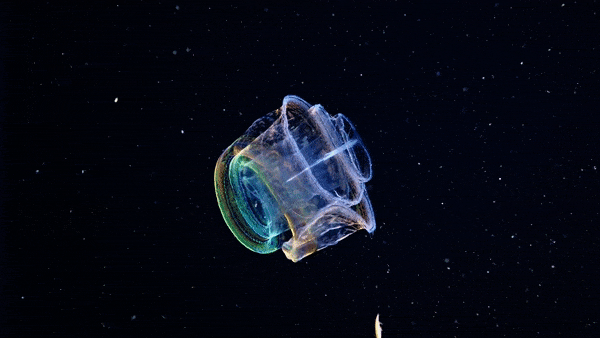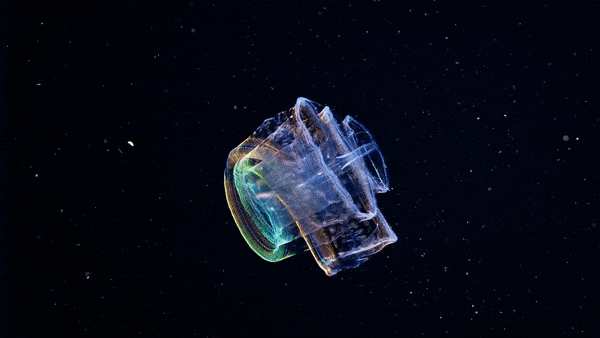
The Venus girdle (Cestum veneris) is a comb jelly in the family Cestidae. The colorless species are transparent when suspended in water, except for their iridescent rows of comb plates. In other words, they majestic as fuck. Love to sea it 🌊

Into the Cosmic Heart, IC 1850 © Aleix Roig

M100: A Grand Design Spiral Galaxy

Nu Scorpii
One of the most interesting areas of the night sky, Scorpius holds a myriad of nebula and beautifully contrasting coloured stars.
Moving towards the tail, you'll find Nu Scorpii a binary star system 7 stars.

If that alone isn't enough to get your mind wondering how all these stars are orbiting each other, the star system itself is the eye of a horses head ! Albeit a nebulous head.

IC 4592 is a reflective nebula, with the blue light reflected from fine dust, that blue light is coming from the Nu Scorpii system above.
Pull out and you'll see the whole region contains many star forming areas with reflective features.

-
 blackpointgame liked this · 3 months ago
blackpointgame liked this · 3 months ago -
 fr33domstarsblog reblogged this · 5 months ago
fr33domstarsblog reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 tr1n1ty-333 reblogged this · 6 months ago
tr1n1ty-333 reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 hilema reblogged this · 6 months ago
hilema reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 hilema liked this · 6 months ago
hilema liked this · 6 months ago -
 sirensmakegraves reblogged this · 6 months ago
sirensmakegraves reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 schwarzebrandung reblogged this · 6 months ago
schwarzebrandung reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 schwarzebrandung liked this · 6 months ago
schwarzebrandung liked this · 6 months ago -
 acridhilarity reblogged this · 7 months ago
acridhilarity reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 acridhilarity liked this · 7 months ago
acridhilarity liked this · 7 months ago -
 trombone2018 liked this · 8 months ago
trombone2018 liked this · 8 months ago -
 imthelostwanderer reblogged this · 8 months ago
imthelostwanderer reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 f-allen-angel liked this · 8 months ago
f-allen-angel liked this · 8 months ago -
 messier47 reblogged this · 8 months ago
messier47 reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 magratheanx reblogged this · 8 months ago
magratheanx reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 magratheanx liked this · 8 months ago
magratheanx liked this · 8 months ago -
 haus-of-commons reblogged this · 1 year ago
haus-of-commons reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 nigittarius reblogged this · 1 year ago
nigittarius reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 nigittarius liked this · 1 year ago
nigittarius liked this · 1 year ago -
 takumikun reblogged this · 1 year ago
takumikun reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 apollomagicspace liked this · 1 year ago
apollomagicspace liked this · 1 year ago -
 oblivioussaturn liked this · 1 year ago
oblivioussaturn liked this · 1 year ago -
 yetanothercriminalmindsfanatic reblogged this · 1 year ago
yetanothercriminalmindsfanatic reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 yourfavepookiebear liked this · 1 year ago
yourfavepookiebear liked this · 1 year ago -
 32127 reblogged this · 1 year ago
32127 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 idontknowwhatsgoingonhelp liked this · 1 year ago
idontknowwhatsgoingonhelp liked this · 1 year ago -
 tiberiusmulder reblogged this · 1 year ago
tiberiusmulder reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 yetanothercriminalmindsfanatic liked this · 1 year ago
yetanothercriminalmindsfanatic liked this · 1 year ago -
 claudiajcregg reblogged this · 1 year ago
claudiajcregg reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 prayfxrgreg liked this · 1 year ago
prayfxrgreg liked this · 1 year ago -
 markushasadeathwish reblogged this · 1 year ago
markushasadeathwish reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 babybunnieeworld reblogged this · 1 year ago
babybunnieeworld reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 broodycrawdad35 liked this · 1 year ago
broodycrawdad35 liked this · 1 year ago -
 blackdog97 reblogged this · 1 year ago
blackdog97 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 dannypandulce reblogged this · 1 year ago
dannypandulce reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 randomov liked this · 1 year ago
randomov liked this · 1 year ago -
 pav-anne reblogged this · 1 year ago
pav-anne reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ad-astra-affecte-spe reblogged this · 1 year ago
ad-astra-affecte-spe reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 the-yearning-astronaut liked this · 1 year ago
the-yearning-astronaut liked this · 1 year ago -
 pav-anne liked this · 1 year ago
pav-anne liked this · 1 year ago -
 hamath liked this · 1 year ago
hamath liked this · 1 year ago -
 messier47 reblogged this · 1 year ago
messier47 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 woyzeeck liked this · 1 year ago
woyzeeck liked this · 1 year ago -
 novopagan-hh liked this · 1 year ago
novopagan-hh liked this · 1 year ago

★•Astronomy, Physics, and Aerospace•★ Original and Reblogged Content curated by a NASA Solar System Ambassador
204 posts




